Aksi Dan Pergerakan Dalam Bola Keranjang
Diunggah oleh
Lee Chun XiangDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Aksi Dan Pergerakan Dalam Bola Keranjang
Diunggah oleh
Lee Chun XiangHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
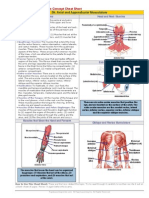
Arms When you shoot a basketball, you are primarily relying on the muscles of your arms to direct your
shot and propel the ball forward. The triceps extend your elbow and play a major role in shooting. The biceps, by contrast, flex the elbow and are important both for aiming and for returning your arm to its normal position after shooting. The muscles of the forearm -- particularly the wrist extensors -play a vital role by moving your wrist and opening and closing your fingers. Shoulders The trapezius, which is located at the collarbone, and the deltoid, which surrounds the joint of the shoulder near the arm, are the primary shoulder muscles involved in shooting a basketball. These muscles help to raise your arm and rotate your shoulders as you aim and then shoot. Chest The pectoral muscles help to move your arms and shoulders forward when leaning forward to shoot and release the basketball. The pectoralis major, the most visible pectoral muscle, and the pectoralis minor, which is located under the pectoralis major, both help to move your shoulders and arms forward. Hands There are 17 muscles in the hand, and when you grip a basketball, shift the positioning of your fingers or lose your grip, these muscles play a role. The long flexors and extensors that extend throughout the hand are the most important muscle group involved in shooting a basketball. Legs While you don't have to use your legs to shoot a basketball, proper form requires that your quadriceps be engaged to bend your knees. When you jump while shooting, the calves work to bend your feet to give you momentum.
Analisis aksi (jaringan statik)
Jaringan statik
Rajah jaringan statik Posisi pertama
Bagi pemain tangan kanan, kaki dan bahu kanan mereka perlu hala ke sasaran . Kemudian, mereka perlu halakan siku tangan yang menolak bola ke arah gol. Selepas itu, mereka perlu mengambil bola dengan menggunakan jari dan mempunyai sedikit ruang di antara bola dengan tapak tangan. Selepas itu, membawa bola turun ke paras dada dengan bengkokkan kedua belah lutut. Sekarang tangan dan kaki berada dalam keadaan fleksi dan otot bisep mengecut manakala otot trisep mengendur. Trapezius dan deltoid juga digunakan untuk mengangkat bahu hala ke sasaran. Otot besar bicep femoris dan gastrocnemius juga digunakan untuk menbengkokkan kaki.
Posisi kedua
Tinggikan badan semula dan mulakan pergerakan bahagian kaki, diikuti oleh badan, lengan, tangan dan akhirnya jari. Gunakan Ikut lajak pergerakan sehingga tumit tergantung di udara atau kedua belah kaki melonjak ke atas. Pada masa ini, tangan dan kaki berada dalam keadaan ekstensi dan otot bisep mengendur manakala otot trisep mengecut. Semasa melompat, otot hamstring memainkan peranan yang sangat penting. Otot hamstring terdiri daripada biceps femoris, semimenbranosus dan semi-tendinosus.
Posisi ketiga
Pergelangan tangan akan bertindak secara hyperextension iaitu bergerak ke arah badan kita semasa menolak bola ke arah gol dan seterusnya bertindak secara fleksi semasa menolak bola dan akhirnya pergerakan ekstensi. Pemain haruslah menlontar bola sebelum mencapai ketinggian sebenar.
1 2 3 4
7 8 9 10 Pergerakan 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Falanges Karpal, metakarpal Radius , ulna humerus skapula femur Patela femur Tarsel metatarsel Tulang
1 2
3 4
6 7
Pergerakan 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Otot Cut tendon of extensor digitorum Flekstor karpiradial, Karpi ulnaris Triseps, Biseps Pectoris major, deltoid , trapezius quadricep Gastrocnemius, tendon achilles, Solues Plantar fascitis, plantar fascia
1 2 3
pergerakan 1 2 3 4 5
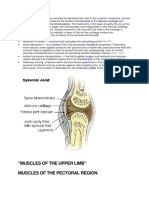
sendi Sendi Kondil( pergelangan tangan) Sendi engsel(siku) Sendi lesung(bahu) Sendi engsel(lutut) Sendi Kondil( pergelangan kaki)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Analysis of MovementDokumen18 halamanAnalysis of MovementEfren Jonicel Daguio Domingo50% (2)
- Muscles Used in RowingDokumen4 halamanMuscles Used in RowingCristine EchaveBelum ada peringkat
- Peter Barbera's BSC2085 Unit 3 reportDokumen3 halamanPeter Barbera's BSC2085 Unit 3 reportjohnnysackBelum ada peringkat
- Upper CalvesDokumen22 halamanUpper Calvesgabriel tbBelum ada peringkat
- The Term Muscle TissueDokumen3 halamanThe Term Muscle Tissueximipa5.almadisyafarelinBelum ada peringkat
- Name. Zainulabidin Roll No. DPT02201029 Assignment. Kinesiology Submitted To. Dr. Ayesha NoureenDokumen13 halamanName. Zainulabidin Roll No. DPT02201029 Assignment. Kinesiology Submitted To. Dr. Ayesha Noureenzain jutt100% (2)
- Arm Muscles OverviewDokumen20 halamanArm Muscles OverviewLilian JerotichBelum ada peringkat
- Major Muscle Groups ExplainedDokumen4 halamanMajor Muscle Groups ExplainedChris Sevilla BurhamBelum ada peringkat
- Muscular SystemDokumen47 halamanMuscular SystemKrystal Kaye AczonBelum ada peringkat
- Human Muscle SystemDokumen6 halamanHuman Muscle SystemmehmatiqBelum ada peringkat
- Biomechanics of Shooting A Free ThrowDokumen20 halamanBiomechanics of Shooting A Free Throwapi-244839574Belum ada peringkat
- Matt and MariaDokumen4 halamanMatt and MariaJanelle05110% (1)
- Sport Presentation: by Scott CadmoreDokumen55 halamanSport Presentation: by Scott CadmorescadmoreBelum ada peringkat
- Discuss Throw PracticalsDokumen15 halamanDiscuss Throw PracticalsDruh RawatBelum ada peringkat
- BiomechDokumen2 halamanBiomechKisha KhuranaBelum ada peringkat
- Human Anatomy,: Chapter 12 Lecture Outline: Appendicular MusclesDokumen70 halamanHuman Anatomy,: Chapter 12 Lecture Outline: Appendicular MusclesdewkmcBelum ada peringkat
- Human Anatomy. The Human Muscles.Dokumen70 halamanHuman Anatomy. The Human Muscles.Stefania Ungureanu100% (1)
- Anatomy of LEG TrainingDokumen53 halamanAnatomy of LEG TrainingDiego Tzompa AcostaBelum ada peringkat
- Week 10 Static StretchingDokumen25 halamanWeek 10 Static StretchingHaruhi MaenoBelum ada peringkat
- PE Fitness ReviewerDokumen6 halamanPE Fitness ReviewerMyles BeatrizBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Hip JointDokumen6 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of the Hip JointSundaraBharathiBelum ada peringkat
- Muscles NamingDokumen17 halamanMuscles NamingAbraham MendezBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6 - Muscles of Upper LimbDokumen61 halamanChapter 6 - Muscles of Upper LimbMahendran Jayaraman100% (1)
- Muscles of The BodyDokumen86 halamanMuscles of The BodyFadhli Quzwain100% (2)
- Therapeutic Exercise Movement AssignmentDokumen4 halamanTherapeutic Exercise Movement Assignmentapi-272092949Belum ada peringkat
- The Anatomy of the Vertical Jump in BasketballDokumen3 halamanThe Anatomy of the Vertical Jump in Basketballewer27Belum ada peringkat
- Natsci ReportDokumen2 halamanNatsci ReportRaven Claire PelongcoBelum ada peringkat
- Activiy AnalysisDokumen13 halamanActiviy AnalysisSean Loran100% (2)
- Muscular Analysis PaperDokumen12 halamanMuscular Analysis Paperapi-547830791Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 BiomechanicsDokumen7 halamanChapter 8 BiomechanicsSakshamBelum ada peringkat
- Nama Otot Yang Terlibat Dalam Aktiviti Teh TarikDokumen2 halamanNama Otot Yang Terlibat Dalam Aktiviti Teh TarikKhanz WongBelum ada peringkat
- Dead LiftsDokumen8 halamanDead LiftsjwarswolvesBelum ada peringkat
- Muscles of the ThighDokumen9 halamanMuscles of the ThighZA IDBelum ada peringkat
- Discuss ThrowDokumen15 halamanDiscuss ThrowDruh RawatBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy LegDokumen2 halamanAnatomy LegpawnayBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomi - Olah Raga 1st MeetingDokumen79 halamanAnatomi - Olah Raga 1st MeetingR DarmawanBelum ada peringkat
- Muscle GroupsDokumen25 halamanMuscle GroupsRoxana LorenteBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy & Physiology: To) - The Is LocatedDokumen2 halamanAnatomy & Physiology: To) - The Is LocatedWynton De JesusBelum ada peringkat
- The Process of The SquatDokumen8 halamanThe Process of The SquatespositodominicBelum ada peringkat
- Phases of The PushupDokumen2 halamanPhases of The PushupMaryane AngelaBelum ada peringkat
- Axial and Appendicular Muscles GuideDokumen10 halamanAxial and Appendicular Muscles GuideYasmeen AlnajjarBelum ada peringkat
- "Muscles of The Upper Limb" Muscles of The Pectoral Region: Weeping LubricationDokumen17 halaman"Muscles of The Upper Limb" Muscles of The Pectoral Region: Weeping LubricationKesyaBelum ada peringkat
- VB Muscle Premium Preview 033015Dokumen15 halamanVB Muscle Premium Preview 033015John DavidBelum ada peringkat
- Lower Limb Muscles Guide: Actions and FunctionsDokumen4 halamanLower Limb Muscles Guide: Actions and FunctionsTrisha TamsiBelum ada peringkat
- Muscles and Movement in ExerciseDokumen4 halamanMuscles and Movement in ExerciseRajinderBelum ada peringkat
- Why Anterior Muscles Are Extensors and Posterior Are Flexors? Answer: Muscles of LegDokumen1 halamanWhy Anterior Muscles Are Extensors and Posterior Are Flexors? Answer: Muscles of LegMedic GuruBelum ada peringkat
- BTEC Sport - Anatomy - Muscle GroupsDokumen18 halamanBTEC Sport - Anatomy - Muscle Groupsbenjenkins21Belum ada peringkat
- Revised - How To Kick A Soccer BallDokumen9 halamanRevised - How To Kick A Soccer Ballapi-666641423Belum ada peringkat
- Lower Leg and FootDokumen40 halamanLower Leg and Footapi-295870055Belum ada peringkat
- Boyd J hhpk335 PitchingDokumen14 halamanBoyd J hhpk335 Pitchingapi-240118505Belum ada peringkat
- Stretching: Muscle Strength For SpeedDokumen4 halamanStretching: Muscle Strength For SpeedGerardClarkeBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomical Terms, Muscle Movements & Antagonistic PairsDokumen20 halamanAnatomical Terms, Muscle Movements & Antagonistic PairsSheena GaborBelum ada peringkat
- Reviewer PathfitDokumen8 halamanReviewer PathfitRandom PersonBelum ada peringkat
- Muscular SystemDokumen1 halamanMuscular SystemChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Locomotor and NonDokumen6 halamanLocomotor and NonBernadette PaduaBelum ada peringkat
- Muscoli BiarticolariDokumen2 halamanMuscoli Biarticolarielpibedeoro1993Belum ada peringkat
- Myology: Gansheng-Wei Department of AnatomyDokumen46 halamanMyology: Gansheng-Wei Department of Anatomyprasun_vBelum ada peringkat
- Morphosphysiology of The KneeDokumen18 halamanMorphosphysiology of The KneeAlejo RoseroBelum ada peringkat
- Healthy Hips Handbook: Exercises for Treating and Preventing Common Hip Joint InjuriesDari EverandHealthy Hips Handbook: Exercises for Treating and Preventing Common Hip Joint InjuriesBelum ada peringkat
- Dokumen - Tips Soal Final Neuropsikiatri 2012 Acrom10nDokumen1 halamanDokumen - Tips Soal Final Neuropsikiatri 2012 Acrom10nariqBelum ada peringkat
- Nota Untuk KurusDokumen1 halamanNota Untuk KurusLee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- EwdwdwDokumen1 halamanEwdwdwLee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- Just For Upload 5Dokumen1 halamanJust For Upload 5Lee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- Eula enDokumen7 halamanEula enPantaziu BogdanBelum ada peringkat
- EdDokumen1 halamanEdLee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- EdDokumen1 halamanEdLee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- Uploaded 2Dokumen1 halamanUploaded 2Lee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- UploadDokumen1 halamanUploadLee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- Upload 7Dokumen1 halamanUpload 7Lee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- Just For Upload 3Dokumen1 halamanJust For Upload 3Lee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- Just For Upload 3Dokumen1 halamanJust For Upload 3Lee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- Rubik PerbentanganDokumen13 halamanRubik PerbentanganLee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- UploadDokumen1 halamanUploadLee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- UploadDokumen1 halamanUploadLee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- Pj m3 tutorial after kuliah Psv m4 next weekDokumen1 halamanPj m3 tutorial after kuliah Psv m4 next weekLee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- Just For Uplaod 2Dokumen1 halamanJust For Uplaod 2Lee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- Maria OzawaDokumen1 halamanMaria OzawaLee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- Prinsip KejurulatihanDokumen7 halamanPrinsip KejurulatihanLee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- Rubik PerbentanganDokumen13 halamanRubik PerbentanganLee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- Just For Upload 2Dokumen2 halamanJust For Upload 2Lee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- Rubik PerbentanganDokumen13 halamanRubik PerbentanganLee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDokumen1 halamanNew Microsoft Word DocumentLee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- Jadual Nov 2013 PDFDokumen8 halamanJadual Nov 2013 PDFLee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat
- ELPDokumen5 halamanELPLee Chun XiangBelum ada peringkat