Soal Uas MSM
Diunggah oleh
ogijayapranaJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Soal Uas MSM
Diunggah oleh
ogijayapranaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
7.
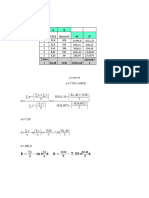
1 Given the data
z
t
10 5 7 19 11 8
y 15 9 3 25 7 13
Fit the linear regression model
]
=[
0
+[
1
z
]t
+e
]
,] =1,2,,6 . Specifically,
calculate the least squares estimates [
`
, the fitted values y, the residual e , and the
residual sum of squares, e
e.
Jawaban :
Terdapat data
z
t
10 5 7 19 11 8
y 15 9 3 25 7 13
Dengan
Z =
1 10
1 5
1 7
1 19
1 11
1 8
, =
15
9
3
25
7
13
, Z
=j
1
10
1
5
1
7
1
19
1
11
1
8
[
Maka
Z
Z =j
6 60
60 720
[ =j
1 10
10 120
[
, (Z
Z)
-1
=
1
20
j
120 10
10 1
[
, Z
y =j
72
872
[
Dicari nilai
[
`
=(Z
Z)
-1
Z
y =
1
20
j
120 10
10 1
[ j
72
872
[ =
1
20
j
80
152
[ =
1
5
j
20
38
[ =j
4
7,6
[
y =Z.[
`
=
1 10
1 5
1 7
1 19
1 11
1 8
1
5
j
20
38
[ =
1
5
360
170
246
702
398
284
72
34
49,2
140,4
79,6
56,8
Selanjutnya
e =y y =
15
9
3
25
7
13
72
34
49,2
140,4
79,6
56,8
57
25
46,2
115.4
72,6
43,8
Sehingga didapatkan Residual sum of squares :
e
e =[57 25 46,2 115,4 72,6 43,8]
57
25
46,2
115.4
72,6
43,8
=26514,8
Jadi Persamaan yang memenuhinya : y =4+7,6 z
I
8.3. Let
=_
2 0 0
0 4 0
0 0 4
_
Determine the principal components Y
1
, Y
2
, and Y
3
. What can you say about the
eigen value-vector (and principal components) associated with eigenvalues that are
not distinct?
Jawab :
Pertama kita cari dulu eigen value
det(zI ) =_
z 0 0
0 z 0
0 0 z
_ _
1 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 1
_ _
2 0 0
0 4 0
0 0 4
_
det(zI ) =_
z 0 0
0 z 0
0 0 z
_ _
2 0 0
0 4 0
0 0 4
_
det(zI ) =_
z 2 0 0
0 z 4 0
0 0 z 4
_ =0
(z 2) j
z 4 0
0 z 4
[ =0
(z 2)(z 4)
2
=0
(z 2)(z
2
8z +16) =0
z
3
10z
2
+32z 32) =0
moko niloi cigcnnyo z
1
=2,z
2
=4 ,z
3
=4
Untuk mencari nilai vector eigennya
Misal x =_
x
1
x
2
x
3
_adalah vektor eigen dari dan x adalah penyelesaian dari sistem
persamaan linear
( I) x = 0 atau ( I - )x =0
__
z 2 0 0
0 z 4 0
0 0 z 4
___
x
1
x
2
x
3
_ =0
Untuk 2
1
=2 , maka persamaan menjadi:
__
0 0 0
0 2 0
0 0 2
___
x
1
x
2
x
3
_ =_
0
0
0
_
2x
2
=0
2x
3
=0
x
1
=t R ,x
2
=0,x
3
=0
Vektor-vektor eigen yang bersesuaian dengan z
1
=2 adalah vektor tak nol yang
berbentuk
c
1
=x =_
t
0
0
_ =_
1
0
0
_ t
Jadi, vector _
1
0
0
_ merupakan suatu basis untuk ruang eigen dari matriks yang
bersesuaian dengan z
1
=2 .
Untuk 2
2
=4 , maka persamaan menjadi:
__
2 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
___
x
1
x
2
x
3
_ =_
0
0
0
_
2x
1
=0
x
1
=0,x
2
=t R ,x
3
=0
Vektor-vektor eigen yang bersesuaian dengan z
2
=4 adalah vektor tak nol yang
berbentuk
c
2
=x =_
0
t
0
_ =_
0
1
0
_ t
Jadi, vector _
0
1
0
_ merupakan suatu basis untuk ruang eigen dari matriks yang
bersesuaian dengan z
2
=4.
Untuk 2
3
=4 , maka persamaan menjadi:
__
2 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
___
x
1
x
2
x
3
_ =_
0
0
0
_
2x
1
=0
x
1
=0,x
2
=0 ,x
3
=t R
Vektor-vektor eigen yang bersesuaian dengan z
2
=4 adalah vektor tak nol yang
berbentuk
c
3
=x =_
0
0
t
_ =_
0
0
1
_ t
Jadi, vector _
0
0
1
_ merupakan suatu basis untuk ruang eigen dari matriks yang
bersesuaian dengan z
3
=4.
Eigen values of adalah 2,4,4. Eigen vector berhubungan dengan eigen values 4,4
yang tidak unik yaitu c
2
=[
0 1 0
] dan c
3
=[
0 0 1
]. Dengan pernyataan
tersebut dari principal component maka
1
=X
1
,
2
=X
2
Jon
3
=X
3
.
9.10 The correlation matrix for chicken-bone measurement( see Example 9.14) is
1.00
.505 1.00
.569 .422 1.00
.602 .467 .926
.621 .482 .877
.603 .450 .878
1.00
.874 1.00
.894 .937 1.00
The following estimates factor loadings were extracted by the maximum likelihood
procedure.
Variable
Estimated Faktor
Loadings
Varimax rotated
estimated factor
Loading
F
1
F
2 F
1
F
2
1.Skull length .602 .200 .484 .411
2.Skull breadth .467 .154 .375 .319
3. Femur length .926 .143 .603 .717
4.Tibia length 1.000 .000 .519 .855
5.Humerus length .874 .476 .861 .499
6. Ulna length .894 .327 .744 .594
Using the unrotated estimated factor loadings, obtain the maximum likelihood
estimates of the following.
(a) The specific variances.
(b) The communalities.
(c) The proportion of variance explained by each factor.
(d) The residual matrix R I
z
I
z
=
z
Jawab:
(a) The specific variances.
Cara mencari specifik variansi dari estimasi factor loading unrotasi digunakan
rumus
=1
i
2
i
2
=l
i1
2
+ l
i2
2
+ l
i3
2
+ .+ l
im
2
, i=1,2,,p
1
2
=0,4024 maka nilai
1
=1
1
2
=1-0,4024=0,5976
2
2
=0,2418 maka nilai
2
=1
2
2
=10,2418=0,7582
3
2
=0,8779 maka nilai
3
=1
3
2
=10,8779=0,1221
4
2
=1,000 maka nilai
4
=1
4
2
=1 1,000=0,000
5
2
=0,9905 maka nilai
5
=1
5
2
=1 0,9905=0,0095
6
2
=0,9062 maka nilai
6
=1
6
2
=1 0,9062=0,938
Jadi nilai Spesifik Variansinya adalah
Variabel Spesifik variansi
Skull length 0,5976
Skull breadth 0,7582
Femur length 0,1221
Tibia length 0,000
Humerus length 0,0095
Ulna length 0,0938
(b) ) The communalities
Untuk mencari nilai communalitinya adalah
i
2
=l
i1
2
+ l
i2
2
+ l
i3
2
+ .+ l
im
2
, i=1,2,,p
1
2
=(0,602)
2
+(0,200)
2
=0,4024
2
2
=(0,467)
2
+(0,154)
2
=0,2418
3
2
=(0,926)
2
+(0,143)
2
=0,8779
4
2
=(1,000)
2
+(0,000)
2
=1,000
5
2
=(0,874)
2
+(0,476)
2
=0,9905
6
2
=(0,894)
2
+(0,327)
2
=0,9062
Jadi nilai communalitinya adalah
Variabel Communaliti
Skull length 0,4024
Skull breadth 0,2418
Femur length 0,8779
Tibia length 1,000
Humerus length 0,9905
Ulna length 0,9062
(c) The proportion of variance explained by each factor.
(Proporsi totol somplc :orions) =
i
2
=l
]1
2
+ l
]2
2
+ l
]3
2
+ .+ l
]p
2
p
( oktor 1) =
(0,602)
2
+(0,467)
2
+(0,926)
2
+(1,00)
2
+(0,874)
2
+(0,894)
2
6
=
4,0001
6
=0,667 otou 66,7%
( oktor 2) =
(0,200)
2
+(0,154)
2
+(0,143)
2
+(0,00)
2
+(0,476)
2
+(0,327)
2
6
=
0,4177
6
=0,067 otou 6,7%
(d) The residual matrix R I
z
I
z
z
R I
z
I
z
1,000
0,505 1,000
0,596 0,422 1,000
0,602 0,467 0,926
0,621 0,482 0,877
0,603 0,450 0,878
1,000
0,874 1,000
0,894 0,937 1,000
0,602 0,200
0,467 0,154
0,926 0,143
1,000 0,000
0,874 0,476
0,894 0,327
j
0,602 0,467 0,926
0,200 0,154 0,143
1,000 0,874 0,894
0,000 0,476 0,327
[
0938 , 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0095 , 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 000 , 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1221 , 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 7582 , 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 5976 , 0
R I
z
I
z
0 000 , 0 000 , 0 003 , 0 018 , 0 000 , 0
0 0 000 , 0 000 , 0 001 , 0 000 , 0
0 0 0 000 , 0 000 , 0 000 , 0
0 0 0 0 032 , 0 017 , 0
0 0 0 0 0 193 , 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
10.9 H. Hotelling [4] report that n=140 seventh-grade children received four tests on
X
1
(1)
=reading speed, X
2
(1)
=reading power, X
1
(2)
=arithmetic speed, and
X
2
(2)
=arithmetic power. The correlations for performance are
R =_
R
11
R
12
R
21
R
22
_ =_
1.0 .6328
.6328 1.0
.2412 .0586
.0553 .0655
.2412 .0553
.0585 .0655
1.0 .4248
.4248 1.0
_
(a) Find all the sample canonical correlations and the sample canonical variates
(b) Stating any assumptions you make, test the hypotheses
E
0
:
12
=p
12
=0 (p
1
=p
2
=0)
E
0
:
12
=p
12
0
At the o =.05 level of significance. If H
0
is rejected, test
E
0
(1)
:p
1
0,p
2
=0
E
1
(1)
:p
2
0
With a significance level of o =.05. Does reading ability (as measured by the
two tests) correlate with arithmetic ability (as measured by the two tests) ?
Discuss.
(c) Evaluate the matrices of approximation errors for R
11
, R
22
, and R
12
determined by
the first sample canonical variate pair u
1
, I
1
.
Jawaban :
(a) Sample korelasi kanonikal dan sample varabel kanonikal dari
R =_
R
11
R
12
R
21
R
22
_ =_
1.0 .6328
.6328 1.0
.2412 .0586
.0553 .0655
.2412 .0553
.0585 .0655
1.0 .4248
.4248 1.0
_
Maka didapatkan
p
1
=0,39 ; p
2
=0,07
Sehingga diperoleh juga
u
1
=1,26z
1
(1)
1,03z
2
(1)
;u
2
=0,30z
1
(1)
+0,79z
2
(1)
I
1
=1,10z
1
(2)
0,45z
2
(2)
;I
2
=0,02z
1
(2)
+1,01z
2
(2)
Dimana z
(1)
,i =1,2 dan z
(2)
,i =1,2adalah data nilai standard untuk set 1 dan 2
(b) Dengan menguji hipotesis dimana n=140, p =2, q = 2,
maka n 1
1
2
(p +q +1) =136,5
dari hipoetesis
E
0
:
12
=p
12
=0 (p
1
=p
2
=0)
E
0
:
12
=p
12
0
Signifikansi o =.05.J ika H
0
ditolak
Dimana tabel menunjukkan
Null Hypothesis Value of Test Statistik Degrees of
Freedom
Upper 5% point of
x
2
distribution
E
0
:
12
=p
12
=0
-136,5ln(0,8444)(0,9953) =
23,74
4 9,48
E
0
(1)
: p
1
p
2
=0
-136,5 ln (0,9953) =0,65 1 3,84
Oleh karena itu, menolak E
0
tapi tidak menolakE
0
(1)
. kemampuan membaca
(ditulis u
1
) tidak berkorelasi dengan kemampuan aritmatika (ditulis I
1
) tetapi
korelasi (yang diwakili oleh p
1
=0,39) tidak terlalu kuat.
(c) Matriks error aprosimaksi dari R
11
, R
22
, and R
12
dary pasangan sample canonical
variat u
1
, I
1
.
A
z
-1
=j
1,26 1,03
0,3 0,79
[
-1
=
1
1,3044
j
0,79 1,03
0,3 1,26
[ =j
0,606 0,79
0,23 0,966
[
B
z
-1
=j
0,06 0,944
2,648 2,475
[
-1
=
1
2,599
_
2,475 0,944
2,648 0,06
_ =_
0,952 0,363
1,019 0,023
_
R
12
s.Co:[z
(1)
,
z
(2)
=_
0,2412 0,586
0,055 0,0655
_ (0,07) j
0,79
0,966
[ [0,363 0,023]
=_
0,2412 0,586
0,055 0,0655
_ (0,018)
=j
0,2430 0,604
0,037 0,0835
[
R
11
s.Co:[z
(1)
=j
1,0 0,6328
0,6328 1,0
[ j
0,79
0,966
[ [0.79 0,966]
=j
1,0 0,6328
0,6328 1,0
[ 1,557
=_
0,557 0,9242
0,9242 0,557
_
R
22
s.Co:[z
(2)
=j
1,0 0,4248
0,4248 1,0
[ j
0,363
0,023
[ [0,363 0,023]
=j
1,0 0,4248
0,4248 1,0
[ 0,1325
=_
0,8675 0,2923
0,2923 0,8675
_
11.2 (a) Develop a linear classification function for the data in Example 11.1 using (11-
19).
(b) Using the function in (a) and (11-20), construct the confusion matrix by
classifying the given observations. Compare your classification results with those
of Figure 11.1 where the classification regions were determined by eye(see
Example 11.5).
(c) Given the result in (b), calculate the apparent error rate (APER).
(d) State any assumptions you make to justify the use of the method in parts a and b.
Jawab:
(a) fungsi linear classifikasi dari contoh 11.1
dimana
n
1
RiJing mowcr owncr; n
2
Nonowncr
Dari tabel 11.1 diperoleh :
x
1
=_
109,475
20,267
_ , x
2
=j
87,400
17,633
[
Nonowner
Observasi l.x
0
Klasifikasi
1 25,886 Owner
2 24,608 Nonowner
3 22,982 Nonowner
4 23,334 Nonowner
5 25,216 Owner
6 21,736 Nonowner
7 21,500 Nonowner
8 24,044 Nonowner
9 20,614 Nonowner
10 21,058 Nonowner
11 19,090 Nonowner
12 20,918 Nonowner
S
1
=_
352,644 11,818
11,818 4,082
_ , S
2
=_
200,705 2,589
2,589 4,464
_
S
pooIcd
=_
276,675 7,204
7.204 4,273
_ , S
spooIcd
-1
=j
0,00378 0,00637
0,00637 0,24475
[
Fungsi linear klasifikasi menggunakan rumus
y =(x
1
x
2
)
i
S
spooIcd
-1
.x =l.x
y =[_
109,475
20,267
_ j
87,400
17,633
[
i
j
0,00378 0,00637
0,00637 0,24475
[ .x
y =[22,075 2,634]j
0,00378 0,00637
0,00637 0,24475
[ .x =[0,100 0,785]x
Dimana
m =
1
2
(y
1
+y
2
) =
1
2
(l.x
1
+l.x
2
)
m =[0,100 0,785]._
109,475
20,267
_ +[0,100 0,785].j
87,400
17,633
[ =24,719
(b) Dipilih bahwa observasi x untuk n
1
jika:
0,100 x
1
+0,785 x
2
24,719
Dan laiinnya dipilih x untuk n
2
Maka observasi dan pengklasifikasiannya adalah
Dari table diatas kita bisa buat matriks confusion:
Predicted Membership
n
1
n
2
Total
Actual
Membership
n
1
11 1 12
n
2
2 10 12
Owner
Observasi l.x
0
Klasifikasi
1 23,444 Nonowner
2 24,738 Owner
3 26,436 Owner
4 25,478 Owner
5 30,226 Owner
6 29,082 Owner
7 27,616 Owner
8 28,864 Owner
9 25,600 Owner
10 28,628 Owner
11 25,370 Owner
12 26,800 Owner
(c) Apparent error rate
APER =_
crror prcJictcJ mcmbcrsip +crror octuol mcmbcrsip
totol Joto oscr:osi 1+totol Jot obscr:osi 2
]100%
APER =_
1+2
12+12
] 100%=0,125 .100%=12,5%
(d) Jadi asumsi observasi dari n
1
dan n
2
dengan distribusi multivariat normal
mempunyai persamaan matriks
1
=
2
=
12.10 Suppose we measure two variables X
1
, and X
2
for four items A, B, C, and D. The
data are as follows.
Item
Observations
X
1
X
2
A
B
C
D
5
1
-1
3
4
-2
1
1
Use the K-means clustering technique to divide the items into K=2 cluster. Start
with the initial groups (AB) and (CD)
Jawab:
Dengan metode K-Means data diatas dapat dibagi ke dalam 2 cluster.Dimana
diawali dengan group (AB) dan (CD)
Perhitungan koordinat (x
1
,x
2
) dari cluster centroit (mean). Pada langkah 1 kita
punya:
Cluster
Kordinat centroit
x
1
x
2
(AB) 5+1
2
=3
4+(2)
2
=1
(CD)
1+3
2
=1
1+1
2
=1
Pada langkah ke-2 dihitung jarak Euclid untuk setiap item dari group centroit dan
cari item yang memiliki jarak group paling kecil/dekat. Dihitung dengan jarak
kuadrat pada setiap group yang akan digabungkan
J
2
(A,(AB)) =(5 3)
2
+(41)
2
=13
J
2
(A,(C)) =(5 1)
2
+(41)
2
=25
J
2
(B,(AB)) =(1 3)
2
+(2 1)
2
=13
J
2
(B,(C)) =(1 1)
2
+(2 1)
2
=9
Karena B memiliki jarak yang lebih dekat/pendek maka B bergabung dengan
group (CD) menjadi (BCD)
dan sekarang kordinat centroit menjadi
Cluster
Kordinat centroit
x
1
x
2
A 5 4
(BCD) 1 0
Cluster
Jarak Kuadrat group centroit
Item
A B C D
A 0 52 45 13
(BCD) 32 4 5 5
Sekarang telah ditetapkan bahwa jarak dengan centroit(mean) yang paling dekat/kecil
akan menjadi satu cluster disini karena dibagi 2 kelompok(K=2) maka cluster yang di
dapat adalah A dan (BCD).
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 2-Boletin Matrices - Determinantes BDokumen9 halaman2-Boletin Matrices - Determinantes BSamuelBelum ada peringkat
- A3 Espazos VectoriaisDokumen12 halamanA3 Espazos VectoriaisMaydayBelum ada peringkat
- Boletin 4 Inferencia SolucionesDokumen24 halamanBoletin 4 Inferencia Solucionesana riveiroBelum ada peringkat
- Listado5 Solución EMDokumen2 halamanListado5 Solución EMreypincheiraBelum ada peringkat
- Exercicios T0derivada2019-20jpgDokumen6 halamanExercicios T0derivada2019-20jpgManuel Caeiro MatinBelum ada peringkat
- Solución Extraordinaria Matemáticas 2014Dokumen8 halamanSolución Extraordinaria Matemáticas 2014Alejandro Iglesias GilBelum ada peringkat
- Boletin 7 DiagonalizacionDokumen5 halamanBoletin 7 DiagonalizacionSamuelBelum ada peringkat
- Identidades TrigonométricasDokumen9 halamanIdentidades TrigonométricasCarlos David Laura Quispe100% (1)
- 2oBachCC EBAU Galicia 2020-Ordinaria Resuelto CiuGDokumen8 halaman2oBachCC EBAU Galicia 2020-Ordinaria Resuelto CiuGCarla Castillo FernándezBelum ada peringkat
- 310ea3100104 01Dokumen12 halaman310ea3100104 01Yair De La PeñaBelum ada peringkat
- FUNCIONESDokumen3 halamanFUNCIONESIgnacio Arroyo CunhaBelum ada peringkat
- Practica 4Dokumen4 halamanPractica 4yagormarquezBelum ada peringkat
- TALLER 3 METODOS Segundo CorteDokumen22 halamanTALLER 3 METODOS Segundo CorteMaria Del Pilar ArciniegasBelum ada peringkat
- Func DerivablesDokumen9 halamanFunc DerivablesAlejandro Barrosa CampilloBelum ada peringkat
- B03GDokumen8 halamanB03Gbvsfkwdgw9Belum ada peringkat
- Boletin 2Dokumen4 halamanBoletin 2Yago Carbonell VázquezBelum ada peringkat
- 1-Boletin Iniciacion Complexos 7062016 C PDFDokumen4 halaman1-Boletin Iniciacion Complexos 7062016 C PDFSamuelBelum ada peringkat
- Solución Matemáticas 2014Dokumen8 halamanSolución Matemáticas 2014Alejandro Iglesias GilBelum ada peringkat
- Boletin 7Dokumen2 halamanBoletin 7sergiovicentegomezBelum ada peringkat
- 20 MatematicasDokumen2 halaman20 Matematicasv.arroyomanasseroBelum ada peringkat
- Exame 05 - 04 - 24Dokumen13 halamanExame 05 - 04 - 24luciavilaboy06Belum ada peringkat
- Lista 1 EDODokumen2 halamanLista 1 EDOEneias Moreira JuniorBelum ada peringkat
- Propostas de Resolução (Caderno de Fichas) PDFDokumen91 halamanPropostas de Resolução (Caderno de Fichas) PDFdwiwhfiwjbfsfnBelum ada peringkat
- Xeometría e Análise 2021Dokumen2 halamanXeometría e Análise 2021Lola Cousido PiñeiroBelum ada peringkat
- Reforzo UD 5 - Xeometría AnalíticaDokumen1 halamanReforzo UD 5 - Xeometría AnalíticamartinixvcBelum ada peringkat
- 20 MatematicasuyvuygDokumen21 halaman20 MatematicasuyvuyglaurapazosssssBelum ada peringkat
- 2022 AbauDokumen31 halaman2022 AbauPabloffvigoBelum ada peringkat
- Estimacià N IIDokumen2 halamanEstimacià N IISergio García MartínBelum ada peringkat
- EXAMEN PARCIAL 01 - SoluciónDokumen15 halamanEXAMEN PARCIAL 01 - Soluciónjairisaacdiazlozano83Belum ada peringkat
- Solución Examen Matemáticas II de Galicia (Ordinaria de 2015)Dokumen9 halamanSolución Examen Matemáticas II de Galicia (Ordinaria de 2015)Alejandro Iglesias GilBelum ada peringkat
- ENQ 2015 1 GabaritoDokumen10 halamanENQ 2015 1 GabaritoLoveleeGirlBelum ada peringkat
- Correccion T1Dokumen5 halamanCorreccion T1María Ángel OHBelum ada peringkat
- Ecuaciones Líneales 4Dokumen7 halamanEcuaciones Líneales 4Yair De La PeñaBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercicios Cap7Dokumen10 halamanEjercicios Cap7Geovanni GonzalezBelum ada peringkat
- Números Complexos: Unidade Didáctica 8Dokumen1 halamanNúmeros Complexos: Unidade Didáctica 8Almendrillas AlmendrasBelum ada peringkat
- Examen Matematicas A Acceso Grado Superior Galicia 2014Dokumen11 halamanExamen Matematicas A Acceso Grado Superior Galicia 2014Pablo VarelaBelum ada peringkat
- Beamer CanDokumen27 halamanBeamer CanHugo Carreira RialBelum ada peringkat
- Matematicas IIIDokumen185 halamanMatematicas IIIMacbookaluBelum ada peringkat
- P1 F4 2023 2 VF GABADokumen18 halamanP1 F4 2023 2 VF GABAjgato906Belum ada peringkat
- Solución 1 Aval 2 ExameDokumen2 halamanSolución 1 Aval 2 Exameanamatesverin1321Belum ada peringkat
- Minimos CudaradosDokumen1 halamanMinimos CudaradosFAVIANA ANDREA ZAPATA VALLEJOBelum ada peringkat
- Ecuaciones-Trigonometricas GalegoDokumen4 halamanEcuaciones-Trigonometricas GalegoeuholandeserranteBelum ada peringkat
- 20 MatemDokumen32 halaman20 MatemlaurapazosssssBelum ada peringkat
- Solución Examen Matemáticas II de Galicia (Extraordinaria de 2015)Dokumen8 halamanSolución Examen Matemáticas II de Galicia (Extraordinaria de 2015)Alejandro Iglesias GilBelum ada peringkat
- Boletín DiferenciaciónDokumen4 halamanBoletín DiferenciaciónAndrea ExpidoBelum ada peringkat
- Algebra PDFDokumen1 halamanAlgebra PDFSamuel Abreu PradoBelum ada peringkat
- FórmulasDokumen3 halamanFórmulasDiana OsorioBelum ada peringkat
- Segunda Proba 09 11 2017Dokumen5 halamanSegunda Proba 09 11 2017Kika EsBelum ada peringkat
- Boletin 1.1 5Dokumen2 halamanBoletin 1.1 5claudiagBelum ada peringkat
- A1 Reais ComplexosDokumen9 halamanA1 Reais ComplexosMaydayBelum ada peringkat
- Integración Funciones RacionalesDokumen3 halamanIntegración Funciones RacionalesHaytham EssahmBelum ada peringkat
- Exame Xaneiro 2015Dokumen2 halamanExame Xaneiro 2015Mauricio Andres Reyes NaranjoBelum ada peringkat
- Exercicios Resolvidos Calculo de Deslocamentos TTV Matricial 26fev15 PDFDokumen13 halamanExercicios Resolvidos Calculo de Deslocamentos TTV Matricial 26fev15 PDFRosalia Jacinto MagueleBelum ada peringkat
- Boletin AplicaciónsLinearesDokumen5 halamanBoletin AplicaciónsLinearesAndrea ExpidoBelum ada peringkat
- 1âºav2201 Alxebra (Sol)Dokumen2 halaman1âºav2201 Alxebra (Sol)bbyggrllBelum ada peringkat
- EstadísticaDokumen9 halamanEstadísticaHugo Carreira RialBelum ada peringkat
- 2022年imo预选题及其解答 王正、陈晨 (学而思教育集团)Dokumen23 halaman2022年imo预选题及其解答 王正、陈晨 (学而思教育集团)lingxu maoBelum ada peringkat
- Identidades Trigonométricas IDokumen1 halamanIdentidades Trigonométricas IBranco ChallapaBelum ada peringkat