Ashley's Research
Diunggah oleh
cuideasJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Ashley's Research
Diunggah oleh
cuideasHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Ashley Haydock 12/20/12 Research Topics: My research focuses on developing a time-based weighted support vector machine prognostic algorithm
for the remaining useful life estimation of a historic masonry monument, Fort Sumter. In recent years, a significant amount of research has been directed towards the development of prognostic methodologies predicting the future condition of an engineering system to assist condition based maintenance. However, these methods, possessing potential to further the structural health management of engineering systems, have yet to be applied to historic masonry.
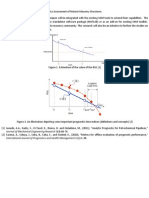
Figure 1. Benefit of prognostic techniques incorporated into condition based maintenance to extend a systems remaining useful life (RUL) (EI-Tawil et al., 2011).
I will develop a weighted support vector regression prognostic technique that allows increased importance of data points closer to the prediction window with the intent of improving predictions for application to simulated data from an ANSYS finite element model of a historic masonry casement within Fort Sumter (Figure 2). Parametric studies will then be performed to compare the prediction accuracy of several shapes of weighting functions to maximize the potential of this unique weighted support vector regression approach in predicting the behavior of Fort Sumter.
Figure 2. Finite element model of the Fort Sumter casement for prognostic application.
My thesis will contribute to the knowledge base by providing an evaluation of existing prognostic techniques for their adaptability to historic masonry structures as well as a discussion of the challenges in this application. In addition, a unique weighted support vector regression prognostic algorithm will be
Ashley Haydock 12/20/12 introduced in application to a historic masonry fortification, Fort Sumter with recommendations for maximizing the potential of this prognostic algorithm. References EI-Tawil, K., Kadry, S., Jaoude, A., Noura, H., and Ouladsine, M. 2011. Analytic Prognostic for Petrochemical Pipelines, Journal of Mechanical Engineering Research, 3(3): 64-74.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Atamturktur ResumeDokumen10 halamanAtamturktur ResumecuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Sez Atamturktur - BiographyDokumen1 halamanSez Atamturktur - BiographycuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Atamturktur LAUR Report LA-14414 (V&V Study)Dokumen132 halamanAtamturktur LAUR Report LA-14414 (V&V Study)cuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Saurabh ResumeDokumen3 halamanSaurabh ResumecuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Curriculum Vitae-April 2013Dokumen18 halamanCurriculum Vitae-April 2013cuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Curriculum Vitae-September - 2013Dokumen17 halamanCurriculum Vitae-September - 2013cuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Curriculum Vitae-April 2013Dokumen17 halamanCurriculum Vitae-April 2013cuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Ismail ResumeDokumen3 halamanIsmail ResumecuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Karma YontenDokumen1 halamanKarma YontencuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Murat HamutcuogluDokumen1 halamanMurat HamutcuoglucuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Ismail BioDokumen2 halamanIsmail BiocuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Hailong SunDokumen1 halamanHailong SuncuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Murray FisherDokumen1 halamanMurray FishercuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Matthew's ResearchDokumen1 halamanMatthew's ResearchcuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Andy SheldonDokumen1 halamanAndy SheldoncuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Josh HegenderferDokumen2 halamanJosh HegenderfercuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Zhifeng LiuDokumen1 halamanZhifeng LiucuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Saurabh PrabhuDokumen2 halamanSaurabh PrabhucuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Tun LiDokumen2 halamanTun LicuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Ismail FarajpourDokumen1 halamanIsmail FarajpourcuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Kendra Van BurenDokumen1 halamanKendra Van BurencuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Atamturktur CVDokumen13 halamanAtamturktur CVcuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Austin GillenDokumen1 halamanAustin GillencuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Emma FuDokumen1 halamanEmma FucuideasBelum ada peringkat
- Rodrick TuckerDokumen1 halamanRodrick TuckercuideasBelum ada peringkat