A F Af Af: Fault On Station A
Diunggah oleh
ممشطDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
A F Af Af: Fault On Station A
Diunggah oleh
ممشطHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
410
% Reactance of interconnector on the base MVA % XI =
3
Principles of Power System
akVAf X = (100 10 ) 1 = 918% 10 akVf 10 a33f
2 2
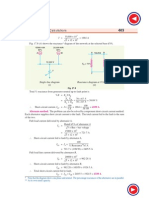
The reactance diagram is shown in Fig. 17.18 (ii). Fault on station A. When a fault occurs on power station A (point F1), the total percentage reactance from generator neutral upto fault point F1 is the parallel combination of (833% + 918%) and 667% i.e. Total % reactance upto fault point F1 17 51 6 67 = = 483% 17 51 + 6 67 100 Short-circuit MVA = Base MVA % Reactance = 100 100/483 = 2070 Fault on station B. When a fault occurs on power station B (point F2), the total percentage reactance from generator neutral upto fault point F2 is the parallel combination of (667% + 918%) and 833% i.e. Total % reactance upto fault point F2 15 85 8 33 = = 546% 15 85 + 8 33 Short-circuit MVA = 100 100/546 = 1831 Example 17.8. A generating station has three section bus-bars connected with a tie-bar through 6% reactors rated at 5000 kVA. Each generator is of 5000 kVA with 12% reactance and is connected to one section of bus-bars. Find the total steady input to a dead short-circuit between the lines on one of the sections of bus-bar (i) with reactors and (ii) without reactors.
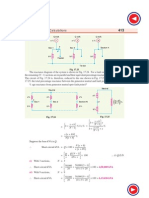
Solution. Fig. 17.19 shows the single line diagram of the system. Let 5000 kVA be the base kVA. As generators and reactors are rated at this kVA, therefore, their percentage reactances remain the same. (i) With reactors. Suppose a 3-phase short-circuit fault occurs on section 3 of the bus-bar (point F in Fig. 17.19). The reactance diagram at the selected base kVA will be as shown in Fig. 17.20 (i). The equivalent reactance of the parallel branches is (18/2)% = 9% and the circuit reduces to Fig. 17.20 (ii).
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Symmetrical Fault Calculations: Example 17.14Dokumen1 halamanSymmetrical Fault Calculations: Example 17.14ممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Power System Short Circuit Current CalculationDokumen1 halamanPrinciples of Power System Short Circuit Current CalculationممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Principle of Power System V K Mehata 21Dokumen1 halamanPrinciple of Power System V K Mehata 21ممشط100% (1)
- Web For Power Systems II B.tech 6th SemDokumen16 halamanWeb For Power Systems II B.tech 6th Semskyline1122Belum ada peringkat
- High VoltageDokumen1 halamanHigh VoltageممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Symmetrical Fault Calculations: 4330 A Alternate MethodDokumen1 halamanSymmetrical Fault Calculations: 4330 A Alternate MethodممشطBelum ada peringkat
- SsDokumen1 halamanSsممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Figure For Question No. 1Dokumen4 halamanFigure For Question No. 1noybit mondalBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment No 1 (PSP) RP-17-EE-404Dokumen3 halamanAssignment No 1 (PSP) RP-17-EE-404hamzaBelum ada peringkat
- Ee306 ADokumen3 halamanEe306 AAparna JoseBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematical ProblemDokumen3 halamanMathematical ProblemMrinmoy Rahman100% (1)
- 2018 April Power Systems Analysis - EE306-A - Ktu QbankDokumen3 halaman2018 April Power Systems Analysis - EE306-A - Ktu QbankJeril joseBelum ada peringkat
- PSE 6TH SEM UNIT 1 & 2 PER UNIT IMPEDANCE DIAGRAMSDokumen33 halamanPSE 6TH SEM UNIT 1 & 2 PER UNIT IMPEDANCE DIAGRAMSMahesh SinghBelum ada peringkat
- 電機 期末 109Dokumen5 halaman電機 期末 109e24106466Belum ada peringkat
- Fitzgerald Chap 5 SolutionsDokumen19 halamanFitzgerald Chap 5 SolutionsvainateyagoldarBelum ada peringkat
- EE141 RemExam 5Dokumen1 halamanEE141 RemExam 5Alliver SapitulaBelum ada peringkat
- Assigment EPSD Lab PDFDokumen5 halamanAssigment EPSD Lab PDFArjit AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Assignments - 2 July - December 2021Dokumen5 halamanAssignments - 2 July - December 2021Ayush AgrwalBelum ada peringkat
- EEEN 40400 Wind Energy Exam QuestionsDokumen7 halamanEEEN 40400 Wind Energy Exam QuestionsIsmail HussainBelum ada peringkat
- ContinueDokumen1 halamanContinueممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Short - Circuit Problems With SolutionsDokumen22 halamanShort - Circuit Problems With Solutionsgsantosh06Belum ada peringkat
- Question Paper CodeDokumen6 halamanQuestion Paper Codeprasad powerBelum ada peringkat
- How To Solve Short Circuit Calculation Using Point To Point Method PDFDokumen6 halamanHow To Solve Short Circuit Calculation Using Point To Point Method PDFMenaBelum ada peringkat
- EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT-I INTRODUCTIONDokumen11 halamanEE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT-I INTRODUCTIONdrmsrmurty9473Belum ada peringkat
- Tutorial PSE 2011-2012Dokumen23 halamanTutorial PSE 2011-2012Mahesh Singh100% (1)
- ABB Manual 10E 03 Print 07 PDFDokumen10 halamanABB Manual 10E 03 Print 07 PDFosmpotBelum ada peringkat
- 3-Phase Short Circuit Protection NumericalsDokumen6 halaman3-Phase Short Circuit Protection NumericalsIzhar Ahmed NoohpotoBelum ada peringkat
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Dokumen3 halamanQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Nithiya MaharajanBelum ada peringkat
- Unit PsaDokumen14 halamanUnit Psasulthan_81100% (1)
- ESO203A Quiz – Unity PF CalculationDokumen4 halamanESO203A Quiz – Unity PF CalculationAk AkBelum ada peringkat
- 1Dokumen15 halaman1Saravanaraja KumaresanBelum ada peringkat
- Ee 6501-Power System Analysis: Maximum Marks:100 Duration: 3 HrsDokumen3 halamanEe 6501-Power System Analysis: Maximum Marks:100 Duration: 3 HrskarthikBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment IDokumen5 halamanAssignment IPrasenjit DeyBelum ada peringkat
- 5 25961 628Dokumen9 halaman5 25961 628Belayneh TadesseBelum ada peringkat
- Point To Point Method Short Circuit Current CalculationDokumen7 halamanPoint To Point Method Short Circuit Current CalculationMuhammad Irfan ArdiansyahBelum ada peringkat
- Fault current and impedance analysis of power systemsDokumen2 halamanFault current and impedance analysis of power systemsTabishBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Faults - Update - 020413 - SV PDFDokumen6 halamanTutorial Faults - Update - 020413 - SV PDFnanangBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Pse - 2012-2013Dokumen23 halamanTutorial Pse - 2012-2013Mahesh SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Power Systems-II Question Bank: Unit-IDokumen8 halamanPower Systems-II Question Bank: Unit-ISoniya GJBelum ada peringkat
- EE61 Power System AnalysisDokumen3 halamanEE61 Power System AnalysisMartin De Boras PragashBelum ada peringkat
- Model QPDokumen2 halamanModel QPJayamurugan MookkanBelum ada peringkat
- (5058) - 347 T.E. (Electrical) Power System - Ii (2012 Course)Dokumen3 halaman(5058) - 347 T.E. (Electrical) Power System - Ii (2012 Course)Shubham KaklijBelum ada peringkat
- GATE Lectures by KN Rao: Machines Problem Set - Synchronous MachinesDokumen8 halamanGATE Lectures by KN Rao: Machines Problem Set - Synchronous MachinesGUJJALA TARUN MANIKYA KIRANBelum ada peringkat
- CT ratio error calculations and limitsDokumen4 halamanCT ratio error calculations and limitsKamal NorlieBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4Dokumen5 halamanUnit 4Sri Ram KBelum ada peringkat
- Sheet 1Dokumen5 halamanSheet 1meeedooo.abo.elenenBelum ada peringkat
- Power SystemDokumen4 halamanPower Systemj settyBelum ada peringkat
- How to Calculate Short Circuits Using the Point-to-Point MethodDokumen9 halamanHow to Calculate Short Circuits Using the Point-to-Point MethodMuhammad Irfan Ardiansyah100% (1)
- Fault analysis and sequence networks of power systemsDokumen7 halamanFault analysis and sequence networks of power systemsDenish Gupta0% (1)
- Synchronous Generator Tutorial: Per-Phase Equivalent Circuit and Power EquationDokumen11 halamanSynchronous Generator Tutorial: Per-Phase Equivalent Circuit and Power EquationSimon LarssonBelum ada peringkat
- Ee 6501 - Power System Analysis Unit-3 Fault Analysis-Balanced Faults Part ADokumen4 halamanEe 6501 - Power System Analysis Unit-3 Fault Analysis-Balanced Faults Part AVbalaji VaithiyanathanBelum ada peringkat
- Psa ModelDokumen2 halamanPsa ModelSyed MeerBelum ada peringkat
- PFIDokumen16 halamanPFIumairBelum ada peringkat
- ECE 476 Exam #1 AnswersDokumen5 halamanECE 476 Exam #1 AnswersUlaş YoldaşBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 1Dokumen8 halamanTutorial 1Pradeep Kumar SahooBelum ada peringkat
- ECE 476 Exam #1 Tuesday, October 6, 2015: NameDokumen7 halamanECE 476 Exam #1 Tuesday, October 6, 2015: NameTaher JebreelBelum ada peringkat
- Elec Engg Exit Exam 2018 (Part 9)Dokumen10 halamanElec Engg Exit Exam 2018 (Part 9)Master JaguarBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesDari EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesBelum ada peringkat
- Line Loss Analysis and Calculation of Electric Power SystemsDari EverandLine Loss Analysis and Calculation of Electric Power SystemsBelum ada peringkat
- Partial Discharge Detection For Gas-Insulated Switchgear in ServiceDokumen38 halamanPartial Discharge Detection For Gas-Insulated Switchgear in ServiceممشطBelum ada peringkat
- PD History and FutureDokumen0 halamanPD History and FutureممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Management and Safe Handling Procedures For (Sf6) GasDokumen21 halamanManagement and Safe Handling Procedures For (Sf6) GasKhaled KhaledBelum ada peringkat
- High Voltage TechniquesDokumen108 halamanHigh Voltage Techniquesممشط75% (4)
- Gas-Insulated Switchgear From 72.5 To 800 KV: Excellent Systems That Create Lasting ValueDokumen16 halamanGas-Insulated Switchgear From 72.5 To 800 KV: Excellent Systems That Create Lasting ValueممشطBelum ada peringkat
- HV Test MeasurementsDokumen11 halamanHV Test Measurementsreza515heiBelum ada peringkat
- Gis PDFDokumen28 halamanGis PDFgloby_pnbBelum ada peringkat
- Gas Insulated Transmission Lines GILDokumen2 halamanGas Insulated Transmission Lines GILممشط100% (1)
- 0909 Social AcceptanceDokumen6 halaman0909 Social AcceptanceممشطBelum ada peringkat
- DCDokumen23 halamanDCممشطBelum ada peringkat
- SF6 HandlingDokumen4 halamanSF6 HandlingممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Handling and Use of Sulfur Hexafluoride GasDokumen8 halamanHandling and Use of Sulfur Hexafluoride GasممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Circuit Breakers Timing Test SystemDokumen4 halamanCircuit Breakers Timing Test SystemSusan PintoBelum ada peringkat
- HV Test MeasurementsDokumen11 halamanHV Test Measurementsreza515heiBelum ada peringkat
- Section 1: Mechanical Check and Visual Inspection:: Testing Engineer Nour QC Maaden WitnessDokumen5 halamanSection 1: Mechanical Check and Visual Inspection:: Testing Engineer Nour QC Maaden WitnessMourad BenderradjiBelum ada peringkat
- Circuit Breakers Timing Test SystemDokumen4 halamanCircuit Breakers Timing Test SystemSusan PintoBelum ada peringkat
- Circuit Breakers Timing Test SystemDokumen4 halamanCircuit Breakers Timing Test SystemSusan PintoBelum ada peringkat
- الفحوصات الكهربائيةDokumen14 halamanالفحوصات الكهربائيةMustafa MurshedBelum ada peringkat
- Section 1: Mechanical Check and Visual Inspection:: Testing Engineer Nour QC Maaden WitnessDokumen5 halamanSection 1: Mechanical Check and Visual Inspection:: Testing Engineer Nour QC Maaden WitnessMourad BenderradjiBelum ada peringkat
- Skin Effect Is DefinedDokumen2 halamanSkin Effect Is DefinedممشطBelum ada peringkat
- GISDokumen10 halamanGISممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Power TransformerDokumen54 halamanPower TransformerممشطBelum ada peringkat
- SsDokumen1 halamanSsممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Power TransformerDokumen54 halamanPower TransformerممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Unsymmetrical Fault Calculations: With The Help of Scientific Calculator, Can Be Directly Changed To and ViceDokumen1 halamanUnsymmetrical Fault Calculations: With The Help of Scientific Calculator, Can Be Directly Changed To and ViceممشطBelum ada peringkat
- Partial discharge display: void; point to planeDokumen1 halamanPartial discharge display: void; point to planeممشطBelum ada peringkat
- 2005 16 Autumn Wiring Matters Earthing Your Questions AnsweredDokumen7 halaman2005 16 Autumn Wiring Matters Earthing Your Questions AnsweredAbhijeet KulkarniBelum ada peringkat
- Blank Page TemplateDokumen1 halamanBlank Page TemplateممشطBelum ada peringkat