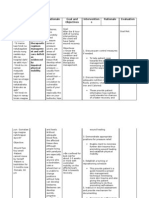
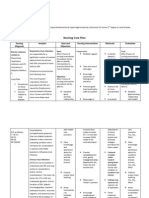
Nursing Care Plan: Cues and Data Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Diunggah oleh
Paul CubacubDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
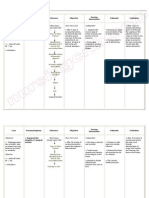
Nursing Care Plan: Cues and Data Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Diunggah oleh
Paul CubacubHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Cabacub, Paul John BSN407/ Group 25
NURSING CARE PLAN
Cues and Data Objective: Nursing Diagnosis Analysis
Pressure ulcers (pressure sores) continue to be a common health problem, particularly among the physically limited or bedridden elderly. The problem exists within the entire health framework, including hospitals, clinics, long-term care facilities and private homes. For many elderly patients, pressure ulcers may become chronic for no apparent reason and remain so for prolonged periods, even for the remainder of the patient's lifetime. A large number of
Goal and objectives After 20 mins of discussion, the patient and relative will gain enough knowledge regarding the contributing factors of pressure ulcer and ways to prevent it.
Interventions
Independent:
Rationale
Evaluation After 20 mins of nursing interventions, the patient and relative was able to verbalize understanding of the contributing factors of pressure ulcer and ways to prevent it.
Risk for Impaired -Body skin weakness integrity related to -An area on body the patients weakness buttocks (Temporary was immobility) reddened
and warm to touch. -Relative ask for nursing stuff help to reposition patient.
Educate patient and relative on the importan ce of proper dieting and food intake. Educate the pt on the importan ce of keeping the skin clean and dry.
Nutrition is fundamen tal to normal cellular integrity and tissue repair. (Potter and Perry, 2008, p. 1310) Moisture softens the skin and causes a break in the skin integrity. (Potter & Perry,
After 10 mins of demostratio n the
Teach
After 10 mins of demonstration
grade 3 and 4 pressure ulcers become chronic wounds, and the afflicted patient may even die from an ulcer complication (sepsis or osteomyelitis). The presence of a pressure ulcer constitutes a geriatric syndrome consisting of multifactorial pathological conditions. The accumulated effects of impairment due to immobility, nutritional deficiency and chronic diseases involving multiple systems predispose the aging skin of the elderly person to increasing vulnerability.
relative will be able to know the proper turning and positioning of the patient.
relative proper repositio n of patient and reposito n pt at least once every two hours.
2009, p. 1302) Positionin g interventi ons reduce pressure and shearing force to the skin. (Potter & Perry, 2009, p. 1305) Moisture softens the skin and causes a break in the skin integrity. (Potter & Perry, 2009, p. 1302) Systemati c
the relative was able to properly turned and positioned the patient.
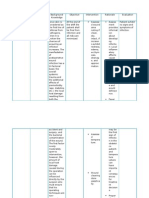
Keep the skin clean and dry
Monitor
skin conditio n at least once a day for color or
texture changes, dermatol ogical conditio ns, or lesions.
Passive
inspectio n can identify impendin g problems early. (Ackley & Ladwig, 2008, p. 754)
Range of motion exercise
This promote proper blood circulatio n
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- NCP Impaired Skintissue IntegrityDokumen5 halamanNCP Impaired Skintissue IntegrityArt Christian RamosBelum ada peringkat
- NCP-Impaired Skin IntegrityDokumen2 halamanNCP-Impaired Skin IntegrityMikee Ann Valdez96% (26)
- NCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDokumen5 halamanNCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDarkCeades100% (2)
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDokumen2 halamanImpaired Skin IntegrityBesael BaccolBelum ada peringkat
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDokumen2 halamanImpaired Skin IntegrityBesael Baccol100% (1)
- NCP LocDokumen2 halamanNCP LocMel RodolfoBelum ada peringkat
- Impaired skin integrity assessmentDokumen2 halamanImpaired skin integrity assessmentJerryson Justo100% (2)
- NCP Fracture Risk For InfectionDokumen3 halamanNCP Fracture Risk For InfectionMiggsBelum ada peringkat
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDokumen1 halamanNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraBelum ada peringkat
- NCP For Impaired Physical MobilityDokumen1 halamanNCP For Impaired Physical Mobilityitzme_andreaBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Impaired Skin IntegrityDokumen2 halamanNCP Impaired Skin IntegrityAshley Kate SantosBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Impaired SkinDokumen2 halamanNCP Impaired Skinarjay2306_obcq100% (1)
- NCP - Impaired Skin IntegrityDokumen1 halamanNCP - Impaired Skin Integrityjanelee28240% (2)
- Skin Integrity Nursing Care for ElderlyDokumen2 halamanSkin Integrity Nursing Care for ElderlyRazz Domenique Reyes Escaros100% (5)
- NCP: Patient With A Pressure UlcerDokumen2 halamanNCP: Patient With A Pressure UlcerICa MarlinaBelum ada peringkat
- NCP - Impaired Skin IntegrityDokumen4 halamanNCP - Impaired Skin IntegrityColette Marie PerezBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDokumen2 halamanNCP Impaired Physical MobilityKristine Young0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Impaire Physical MobilityDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan Impaire Physical Mobilityderic90% (10)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokumen19 halamanCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationEmeEmeka100% (1)
- NCP Epidural HemDokumen32 halamanNCP Epidural HemKatrina PonceBelum ada peringkat
- BSN 3e Duropan Ncp-Knowledge DeficitDokumen12 halamanBSN 3e Duropan Ncp-Knowledge DeficitJane DuropanBelum ada peringkat
- NCP DMDokumen4 halamanNCP DMAarav (мя Ρєяfєт)Belum ada peringkat
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDokumen4 halamanImpaired Skin IntegrityMarjorie Jofel Cerrudo PaciaBelum ada peringkat
- Discharge PlanDokumen5 halamanDischarge PlanRaymond BasiloniaBelum ada peringkat
- Fistula NCPDokumen1 halamanFistula NCPHasna LisnaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan for Skin IntegrityDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan for Skin IntegrityCrystal Joy Misa100% (1)
- Impaired Skin DMDokumen3 halamanImpaired Skin DMimnotdatsunny100% (1)
- Assessing and Preventing Pressure UlcersDokumen8 halamanAssessing and Preventing Pressure UlcersTamil VillardoBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen4 halamanNCPRachel PerandoBelum ada peringkat
- Disturbed Body ImageDokumen3 halamanDisturbed Body Imagenura100% (1)
- NCP Gouty ArthritisDokumen21 halamanNCP Gouty ArthritisArianne Kamille Andes67% (3)
- NCP For Impaired Skin IntegrityDokumen3 halamanNCP For Impaired Skin IntegrityAemz Alacasnap Ainegud100% (1)
- NCP ImmobilityDokumen2 halamanNCP Immobilityxxxcamzxxx67% (6)
- Tarasoff CaseDokumen2 halamanTarasoff Casealyssa marie salcedo100% (1)
- Fluid Volume Deficient Patient with Diabetes MellitusDokumen2 halamanFluid Volume Deficient Patient with Diabetes MellitusMarlon AnryBelum ada peringkat
- NCP - Risk For Peripheral Neurovascular DysfunctionDokumen2 halamanNCP - Risk For Peripheral Neurovascular DysfunctionRene John Francisco50% (4)
- NCP For Post Op Wound and FractureDokumen6 halamanNCP For Post Op Wound and FractureAlyssa Marie0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Fracture PN303Dokumen10 halamanNursing Care Plan For Fracture PN303Fryam Bells100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan for Skin AbscessDokumen1 halamanNursing Care Plan for Skin AbscessKriz_sakuradreamBelum ada peringkat
- Post-Throidectomy Nursing Care PlanDokumen2 halamanPost-Throidectomy Nursing Care PlanCyrus De AsisBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan (ImpairedphyssicalDokumen5 halamanNursing Care Plan (ImpairedphyssicalkuroroexileBelum ada peringkat
- NCP - Risk Impaired Skin RT Altered Circulation (Spinal Injury)Dokumen2 halamanNCP - Risk Impaired Skin RT Altered Circulation (Spinal Injury)yanny0350% (2)
- Managing Chronic Pain Through Holistic Nursing InterventionsDokumen9 halamanManaging Chronic Pain Through Holistic Nursing InterventionsEden Marie FranciscoBelum ada peringkat
- Patient medical record formDokumen4 halamanPatient medical record formSTORAGE FILEBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Impaired Physical Mobility-2Dokumen4 halamanNCP Impaired Physical Mobility-2ejoanbBelum ada peringkat
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Eczema: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDokumen1 halamanNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Eczema: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina Aubrey100% (1)
- Cancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionDokumen2 halamanCancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionAngie MandeoyaBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen2 halamanNCPJhel NabosBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Impaired MobilityDokumen4 halamanNCP Impaired MobilityLouis LazaroBelum ada peringkat
- Motor Vehicle Accident Leads to Multiple Fracture InjuriesDokumen2 halamanMotor Vehicle Accident Leads to Multiple Fracture Injuriesjunifer laynoBelum ada peringkat
- NCP For StrokeDokumen4 halamanNCP For StrokeJASON OGALESCOBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokumen5 halamanAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationArian May MarcosBelum ada peringkat
- NCP CVDDokumen4 halamanNCP CVDNadeene Corpuz SubradoBelum ada peringkat
- Preventing Pressure Ulcers in The Immobile ClientDokumen9 halamanPreventing Pressure Ulcers in The Immobile Clientapi-275839501Belum ada peringkat
- Nursing Diagnosis for TonsillitisDokumen3 halamanNursing Diagnosis for TonsillitisVaneca Go67% (9)
- Clinical Notebook A Quick Mnemonic For Predicting Pressure Sores in ED PatientsDokumen2 halamanClinical Notebook A Quick Mnemonic For Predicting Pressure Sores in ED PatientsChantal CarnesBelum ada peringkat
- Impaired Tissue IntegritiyDokumen2 halamanImpaired Tissue IntegritiyPaolo Martin CuaycongBelum ada peringkat
- Full Download Test Bank For Saunders Comprehensive Review For The Nclex RN Examination 7th Edition Linda Anne Silvestri PDF Full ChapterDokumen36 halamanFull Download Test Bank For Saunders Comprehensive Review For The Nclex RN Examination 7th Edition Linda Anne Silvestri PDF Full Chapterkilter.murk0nj3mx100% (20)
- Test Bank For Saunders Comprehensive Review For The Nclex RN Examination 7th Edition Linda Anne SilvestriDokumen21 halamanTest Bank For Saunders Comprehensive Review For The Nclex RN Examination 7th Edition Linda Anne Silvestribeatermany.imubd2100% (34)
- Preoperative Assessment: Case StudyDokumen5 halamanPreoperative Assessment: Case StudyBernadette Jiz De OrtegaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationPaul Cubacub100% (1)
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDokumen3 halamanNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN FOR ASTHMA MANAGEMENTDokumen3 halamanNURSING CARE PLAN FOR ASTHMA MANAGEMENTPaul Cubacub100% (1)
- Definition of PyelonephritisDokumen3 halamanDefinition of PyelonephritisPaul CubacubBelum ada peringkat
- 707 Area Code FacilitiesDokumen13 halaman707 Area Code FacilitiesEmerson BigginsBelum ada peringkat
- afibHRVtechnics PDFDokumen30 halamanafibHRVtechnics PDFGyörgy BáthoriBelum ada peringkat
- (UGM) Pengumuman Abstrak NSCE 2018Dokumen4 halaman(UGM) Pengumuman Abstrak NSCE 2018ahmadBelum ada peringkat
- PTIDokumen19 halamanPTIDick Jerzy Salazar FranciaBelum ada peringkat
- Illness Script For DiabetesDokumen2 halamanIllness Script For Diabetesapi-371785797Belum ada peringkat
- 2016 Contrast MediaDokumen128 halaman2016 Contrast MediabayarearadBelum ada peringkat
- 02-Clinical Study Leaflet FinalDokumen4 halaman02-Clinical Study Leaflet FinalFakeGBelum ada peringkat
- KPJ Annual Report Highlights Record Financial ResultsDokumen183 halamanKPJ Annual Report Highlights Record Financial Resultsrafiuddinrafiq197Belum ada peringkat
- Moderate Hypoxia On Selected Physiological Variables of Middle and Long Distance RunnersDokumen5 halamanModerate Hypoxia On Selected Physiological Variables of Middle and Long Distance RunnerspodamakriBelum ada peringkat
- Disorders of The Thyroid Gland Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 19eDokumen21 halamanDisorders of The Thyroid Gland Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 19ePeterBelum ada peringkat
- Erasmus: I Am One of The Two Million Who Did It!Dokumen76 halamanErasmus: I Am One of The Two Million Who Did It!eyaslicaBelum ada peringkat
- Residential Nursing Home ProposalDokumen22 halamanResidential Nursing Home Proposalapi-324136209Belum ada peringkat
- 5P Handoff SheetDokumen1 halaman5P Handoff SheetBarry SeeboBelum ada peringkat
- 0901b803800d81e5 PDFDokumen2 halaman0901b803800d81e5 PDFShasikant ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Biostrath PregnancyDokumen1 halamanBiostrath PregnancyAbuHumayraBelum ada peringkat
- CancerDokumen84 halamanCancerKaruna KumariBelum ada peringkat
- Occlusogram Guide for Orthodontic Treatment PlanningDokumen83 halamanOcclusogram Guide for Orthodontic Treatment PlanningEmad Ahmad Anis50% (2)
- Tech Spec Hpia & Spec Indicators 2016-1Dokumen45 halamanTech Spec Hpia & Spec Indicators 2016-1HisyamAl-Muhammadi100% (1)
- International Business: Anglo American PLC Case StudyDokumen10 halamanInternational Business: Anglo American PLC Case StudySujeet KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacy Model Agree CDTM HospitalDokumen7 halamanPharmacy Model Agree CDTM HospitalAyu Dewiani Yuharnanda PutriBelum ada peringkat
- DR - Dr. Fardah Akil, SP - PD (K) Geh Paracetamol 500mg/6jam/oral (Selama 3x24jam) Dr. Faisal Muchtar, SP - An-KICDokumen2 halamanDR - Dr. Fardah Akil, SP - PD (K) Geh Paracetamol 500mg/6jam/oral (Selama 3x24jam) Dr. Faisal Muchtar, SP - An-KICfatimah syamBelum ada peringkat
- Neurophysiology of Juvenile Myoclonic EpilepsyDokumen10 halamanNeurophysiology of Juvenile Myoclonic EpilepsyDiana Marcela Cornejo SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- The Edmonton Zone 2030 PlanDokumen101 halamanThe Edmonton Zone 2030 PlanpkGlobalBelum ada peringkat
- Sun Pharma Presentation on Problems and SolutionsDokumen7 halamanSun Pharma Presentation on Problems and SolutionsKriti SoniBelum ada peringkat
- Supra Ventricular Tachycardia in PregnancyDokumen2 halamanSupra Ventricular Tachycardia in PregnancylulzimkamberiBelum ada peringkat
- Cornell Notes TemplateDokumen3 halamanCornell Notes Templateapi-385916500100% (1)
- Myasthenia GravisDokumen3 halamanMyasthenia GravisEimor PortezBelum ada peringkat
- Soal Bahasa Inggris Letter Writing Smester 2Dokumen29 halamanSoal Bahasa Inggris Letter Writing Smester 2Mutia Rezky FebrianaBelum ada peringkat
- Astern Introdigest Handout PDFDokumen11 halamanAstern Introdigest Handout PDFBenito Camelas LopezBelum ada peringkat
- Teri Maa KiDokumen9 halamanTeri Maa KibeboanilBelum ada peringkat