Nematoda: Stephanurus Dentatus Metastrongylus Spp. Muellerius Capillaris Ascaris Suum Toxocara Vitulorum
Diunggah oleh
Janice LiJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Nematoda: Stephanurus Dentatus Metastrongylus Spp. Muellerius Capillaris Ascaris Suum Toxocara Vitulorum
Diunggah oleh
Janice LiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Nematoda
Stephanurus dentatus Metastrongylus spp. Muellerius capillaris Ascaris suum Toxocara vitulorum
Intermediat e host
earthworm
snails and slugs
Predilection site in intermediat e host Final host Predilection site in final host
body cavity
body cavity
pig, rarely cattle kidney, peri-renal fat
pig lung or pulmonary blood vessels
sheep lung
pig, cattle, man small intestine
cattle, rarely sheep small intestine
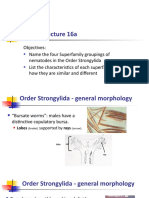
Presence of bursate Other remarks
Yes transport host: earthworm, 3 modes infection, ingestion L3, ingestion earthworm with L3, percutaneous penetration, L4 go to liver in blood, from intestine via portal vein, from skin, final moult, pierce capsule, migrate to peritoneal cavity, form cyst, cyst communicate with renal pelvis lumen or ureter or by fine connecting canal, encapsulation in lung, spleen, spinal cord, kidney, cirrhosis, thickened ureter, poor growth, nodules in skin
Yes , L3 release by digestion, to heart via mesenteric lymph nodes, to lungs via lymphatic-vascular route, L4 develop in lung, egg cough up respiratory tract, catarrhal bronchiolitis, bronchitis, pneumonia
Yes , route in final host same as , heavy infection cause secondary infection
No large roundworm, thick shell egg, disinfectant cant kill eggs, egg hatch in small intestine, L3 penetrate intestinal mucosa, to liver, to lungs via blood, to small intestine via bronchi, trachea, pharynx, L4 inhabit in small intestine, emphysema, milk spot liver, intestinal obstruction, obstruction jaundice, poor growth; man: contact dermatitis, asthma, abdominal pain, intestinal obstruction, vomiting, gut perforation, appendicitis
No ingestion of L3 with subsequent tracheal migration, break out of alveoli, to bronchioles, bronchi, trachea, pharynx, small intestine, catarrhal enteritis, intestinal obstruction, gut perforation, peritonitis, cholangitis
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Diseases Caused by Parasites (Helminths) 1. FascioliasisDokumen14 halamanDiseases Caused by Parasites (Helminths) 1. FascioliasisTejpalBelum ada peringkat
- TrematodesDokumen10 halamanTrematodesUhjafwnuijhnfa Kmerkgoe100% (1)
- Class Trematoda: FlukesDokumen3 halamanClass Trematoda: FlukesChan LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Ascariasis in livestock and petsDokumen23 halamanAscariasis in livestock and petsPiyush SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Trichinella and TrichurisDokumen36 halamanTrichinella and TrichurisCristine BarrozaBelum ada peringkat
- Strongylus (Uzal)Dokumen16 halamanStrongylus (Uzal)Fredy MoralesBelum ada peringkat
- Cestodes and NematodesDokumen19 halamanCestodes and Nematodespancake pancakeBelum ada peringkat
- whipworm 11 _(4)_.pdf - 2023.04.17 - 06.16.03pmDokumen5 halamanwhipworm 11 _(4)_.pdf - 2023.04.17 - 06.16.03pmHussainBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 16Dokumen34 halamanLecture 16Nicolae ZdragusBelum ada peringkat
- 5 - Stephanurus, Heterakis and SpiruridsDokumen78 halaman5 - Stephanurus, Heterakis and Spiruridsaniel_bmBelum ada peringkat
- Tables - CestodesDokumen8 halamanTables - CestodesSid Loverholic50% (4)
- Prof. DR Fahim ShaltoutDokumen55 halamanProf. DR Fahim ShaltoutSumit SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Intestinal NematodesDokumen88 halamanIntestinal NematodesVincent Manganaan100% (1)
- Selma CestodesDokumen23 halamanSelma CestodesAhmed EisaBelum ada peringkat
- Infex para SupplementDokumen27 halamanInfex para SupplementShubh ChoudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Parasitic Flatworms and Tapeworms Classification and CharacteristicsDokumen54 halamanParasitic Flatworms and Tapeworms Classification and CharacteristicsMewa MahartaBelum ada peringkat
- Fasciola HepaticaDokumen4 halamanFasciola Hepaticam1ha1davidBelum ada peringkat
- Taxonomic: StatusDokumen14 halamanTaxonomic: StatusS. M. AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- Untitled Document PDFDokumen5 halamanUntitled Document PDFRizzy VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- Female Reproductive System AnatomyDokumen57 halamanFemale Reproductive System AnatomyEstellaBelum ada peringkat
- N M To Es: Dr. Wafaa Ezz ElarabDokumen31 halamanN M To Es: Dr. Wafaa Ezz Elarabshoroq zaki100% (1)
- 15 Theorical Entomology1Dokumen91 halaman15 Theorical Entomology1hhupBelum ada peringkat
- HookwormDokumen5 halamanHookwormImee Jen AbadianoBelum ada peringkat
- Petrache, Joseph Dacanay, Gilian Medina, Julius Co, Kenneth Jr. Corcelles, KevinDokumen120 halamanPetrache, Joseph Dacanay, Gilian Medina, Julius Co, Kenneth Jr. Corcelles, KevinGilian Dacanay100% (2)
- Ticks, Mites, Fleas, Lice As A VectorDokumen24 halamanTicks, Mites, Fleas, Lice As A VectorAditya Rachman Van Der ArjunaqueeBelum ada peringkat
- Enterobius VermicularisDokumen10 halamanEnterobius VermicularisSree GouriBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of Medically Significant NematodesDokumen134 halamanClassification of Medically Significant Nematodesblue_blooded23100% (1)
- CestodesDokumen7 halamanCestodesSiti NabilaBelum ada peringkat
- HelmenthsDokumen38 halamanHelmenthsKarwanBelum ada peringkat
- The Intestinal NematodesDokumen107 halamanThe Intestinal Nematodesblue_blooded23100% (1)
- A. Taxonomi: Clonorchis SinensisDokumen4 halamanA. Taxonomi: Clonorchis SinensisFadhilahBelum ada peringkat
- Dokumen94 halaman blue_blooded23Belum ada peringkat
- BIO 342 Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy Lecture Notes 10 - Urogenital SystemDokumen4 halamanBIO 342 Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy Lecture Notes 10 - Urogenital SystemKatrina Lee GaganBelum ada peringkat
- Trichinella SpiralisDokumen2 halamanTrichinella SpiralisJayricDepalobosBelum ada peringkat
- T Spiralis and FriendsDokumen4 halamanT Spiralis and Friendssmcm11Belum ada peringkat
- Amphistomate & Distomate FlukeDokumen12 halamanAmphistomate & Distomate FlukeJayricDepalobosBelum ada peringkat
- AscarisDokumen16 halamanAscarisNicolas CisséBelum ada peringkat
- AssignmentDokumen9 halamanAssignmentDr Anais AsimBelum ada peringkat
- Toxocara CaDokumen4 halamanToxocara CaDr Anais AsimBelum ada peringkat
- Spirometra, Hymenolepis NanaDokumen5 halamanSpirometra, Hymenolepis NanaJayricDepalobosBelum ada peringkat
- Protozoa RevisionDokumen6 halamanProtozoa Revisionfiena92100% (1)
- AnthraxDokumen27 halamanAnthraxSantosh BhandariBelum ada peringkat
- TRIBLASTICADokumen31 halamanTRIBLASTICAcircovaesterkaBelum ada peringkat
- Parasitology - Trematodes - S. Mansoni, S. Haematobium, P. WestermaniDokumen51 halamanParasitology - Trematodes - S. Mansoni, S. Haematobium, P. WestermaniNicole ManogBelum ada peringkat
- Ascaris: LumbricoidesDokumen5 halamanAscaris: LumbricoidessibinBelum ada peringkat
- Parasite Project BIOLOGY EditedDokumen21 halamanParasite Project BIOLOGY EditedPadma CharanBelum ada peringkat
- Cyclophyllidean CestodesDokumen92 halamanCyclophyllidean CestodesPauline AñesBelum ada peringkat
- Paragonimus WestermaniDokumen3 halamanParagonimus WestermaniHanisha EricaBelum ada peringkat
- HelminthsDokumen35 halamanHelminthsBr1nfoBelum ada peringkat
- TrichostrongyloideaDokumen30 halamanTrichostrongyloideahisto anatomyBelum ada peringkat
- LECT 2anatomy and Physiology of Pregnancy 2Dokumen45 halamanLECT 2anatomy and Physiology of Pregnancy 2Umer RafiqBelum ada peringkat
- The Male Reproductive SystemDokumen29 halamanThe Male Reproductive SystemadystiBelum ada peringkat
- Digestive System of GrasshopperDokumen8 halamanDigestive System of GrasshopperAshish SharMa100% (1)
- Diseases of Horses - The Respiratory Organs and the Alimentary Canal - With Information on Diagnosis and TreatmentDari EverandDiseases of Horses - The Respiratory Organs and the Alimentary Canal - With Information on Diagnosis and TreatmentBelum ada peringkat
- How to Stuff Birds and Animals: A valuable book giving instruction in collecting, preparing, mounting, and preserving birds, animals, and insectsDari EverandHow to Stuff Birds and Animals: A valuable book giving instruction in collecting, preparing, mounting, and preserving birds, animals, and insectsBelum ada peringkat
- Diseases of the Horse - With Information on Diagnosis and TreatmentDari EverandDiseases of the Horse - With Information on Diagnosis and TreatmentBelum ada peringkat
- Natural History of the Prairie Vole (Mammalian Genus Microtus) [KU. Vol. 1 No. 7]Dari EverandNatural History of the Prairie Vole (Mammalian Genus Microtus) [KU. Vol. 1 No. 7]Belum ada peringkat
- Cattle Slaughter Process PDFDokumen10 halamanCattle Slaughter Process PDFJanice LiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 Specific Diseases of Sheep and Goats PDFDokumen38 halamanChapter 5 Specific Diseases of Sheep and Goats PDFJanice LiBelum ada peringkat
- Bovine Meat Inspection-Parasites of Cattle PDFDokumen21 halamanBovine Meat Inspection-Parasites of Cattle PDFJanice Li100% (1)
- 53 Mycoplasma 09Dokumen21 halaman53 Mycoplasma 09Janice LiBelum ada peringkat
- Meat Inspection ProceduresDokumen28 halamanMeat Inspection ProceduresJanice Li100% (3)
- Chapter 1 Meat Inspection ProceduresDokumen28 halamanChapter 1 Meat Inspection ProceduresJanice LiBelum ada peringkat
- 30 Brower Cestode S 2009Dokumen5 halaman30 Brower Cestode S 2009Janice LiBelum ada peringkat
- Brucella, Francisella and Yersinia Pestis: Gram Negative Rods of ZoonosesDokumen12 halamanBrucella, Francisella and Yersinia Pestis: Gram Negative Rods of ZoonosesJanice LiBelum ada peringkat
- Key features of triploblastic wormsDokumen7 halamanKey features of triploblastic wormsJanice Li100% (1)
- Meat Inspection ProceduresDokumen28 halamanMeat Inspection ProceduresJanice Li100% (3)
- Intestinal Parasitosis FinalDokumen137 halamanIntestinal Parasitosis FinalJanice LiBelum ada peringkat
- B 212Dokumen5 halamanB 212Janice LiBelum ada peringkat
- Fasciolo Fact SheetDokumen8 halamanFasciolo Fact SheetJanice LiBelum ada peringkat
- FasciolaDokumen4 halamanFasciolaJanice LiBelum ada peringkat
- AVCR Radiology AnatomyDokumen63 halamanAVCR Radiology AnatomySam BotBelum ada peringkat
- Reproductive Organs of Farm AnimalsDokumen54 halamanReproductive Organs of Farm AnimalsJanice LiBelum ada peringkat
- Reproductive Diseases in Cattle: Brucellosis (Bang's Disease)Dokumen4 halamanReproductive Diseases in Cattle: Brucellosis (Bang's Disease)Janice Li100% (1)
- Reproductive Diseases in Cattle: Brucellosis (Bang's Disease)Dokumen4 halamanReproductive Diseases in Cattle: Brucellosis (Bang's Disease)Janice Li100% (1)
- WR PaperDokumen2 halamanWR PaperJanice LiBelum ada peringkat























































![Natural History of the Prairie Vole (Mammalian Genus Microtus)
[KU. Vol. 1 No. 7]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/187449742/149x198/0dd3bfb37c/1579722463?v=1)
















