PL1 3
Diunggah oleh
Dennis ValdezJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
PL1 3
Diunggah oleh
Dennis ValdezHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
BioSciLab
Valdez, Dennis Bryan A.
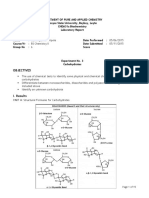
Experiment 3: Metaplasmic Materials in Cells Metaplasmic Materials - non-living - not a natural part of function of a cell - aid in cell defense, structural maintenance, and storage 3 Categories 1. Reserved Material - carbohydrates, fats, oils, nitrogenous substances (e.g. protein) 2. Secretory Material - enzymes (catalyzes reactions)
o AST Aspartate Aminotransferase
Found in RBC, Lymphocytes nectar, pigment
3. Waste Material - nitrogenous and non-nitrogenous substances - e.g. Ammonia, creatinine - others: alkaloids, glucosides, tannins, gums, mucilages, resins, latex, organic acids, essential oils, mineral crystals, raphides, sphaerophides.
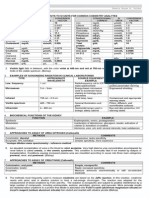
Sliced Section Potato Stain / Reagent Iodine Positive Result Violet, Blue Blue-violet, Black Reactive Material Starch - amylopectin (80% - 90%) - amylose (10% - 20%) Additional Remarks Iodine slides into starch coil to give a positive result.
Banana
Benedict Solution
Yellow, orange, yellow orange
Sugar - reducing sugar
Also used to test presence of sugar in urine
Peanut
Sudan III
Red
Triglycerides
Sudan III is a Lysochrome (lipid soluble dye) Also used to detect fat in stool DZ: Streotorrhea
White Bean
10% HNO3 - heat NH3
Orange Yellow green
Tryptophan Tyrosine
a.k.a. Xanthoproteic test - nitration of aromatic compounds
BioSciLab
Valdez, Dennis Bryan A.
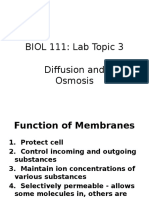
Experiment 4: HOMEOSTASIS AND THE PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE CELLS HOMEOSTASIS balance or equilibrium - State of equilibrium in the body with respect to functions, composition of fluids and tissues. 1. OSMOSIS - movement of water across the selectively permeable membrane from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. a. In a liquid o Water + KMnO4 b. In a colloidal medium o Eosin dye on solidified gelatin c. Through a membrane o Sugar solution (osmometer) 3. ACTIVE TRANSPORT - carrier-mediated process that requires ATP and can move substances against a concentration gradient. - movement of solute from lower concentration to higher concentration. - needs ATP (energy) Ex: Sodium-Potassium Pump 4. FILTRATION - movement, due to a pressure difference, of a liquid through a filter that prevents some or all of the substances in the liquid from passing through. - the fluid movement results from the pressure or weight of the fluid, pushing against the partition. - the fluid or substance small enough to pass through the holes move to the substances larger than the holes do not pass through. Ex: kidney (glomerular filtration) 5. ADSORPTION - bring substances near each other thus, promoting chemical reaction; molecules continually pass into and away from it. - Adhesion stick on the surface 6. IMBIBING ACTION - To drink, suck, receive Ex: sponge 7. SURFACE TENSION - molecules in the interior of the homogenous liquid are attracted in all directions by surrounding molecules to move freely in all directions. 8. VISCOSITY - resistance of fluid to flow Research: 5% NaCl Hypertonic Not same concentration of NaCl in blood 5% Glucose Isotonic Same glucose concentration in the blood
a. Osmotic Pressure - force required to prevent the movement of water across a selectively semi-permeable membrane. b. Osmotic potential - Minimum pressure required to prevent fluid from moving as a result of osmosis. HYPOTONIC ISOTONIC HYPERTONIC (0.5% NaCl) (0.9% NaCl NSS) (5% NaCl)
HEMOLYSIS - swell, burst (lysis)
NORMAL - equilibrium - no net movement
CRENATION - shrink, crenate
NSS - Normal Saline Solution - wash RBC to make RCS - RCS Red Cell Suspension o Blood transfusion for cross matching. 2. DIFFUSION - tendency for solute molecules to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration in solution - the product of the constant random motion of all atoms, molecules, or ions in a solution.
EXPERIMENT 5: BUFFER - chemical that resists change of pH by either an acid or a base is added to a solution containing a buffer. - when an acid is added to a buffered solution, the buffer binds to the [H+] from causing a decrease in pH of the solution. - any substance that can reversibly bind H+. Example: 1. Bicarbonate-Carbonic Acid Buffer System H+ + HCO3- H2CO3 CO2 + H2O
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Osazone Test PDFDokumen10 halamanOsazone Test PDFreddyBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Complex Ions Intro and ShapeDokumen10 halaman2 Complex Ions Intro and ShapeSilvia WulandariBelum ada peringkat
- Enzyme Classification Nomenclature PDFDokumen11 halamanEnzyme Classification Nomenclature PDFramsrivatsan100% (1)
- Rosemarie Parse PDFDokumen4 halamanRosemarie Parse PDF李思雨Belum ada peringkat
- Buffers Booklet - CalbiochemDokumen37 halamanBuffers Booklet - CalbiochemAMPBelum ada peringkat
- PolysaccharidesDokumen12 halamanPolysaccharidesMuhammad AzimBelum ada peringkat
- CARBOHYDRATES For Biochem Lab-1Dokumen28 halamanCARBOHYDRATES For Biochem Lab-1xylentknightBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 - Proteins NotesDokumen16 halamanUnit 2 - Proteins NotesPRIYA SHEETAK100% (1)
- Heteropolysaccharides Lecture For 1st Yr MBBS by DR Waseem KausarDokumen20 halamanHeteropolysaccharides Lecture For 1st Yr MBBS by DR Waseem KausarIMDCBiochem67% (6)
- Qualitative Test For CarbohydratesDokumen2 halamanQualitative Test For CarbohydratesMomerBelum ada peringkat
- Anaphy Prelims ReviewerDokumen11 halamanAnaphy Prelims ReviewerMariz Elizabeth TaytayBelum ada peringkat
- Isolation of Phosphorylated and Non - Phosphorylated Lipids From Bos Taurus Brain and Characterization of Isolated Lipids and Standards Using Various Chemical TestsDokumen20 halamanIsolation of Phosphorylated and Non - Phosphorylated Lipids From Bos Taurus Brain and Characterization of Isolated Lipids and Standards Using Various Chemical TestsShiba FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Protein Notes PDFDokumen38 halamanProtein Notes PDFLUi Anne Mateo LatogBelum ada peringkat
- Epimer of GlucoseDokumen8 halamanEpimer of GlucoseMohammad BaberBelum ada peringkat
- BCM 202Dokumen49 halamanBCM 202Naufal QaweimBelum ada peringkat
- Classification and Nomenclature of EnzymesDokumen12 halamanClassification and Nomenclature of EnzymesmcgilicuttyBelum ada peringkat
- Week 2 Practical - Chemistry of CarbohydratesDokumen7 halamanWeek 2 Practical - Chemistry of CarbohydratesPranabes Bhattacharyya100% (1)
- Lecture 3 - Alkenes and AlkynesDokumen55 halamanLecture 3 - Alkenes and AlkynesS JBelum ada peringkat
- Tubular Reabsorption & SecretionDokumen25 halamanTubular Reabsorption & SecretionRishabh DangiBelum ada peringkat
- Psychology KMTCDokumen250 halamanPsychology KMTCMercy AdeolaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Bio ChemDokumen23 halaman1 Bio ChemRuwi Loren Villocino100% (2)
- BiochemistryDokumen21 halamanBiochemistryJaymarie ZabateBelum ada peringkat
- Regulation of Blood GlucoseDokumen21 halamanRegulation of Blood GlucoseDimple PatelBelum ada peringkat
- HW - Carbohydrate Metabolism II & Lipid MetabolismDokumen2 halamanHW - Carbohydrate Metabolism II & Lipid MetabolismyanBelum ada peringkat
- Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary Structures of A ProteinDokumen21 halamanPrimary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary Structures of A ProteinDALITSO CHIKOYA100% (1)
- Heart Dissection Lab Report Guide2Dokumen7 halamanHeart Dissection Lab Report Guide2Dylan FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Oxidase Test Principle:: Campylobacter Andpasteurella Species (Oxidase Positive)Dokumen5 halamanOxidase Test Principle:: Campylobacter Andpasteurella Species (Oxidase Positive)Janina MedicieloBelum ada peringkat
- BenedictDokumen10 halamanBenedictJose Ian Pagarigan BautistaBelum ada peringkat
- Acidosis and AlkolosisDokumen4 halamanAcidosis and AlkolosisDani PhilipBelum ada peringkat
- Structure and Function of CellsDokumen93 halamanStructure and Function of CellsRonald BakangBelum ada peringkat
- Carbohydrates TestsDokumen3 halamanCarbohydrates TestsChara LomitengBelum ada peringkat
- Isolation and Characterization of Saponifiable and NonDokumen18 halamanIsolation and Characterization of Saponifiable and NonJhoanna Rein Duzon100% (2)
- Kidney Nephron Structure and FunctionDokumen4 halamanKidney Nephron Structure and Functionxanxan4321Belum ada peringkat
- Lec 1 - Biochemistry and MedicineDokumen89 halamanLec 1 - Biochemistry and MedicineLloyd Jay Lin100% (1)
- Part I Lab Manual 2013Dokumen44 halamanPart I Lab Manual 2013Professor Rakesh Sharma Biochemistry Lectures100% (1)
- Benedict - S Test - FinalDokumen28 halamanBenedict - S Test - FinalTom Anthony TonguiaBelum ada peringkat
- Water and PHDokumen154 halamanWater and PHIMDCBiochemBelum ada peringkat
- What Are CarbohydratesDokumen36 halamanWhat Are CarbohydratesPINNACLE CAFEBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry: DR - Radhwan M. Asal Bsc. Pharmacy MSC, PHD Clinical BiochemistryDokumen13 halamanBiochemistry: DR - Radhwan M. Asal Bsc. Pharmacy MSC, PHD Clinical BiochemistryAnas SeghayerBelum ada peringkat
- Denaturation of ProteinsDokumen32 halamanDenaturation of ProteinsAhmad KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Properties of BloodDokumen3 halamanProperties of BloodRaj SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Color Reactions of ProteinsDokumen1 halamanColor Reactions of ProteinsZarah Pauline JimenezBelum ada peringkat
- CarbohydratesDokumen156 halamanCarbohydrateseiddnewBelum ada peringkat
- Tests For Carbohydrates: Group IiDokumen17 halamanTests For Carbohydrates: Group IiAnanda VijayasarathyBelum ada peringkat
- Cell HomogenizationDokumen6 halamanCell Homogenizationfrancis harvey rodulfoBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of Lipids: Bio-Molecules Categorized As Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids and Nucleic Acids LipidsDokumen5 halamanClassification of Lipids: Bio-Molecules Categorized As Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids and Nucleic Acids Lipidsjoi orpillaBelum ada peringkat
- Tissues ReviewerDokumen5 halamanTissues ReviewerJoannah MarieBelum ada peringkat
- Milk - Experiment 11Dokumen16 halamanMilk - Experiment 11Joshuel MontecilloBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry PowerpointDokumen14 halamanBiochemistry PowerpointLelaBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 9Dokumen3 halamanExperiment 9cherokeeBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 3 - CarbohydratesDokumen15 halamanExperiment 3 - CarbohydratesNur Setsu100% (1)
- Lab 3 Diffusion and OsmosisDokumen20 halamanLab 3 Diffusion and OsmosisrashadwcartwrightBelum ada peringkat
- (1stsem MANUAL) Biochemistry LecDokumen150 halaman(1stsem MANUAL) Biochemistry LecAngela Louise SmithsBelum ada peringkat
- 2.1 Lipid Chemistry Part 1Dokumen6 halaman2.1 Lipid Chemistry Part 1Alexandra DalisayBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry Experiment1 CarbohydratesDokumen10 halamanBiochemistry Experiment1 CarbohydratesChery-an PletBelum ada peringkat
- Polysaccharides: Submitted By:Dph Momina, Fallah, Noor, Cemal, Ayesha, Uzma, Nimra & AmmaraDokumen21 halamanPolysaccharides: Submitted By:Dph Momina, Fallah, Noor, Cemal, Ayesha, Uzma, Nimra & AmmaraCemal SarwarBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry of Kidneys and UrineDokumen18 halamanBiochemistry of Kidneys and UrineAndrias PutriBelum ada peringkat
- The Chemistry and Pharmacology of Taxol® and its DerivativesDari EverandThe Chemistry and Pharmacology of Taxol® and its DerivativesBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Sample Blood + 0.30% Nacl Solution: Activity No. 2: Osmotic Behavior of Red Blood Cells Experimental PlatesDokumen1 halamanBlood Sample Blood + 0.30% Nacl Solution: Activity No. 2: Osmotic Behavior of Red Blood Cells Experimental PlatesDennis ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Ti Bajssít Ajkáyo NaljjajjegénjDokumen8 halamanTi Bajssít Ajkáyo NaljjajjegénjDennis ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Grams: Allowable Actual Weight of Blood: 532 - 627Dokumen1 halamanGrams: Allowable Actual Weight of Blood: 532 - 627Dennis ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Alcamo's Laboratory Fundamentals of Microbiology: by Jeffrey C. PommervilleDokumen2 halamanAlcamo's Laboratory Fundamentals of Microbiology: by Jeffrey C. PommervilleDennis ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Mi..cr..o ...... Ans - Wer.s.h..eet....Dokumen67 halamanMi..cr..o ...... Ans - Wer.s.h..eet....Dennis ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Erythropoiesis: Stages of MaturationDokumen3 halamanErythropoiesis: Stages of MaturationDennis ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Prion Diseases: Primary StructuresDokumen4 halamanPrion Diseases: Primary StructuresDennis ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Significance: Endothelial DysfunctionDokumen1 halamanSignificance: Endothelial DysfunctionDennis ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- CrazyDokumen1 halamanCrazyDennis ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Q U Ota T Ion.p DFDokumen1 halamanQ U Ota T Ion.p DFDennis ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Food Preferences of Dmmmsu Laboratory High Schoolstudents: Their Implications To Nutrition EducationDokumen1 halamanFood Preferences of Dmmmsu Laboratory High Schoolstudents: Their Implications To Nutrition EducationDennis ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Dennis Bryan A. ValdezDokumen58 halamanDennis Bryan A. ValdezDennis ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Blood and Tissue FlafellatesDokumen4 halamanBlood and Tissue FlafellatesDennis ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Antibodies Produced Against RH AntigensDokumen1 halamanAntibodies Produced Against RH AntigensDennis ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Transcription and Translation Practice WorksheetDokumen4 halamanTranscription and Translation Practice Worksheetsmith joeBelum ada peringkat
- BIO270 Prelab 1 Assignment 2014Dokumen8 halamanBIO270 Prelab 1 Assignment 2014noahyuyanBelum ada peringkat
- PlasmodiumDokumen10 halamanPlasmodiumBadar MinhasBelum ada peringkat
- Daily Lesson Plan: 7e's ApproachDokumen6 halamanDaily Lesson Plan: 7e's ApproachSonny MagdadaroBelum ada peringkat
- QA Lesson Plan L3 First Aid at Work RQF - Including Catastrophic BleedingDokumen41 halamanQA Lesson Plan L3 First Aid at Work RQF - Including Catastrophic BleedingPhysical Education Scotland88% (8)
- T Cell Development Thymic Education of T CellDokumen34 halamanT Cell Development Thymic Education of T Cellapi-273068056Belum ada peringkat
- LipidDokumen36 halamanLipidSina AgataBelum ada peringkat
- Is Childhood A Universal Experience?Dokumen8 halamanIs Childhood A Universal Experience?camilo jamesBelum ada peringkat
- Pener1991, Locust Phase Polymorphism and Its EndocrineDokumen79 halamanPener1991, Locust Phase Polymorphism and Its EndocrineAdriano Medeiros de SiqueiraBelum ada peringkat
- PG I IflashDokumen4 halamanPG I IflashNIGHT tubeBelum ada peringkat
- Umbilical Cord Blood BankingDokumen290 halamanUmbilical Cord Blood BankingcmBelum ada peringkat
- XI NEET - Dakshana Test ScheduleDokumen5 halamanXI NEET - Dakshana Test SchedulePoornima K TBelum ada peringkat
- 2794-Article Text-8720-1-10-20191103Dokumen9 halaman2794-Article Text-8720-1-10-20191103blowyour mindBelum ada peringkat
- Filogenia de Briofitos SensulatoDokumen1 halamanFilogenia de Briofitos SensulatoYuyitoS2714Belum ada peringkat
- RHS Masterclass On Rose Pruning PDFDokumen3 halamanRHS Masterclass On Rose Pruning PDFCebotari Tatiana50% (2)
- Apostolou Wang 2020Dokumen11 halamanApostolou Wang 2020Riotgryph LepitorusBelum ada peringkat
- Origin of Eukaryotic Cell PDFDokumen8 halamanOrigin of Eukaryotic Cell PDFaco_golarBelum ada peringkat
- Enteropathogenic Escherichia Coli RESISTEN ANTIBIOTIK: Infektifitas Fage Litik Dari Limbah Cair Rumah Tangga TerhadapDokumen61 halamanEnteropathogenic Escherichia Coli RESISTEN ANTIBIOTIK: Infektifitas Fage Litik Dari Limbah Cair Rumah Tangga TerhadapAisyah AminiBelum ada peringkat
- The Muscular System: Powerpoint Lecture SlidesDokumen130 halamanThe Muscular System: Powerpoint Lecture SlidesTricia Mae CorpuzBelum ada peringkat
- Complete Abstract Book ASTMH - Atlanta 2012-USADokumen3 halamanComplete Abstract Book ASTMH - Atlanta 2012-USAPercy Lezama VigoBelum ada peringkat
- Microbiomes Health and The Environment 1676562923Dokumen733 halamanMicrobiomes Health and The Environment 1676562923SagenxBelum ada peringkat
- Fascia of The Head & NeckDokumen8 halamanFascia of The Head & NeckMahesh Jung KhadkaBelum ada peringkat
- Bioenergetics and Biological Oxidation 2: Biochemistry: Shift 1 - Trans 4Dokumen9 halamanBioenergetics and Biological Oxidation 2: Biochemistry: Shift 1 - Trans 4Gemay DanglayBelum ada peringkat
- The Involvement of Hippocampal Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress in The Pathogenesis of ASDDokumen13 halamanThe Involvement of Hippocampal Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress in The Pathogenesis of ASDZeljko LekovicBelum ada peringkat
- Growth Kinetics 2014Dokumen33 halamanGrowth Kinetics 2014Ivan Aulia BigbandBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Growth 2Dokumen2 halamanPlant Growth 2Asnani AsudinBelum ada peringkat
- Autonomic ReflexesDokumen21 halamanAutonomic ReflexesJoe WeahBelum ada peringkat
- Ecozone Dichotomous KeyDokumen3 halamanEcozone Dichotomous Keyqmtkqz72vhBelum ada peringkat
- International Union For The Protection of New Varieties of PlantsDokumen31 halamanInternational Union For The Protection of New Varieties of PlantsBimo HariokusumoBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing ProcessDokumen23 halamanNursing Processjulesubayubay5428100% (6)