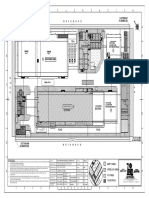
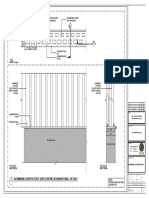
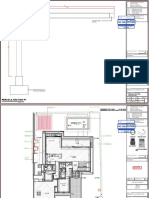
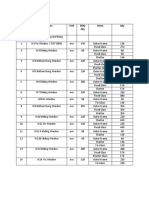
Project
Diunggah oleh
Jacob PriyadharshanHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Project
Diunggah oleh
Jacob PriyadharshanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
The basic idea is to distributively group mobile nodes with similar mobility pattern into a cluster, which can
then interchangeably share their resources for overhead reduction and load balancing, aiming to achieve efficient and scalable routing in DTMN. Due to the lack of continuous communications among mobile nodes and possible errors in the estimation of nodal contact probability, convergence and stability become major challenges in distributed clustering in DTMN. To this end, an exponentially weighted moving average (EWMA) scheme is employed for on-line updating nodal contact probability, with its mean proven to converge to the true contact probability.
Various clustering algorithms have been investigated in the context of mobile ad hoc networks. However, none of them can be applied directly to DTN, because they are designed for well-connected networks DTN hierarchical routing (DHR) protocol to improve routing scalability. DHR is based on a deterministic mobility model, where all nodes move according to strict, repetitive patterns, which are known by the routing and clustering algorithms. It cannot be generalized to such networks with unknown mobility as DTN-based peer-to-peer mobile ad hoc networks. Although it is largely understood by the research community that clustering helps to improve network scalability, no previous work has been done in such emerging unique networks.
K. Fall, A delay-tolerant network architecture for challenged Internets, in Proc. ACM SIGCOMM, pp. 2734, 2003. S. Burleigh, A. Hooke, L. Torgerson, K. Fall, V. Cerf, B. Durst, K. Scott, and H. Weiss, Delay-tolerant networkingan approach to interplanetary Internet, IEEE Commun. Mag., vol. 41, no. 6, pp. 128136, 2003. http://www.princeton.edu/ mrm/zebranet.html. T. Small and Z. J. Haas, The shared wireless infostation model: a new ad hoc networking paradigm (or where there is a whale, there is a way), in Proc. MobiHOC, pp. 233244, 2003. Y. Wang and H. Wu, DFT-MSN: the delay fault tolerant mobile sensor network for pervasive information gathering, in Proc. 26th Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies (INFOCOM07), pp. 12351243, 2006.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- UntitledDokumen15 halamanUntitledJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Expert Series:: Glass Acoustic PerformanceDokumen3 halamanExpert Series:: Glass Acoustic PerformanceJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Dec. 26, 1967 R. T. Casebolt 3,359,573: Vouss), '43 Guns)Dokumen4 halamanDec. 26, 1967 R. T. Casebolt 3,359,573: Vouss), '43 Guns)Jacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Plastic Glazing SpecsDokumen9 halamanPlastic Glazing SpecsJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Marina MenuDokumen1 halamanMarina MenuJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- UntitledDokumen88 halamanUntitledJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Print Ratecard W.E.F. 1st January 2022: Khaleej Times Base Rates City TimesDokumen1 halamanPrint Ratecard W.E.F. 1st January 2022: Khaleej Times Base Rates City TimesJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- 2363 - Bill of QuantitiesDokumen32 halaman2363 - Bill of QuantitiesJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- Aluminium Louvers Fence Over Existing Boundary Wall Details 1Dokumen1 halamanAluminium Louvers Fence Over Existing Boundary Wall Details 1Jacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Individual and Family Application Checklist (Uae) : How To ApplyDokumen9 halamanIndividual and Family Application Checklist (Uae) : How To ApplyJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Kompass - Aircrete Building Materials EN PrintDokumen6 halamanKompass - Aircrete Building Materials EN PrintJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Catted Values: English - Short Long - DescriptioDokumen2 halamanCatted Values: English - Short Long - DescriptioJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Identification of Trash and of Ginned Cotton Soft TechniquesDokumen4 halamanIdentification of Trash and of Ginned Cotton Soft TechniquesJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDokumen18 halamanDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Mic-Value Analyse and Test Design: Fanlimin1 Huanghao3Dokumen3 halamanMic-Value Analyse and Test Design: Fanlimin1 Huanghao3Jacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Pergola Section P1: AdditionDokumen6 halamanPergola Section P1: AdditionJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- Plan-Pergola Section-Aa: Ur BanDokumen1 halamanPlan-Pergola Section-Aa: Ur BanJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- Moisture Sensing in Baled CropsDokumen132 halamanMoisture Sensing in Baled CropsJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Development of Cotton-Yarn-Quality Predicting System: Ying XiaoDokumen4 halamanThe Development of Cotton-Yarn-Quality Predicting System: Ying XiaoJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- SL - No Particulars Unit BOQ Qty Items QtyDokumen2 halamanSL - No Particulars Unit BOQ Qty Items QtyJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- Cummulative Work Report-17.04.2019Dokumen1 halamanCummulative Work Report-17.04.2019Jacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Missing ValuesDokumen361 halamanMissing ValuesJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Bhatia Installation 22-11-15Dokumen1 halamanBhatia Installation 22-11-15Jacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- M/S: Airolink International Construction LLC.: Project: International Indian School, Abu Dhabi Details As Per BoqDokumen8 halamanM/S: Airolink International Construction LLC.: Project: International Indian School, Abu Dhabi Details As Per BoqJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- CW50MM Page42Dokumen106 halamanCW50MM Page42Jacob Priyadharshan100% (1)
- Asg Ant MS 002Dokumen1 halamanAsg Ant MS 002Jacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Material Submittal AluminiumDokumen1 halamanMaterial Submittal AluminiumJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- Al Qaffy G+1 Staff AccoDokumen10 halamanAl Qaffy G+1 Staff AccoJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- Central Contracting (G+2)Dokumen4 halamanCentral Contracting (G+2)Jacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- Side Arm Selection Calculation: W22-Window Is Selected For Calculation. Window Size - 850mm X 1650mmDokumen2 halamanSide Arm Selection Calculation: W22-Window Is Selected For Calculation. Window Size - 850mm X 1650mmJacob PriyadharshanBelum ada peringkat
- VFW Report 2022Dokumen15 halamanVFW Report 2022James CastillonBelum ada peringkat
- Resume Network EngineerDokumen1 halamanResume Network Engineerannisa85Belum ada peringkat
- Number: 350-401 Passing Score: 825 Time Limit: 140 Min File Version: 1.0Dokumen45 halamanNumber: 350-401 Passing Score: 825 Time Limit: 140 Min File Version: 1.0MacKenzie KymberBelum ada peringkat
- Hwids - 2003 03 29 - 00 11 54Dokumen6 halamanHwids - 2003 03 29 - 00 11 54Servicios Inteligentes LtdaBelum ada peringkat
- Cat Intercom Eng 0922 WebDokumen31 halamanCat Intercom Eng 0922 WebHabtamu TadesseBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco Nexus 9200 Platform SwitchesDokumen16 halamanCisco Nexus 9200 Platform SwitchesRobert UrquiaBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Network: Meeting 9Dokumen14 halamanComputer Network: Meeting 9FaldyBelum ada peringkat
- 15CS81 - M3 - OPTIMIZING IP For IoT PDFDokumen28 halaman15CS81 - M3 - OPTIMIZING IP For IoT PDFTushar Singhal100% (1)
- Nma Unit I SolutionDokumen4 halamanNma Unit I SolutionRutu BhattBelum ada peringkat
- IB Specification Vol 1-Release-1.4-2020!04!07Dokumen1.981 halamanIB Specification Vol 1-Release-1.4-2020!04!07margaryandavid111Belum ada peringkat
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- BSNL VMC AN1020-21 (Detailed Visual Guide)Dokumen14 halamanBSNL VMC AN1020-21 (Detailed Visual Guide)Nagaraju Gunturu100% (1)
- Schneider NF3500G4 Product Overview PDFDokumen2 halamanSchneider NF3500G4 Product Overview PDFisaac oropezaBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1 Answer SheetDokumen3 halamanAssignment 1 Answer Sheetmihipa8592Belum ada peringkat
- Kib Migrasi - (SMKN 1 Koto Balingka)Dokumen30 halamanKib Migrasi - (SMKN 1 Koto Balingka)Jamal SyarifBelum ada peringkat
- An Edge Computing Architecture in The Internet of ThingsDokumen4 halamanAn Edge Computing Architecture in The Internet of Thingsjuanito bananasBelum ada peringkat
- Mastering 5G Network Design, Implementation, and OperationsDokumen434 halamanMastering 5G Network Design, Implementation, and OperationsJuan Flores DíazBelum ada peringkat
- ComputerNetworks LabManual PDFDokumen56 halamanComputerNetworks LabManual PDFcityBelum ada peringkat
- Model Answers Summer 2019Dokumen17 halamanModel Answers Summer 2019IF -Nikita GhuleBelum ada peringkat
- Switching - Data CommunicationsDokumen37 halamanSwitching - Data CommunicationsPBelum ada peringkat
- A TC3844 5 Ethernet Over OC3 DatasheetDokumen2 halamanA TC3844 5 Ethernet Over OC3 DatasheetJoseBelum ada peringkat
- Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm: Fifteenth EditionDokumen48 halamanManagement Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm: Fifteenth EditionLicia SalimBelum ada peringkat
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Exam - Free Actual Q&As, Page 15 - ExamTopicsDokumen3 halamanAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Exam - Free Actual Q&As, Page 15 - ExamTopicsParag Anil Wani50% (2)
- Novell OSI ModelDokumen6 halamanNovell OSI Modelmuneeba_2Belum ada peringkat
- Scenario B: Running Ripv1 With Subnets and Between Classful Networks Topology DiagramDokumen4 halamanScenario B: Running Ripv1 With Subnets and Between Classful Networks Topology DiagramNader AbdessayedBelum ada peringkat
- Wireless Fidelity: Technology and ApplicationsDokumen22 halamanWireless Fidelity: Technology and ApplicationsPurboday GhoshBelum ada peringkat
- Session Plan: Computer Systems Servicing NC IIDokumen7 halamanSession Plan: Computer Systems Servicing NC IIFernando PradoBelum ada peringkat
- Level One Dante Certification Program Introduction Audinate Pres NotesDokumen76 halamanLevel One Dante Certification Program Introduction Audinate Pres NotestcbsaccosBelum ada peringkat
- Eelink Protocol V2.1Dokumen136 halamanEelink Protocol V2.1John DoeBelum ada peringkat
- A Complete Guide About Linksys RE6700 ExtenderDokumen7 halamanA Complete Guide About Linksys RE6700 ExtenderExtender Linksys SetupBelum ada peringkat
- PUBLIC - Rockwell E-Learning Content and FY20 ReleasesDokumen1 halamanPUBLIC - Rockwell E-Learning Content and FY20 ReleasesRidho AnjikoBelum ada peringkat
- The Game: Penetrating the Secret Society of Pickup ArtistsDari EverandThe Game: Penetrating the Secret Society of Pickup ArtistsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (131)
- Secrets of the Millionaire Mind: Mastering the Inner Game of WealthDari EverandSecrets of the Millionaire Mind: Mastering the Inner Game of WealthPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (197)
- Proof of Heaven: A Neurosurgeon's Journey into the AfterlifeDari EverandProof of Heaven: A Neurosurgeon's Journey into the AfterlifePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (165)
- New Zealand Adventure Travel GuideDari EverandNew Zealand Adventure Travel GuidePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (14)