Symmetrical Fault Calculations: Example 17.14
Diunggah oleh
ممشطDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Symmetrical Fault Calculations: Example 17.14
Diunggah oleh
ممشطHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Symmetrical Fault Calculations
417
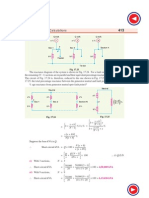
When fault occurs at point F, the reactance diagram at the selected base MVA will be as shown in Fig. 17.29 (i). The reactances of generators A and B are in parallel and their equivalent reactance = 8%/2 = 4%. The circuit then reduces to the one shown in Fig. 17.29 (ii). This further reduces to the one shown in Fig. 17.29 (iii).
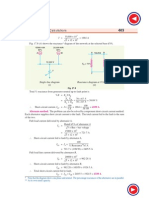
Total % reactance from generator neutral upto fault point F 12 27 5 = 12 % || 275 % = 12 +27 5 = 835 % 100 100 = 10 Fault MVA = Base MVA = 1198 MVA % Reactance 8 35 Example 17.14. A 10 MVA, 66 kV, 3-phase star-connected alternator having a reactance of 20% is connected through a 5 MVA, 66 kV/33 kV transformer of 10% reactance to a transmission line having a resistance and reactance per conductor per kilometre of 02 and 1 respectively. Fifty kilometres along the line, a short-circuit occurs between the three conductors. Find the current fed to the fault by the alternator.
Solution. Fig. 17.30 shows the single line diagram of the network. Let 10 MVA (= 10 kVA) be the base MVA. % reactance of the alternator on base MVA is 10 20 = 20 % % XA = 10 % reactance of the transformer on base MVA is 10 10 = 20 % % XT = 5 % reactance of the transmission line is
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- EE 13 FaultsDokumen11 halamanEE 13 FaultsLowie Fremista Tarantan100% (2)
- Assignment IDokumen5 halamanAssignment IPrasenjit DeyBelum ada peringkat
- A F Af Af: Fault On Station ADokumen1 halamanA F Af Af: Fault On Station AممشطBelum ada peringkat
- SWDokumen1 halamanSWممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Principle of Power System V K Mehata 21Dokumen1 halamanPrinciple of Power System V K Mehata 21ممشط100% (1)
- SsDokumen1 halamanSsممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematical ProblemDokumen3 halamanMathematical ProblemMrinmoy Rahman100% (1)
- Web For Power Systems II B.tech 6th SemDokumen16 halamanWeb For Power Systems II B.tech 6th Semskyline1122Belum ada peringkat
- High VoltageDokumen1 halamanHigh VoltageممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Assignments - 2 July - December 2021Dokumen5 halamanAssignments - 2 July - December 2021Ayush AgrwalBelum ada peringkat
- EE141 RemExam 5Dokumen1 halamanEE141 RemExam 5Alliver SapitulaBelum ada peringkat
- Pse 1 5 (7 Marks)Dokumen33 halamanPse 1 5 (7 Marks)Mahesh SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Unit PsaDokumen14 halamanUnit Psasulthan_81100% (1)
- Assignment No 1 (PSP) RP-17-EE-404Dokumen3 halamanAssignment No 1 (PSP) RP-17-EE-404hamzaBelum ada peringkat
- PSP 2Dokumen6 halamanPSP 2Izhar Ahmed NoohpotoBelum ada peringkat
- Ee 6501 - Power System Analysis Unit-3 Fault Analysis-Balanced Faults Part ADokumen4 halamanEe 6501 - Power System Analysis Unit-3 Fault Analysis-Balanced Faults Part AVbalaji VaithiyanathanBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4Dokumen5 halamanUnit 4Sri Ram KBelum ada peringkat
- Sheet 1Dokumen5 halamanSheet 1meeedooo.abo.elenenBelum ada peringkat
- 5 25961 628Dokumen9 halaman5 25961 628Belayneh TadesseBelum ada peringkat
- Compiled Board Exam Electric Power System II KeyDokumen14 halamanCompiled Board Exam Electric Power System II Keyshaito100% (1)
- Psa Imp QuestDokumen11 halamanPsa Imp Questdrmsrmurty9473Belum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 1Dokumen8 halamanTutorial 1Pradeep Kumar SahooBelum ada peringkat
- Ass004 Symmetrical Fault 1Dokumen1 halamanAss004 Symmetrical Fault 1James Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- Tutorial PSE 2011-2012Dokumen23 halamanTutorial PSE 2011-2012Mahesh Singh100% (1)
- FPSD52L - Activity 5Dokumen1 halamanFPSD52L - Activity 5Gelowa PogiBelum ada peringkat
- MUJ PSA Assignment-I Power System Analysis (EEE1505)Dokumen7 halamanMUJ PSA Assignment-I Power System Analysis (EEE1505)Denish Gupta0% (1)
- Tutorial Pse - 2012-2013Dokumen23 halamanTutorial Pse - 2012-2013Mahesh SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Power System Stability Analysis: 500 MVA 11kV/400kV X 100Dokumen8 halamanPower System Stability Analysis: 500 MVA 11kV/400kV X 100Kumar AbhinavBelum ada peringkat
- Ee Pre-Board 1Dokumen6 halamanEe Pre-Board 1Shaira Sto TomasBelum ada peringkat
- Short - Circuit Problems With SolutionsDokumen22 halamanShort - Circuit Problems With Solutionsgsantosh06Belum ada peringkat
- EE61 Power System AnalysisDokumen3 halamanEE61 Power System AnalysisMartin De Boras PragashBelum ada peringkat
- QuestionDokumen8 halamanQuestionewan koBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment1 of FaultDokumen2 halamanAssignment1 of FaultsethBelum ada peringkat
- Traduccion Deber 9.1 9.2 9.3Dokumen3 halamanTraduccion Deber 9.1 9.2 9.3Fernando VacaBelum ada peringkat
- Figure For Question No. 1Dokumen4 halamanFigure For Question No. 1noybit mondalBelum ada peringkat
- Unit - 2 Short Questions (2 & 3 Marks)Dokumen6 halamanUnit - 2 Short Questions (2 & 3 Marks)Sujit KumarBelum ada peringkat
- ContinueDokumen1 halamanContinueممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Question Paper CodeDokumen6 halamanQuestion Paper Codeprasad powerBelum ada peringkat
- Symmetrical Fault Calculations: 4330 A Alternate MethodDokumen1 halamanSymmetrical Fault Calculations: 4330 A Alternate MethodممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Power System Compre PaperDokumen3 halamanPower System Compre PaperAmandeep GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Switch Gear and Protection 1Dokumen5 halamanSwitch Gear and Protection 1Irfan UllahBelum ada peringkat
- Elec Engg Exit Exam 2018 (Part 9)Dokumen10 halamanElec Engg Exit Exam 2018 (Part 9)Master JaguarBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment#02Dokumen2 halamanAssignment#02deepanshuBelum ada peringkat
- Core 1 1: ElectricityDokumen16 halamanCore 1 1: ElectricityfarsxdchgBelum ada peringkat
- Case 1: Equal Impedance, Ratios and Same kVA: ExampleDokumen2 halamanCase 1: Equal Impedance, Ratios and Same kVA: ExampleSohail ABelum ada peringkat
- TransformerDokumen4 halamanTransformerSalu ShigriBelum ada peringkat
- 02-Alternator On LoadDokumen12 halaman02-Alternator On Loadcooldude99344100% (1)
- QueBank - Unit 3 - Unsymmetrical Fault AnalysisDokumen3 halamanQueBank - Unit 3 - Unsymmetrical Fault AnalysisBelayneh TadesseBelum ada peringkat
- EE700 Assignment 2 QuestionsDokumen2 halamanEE700 Assignment 2 QuestionsAnil GugulothBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Faults - Update - 020413 - SV PDFDokumen6 halamanTutorial Faults - Update - 020413 - SV PDFnanangBelum ada peringkat
- B. 1.35 Mega-Ohms. D. 2.0 Mega-OhmsDokumen5 halamanB. 1.35 Mega-Ohms. D. 2.0 Mega-OhmsPao CastillonBelum ada peringkat
- EPS 2 Tut1Dokumen7 halamanEPS 2 Tut1Deep ShethBelum ada peringkat
- Power System Analysis: Transformers, Per UnitDokumen43 halamanPower System Analysis: Transformers, Per UnitMamta MrjnBelum ada peringkat
- Line Loss Analysis and Calculation of Electric Power SystemsDari EverandLine Loss Analysis and Calculation of Electric Power SystemsBelum ada peringkat
- Handbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsDari EverandHandbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Foundations of Electromagnetic Compatibility: with Practical ApplicationsDari EverandFoundations of Electromagnetic Compatibility: with Practical ApplicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Dari EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Gas Insulated Transmission Lines GILDokumen2 halamanGas Insulated Transmission Lines GILممشط100% (1)
- Management and Safe Handling Procedures For (Sf6) GasDokumen21 halamanManagement and Safe Handling Procedures For (Sf6) GasKhaled KhaledBelum ada peringkat
- Gas-Insulated Switchgear From 72.5 To 800 KV: Excellent Systems That Create Lasting ValueDokumen16 halamanGas-Insulated Switchgear From 72.5 To 800 KV: Excellent Systems That Create Lasting ValueممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Partial Discharge Detection For Gas-Insulated Switchgear in ServiceDokumen38 halamanPartial Discharge Detection For Gas-Insulated Switchgear in ServiceممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Handling and Use of Sulfur Hexafluoride GasDokumen8 halamanHandling and Use of Sulfur Hexafluoride GasممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Section 1: Mechanical Check and Visual Inspection:: Testing Engineer Nour QC Maaden WitnessDokumen5 halamanSection 1: Mechanical Check and Visual Inspection:: Testing Engineer Nour QC Maaden WitnessMourad BenderradjiBelum ada peringkat
- HV Test MeasurementsDokumen11 halamanHV Test Measurementsreza515heiBelum ada peringkat
- A Balanced Star Connected Load Takes 90 A From A Balanced 3-Phase, 4-Wire Supply. If The Fuses in The Y and B Phases Are Removed, Find The Symmetrical Components of The Line CurrentsDokumen1 halamanA Balanced Star Connected Load Takes 90 A From A Balanced 3-Phase, 4-Wire Supply. If The Fuses in The Y and B Phases Are Removed, Find The Symmetrical Components of The Line CurrentsممشطBelum ada peringkat
- High Voltage TechniquesDokumen108 halamanHigh Voltage Techniquesممشط75% (4)
- Skin Effect Is DefinedDokumen2 halamanSkin Effect Is DefinedممشطBelum ada peringkat
- This Page Intentionally Left BlankDokumen1 halamanThis Page Intentionally Left BlankممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Partial Discharge Display: (A) Void Point To Plane.: CB CBDokumen1 halamanPartial Discharge Display: (A) Void Point To Plane.: CB CBممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Unsymmetrical Fault Calculations: With The Help of Scientific Calculator, Can Be Directly Changed To and ViceDokumen1 halamanUnsymmetrical Fault Calculations: With The Help of Scientific Calculator, Can Be Directly Changed To and ViceممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Symmetrical Fault Calculations: 4330 A Alternate MethodDokumen1 halamanSymmetrical Fault Calculations: 4330 A Alternate MethodممشطBelum ada peringkat
- A Pressure Reservoir at One Cable End Is Applied To Short Lengths ofDokumen1 halamanA Pressure Reservoir at One Cable End Is Applied To Short Lengths ofممشطBelum ada peringkat
- 2, It Usually Needs More Supports and InsulatorsDokumen1 halaman2, It Usually Needs More Supports and InsulatorsممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Voltage ControlDokumen1 halamanVoltage ControlممشطBelum ada peringkat
- (I) (Ii) (Iii) : Positive Phase Sequence Components. Negative Phase Sequence Components. Zero Phase Sequence ComponentsDokumen1 halaman(I) (Ii) (Iii) : Positive Phase Sequence Components. Negative Phase Sequence Components. Zero Phase Sequence ComponentsممشطBelum ada peringkat
- WillisDokumen1 halamanWillisممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Double BusbarsDokumen1 halamanDouble BusbarsممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Unsymmetrical Fault Calculations: I I I I I I I I I I I IDokumen1 halamanUnsymmetrical Fault Calculations: I I I I I I I I I I I IممشطBelum ada peringkat