Definition of Matrix
Diunggah oleh
Flora FloraDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Definition of Matrix
Diunggah oleh
Flora FloraHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Definition of Matrix
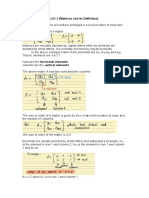
A matrix is a collection of numbers arranged into a fixed number of rows and columns. Usually the numbers are real numbers. In general, matrices can contain complex numbers but we won't see those here. Here is an example of a matrix with three rows and three columns:
The top row is row 1. The leftmost column is column 1. This matrix is a 3x3 matrix because it has three rows and three columns. In describing matrices, the format is:
rows X columns
Each number that makes up a matrix is called an element of the matrix. The elements in a matrix have specific locations. The upper left corner of the matrix is row 1 column 1. In the above matrix the element at row 1 col 1 is the value 1. The element at row 2 column 3 is the value 4.6.
Row equivalence
In linear algebra, two matrices are row equivalent if one can be changed to the other by a sequence of elementary row operations. Alternatively, two m n matrices are row equivalent if and only if they have the same row space. The concept is most commonly applied to matrices that represent systems of linear equations, in which case two matrices of the same size are row equivalent if and only if the corresponding homogeneous systems have the same set of solutions, or equivalently the matrices have the same null space. Because elementary row operations are reversible, row equivalence is an equivalence relation. It is commonly denoted by a tilde (~). There is a similar notion of column equivalence, defined by elementary column operations; two matrices are column equivalent if and only if their transpose matrices are row equivalent. Two rectangular matrices that can be converted into one another allowing both elementary row and column operations are called simply equivalent.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Introduction To Linear Algebra 5th Edition Johnson Solutions ManualDokumen17 halamanIntroduction To Linear Algebra 5th Edition Johnson Solutions ManualJessicaTerrysaoyj100% (14)
- BCA - 1st - SEMESTER - MATH NotesDokumen25 halamanBCA - 1st - SEMESTER - MATH Noteskiller botBelum ada peringkat
- System of Linear EquationsDokumen13 halamanSystem of Linear EquationsKomal ShujaatBelum ada peringkat
- Daddy by Sylvia PlathDokumen10 halamanDaddy by Sylvia PlathFlora Flora50% (2)
- Exercises LinalgDokumen65 halamanExercises LinalgTop trending and funny videoBelum ada peringkat
- 061585673X CodingDokumen689 halaman061585673X CodingHawkins Chin100% (2)
- On The Topic: Submitted byDokumen10 halamanOn The Topic: Submitted byAkshay KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Linear Algebra IDokumen43 halamanLinear Algebra IDaniel GreenBelum ada peringkat
- Linear Algebra Week 1Dokumen19 halamanLinear Algebra Week 1Albert GenceBelum ada peringkat
- MatrixDokumen2 halamanMatrixvijay kumar honnaliBelum ada peringkat
- Matrix (Mathematics)Dokumen19 halamanMatrix (Mathematics)Teka KamBelum ada peringkat
- Maths ProjectDokumen21 halamanMaths ProjectRida Mukhtar HussainBelum ada peringkat
- STPM Sem 1 Mathematics Assignment (Matrice)Dokumen7 halamanSTPM Sem 1 Mathematics Assignment (Matrice)Lai ChungyiBelum ada peringkat
- Wikipedia: MatrixDokumen19 halamanWikipedia: MatrixMaiara e maraiara100% (1)
- Lesson 2 - MatricesDokumen5 halamanLesson 2 - MatricesAletheia Annaliese LamperougeBelum ada peringkat
- X Maths MatricesDokumen26 halamanX Maths MatricesnvktvrBelum ada peringkat
- Kashif Khan Assignment of Linear Algebra.Dokumen10 halamanKashif Khan Assignment of Linear Algebra.engineerkashif97Belum ada peringkat
- MatricesDokumen10 halamanMatricesKrystal Edlyn JohnBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 of MatricesDokumen12 halamanChapter 3 of MatricesSurindra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- LA3B 20022024 015116pmDokumen32 halamanLA3B 20022024 015116pmawaissatti292Belum ada peringkat
- L2 - Linear Algebra - Matrices-NewDokumen20 halamanL2 - Linear Algebra - Matrices-New1ST SEMESTERBelum ada peringkat
- MR 2015matricesDokumen9 halamanMR 2015matricesManisha AldaBelum ada peringkat
- Matrices & It'S ApplicationsDokumen28 halamanMatrices & It'S ApplicationsDoctor StrangerBelum ada peringkat
- VCLA ALA DIV-C Group 12Dokumen13 halamanVCLA ALA DIV-C Group 12Parth GajjarBelum ada peringkat
- Maths ApplicationDokumen3 halamanMaths Applicationdhaval2410Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 2Dokumen17 halamanUnit 2cooooool1927Belum ada peringkat
- Matrix (Mathematics) : Matrix Matrix String TheoryDokumen2 halamanMatrix (Mathematics) : Matrix Matrix String TheoryANMOLBelum ada peringkat
- Vectors and MatricesDokumen9 halamanVectors and MatricesAlfaroBelum ada peringkat
- Z-Matrix (Mathematics) PDFDokumen7 halamanZ-Matrix (Mathematics) PDFmarsBelum ada peringkat
- MatricesDokumen14 halamanMatricesRenuka BhambhaniBelum ada peringkat
- Determinant: Geometric ViewDokumen2 halamanDeterminant: Geometric ViewaleperezmeBelum ada peringkat
- Matrices and Systems of Linear EquationsDokumen2 halamanMatrices and Systems of Linear EquationsGus EdiBelum ada peringkat
- System of Linear EquationsDokumen11 halamanSystem of Linear EquationsPaul ValdiviezoBelum ada peringkat
- Matrix AlgebraDokumen39 halamanMatrix Algebraamosoundo59Belum ada peringkat
- Exercises of Matrices and Linear AlgebraDari EverandExercises of Matrices and Linear AlgebraPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- L01. Review of Mathematical Foundation MatricesDokumen26 halamanL01. Review of Mathematical Foundation MatricesCrystal Renz TibayanBelum ada peringkat
- Fom Assignment 1Dokumen23 halamanFom Assignment 11BACS ABHISHEK KUMARBelum ada peringkat
- System of Linear EquationsDokumen37 halamanSystem of Linear EquationsHucen Nashyd MohamedBelum ada peringkat
- Matrix (Mathematics) : For Other Uses, See - "Matrix Theory" Redirects Here. For The Physics Topic, SeeDokumen25 halamanMatrix (Mathematics) : For Other Uses, See - "Matrix Theory" Redirects Here. For The Physics Topic, SeeMUHWANA TIMOTHYBelum ada peringkat
- Equatons of Straight LineDokumen7 halamanEquatons of Straight LineBilly CheungBelum ada peringkat
- Matrices - Basic ConceptsDokumen13 halamanMatrices - Basic ConceptsMica L. SanoBelum ada peringkat
- Matrix ManipulateDokumen59 halamanMatrix ManipulatesudhirBelum ada peringkat
- Solving Simultaneous Linear Equations: Presented By: Soha Tharwat Aly Abd El-Rahman Makhyoun Presented ToDokumen11 halamanSolving Simultaneous Linear Equations: Presented By: Soha Tharwat Aly Abd El-Rahman Makhyoun Presented ToSoha MakhyounBelum ada peringkat
- Matrices: Definition and ClassificationDokumen4 halamanMatrices: Definition and ClassificationGyanendra VermaBelum ada peringkat
- Systems of Linear Equations Math 130 Linear AlgebraDokumen4 halamanSystems of Linear Equations Math 130 Linear AlgebraCody SageBelum ada peringkat
- Cap 3 - Systematic Calculation of Dimensionless Products - LanghaarDokumen15 halamanCap 3 - Systematic Calculation of Dimensionless Products - LanghaarKaren HerreraBelum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen16 halamanUntitledKimberly BautistaBelum ada peringkat
- Business Maths - BBA - 1yr - Unit 3Dokumen141 halamanBusiness Maths - BBA - 1yr - Unit 3ADISH JAINBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 Matrices and Systems of Linear Equations - t2Dokumen35 halamanChapter 5 Matrices and Systems of Linear Equations - t2ASHVEIN KUMARAN A L RANGASAMYBelum ada peringkat
- MatricesDokumen2 halamanMatricesShriram ArvinthBelum ada peringkat
- What Is MatrixDokumen8 halamanWhat Is Matrixhb749856Belum ada peringkat
- Hanilen G. Catama February 5, 2014 Bscoe 3 Emath11Dokumen5 halamanHanilen G. Catama February 5, 2014 Bscoe 3 Emath11Hanilen CatamaBelum ada peringkat
- Matrices and Its Applications 4Dokumen4 halamanMatrices and Its Applications 4raeesandip10Belum ada peringkat
- Math 10 UNIT 1 Lesson 2Dokumen11 halamanMath 10 UNIT 1 Lesson 2Rujhon Nabablit BahallaBelum ada peringkat
- Applied Mathematics-Ii: C. Lakshmi Vara PrasadDokumen73 halamanApplied Mathematics-Ii: C. Lakshmi Vara PrasadC L V PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- System of Linear Equations: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen8 halamanSystem of Linear Equations: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaPenghuni KontrakanBelum ada peringkat
- (A) Personal Details Role Name Affiliation: Matrices, Representation of Equations in Matrix Form and Their SolutionDokumen10 halaman(A) Personal Details Role Name Affiliation: Matrices, Representation of Equations in Matrix Form and Their SolutionVishal SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Matrix Theory and Linear AlgebraDokumen4 halamanMatrix Theory and Linear AlgebraMuhammad Shamoeel100% (1)
- Ep&Nm - Extra - Linear AlgebraDokumen62 halamanEp&Nm - Extra - Linear AlgebrakyungmunBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 P1Dokumen11 halamanUnit 1 P1Sahil SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Matrices DefinitionDokumen32 halamanMatrices Definitionshantan02100% (1)
- System of Linear Equations - Linear Algebra WithDokumen37 halamanSystem of Linear Equations - Linear Algebra Withradhikaseelam1Belum ada peringkat
- Img 0002Dokumen1 halamanImg 0002Flora FloraBelum ada peringkat
- Ofed-Nfq Il CRQTRPHM and Trrtlra /: 2, Line6Dokumen1 halamanOfed-Nfq Il CRQTRPHM and Trrtlra /: 2, Line6Flora FloraBelum ada peringkat
- ELP NotaDokumen9 halamanELP NotaFlora FloraBelum ada peringkat
- Il Il: RuaaDokumen1 halamanIl Il: RuaaFlora FloraBelum ada peringkat
- FR' (LLFTT ( T.-.-": Fi Z.T Ffi#Dokumen1 halamanFR' (LLFTT ( T.-.-": Fi Z.T Ffi#Flora FloraBelum ada peringkat
- Fi - E' T, Tffi,:, ,) +l6j%fr.o ', 'Dokumen1 halamanFi - E' T, Tffi,:, ,) +l6j%fr.o ', 'Flora FloraBelum ada peringkat
- +E TRR FRHFR H4 +E N: RH# +ffi I5GDokumen1 halaman+E TRR FRHFR H4 +E N: RH# +ffi I5GFlora FloraBelum ada peringkat
- Img 0004Dokumen1 halamanImg 0004Flora FloraBelum ada peringkat
- T, ' HTX: #Ezf-Ffi#Dokumen1 halamanT, ' HTX: #Ezf-Ffi#Flora FloraBelum ada peringkat
- Advice 4 Mentor Working With DyslexiaDokumen13 halamanAdvice 4 Mentor Working With DyslexiaFlora FloraBelum ada peringkat
- Ffiftq: TF # Fre FfifrDokumen1 halamanFfiftq: TF # Fre FfifrFlora FloraBelum ada peringkat
- Combine (Diskalkulia)Dokumen16 halamanCombine (Diskalkulia)shivani4598Belum ada peringkat
- Yellow Pink Red Orange Green BlueDokumen2 halamanYellow Pink Red Orange Green BlueFlora FloraBelum ada peringkat
- Circle - Grey Square - Blue Triangle - Green Rectangle - YellowDokumen1 halamanCircle - Grey Square - Blue Triangle - Green Rectangle - YellowFlora FloraBelum ada peringkat
- LU Decomposition and Inverse MatrixDokumen15 halamanLU Decomposition and Inverse MatrixCarmela Elaco VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- Chaks Pure Maths P2 Ex 2 Pure MathematicsDokumen2 halamanChaks Pure Maths P2 Ex 2 Pure MathematicsDennis MumanyiBelum ada peringkat
- MathematicsDokumen131 halamanMathematicsAbhishek PadvalBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Final Exam SolutionsDokumen5 halamanPractice Final Exam SolutionsJohn ParkBelum ada peringkat
- Matrix AlgebraDokumen87 halamanMatrix AlgebraRhythm NafiBelum ada peringkat
- Es 204 PSDokumen14 halamanEs 204 PSKester Ray de VeraBelum ada peringkat
- RNMagic SquareDokumen17 halamanRNMagic SquareParivalavan ManoharanBelum ada peringkat
- Matrices Test ReviewDokumen5 halamanMatrices Test ReviewmohamedBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-2-Matrix Algebra and It's ApplicationsDokumen44 halamanUnit-2-Matrix Algebra and It's ApplicationsgedayeBelum ada peringkat
- The Solution of A System of Linear Equations by An Improved LU-Decomposition MethodDokumen2 halamanThe Solution of A System of Linear Equations by An Improved LU-Decomposition MethodsardinetaBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 3: Markov Chain: Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman (Utar) UDPS 2133mathematical ProgrammingDokumen4 halamanTutorial 3: Markov Chain: Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman (Utar) UDPS 2133mathematical ProgrammingceliomBelum ada peringkat
- Labsheet 1 (Int)Dokumen3 halamanLabsheet 1 (Int)mail meBelum ada peringkat
- Phase Equiva-Er'-': Methods BJTDokumen2 halamanPhase Equiva-Er'-': Methods BJTAsaduzzaman Khan PoranBelum ada peringkat
- NCERT Solutons For Class 12 Maths Chapter 3 Matrices PDFDokumen76 halamanNCERT Solutons For Class 12 Maths Chapter 3 Matrices PDFDEEPTHI VikramBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Matrices and Their Applications PDFDokumen94 halaman1 - Matrices and Their Applications PDFUjjwal NathBelum ada peringkat
- Ce-222 HandoutDokumen30 halamanCe-222 HandoutJulius Codiamat0% (1)
- NAST Practical FileDokumen18 halamanNAST Practical Filesachin prajapatiBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics For Inverse Kinematics PDFDokumen30 halamanMathematics For Inverse Kinematics PDFkraskromBelum ada peringkat
- 12th Maths Preboard-1 2021Dokumen7 halaman12th Maths Preboard-1 2021dev sharmaBelum ada peringkat
- D'Engineering Mathematics I PDFDokumen160 halamanD'Engineering Mathematics I PDFElakkiya EBelum ada peringkat
- DeterminantsDokumen11 halamanDeterminantsMouhamadou Lamine DiakhameBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 5B Linear AlgebraDokumen2 halamanAssignment 5B Linear AlgebraMd Minhaj Ahmed AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Numerical Linear Algebra Biswa Nath Datta PART I - Ch1-6Dokumen413 halamanNumerical Linear Algebra Biswa Nath Datta PART I - Ch1-6lpvasam100% (5)
- Pca - STATADokumen17 halamanPca - STATAAnonymous U5RYS6NqBelum ada peringkat
- 10.1 Properties of Markov Chains: Markov Chain Which Is Named After A Russian Mathematician CalledDokumen28 halaman10.1 Properties of Markov Chains: Markov Chain Which Is Named After A Russian Mathematician CalledVishnuvardhanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 Systems of Equations Section 5.1 Gaussian Elimination Matrix Form of A System of EquationsDokumen18 halamanChapter 5 Systems of Equations Section 5.1 Gaussian Elimination Matrix Form of A System of EquationsvictorBelum ada peringkat
- Matrix EquationsDokumen40 halamanMatrix EquationsMohan RajBelum ada peringkat