Class Example: Superposition Method
Diunggah oleh
Nataly Medina0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
19 tayangan2 halamanA basic example for Resistive Circuits
Judul Asli
Superposition
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniA basic example for Resistive Circuits
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
19 tayangan2 halamanClass Example: Superposition Method
Diunggah oleh
Nataly MedinaA basic example for Resistive Circuits
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
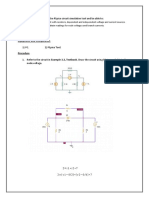
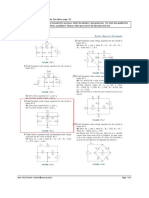
Class example: Superposition Method
A novel method for analyzing circuits with multiple sources
Steps:
1. We remove all the independent sources, except one, and analyze the circuit for that one. We
dont turn off dependent sources.
2. Then we repeat the procedure for another source, and so on.
3. Finally, the net result is found by summing all source results.
Instructions: Find current | using the Superposition Method.
Solution
1. Turn off the current source by replacing it with an open circuit.
Using KVL:
Si
1
+ 2i
1
+ Si
1
_ 24I = u (1)
i
1
= SA
Class e
2. N
First, we
(reference
Using KCL
into a nod
Current i
x
Then KCL
Substituti
Finally, ne
example:
ow, turn off t
need to iden
e) to node :
u
L for node :
u
de equals the
x
across R2 is
for node :
u
b
ng :
u
on (6) a
et result is:
Superpos
the voltage so
ntify current i
u
, so current i
u
(remember
sum of the c
:
becomes:
|
and solving fo
|
sition Me
ource by repl
i
2
, we know
i
2
is:
i
2
=
u -:
S
:
u
= -
: Kirchhoffs
currents flowi
|
2
+7A -
i
x
=
:
u
|
2
+ 7A -
u
a
or i
2
:
i
2
-
-Si
2
-
2
i
2
= -
7
4
=
= i
1
+ i
2
=
ethod
acing it with
that this cur
:
u
= -
:
u
S
-Si
2
current law s
ng out of the
- |
x
= u
u
- Si
2
2
a
-3|
2
2u
= u
-Si
2
2
= -7
= -1.7SA
SA - 1.7SA
a short circui
rrent is flowin
(2)
(S)
states that th
e node):
(4)
(S)
(6)
(7)
(8)
= 1. 25A
|
x
it.
ng from the
he sum of th
0V potential
e currents flo
node
owing
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Advanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionDari EverandAdvanced Electric Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionBelum ada peringkat
- Network Analysis: Branch Node Loop Mesh Short CircuitDokumen13 halamanNetwork Analysis: Branch Node Loop Mesh Short CircuitMathew ClewlowBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDokumen181 halamanBasic Electrical EngineeringPrakash Chandran CBelum ada peringkat
- Modelling and Simulation of Mechatronic SystemsDokumen31 halamanModelling and Simulation of Mechatronic SystemsEnes Umur GökçekBelum ada peringkat
- Theory: To Familiarize Students With The Pspice Circuit Simulation Tool and Be Able ToDokumen4 halamanTheory: To Familiarize Students With The Pspice Circuit Simulation Tool and Be Able Toعصير نفيشBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture #35: Analysis of Electrical Networks With Initial ConditionsDokumen13 halamanLecture #35: Analysis of Electrical Networks With Initial ConditionsSaneesh KarayilBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsDari EverandFundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsBelum ada peringkat
- First LE: Mar 6 12-2PMDokumen22 halamanFirst LE: Mar 6 12-2PMByron BanzonBelum ada peringkat
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsDari EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- CCDC 2010 5498813Dokumen6 halamanCCDC 2010 5498813rajareddy235Belum ada peringkat
- SU14 2 ENG17 Midterm SolDokumen5 halamanSU14 2 ENG17 Midterm SolTiffany LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Mesh Nodal Analysis 1Dokumen20 halamanMesh Nodal Analysis 1subasriramiahBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter3 NodalDokumen45 halamanChapter3 Nodalpsychic_jason0071319Belum ada peringkat
- EECE210 Spring2021 Chap+4Dokumen55 halamanEECE210 Spring2021 Chap+4starboyBelum ada peringkat
- EEE105 Chapter10Dokumen58 halamanEEE105 Chapter10phavitthra vadivel muruganBelum ada peringkat
- Application of Laplace To CircuitsDokumen45 halamanApplication of Laplace To CircuitsdalbaasBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Resonant CircuitsDokumen31 halamanIntroduction To Resonant Circuitshodeegits9526Belum ada peringkat
- Nodal and Mesh Analysis: Galgotias UniversityDokumen21 halamanNodal and Mesh Analysis: Galgotias UniversityAgnivesh SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Loop Analysis of DC CKTDokumen10 halamanLoop Analysis of DC CKTDev SwainBelum ada peringkat
- Loop Analysis of Resistive CircuitDokumen11 halamanLoop Analysis of Resistive CircuitVikash Ram MahuriBelum ada peringkat
- Softlab 1Dokumen9 halamanSoftlab 1Mission DeyBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Circuit Analysis Eighfh EditDokumen2 halamanEngineering Circuit Analysis Eighfh EditbrnlmdzBelum ada peringkat
- CE 351 Part 3 Chapter 4 B Pipe Network PDFDokumen31 halamanCE 351 Part 3 Chapter 4 B Pipe Network PDFAli M. ChehadehBelum ada peringkat
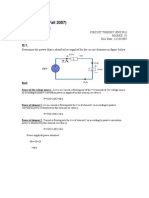
- Circuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2007Dokumen30 halamanCircuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2007Muhammad UmairBelum ada peringkat
- DC CIRCUITS - Methods of AnalysisDokumen22 halamanDC CIRCUITS - Methods of AnalysisLuthfan TaufiqBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 3.1Dokumen27 halamanChap 3.1Muhd RzwanBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 2 - Circuit AnalysisDokumen22 halamanChap 2 - Circuit AnalysisYang Yew RenBelum ada peringkat
- Resonant CircuitsDokumen51 halamanResonant CircuitsHaris Bin KhalidBelum ada peringkat
- 15.082J and 6.855J and ESD.78J November 4, 2010: The Network Simplex AlgorithmDokumen42 halaman15.082J and 6.855J and ESD.78J November 4, 2010: The Network Simplex AlgorithmeviroyerBelum ada peringkat
- Uo (W), Vo (W, UO (W) : T2 (W) Are Given by W 2, V 0 (W) w2Dokumen4 halamanUo (W), Vo (W, UO (W) : T2 (W) Are Given by W 2, V 0 (W) w2menguemengueBelum ada peringkat
- ChapterDokumen26 halamanChapterdvdmega0% (1)
- Dept. of Electronics and Communication Engineering: Sem / Year: Ii / IDokumen41 halamanDept. of Electronics and Communication Engineering: Sem / Year: Ii / Ivalan_carl07Belum ada peringkat
- TD1 CorrectionDokumen20 halamanTD1 CorrectionYoussef ElalaouiBelum ada peringkat
- SAB2513 Hydraulic Chapter 7Dokumen37 halamanSAB2513 Hydraulic Chapter 7Tuan JalaiBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 - Part 3 - D.C. Network AnalysisDokumen26 halamanUnit 1 - Part 3 - D.C. Network Analysisgenius studentBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Report #4Dokumen6 halamanLab Report #4Aisha NurymgaliBelum ada peringkat
- First-Order Circuits: DX DLDokumen11 halamanFirst-Order Circuits: DX DLAna Kary Justo RamosBelum ada peringkat
- DC-Lab Report 05Dokumen9 halamanDC-Lab Report 05Shahriar Ahsan JohaBelum ada peringkat
- BENG 3013 - Chapter 1 - DeltaDokumen39 halamanBENG 3013 - Chapter 1 - DeltaWan MamatkBelum ada peringkat
- We Have Seen The Idea of Equivalency Used in Several Instances Already. Same AsDokumen19 halamanWe Have Seen The Idea of Equivalency Used in Several Instances Already. Same Assurag1982Belum ada peringkat
- CL CL CL CL Class ASS ASS ASS ASS TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014Dokumen7 halamanCL CL CL CL Class ASS ASS ASS ASS TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014 TEST - 2014saurabhdabas7Belum ada peringkat
- Nominal Π Representation of a Medium Transmission Line: I I I I I IDokumen5 halamanNominal Π Representation of a Medium Transmission Line: I I I I I IVedaste NdayishimiyeBelum ada peringkat
- HW 2 SolnDokumen15 halamanHW 2 Solnakjhasd kjhasdkjhBelum ada peringkat
- HW1 Diode Bridge Rectifiers-Rev0Dokumen28 halamanHW1 Diode Bridge Rectifiers-Rev0nikolakaBelum ada peringkat
- L-05 (GDR) (Et) ( (Ee) Nptel)Dokumen11 halamanL-05 (GDR) (Et) ( (Ee) Nptel)nvnmnitBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3Dokumen27 halamanChapter 3amanuelfitsum589Belum ada peringkat
- Electrical Network Analysis Lab Course: Prepared By: Husan Ali 1Dokumen8 halamanElectrical Network Analysis Lab Course: Prepared By: Husan Ali 1Husan AliBelum ada peringkat
- RLC CktsDokumen20 halamanRLC Ckts6B Qurat-ul-ain Abdul RasheedBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 01 (Adel)Dokumen9 halamanLab 01 (Adel)ADEL OUBBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 7 - Useful Circuit Analysis Technique - IDokumen16 halamanLecture 7 - Useful Circuit Analysis Technique - ISohaibBelum ada peringkat
- Report 2, Phy270Dokumen9 halamanReport 2, Phy270Georges MaaloufBelum ada peringkat
- Hardy CrossDokumen2 halamanHardy CrossFlonja ShytiBelum ada peringkat
- ExamplesDokumen32 halamanExamplesvenki249Belum ada peringkat
- Bus Impedance Matrix in Faults CalculationsDokumen38 halamanBus Impedance Matrix in Faults Calculationsfreddy riveraBelum ada peringkat
- Week 6Dokumen38 halamanWeek 6IGIHOZO HeritierBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical CircuitDokumen12 halamanElectrical CircuitMohamd OssamaBelum ada peringkat
- Vending Machine Class ActivityDokumen2 halamanVending Machine Class ActivityNataly MedinaBelum ada peringkat
- Filters With LabViewDokumen14 halamanFilters With LabViewNataly MedinaBelum ada peringkat
- Field MappingDokumen5 halamanField MappingNataly MedinaBelum ada peringkat
- M525 V1.1 MotherboardDokumen5 halamanM525 V1.1 MotherboardNataly MedinaBelum ada peringkat