Arsenic Trioxide
Diunggah oleh
BigBoostingHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Arsenic Trioxide
Diunggah oleh
BigBoostingHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
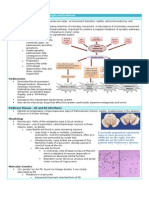
DRUG STUDY AND INFORMATION FORM Generic Name: Arsenic Trioxide Trade Name: Trisenox Drug Class: Differentiating
Agents Structure/Chemistry: As2O3
Pharmacodynamics
Mechanism of Action: Inhibits thioredoxin reductase and thereby generates ROS while inactivating glutathione and other sulfhydryls that scavenge ROS. Arsenic trioxide also upregulates p53, JUN kinase, and caspases associated with the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis and downregulates anti-apoptotic proteins such as bcl-2. It promotes degradation of the APL fusion gene and NF-B (dampens apoptotic response due to genomic damage). It also induces differentiation of leukemic cell lines.
Pharmacologic Effects: Promotes leukemic cell differentiation and creates ROS that contribute to genomic damage.
Drug Resistance or Tolerance:
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption: Well absorbed orally but usually given IV (0.15 mg/kg/day over a 2 hour period for 60 days) Distribution:
Elimination: Eliminated through enzymatic methylation and then excreted in the urine.
Metabolism:
Adverse Side Effects/Toxicity: May experience reversible side effects including hyperglycemia, hepatic enzyme elevations, fatigue, dysesthesias (unpleasant abnormal sense of touch), and lightheadedness. A leukocyte maturation syndrome may develop in 10% of patients that present with pulmonary distress, effusions, and mental status changes (reversed by oxygen, corticosteroids, and temporary discontinuation of arsenic trioxide). May lengthen QT interval because arsenic trioxide inhibits the rapid K+ efflux channels in the myocardium. Drug Interactions: Avoid drugs that lengthen the QT interval such as macrolide antibiotics, quinidine, or methadone.
Therapeutic uses: Given to patients with relapsed APL (acute promyelocytic leukemia) after failed courses of ATRA (tretinoin).
Miscellaneous:
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Mental Status ExaminationDokumen16 halamanThe Mental Status Examinationeloisa.abcedeBelum ada peringkat
- Obgyn Abbreviations For RotationDokumen2 halamanObgyn Abbreviations For RotationBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- Psychosomatic MedicineDokumen14 halamanPsychosomatic MedicineGiuseppe RutiglianiBelum ada peringkat
- GI NotesDokumen19 halamanGI NotesBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- Neurologic Presentationsofaids: Elyse J. Singer,, Miguel Valdes-Sueiras,, Deborah Commins,, Andrew LevineDokumen23 halamanNeurologic Presentationsofaids: Elyse J. Singer,, Miguel Valdes-Sueiras,, Deborah Commins,, Andrew LevineBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- Guideline Watch: Practice Guideline For The Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, 2Nd EditionDokumen9 halamanGuideline Watch: Practice Guideline For The Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, 2Nd EditionBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- GI High YieldDokumen1 halamanGI High YieldBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- Lectura 1 PDFDokumen73 halamanLectura 1 PDFgroudon_18Belum ada peringkat
- Triangles of The Neck Vertebral ArteryDokumen6 halamanTriangles of The Neck Vertebral ArteryBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- Guideline Watch: Practice Guideline For The Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, 2Nd EditionDokumen9 halamanGuideline Watch: Practice Guideline For The Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, 2Nd EditionBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- Psychiatric Genetics: Progress Amid Controversy: Margit Burmeister, Melvin G. Mcinnis and Sebastian ZöllnerDokumen14 halamanPsychiatric Genetics: Progress Amid Controversy: Margit Burmeister, Melvin G. Mcinnis and Sebastian ZöllnerBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- The Mirror Neuron System: Luigi Cattaneo, MD Giacomo Rizzolatti, MDDokumen4 halamanThe Mirror Neuron System: Luigi Cattaneo, MD Giacomo Rizzolatti, MDBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- NervesDokumen139 halamanNervesBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- Bone Cancer Chart 2012Dokumen8 halamanBone Cancer Chart 2012BigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- Neoplasias TableDokumen3 halamanNeoplasias TableBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- Cranial Nerve TractsDokumen2 halamanCranial Nerve TractsBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- Muscles NervesDokumen3 halamanMuscles NervesBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- Cross Sections of Upper LimbDokumen12 halamanCross Sections of Upper LimbBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- Blue Boxes For MusculoskeletalDokumen16 halamanBlue Boxes For MusculoskeletalBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- Neuro Phase Notes MS-1Dokumen43 halamanNeuro Phase Notes MS-1BigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- ThalidomideDokumen2 halamanThalidomideBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- CNS PharmDokumen16 halamanCNS PharmBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- TretinoinDokumen2 halamanTretinoinBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- RituximabDokumen2 halamanRituximabBigBoosting100% (2)
- OfatumumabDokumen2 halamanOfatumumabBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- VincristineDokumen2 halamanVincristineBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- S Mechanism of Action: Inhibits Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Which Leads To The AccumulationDokumen2 halamanS Mechanism of Action: Inhibits Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Which Leads To The AccumulationBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- ProcarbazineDokumen2 halamanProcarbazineBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- NilotinibDokumen2 halamanNilotinibBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- MercaptopurineDokumen2 halamanMercaptopurineBigBoostingBelum ada peringkat