PMP Cheat Sheet PDF
Diunggah oleh
thouartuJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
PMP Cheat Sheet PDF
Diunggah oleh
thouartuHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
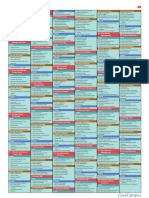
PMP Cheat Sheet and Study Notes
Based on PMBOK V4
The reader is responsible to verify and confirm all information presented herein. Human Resource Management Organizational Structures: Functional, Matrix (weak, balanced, Initiation strong) , Projectized, Composite Planning Maslows Hierarchy of Needs: Physiological, Safety, Social, Self Execution -esteem, Self-actualization. Monitor and Control McGregor: Theory X, Theory Y. Closing Ouchi: Theory Z. Motivated by commitment, opportunity advancement. Herzbergs Theory of Motivation: Hygiene factors, Motivating Agents. Knowledge Areas Leadership Styles: Directing, Facilitating, Coaching, Supporting, Integration Autocratic, Consultative, Consensus. Scope Management Project Manager Powers: Formal (legitimate,) Reward, Penalty Time Management (coercive), Expert, Referent. Cost Management Conflict Management: Withdraw (avoid), Smooth (accommodate), Quality Management Compromise, Force, Collaborate, Confront (problem solving.) Quality Management HR Management Communications Management Ishikawa = Fishbone Diagram: cause and effect. Pareto Diagram: Identify problems and frequency. 80/20 Rule. Procurement Management Flow Charts; Control Charts. Risk Management Just in Time: Reduces inventory; requires additional quality control. Professional Responsibility Quality Theories: Kaizen (continuous improvement,) Six Sigma, TQM (total quality management.) Earned Value Management Kaizen: Small improvements to reduce costs and improve consistency. BAC = Budget At Completion Deming Cycle: Plan, Do Check, Act. EV = Actual % * BAC Cost Management PV = Planned % * BAC Cost Estimating - Accuracy AC = Sum of all incurred costs Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM): -50% to +100% Budgetary: -10% to +25% CV = EV - AC Definitive: -5% to + 10% SV = EV - PV Risk Management CPI = EV / AC Risk Strategies (threats): Avoid, Transfer, Mitigate, Accept. < 1 = Over Budget Risk Strategies (opportunities): Exploit, Share, Enhance, Accept. > 1 = Under Budget Qualitative Risk Analysis: Chance and impact of risk occurrence SPI = EV / PV Results in prioritized list of risks; risk ranking. < 1 = Behind Schedule Quantitative Risk Analysis: Numerical analysis of probability > 1 = Ahead of Schedule and impact. Tools: Interviews, Sensitivity Analysis, Decision Tree Analysis, EAC = BAC / CPI Simulation, Monte Carlo Analysis. EAC = AC + ETC Closing EAC = AC + (BAC + EV) / CPI Contract Close: Before project close ETC = EAC - AC Project or Phase Close: Lessons Learned VAC = BAC - EAC PMI Code of Ethics: Respect, Fair, Honest. BCWS = PV Processes BCWP = EV ACWP = AC Tips: Negative is bad Positive is good If Variance: EV - Something If Index: EV / Something If Cost related use AC If Time related use PV Most formulas start with EV Rules Based on Numbers 80 Hour Rule = Max size of work packages Key Formulas Standard Deviation = (P - O) / 6 PERT = (O + 4M + P) / 6 Total Float = LSES or LF EF Comm Channels = N (N-1) / 2 Where: P = Pessimistic O = Optimistic M = Most likely; Realistic N = # Project Members Benefit Cost Ratio = Cost / Benefits BCR < 1 Unfavorable BCR > 1 Higher is Better Time Management Precedence Diagramming Method PDM: Activity-on-Node (AON) Arrow Diagram Method ADM: Activity-on-Arrow (AOA) Conditional Diagram Method Graphical Evaluation and Review Technique (GERT): Allows loop Crashing: Add more resources Fast Tracking: Tasks in parallel Forward Pass: Early start, early finish Backward Pass: Late start, late finish Float; Slack: activity margin off critical path Free Float: activity margin not impacting early start of next dependant activity Project Float
42 Project Management Processes Project Integration Management 1. Develop Project Charter 2. Develop Project Management Plan 3. Direct / Manage Project Execution 4. Monitor / Control Project Work 5. Perform Integrated Change Control 6. Close Project or Phase Project Scope Management 7. Collect Requirements 8. Define Scope 9. Create WBS 10. Verify Scope 11. Control Scope Project Time Management 12. Define Activities 13. Sequence Activities 14. Estimate Activity Resources 15. Estimate Activity Durations 16. Develop Schedule 17. Control Schedule Project Cost Management 18. Estimate Costs 19. Determine Budget 20. Control Costs Project Quality Management 21. Plan Quality 22. Perform Quality Assurance 23. Perform Quality Control Project Human Resource Management 24. Develop Human Resource Plan 25. Acquire Project Team 26. Develop Project Team 27. Manage Project Team Project Communications Management 28. Identify Stakeholders 29. Plan Communications 30. Distribute Information 31. Manage Stakeholder Expectations 32. Report Performance Project Risk Management 33. Plan Risk Management 34. Identify Risks 35. Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis 36. Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis 37. Plan Risk Responses 38. Monitor and Control Risks Project Procurement Management 39. Plan Procurements 40. Conduct Procurements 41. Administer Procurements 42. Close Procurements Copyright 2009 PMServicesNW All rights reserved www.PMServicesNW.com
Net Present Value = 80/20 Rule = Paretos Law 20% of causes responsible for FV / (1 + r)^n 80% of problems Future Value = PV (1 + i)^n 0/50/100 = Work package completion. No credit until 50% complete. No additional credit until 100% complete. Internal Rate of Return Higher is better Six Sigma: 99.99% defect free
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Project Management Process, Tools & Techniques in 40 CharactersDokumen3 halamanProject Management Process, Tools & Techniques in 40 CharactersRobincrusoe88% (26)
- Q & As for the PMBOK® Guide Sixth EditionDari EverandQ & As for the PMBOK® Guide Sixth EditionPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (18)
- Earned Value Management for the PMP Certification ExamDari EverandEarned Value Management for the PMP Certification ExamPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (15)
- 50 Basic Predictive Project Management Questions: A great primer for the PMP® and CAPM® ExamsDari Everand50 Basic Predictive Project Management Questions: A great primer for the PMP® and CAPM® ExamsBelum ada peringkat
- PMP Project Management Professional Exam Study Guide: 2021 Exam UpdateDari EverandPMP Project Management Professional Exam Study Guide: 2021 Exam UpdatePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5)
- Earned Value Management: 60 Minutes Compact Knowledge: The Best Methods and Tools to Keep Your Project Under ControlDari EverandEarned Value Management: 60 Minutes Compact Knowledge: The Best Methods and Tools to Keep Your Project Under ControlPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- PMP Memory SheetsDokumen6 halamanPMP Memory Sheets1hass197% (29)
- PMP Formulas Cheat SheetDokumen2 halamanPMP Formulas Cheat SheetAn Nguyen100% (12)
- PMP Cheat Sheet in Plain EnglishDokumen6 halamanPMP Cheat Sheet in Plain EnglishSergio Alves100% (11)
- PMP Formulae & Tips Cheat SheetDokumen5 halamanPMP Formulae & Tips Cheat Sheetbhaveshkumar78100% (8)
- PMP® & Capm® Exam Cheat Sheet: (Pmbok Guide 6th Edition)Dokumen6 halamanPMP® & Capm® Exam Cheat Sheet: (Pmbok Guide 6th Edition)phongbkac46100% (8)
- PMP IN 45 DAYSDokumen10 halamanPMP IN 45 DAYSgolfmaniac48% (21)
- PMP Study MaterialsDokumen90 halamanPMP Study Materialsamira_salama100% (4)
- PMBOK Study Notes PDFDokumen83 halamanPMBOK Study Notes PDFshetupuc92% (26)
- PMP Cheat SheetDokumen11 halamanPMP Cheat Sheetsachin.nate525782% (11)
- PMP in Mindmaps, 2018, Ahmed Alsenosy' BookDokumen10 halamanPMP in Mindmaps, 2018, Ahmed Alsenosy' BookIbrahimSamir100% (9)
- ITTO Trick Sheet for PMBOK Guide 6th EditionDokumen26 halamanITTO Trick Sheet for PMBOK Guide 6th EditionAbdulla Jawad Alshemary84% (25)
- Memory Aids For PMP ExamDokumen7 halamanMemory Aids For PMP ExamMustafa100% (18)
- PMP FormulasDokumen3 halamanPMP Formulaspolters100% (8)
- PMP Notes FinalDokumen24 halamanPMP Notes Finalumerillias89% (9)
- PMP Full ExamDokumen51 halamanPMP Full Examrvsreddy197285% (26)
- Project management cheat sheetDokumen2 halamanProject management cheat sheetyogesh sharma89% (9)
- PMP PDFDokumen398 halamanPMP PDFdreamer1982100% (7)
- PMP Study SheetDokumen2 halamanPMP Study SheetAli Abdelmoniem Ahmed75% (4)
- Edward PMP Study NotesDokumen76 halamanEdward PMP Study NotesWaqas Ahmed94% (16)
- PMP Comprehensive Notes - ChowdaryDokumen27 halamanPMP Comprehensive Notes - Chowdarysj1933050% (2)
- Agile Project ManagementDokumen5 halamanAgile Project ManagementAshenafi100% (8)
- 60 Days - PMP Study PlanDokumen3 halaman60 Days - PMP Study PlanShahram Karimi100% (7)
- Cheat-Sheet-PMP As PMBOK 6Dokumen2 halamanCheat-Sheet-PMP As PMBOK 6rimrany86% (14)
- PMBOK6 EnglishDokumen1 halamanPMBOK6 Englishbigprice100% (3)
- A Roadmap to Cracking the Pmp® Exam: A Pmp Exam Preparation Study GuideDari EverandA Roadmap to Cracking the Pmp® Exam: A Pmp Exam Preparation Study GuideBelum ada peringkat
- PMP® Full Exam: 1: 200 Questions and AnswersDari EverandPMP® Full Exam: 1: 200 Questions and AnswersPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (16)
- PMP® Full Exam: 2: 200 Questions and AnswersDari EverandPMP® Full Exam: 2: 200 Questions and AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (4)
- PMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamDari EverandPMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- PfMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersDari EverandPfMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2)
- The Complete Project Management Exam Checklist: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional Certification: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional CertificationDari EverandThe Complete Project Management Exam Checklist: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional Certification: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional CertificationBelum ada peringkat
- How to Pass the PMP Exam on Your Second AttemptDari EverandHow to Pass the PMP Exam on Your Second AttemptPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (4)
- CAPM® in Depth: Certified Associate in Project Management Study Guide for the CAPM® ExamDari EverandCAPM® in Depth: Certified Associate in Project Management Study Guide for the CAPM® ExamBelum ada peringkat
- PMP® Simplified Knowledge Areas: Artifacts and activities of the knowledge areasDari EverandPMP® Simplified Knowledge Areas: Artifacts and activities of the knowledge areasBelum ada peringkat
- CAPM Certified Associate in Project Management Practice ExamsDari EverandCAPM Certified Associate in Project Management Practice ExamsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- The Standard for Program ManagementDari EverandThe Standard for Program ManagementPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- PgMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersDari EverandPgMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2)
- PfMP® Full Exam: 2:170 Questions and AnswersDari EverandPfMP® Full Exam: 2:170 Questions and AnswersPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- PMP/CAPM EXAM PREP: A Basic Guide to Activity-On-Node and Critical Path MethodDari EverandPMP/CAPM EXAM PREP: A Basic Guide to Activity-On-Node and Critical Path MethodBelum ada peringkat
- 300+ PMP Practice Questions Aligned with PMBOK 7, Agile Methods, and Key Process Groups - 2024: First EditionDari Everand300+ PMP Practice Questions Aligned with PMBOK 7, Agile Methods, and Key Process Groups - 2024: First EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Inner Light TechniqueDokumen4 halamanInner Light TechniquethouartuBelum ada peringkat
- The Five Pranas and Their Roles in the BodyDokumen3 halamanThe Five Pranas and Their Roles in the BodythouartuBelum ada peringkat
- Acu Chakra ConnectionflowDokumen2 halamanAcu Chakra ConnectionflowthouartuBelum ada peringkat
- Using A Rule Engine For Distributed Systems Management: An Exploration Using Data Replication Quan PhamDokumen28 halamanUsing A Rule Engine For Distributed Systems Management: An Exploration Using Data Replication Quan PhamthouartuBelum ada peringkat
- Maharishi's Program of Reading The Vedic LiteratureDokumen16 halamanMaharishi's Program of Reading The Vedic LiteratureAMTRBelum ada peringkat
- Key Acupoints PDFDokumen6 halamanKey Acupoints PDFthouartu50% (2)
- A Privacy Framework For Mobile Health and Home-Care Systems: David Kotz Sasikanth Avancha Amit BaxiDokumen12 halamanA Privacy Framework For Mobile Health and Home-Care Systems: David Kotz Sasikanth Avancha Amit BaxithouartuBelum ada peringkat
- Consultative Selling EbookDokumen203 halamanConsultative Selling Ebookjasonwee80Belum ada peringkat
- MongodbDokumen66 halamanMongodbthouartuBelum ada peringkat
- World Religions Views of Holistic HealthDokumen34 halamanWorld Religions Views of Holistic HealththouartuBelum ada peringkat
- Strategy Before Software DevelopmentDokumen9 halamanStrategy Before Software DevelopmentthouartuBelum ada peringkat
- Umlqrc PDFDokumen1 halamanUmlqrc PDFthouartuBelum ada peringkat
- Discover the Ancient Health Science of AyurvedaDokumen18 halamanDiscover the Ancient Health Science of Ayurvedaadith24Belum ada peringkat
- What Sales Winners Do Differently WebDokumen13 halamanWhat Sales Winners Do Differently Websanilg81Belum ada peringkat
- The Spiritual Meaning of Ramayana: WWW - Naradakush.nlDokumen27 halamanThe Spiritual Meaning of Ramayana: WWW - Naradakush.nlthouartuBelum ada peringkat
- Building Information Modeling (BIM) : Now and BeyondDokumen14 halamanBuilding Information Modeling (BIM) : Now and BeyondthouartuBelum ada peringkat
- ss2000 02Dokumen22 halamanss2000 02thouartuBelum ada peringkat
- 09 ArraysDokumen29 halaman09 ArraysthouartuBelum ada peringkat
- Elem Am 98 RepeatabilityDokumen13 halamanElem Am 98 RepeatabilitythouartuBelum ada peringkat
- Detection of Cornering PreprintDokumen11 halamanDetection of Cornering PreprintthouartuBelum ada peringkat
- BA TasksDokumen6 halamanBA TasksthouartuBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Packet Spring13Dokumen6 halaman6 Packet Spring13thouartuBelum ada peringkat
- MX Injection TestingDokumen24 halamanMX Injection TestingthouartuBelum ada peringkat
- 2016itc MS3Dokumen15 halaman2016itc MS3luckylorry8513Belum ada peringkat
- Goldsmith MOJO ScorecardDokumen3 halamanGoldsmith MOJO ScorecardthouartuBelum ada peringkat
- Sfa Readme FirstDokumen1 halamanSfa Readme FirstthouartuBelum ada peringkat
- How a Wishbone, Backbone and Funny Bone Led to SuccessDokumen24 halamanHow a Wishbone, Backbone and Funny Bone Led to SuccessAshok Kumar UBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Packet Spring13Dokumen10 halaman8 Packet Spring13thouartuBelum ada peringkat
- Helm ClashdetectionDokumen7 halamanHelm ClashdetectionMayouran WijayakumarBelum ada peringkat
- Akshamalika UpnishadDokumen5 halamanAkshamalika UpnishadSujeet ShandilyaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 20: Where Is Sapa: 2.look, Read and CompleteDokumen4 halamanUnit 20: Where Is Sapa: 2.look, Read and CompleteNguyenThuyDungBelum ada peringkat
- Safety Guidelines For Direct DrivesDokumen9 halamanSafety Guidelines For Direct DrivesJOseBelum ada peringkat
- Folk Tales of Nepal - Karunakar Vaidya - Compressed PDFDokumen97 halamanFolk Tales of Nepal - Karunakar Vaidya - Compressed PDFSanyukta ShresthaBelum ada peringkat
- Groundwater Control For Cross PassagesDokumen6 halamanGroundwater Control For Cross PassageskrainajackaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Test 1: Vocabulary & GrammarDokumen2 halamanUnit Test 1: Vocabulary & GrammarAlexandraMariaGheorgheBelum ada peringkat
- NUC BIOS Update Readme PDFDokumen3 halamanNUC BIOS Update Readme PDFSuny Zany Anzha MayaBelum ada peringkat
- Integrative Paper Unfolding The SelfDokumen11 halamanIntegrative Paper Unfolding The SelfTrentox XXXBelum ada peringkat
- Geometry First 9 Weeks Test Review 1 2011Dokumen6 halamanGeometry First 9 Weeks Test Review 1 2011esvraka1Belum ada peringkat
- Plants Promoting Happiness: The Effect of Indoor Plants on MoodDokumen11 halamanPlants Promoting Happiness: The Effect of Indoor Plants on MoodWil UfanaBelum ada peringkat
- Global High Temperature Grease Market ReportDokumen6 halamanGlobal High Temperature Grease Market ReportHari PurwadiBelum ada peringkat
- Fernández Kelly - Death in Mexican Folk CultureDokumen21 halamanFernández Kelly - Death in Mexican Folk CultureantoniadelateBelum ada peringkat
- A To Z of Architecture PDFDokumen403 halamanA To Z of Architecture PDFfaizan100% (1)
- Jeff Roth CVDokumen3 halamanJeff Roth CVJoseph MooreBelum ada peringkat
- Gautam KDokumen12 halamanGautam Kgautam kayapakBelum ada peringkat
- OPGWDokumen18 halamanOPGWGuilhermeBelum ada peringkat
- Product Data: Real-Time Frequency Analyzer - Type 2143 Dual Channel Real-Time Frequency Analyzers - Types 2144, 2148/7667Dokumen12 halamanProduct Data: Real-Time Frequency Analyzer - Type 2143 Dual Channel Real-Time Frequency Analyzers - Types 2144, 2148/7667jhon vargasBelum ada peringkat
- ThiruppavaiDokumen157 halamanThiruppavaiajiva_rts100% (49)
- Miles and Snow's Organizational StrategiesDokumen15 halamanMiles and Snow's Organizational StrategiesVirat SahBelum ada peringkat
- MICROHARDNESS TESTER HMV-2 - SeriesDokumen9 halamanMICROHARDNESS TESTER HMV-2 - SeriesRicoBelum ada peringkat
- Exam 2 Study GuideDokumen11 halamanExam 2 Study GuideAnonymous ewJy7jyvNBelum ada peringkat
- Marketing Case Study - MM1 (EPGPX02, GROUP-06)Dokumen5 halamanMarketing Case Study - MM1 (EPGPX02, GROUP-06)kaushal dhapareBelum ada peringkat
- CES Wrong Answer SummaryDokumen4 halamanCES Wrong Answer SummaryZorg UABelum ada peringkat
- Starch Digestion by Amylase Lab ReportDokumen10 halamanStarch Digestion by Amylase Lab Report햇님Belum ada peringkat
- MATHS UNDERSTANDINGDokumen15 halamanMATHS UNDERSTANDINGNurul IzzaBelum ada peringkat
- Shah Wali Ullah Syed Haji Shariat Ullah Ahmad Barelvi (Notes)Dokumen2 halamanShah Wali Ullah Syed Haji Shariat Ullah Ahmad Barelvi (Notes)Samreen KapasiBelum ada peringkat
- 41720105Dokumen4 halaman41720105renu tomarBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Progress Report ASTDokumen1 halamanSample Progress Report ASTzulkefli90Belum ada peringkat
- Ariston Oven ManualDokumen16 halamanAriston Oven ManualJoanne JoanneBelum ada peringkat
- History I.M.PeiDokumen26 halamanHistory I.M.PeiVedasri RachaBelum ada peringkat
- Manoj KR - KakatiDokumen5 halamanManoj KR - Kakatimanoj kakatiBelum ada peringkat