Wetted Wall Column Mass Transfer
Diunggah oleh
Abhishek KumarJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Wetted Wall Column Mass Transfer
Diunggah oleh
Abhishek KumarHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
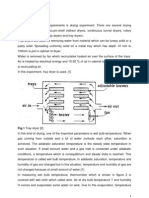
Wetted Wall Column
Aim
Determination of liquid phase mass transfer coefficient in a wetted wall column
using Air Water System
Apparatus Required
Air Water Wetted wall column
Introduction
A wetted wall column is essentially a vertical tube with means of admitting liquid
at the top and causing it to flow downwards along the inside wall of the tube, under the
influence of gravity and means of admitting gas to the inside of the tube, where it flows
through the tower in contact with the liquid. In absence of ripple formation at the liquid
surface, the interfacial area, A, is known and form drag is absent.
Theory
The mass transfer coefficient, K
a
, can be measured in a wetted wall column in
which the area of contact between two phases is known and boundary layer separation
does not take place. A wetted wall column also provides useful information on mass
transfer to and from fluids in turbulent flow.
Various dimensionless groups that control the phenomenon are
Reynolds number, N
Re
= dG/
Schmidt Number, N
sc
= /D
Sherwood Number, N
Sh
= Kd/D
Where,
G = Gas mass velocity, kg/m
2
s
D = Diffusivity coefficient, m
2
/s
d = tube diameter, m
K
a
= mass transfer coefficient.
For turbulent flow mass transfer to pipe wall involving evaporation of liquids in wetted
wall columns, Gilland and Sherwood proposed the correlation
44 . 0 81 . 0
) 023 . 0 (
,
_
,
_
,
_
d
dV
Pd
D
K
G
(1)
For
N
Re
= 2000 3500
N
Sc
= 0.6 2.5
P = 0.1 3 atm
The known flow rate of air at a measured humidity is brought into contact with a film of
water at a certain temperature and vopr pressure. Moisture is absorbed by the air from
water film and the resultant humidity of the exit air and the temperature and vapor
pressure of the entry water measured. The rate of diffusion through the gas film, N
A
, is
given by
m a A
P A K N ) (
(2)
Where,
K
a
= gas film coefficient, kg mole of water transferred. m
2
/h per atmospheric partial
pressure difference.
A = wetted surface of column = dL
(P)
m
= Log mean partial pressure driving force across the ends of the column.
The value of K
a
obtained experimentally can be compared with that predicted
from Sherwood Gilliland correlation.
44 . 0 81 . 0
) 023 . 0 (
,
_
,
_
,
_
d
dV
Pd
D
K
G
(3)
Procedure
1. Switch on the pump to allow the circulating water to flow and regulate the flow
using the valve provided.
2. Measure the water flow rate by the rotameter provided.
3. Start the air circulation and measure the flow rate of air.
4. Note down the wet and dry bulb temperature of air at regular intervals to calculate
the humidity.
5. Also measure the temperature of the water flowing in.
6. Repeat the experiments for different flow rates and temperatures
Formula Used
( ) O P P
P
Humidity
H T
O H
2
2
29
18
1
]
1
,
_
,
_
2
1
1 1
2
1
1
ln
1
1
y
y
y y
y y
y V
PA K
i
i
G
44 . 0 81 . 0
) 023 . 0 (
,
_
,
_
,
_
d
dV
Pd
D
K
G
For the top section
( ) ( ) [ ]
water of fraction mole
a
a
y
+
29
1
18
18
1
For the bottom section
( ) ( ) [ ]
water of fraction mole
b
b
y
+
29
1
18
18
2
from the steam tables, corresponding to water inlet and outlet temperature, calculate the
vapor pressure.
Vapor pressure of water at inlet temperature = P
1
bar
Vapor pressure of water at outlet temperature = P
2
bar
( )
2
2 1
P P
P
avg
+
T
avg
i
P
P
y
, Where P
T
is 1 bar
1
]
1
,
_
,
_
2
1
1 1
2
1
1
ln
1
1
y
y
y y
y y
y V
PA K
i
i
G
Where,
P = 1 bar
A = dL
V = molar flow rate of air [mass flow rate / molecular weight]
Also calculate the theoretical value of K
G
using Sherwood Gilland Equation
Report the following
1. Experimental value of Mass transfer coefficient
2. Theoretical value of mass transfer coefficient using Sherwood Gilliland
correlation
3. Compare the experimental and theoretical values.
4. Five industrial uses of wetted wall column
5. Give any five additional inferences
Observation for wetted wall column
Name: Date:
Group Number:
S.No T
1
T
2
T
3
T
4
T
5
T
6
Air Flow rate,
m
3
/hr
Water flow rate,
m
3
/hr
Specification
T
1
= inlet water temperature
T
2
= outlet water temperature
T
3
= dry bulb temperature of inlet air
T
4
= wet bulb temperature of inlet air
T
5
= dry bulb temperature of outlet air
T
6
= wet bulb temperature of outlet air
Diameter of the column, d = 45 mm
Length of the column, L = 1000 mm
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Wetted - Wall Column PDFDokumen8 halamanWetted - Wall Column PDFSaurab Devanandan33% (3)
- Wetted Wall Column Experiment and Set UPDokumen4 halamanWetted Wall Column Experiment and Set UPvarun kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Manual For Wetted Wall ColumnDokumen8 halamanManual For Wetted Wall ColumnBalRam DhimanBelum ada peringkat
- Wetted-Wall Column ReportDokumen33 halamanWetted-Wall Column ReportmelanBelum ada peringkat
- Exp.50 - Wetted-Wall Absorption ColumnDokumen5 halamanExp.50 - Wetted-Wall Absorption ColumnOzzyBelum ada peringkat
- Wetted Wall ColumnDokumen4 halamanWetted Wall Columnendang dian lestariBelum ada peringkat
- Best Memo ReportDokumen16 halamanBest Memo ReportNadaBelum ada peringkat
- Wetted Wall Column - Docx ReportDokumen20 halamanWetted Wall Column - Docx ReportLookingtowin100% (10)
- Isothermal CSTR PDFDokumen9 halamanIsothermal CSTR PDFprashant_cool_4_uBelum ada peringkat
- Wetted-Wall Column: Separation ProcessDokumen3 halamanWetted-Wall Column: Separation ProcessHuzaifa AftabBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 2 - Forced Draft Cooling TowerDokumen14 halamanExperiment 2 - Forced Draft Cooling TowerSonia YuBelum ada peringkat
- Vapour in Air DiffusionDokumen12 halamanVapour in Air Diffusionshivangsharma105629Belum ada peringkat
- Absorption in Packed Bed Lab ManualDokumen5 halamanAbsorption in Packed Bed Lab ManualAshish Verma100% (1)
- Effect of Temperature on Reaction Rate ConstantDokumen22 halamanEffect of Temperature on Reaction Rate Constantnur athilahBelum ada peringkat
- Absorption of Carbon Dioxide Into WaterDokumen11 halamanAbsorption of Carbon Dioxide Into WaterEstelle Jean CauilanBelum ada peringkat
- Absorption in PackedDokumen21 halamanAbsorption in PackedfreakameBelum ada peringkat
- Wetted Wall Column PDFDokumen4 halamanWetted Wall Column PDFAnupama D. MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Wetted Wall Column AssignDokumen3 halamanWetted Wall Column AssignMuhammad MubasherBelum ada peringkat
- Osbourne ReynoldDokumen13 halamanOsbourne ReynoldN Afiqah Razak0% (1)
- Lab ManualDokumen24 halamanLab ManualAasia FarrukhBelum ada peringkat
- RI Vs Composition Methanol-Water MixtureDokumen12 halamanRI Vs Composition Methanol-Water MixtureAnonymous VeJYFSMWLIBelum ada peringkat
- Bubble Cap Distillation ColumnDokumen3 halamanBubble Cap Distillation Columnnhalieza1067Belum ada peringkat
- Gas Absorption: Determining Drag and Flooding FlowsDokumen5 halamanGas Absorption: Determining Drag and Flooding FlowsDean Joyce AlborotoBelum ada peringkat
- Exp - S1B - Vapor in Air DiffusionDokumen11 halamanExp - S1B - Vapor in Air DiffusionAnuj SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- Wetted Wall ColumnDokumen15 halamanWetted Wall ColumnDEEPAK KUMARBelum ada peringkat
- Helical Coil FlowDokumen4 halamanHelical Coil FlowAshish VermaBelum ada peringkat
- Isothermal Batch ReactorDokumen5 halamanIsothermal Batch ReactorSrikanthBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors (CSTRs) for Chemical Reactions (38 charactersDokumen12 halamanUnderstanding Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors (CSTRs) for Chemical Reactions (38 charactersAisyah Addia AzizanBelum ada peringkat
- Reaction Rate and Rate Constant of The Hydrolysis of Ethyl Acetate With Sodium HydroxideDokumen5 halamanReaction Rate and Rate Constant of The Hydrolysis of Ethyl Acetate With Sodium HydroxideAmyBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory-Scale Cooling Tower Performance AnalysisDokumen17 halamanLaboratory-Scale Cooling Tower Performance AnalysisHazieqah100% (1)
- CHAPTER 03 - 2nd Part - Properties of Pure Fluids-May20Dokumen49 halamanCHAPTER 03 - 2nd Part - Properties of Pure Fluids-May20Scorpion Royal100% (1)
- Vapour in Air DiffusionDokumen4 halamanVapour in Air DiffusionAyush Shrimal100% (1)
- Diffusion Coefficient Full Report TiqaDokumen19 halamanDiffusion Coefficient Full Report TiqaprmzBelum ada peringkat
- Humidification and Air Conditioning: Lecture No. 8Dokumen6 halamanHumidification and Air Conditioning: Lecture No. 8Anonymous UFa1z9XUABelum ada peringkat
- Liquid Phase Chemical Reactor FinalDokumen38 halamanLiquid Phase Chemical Reactor FinalToMemBelum ada peringkat
- Intro CSTRDokumen6 halamanIntro CSTREmmanuel PlazaBelum ada peringkat
- CSTRDokumen20 halamanCSTRSharing Caring100% (1)
- Liquid Level Control SystemDokumen0 halamanLiquid Level Control SystemNajiRihaniBelum ada peringkat
- Gas AbsorptionDokumen24 halamanGas AbsorptionShalini Krishnan100% (1)
- Sieve Plate Distillation ColumnDokumen9 halamanSieve Plate Distillation ColumnAshish VermaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4Dokumen43 halamanChapter 4aliBelum ada peringkat
- Isothermal Semi-Batch Reactor PPT RJC SirDokumen16 halamanIsothermal Semi-Batch Reactor PPT RJC Sirsdjdsf100% (1)
- Lab Report 1 Tray DrierDokumen7 halamanLab Report 1 Tray Drier_never_mind_100% (1)
- Calibration of Peristaltic Pumps - Lab 1Dokumen12 halamanCalibration of Peristaltic Pumps - Lab 1mmccomas08100% (2)
- APT300S Tutorial - RefrigerationDokumen2 halamanAPT300S Tutorial - Refrigerationcarleston thurgood0% (1)
- Final Report PFRDokumen12 halamanFinal Report PFRmark_ancotBelum ada peringkat
- Sieve Plate Distillation Column - Lab ReportDokumen4 halamanSieve Plate Distillation Column - Lab ReportShrankhla NaryaBelum ada peringkat
- Venturimeter and Orifice MeterDokumen5 halamanVenturimeter and Orifice MeterVrushiket Patil100% (1)
- Philipp Louis D#2docxDokumen8 halamanPhilipp Louis D#2docxEymann Jala100% (3)
- Level Control Trainer FinalDokumen6 halamanLevel Control Trainer FinalSiddhartha SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Cre 1 IntroductionDokumen4 halamanCre 1 IntroductionEvangeline LauBelum ada peringkat
- Sedimentation Studies Apparatus DesignDokumen7 halamanSedimentation Studies Apparatus Designgrkhari1100% (2)
- Exp-9 - Liquid Liquid Extraction in A Packed ColumnDokumen5 halamanExp-9 - Liquid Liquid Extraction in A Packed ColumnSiddharth MohapatraBelum ada peringkat
- CSTR FinalDokumen36 halamanCSTR FinalMuhammad Yar KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Mass Transfer Lab ManualDokumen29 halamanMass Transfer Lab ManualPrajwal ChavanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 3 Forced ConvectionDokumen63 halamanChapter - 3 Forced ConvectionRenu Sekaran100% (2)
- Water Vapour Effects in Mass MeasurementDokumen4 halamanWater Vapour Effects in Mass MeasurementaldesanBelum ada peringkat
- Heat and Mass Transfer Calculation of The Intercooler With SprayiDokumen6 halamanHeat and Mass Transfer Calculation of The Intercooler With SprayiBertalan Gyuszi Kristóf0% (1)
- A Critical Investigation Into The Heat and Mass Transfer Analysis of Crossflow Wet Cooling TowersDokumen23 halamanA Critical Investigation Into The Heat and Mass Transfer Analysis of Crossflow Wet Cooling TowersStephen NicholsBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Transfer in Olga 2000Dokumen11 halamanHeat Transfer in Olga 2000Akin MuhammadBelum ada peringkat
- Compulsory License Application 20 January 2016Dokumen15 halamanCompulsory License Application 20 January 2016Abhishek KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Email Id of Controllers PDFDokumen10 halamanEmail Id of Controllers PDFAbhishek KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Geographical Indications ExplainedDokumen23 halamanGeographical Indications ExplainedAbhishek Kumar100% (1)
- Academic and career details of Abhishek KumarDokumen1 halamanAcademic and career details of Abhishek KumarAbhishek KumarBelum ada peringkat
- PVC Rheology and Cone Plate RheometerDokumen6 halamanPVC Rheology and Cone Plate RheometerAbhishek KumarBelum ada peringkat
- HR QuestionsDokumen3 halamanHR QuestionsAbhishek KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Magoosh GRE Ebook PDFDokumen84 halamanMagoosh GRE Ebook PDFJyoti NarangBelum ada peringkat
- Email Id of Controllers PDFDokumen10 halamanEmail Id of Controllers PDFAbhishek KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Dryer DesignDokumen39 halamanDryer DesignPrashanth Chidambaram75% (4)
- Magoosh GRE Ebook PDFDokumen84 halamanMagoosh GRE Ebook PDFJyoti NarangBelum ada peringkat
- Polymer Rheology and ProcessingDokumen57 halamanPolymer Rheology and ProcessingAbhishek KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment On Solar FluxDokumen13 halamanExperiment On Solar FluxAbhishek KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Cone and Plate RheometerDokumen6 halamanCone and Plate RheometerAbhishek KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1Dokumen8 halamanLecture 1brutal_jaxBelum ada peringkat
- Turbulent FlowDokumen17 halamanTurbulent FlowAbhishek KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Pressure Swing Adsorption, Ultrafiltration MembraneDokumen7 halamanPressure Swing Adsorption, Ultrafiltration MembraneAbhishek KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Diffusion CoefficientDokumen5 halamanDiffusion CoefficientAbhishek Kumar0% (1)
- Acid Orange 33 (C H N Na O S) C.I.24780 CAS 6507-77-3Dokumen1 halamanAcid Orange 33 (C H N Na O S) C.I.24780 CAS 6507-77-3Abhishek KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Dimensionless NumbersDokumen5 halamanDimensionless Numbersharry_chemBelum ada peringkat
- FlowsheetDokumen1 halamanFlowsheetAbhishek KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Process Hazards Analysis GuideDokumen90 halamanChemical Process Hazards Analysis GuideAzlan Adnan100% (1)
- CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY GATE-2011 Fats and FertilizersDokumen40 halamanCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY GATE-2011 Fats and FertilizersAbhishek Kumar0% (1)
- KSFL ReportDokumen56 halamanKSFL ReportAbhishek KumarBelum ada peringkat
- How'S The Weather?: Conversation Cheat SheetDokumen2 halamanHow'S The Weather?: Conversation Cheat SheetGaruda WLBelum ada peringkat
- Time Series MethodsDokumen13 halamanTime Series MethodsLuis Alberto IzarraBelum ada peringkat
- ALOHA Final Techdoc and QADokumen51 halamanALOHA Final Techdoc and QAAubrey WessonBelum ada peringkat
- Shaw DewDokumen3 halamanShaw DewrkukgBelum ada peringkat
- Ssmith PDFDokumen42 halamanSsmith PDFannasitBelum ada peringkat
- 335 A320 Landing PerformanceDokumen14 halaman335 A320 Landing Performancepietrovolare79100% (1)
- A Butterfly SmileDokumen15 halamanA Butterfly SmilejenBelum ada peringkat
- POM - Service Facility Layout Organization of FacilitiesDokumen55 halamanPOM - Service Facility Layout Organization of FacilitiesMae Ann KongBelum ada peringkat
- Paris Agreement Report NotesDokumen4 halamanParis Agreement Report NotesLyza PelagioBelum ada peringkat
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 English Hornbill Chapter 2 PDFDokumen4 halamanNCERT Solutions For Class 11 English Hornbill Chapter 2 PDFNS suPER ZoNEBelum ada peringkat
- Shipboard Contingency PlanDokumen2 halamanShipboard Contingency PlanENDO ZIIBelum ada peringkat
- Excavation Guidelines ProcedureDokumen22 halamanExcavation Guidelines ProceduremahmoudbadwyBelum ada peringkat
- Test IntermediateDokumen4 halamanTest IntermediateElitsa BilevaBelum ada peringkat
- Dvorak EIR DiagramDokumen1 halamanDvorak EIR DiagramAndy BollenbacherBelum ada peringkat
- Water Cycle Crossword 1 PDFDokumen2 halamanWater Cycle Crossword 1 PDFMarivic Rioflorido0% (1)
- Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5: Storytelling Traditions Communities Inventions LandmarksDokumen6 halamanWeek 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5: Storytelling Traditions Communities Inventions Landmarksapi-232742605Belum ada peringkat
- Yangkam WordlistDokumen19 halamanYangkam Wordlistxdboy2006Belum ada peringkat
- Watercolor Interpretations PDFDokumen164 halamanWatercolor Interpretations PDFexposus2003100% (3)
- OpenSees Future Direction 2017Dokumen39 halamanOpenSees Future Direction 2017fariasgarciarojasBelum ada peringkat
- Tropical Cyclone NamingDokumen1 halamanTropical Cyclone NamingVenkat NarasimmanBelum ada peringkat
- Wind Resource AssessmentDokumen23 halamanWind Resource AssessmentHmaedBelum ada peringkat
- RLU232 Datasheet enDokumen36 halamanRLU232 Datasheet enMihai ConstantinescuBelum ada peringkat
- Progress in Physical GeographyDokumen41 halamanProgress in Physical GeographyAthziri HernándezBelum ada peringkat
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Solar EnergyDokumen3 halamanAdvantages and Disadvantages of Solar Energyrubenmariadasan100% (1)
- ASCE 7-10 Wind Provisions Effects on Wood DesignDokumen10 halamanASCE 7-10 Wind Provisions Effects on Wood Designtomwells1927Belum ada peringkat
- The Tongue Twister WarDokumen19 halamanThe Tongue Twister Wardianabesoiu4Belum ada peringkat
- Biomes of The Earth-GrasslandsDokumen289 halamanBiomes of The Earth-GrasslandsTurcanu Liliana100% (1)
- Earth: What Makes Our Planet Unique and HabitableDokumen3 halamanEarth: What Makes Our Planet Unique and HabitableJames DelantarBelum ada peringkat
- Haulotte HA16 18PXDokumen74 halamanHaulotte HA16 18PXtiagomacviva100% (1)
- Questions 1-10: Complete The Notes Below. Write For Each AnswerDokumen5 halamanQuestions 1-10: Complete The Notes Below. Write For Each AnswerJanny Torres0% (1)