Natural Selection and Speciation
Diunggah oleh
api-236677776Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Natural Selection and Speciation
Diunggah oleh
api-236677776Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
Learnlng goal: l can explaln
Lhe process of naLural
selecuon and glve examples
of adapLauons LhaL lead Lo
evoluuon.
NATURAL
SELECTION:
HOW
EVOLUTION
OCCURS
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
8LvlLW: Lvoluuon sLarLs wlLh
geneuc varlauon, whlch ls creaLed
by:
Gene Flow
Movement of genes
from one population to
another.
Sex
Sexual reproduction
causes new
combinations of genes.
Mutation
Changes in DNA
Images courtesy of http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/_0_0/
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
Genetic Basis of Evolution
As allele frequency changes, populations evolve.
An allele (BB) could be lost
One allele could dominate and be present 100%, this is
called allele fixation.
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
naLural Selecuon
The process by
which individual
organlsms with
favorable LralLs are
more likely to
survive and
reproduce.
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
rocess of naLural Selecuon
SLep 1: Ceneuc varlauon
1here are dlerenL
forms of one LralL.
Lxample: 8eeLle coaL
color: Lan or green
Green and Brown Beetles
Image courtesy of http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/_0_0
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
SLep 2: LlmlLed resources
lood, space, access Lo maLes,
waLer, safe hablLaL represenL
resources LhaL may be ln shorL
supply (llmlLed) ln an
envlronmenL.
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
Step 3: Competition
Crganlsms wlll compeLe for resources
lnLerspeclc: beLween Lwo dlerenL specles
lnLraspeclc: wlLhln one specles
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
1he brown LralL (whlch
ls more advanLageous ln
hldlng Lhe beeLles from
blrds on Lree bark)
allows Lhe beeLle Lo
survlve and reproduce.
Step 4: Organisms with advantageous
trait will adapt and survive.
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
SLep 3: More beeLles are produced
Lhan survlve
Cverproducuon of
osprlng yeL some
organlsms don'L
survlve because of
envlronmenLal
consLralnLs
D|erenna|
reproducnon
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
SLep 6: 1he advanLageous LralL ls
passed on Lo nexL generauon
1ralL has a geneuc
basls
1hls ls called
hered|ty- LralL can
be passed on
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
Lxamples of AdapLauons creaLed
Lhrough naLural Selecuon
Crchlds fool wasps
lnLo maung
wlLh Lhem, whlch
helps Lhe orchld
polllnaLe lLs
owers
Katydids have
camouage to look
like leaves
Non-poisonous king
snakes mimic
poisonous coral
snakes.
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
Lxample of naLural Selecuon: Lxplaln how anublouc
reslsLance has evolved
WHAT OTHER INDUSTRIES WOULD BE WORRIED ABOUT
RESISTANCE?
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
Spec|anon: Pow uo new Specles
Lvolve?
1hrough reproducuve lsolauon: Lwo populauons
cannoL lnLerbreed
Why?
ulerenL ume of reproducuon (owerlng ume)
ulerenL hablLaL
ulerenL maung rlLuals/courLshlp/calls
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
WhaL ls a specles?
Specles: a group of
organlsms LhaL can
maLe and produce
ferule osprlng
Pybrld: An organlsm
whose parenLs are Lwo
dlerenL specles (e.g.
1lger + Llon = 1lgon),
sLerlle, lnLermedlaLe
morphology
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
keproducnve 8arr|ers
Any mechan|sm LhaL prevents Lwo specles from
produclng fern|e and]or v|ab|e hybr|d ospr|ng.
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
1. re-zygonc 8arr|ers (before fern||zanon)
a. 1empora| |so|anon:
8reedlng occurs aL dlerenL
umes for dlerenL specles.
b. nab|tat |so|anon:
Specles breed ln dlerenL
hablLaLs.
c. 8ehav|ora| |so|anon:
Llule or no sexual auracuon beLween
specles.
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.
All Images and associated captions courtesy of the UC Museum of Paleontology Understanding Evolution:
http://evolution.berkeley.edu.
2.ost-zygonc
8arr|ers-aher fern||zanon
a. nybr|d |nv|ab|||ty:
Pybrld zygoLes fall Lo
develop or fall Lo reach
sexual maLurlLy.
b. nybr|d ster|||ty:
Pybrld falls Lo produce
funcuonal gameLes (eggs
and sperm)
c. nybr|d breakdown:
Csprlng of hybrlds are
weak or lnferule.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- David Wool - Milestones in The Evolving Theory of Evolution-CRC Press (2020)Dokumen344 halamanDavid Wool - Milestones in The Evolving Theory of Evolution-CRC Press (2020)Candy HLBelum ada peringkat
- Evolution and Origin of CellsDokumen59 halamanEvolution and Origin of Cellsani5220100% (1)
- Molecular Population Genetics and Evolution - Masatoshi NeiDokumen290 halamanMolecular Population Genetics and Evolution - Masatoshi NeiGeorge Sebastian Antony100% (2)
- Evolution - Part 1Dokumen29 halamanEvolution - Part 1Wei Zhang100% (1)
- Kiss NotesDokumen38 halamanKiss NotesNalini Prakash100% (2)
- David Westneat, Charles Fox-Evolutionary Behavioral Ecology-Oxford University Press (2010)Dokumen660 halamanDavid Westneat, Charles Fox-Evolutionary Behavioral Ecology-Oxford University Press (2010)bobBelum ada peringkat
- Elements of Ecology, 9e (Smith) Chapter 5 Adaptation and Natural SelectionDokumen15 halamanElements of Ecology, 9e (Smith) Chapter 5 Adaptation and Natural SelectionChinBelum ada peringkat
- Carnivoran Evolution PDFDokumen524 halamanCarnivoran Evolution PDFAna Maria PaschoalBelum ada peringkat
- Historical Development of LanguageDokumen6 halamanHistorical Development of LanguageMhay DingleBelum ada peringkat
- Skeletal Biology of NYABG BurialDokumen236 halamanSkeletal Biology of NYABG BurialW Montague Cobb LabBelum ada peringkat
- Evolution MdcatDokumen32 halamanEvolution MdcatMuhammad Saad TariqBelum ada peringkat
- Bels & Whishaw 2019 - Feeding in VertebratesDokumen873 halamanBels & Whishaw 2019 - Feeding in VertebratesMarcos Akira Umeno100% (2)
- The Shape of Life: Genes, Development, and the Evolution of Animal FormDari EverandThe Shape of Life: Genes, Development, and the Evolution of Animal FormBelum ada peringkat
- Life Out of Balance: Homeostasis and Adaptation in a Darwinian WorldDari EverandLife Out of Balance: Homeostasis and Adaptation in a Darwinian WorldBelum ada peringkat
- (Lily E. Kay) The Molecular Vision of Life CaltecDokumen315 halaman(Lily E. Kay) The Molecular Vision of Life CaltecAriel Olmedo100% (4)
- Evidence For Human EvolutionDokumen6 halamanEvidence For Human EvolutionThanh Khuê LêBelum ada peringkat
- History of EvolutionDokumen37 halamanHistory of EvolutionLatha MahendraBelum ada peringkat
- Summer 2006 Workshop in Biology and Multimedia For High School TeachersDokumen26 halamanSummer 2006 Workshop in Biology and Multimedia For High School TeachersPrasad KSBelum ada peringkat
- Biographical ProfileDokumen1 halamanBiographical ProfileAhmed HassanBelum ada peringkat
- Opening Ceremony Speaker Ahmed Zewail Bio 44th International Chemistry OlympiadDokumen2 halamanOpening Ceremony Speaker Ahmed Zewail Bio 44th International Chemistry OlympiadMaram SyegBelum ada peringkat
- Week 23 BiologyDokumen23 halamanWeek 23 Biologyjames gomezBelum ada peringkat
- Mother Tongue 14 (August 1991)Dokumen65 halamanMother Tongue 14 (August 1991)Allan BomhardBelum ada peringkat
- The Evolutionary Biology of Extinct and Extant OrganismsDari EverandThe Evolutionary Biology of Extinct and Extant OrganismsBelum ada peringkat
- Lamarck AscendingDokumen7 halamanLamarck AscendingJohn RamalhoBelum ada peringkat
- Major Evidence for EvolutionDokumen31 halamanMajor Evidence for EvolutionUsman MaukBelum ada peringkat
- Book Review Tadpoles: The Biology of Anuran Larvae: A Review of by Roy W. Mcdiarmid and Ronald AltigDokumen2 halamanBook Review Tadpoles: The Biology of Anuran Larvae: A Review of by Roy W. Mcdiarmid and Ronald AltigBalduin NainggolanBelum ada peringkat
- Sketches of Nature: A Geneticist's Look at the Biological World During a Golden Era of Molecular EcologyDari EverandSketches of Nature: A Geneticist's Look at the Biological World During a Golden Era of Molecular EcologyBelum ada peringkat
- Human Evolution and Ecology: Who Are We and Where Are We?Dokumen12 halamanHuman Evolution and Ecology: Who Are We and Where Are We?rakhmatov UlanBelum ada peringkat
- Evolutionary Developmental Biology (Evo-Devo) : Past, Present, and FutureDokumen10 halamanEvolutionary Developmental Biology (Evo-Devo) : Past, Present, and Futureteju patneediBelum ada peringkat
- Galbrait - Anne@uwlax - Edu: Lesson Study Final Report (Short Form) Title: Team MembersDokumen5 halamanGalbrait - Anne@uwlax - Edu: Lesson Study Final Report (Short Form) Title: Team MembersLesson Study ProjectBelum ada peringkat
- Evolution Is A FactDokumen6 halamanEvolution Is A FactSangji BABelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Week 11 - Evolution 2Dokumen63 halamanLecture Week 11 - Evolution 2Recep ivedikseverBelum ada peringkat
- Vocatlng: Naomi PasachoffDokumen136 halamanVocatlng: Naomi PasachoffEbook PdfBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 5 - Evolution.Dokumen42 halamanUnit 5 - Evolution.nicolas SeguraBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture #11 - HWE Question + Natural Selection Part IDokumen44 halamanLecture #11 - HWE Question + Natural Selection Part IJenny ZhangBelum ada peringkat
- The Paracellular Channel: Biology, Physiology, and DiseaseDari EverandThe Paracellular Channel: Biology, Physiology, and DiseaseBelum ada peringkat
- Ace Tutorial GST 112 - 023048Dokumen27 halamanAce Tutorial GST 112 - 023048Uteh AghoghoBelum ada peringkat
- Evolutionary Biology and Conservation of Dung BeetlesDokumen570 halamanEvolutionary Biology and Conservation of Dung BeetlesHector AguilarBelum ada peringkat
- List of Masters Theses and Doctoral Dissertations Based On ResearchDokumen34 halamanList of Masters Theses and Doctoral Dissertations Based On ResearchJason BrownBelum ada peringkat
- Evolving Form and Function: Fossils and Development: Derek E. G. Briggs, EditorDokumen24 halamanEvolving Form and Function: Fossils and Development: Derek E. G. Briggs, EditorIaraMacêdoBelum ada peringkat
- Journal of Paleontology/FossilsDokumen22 halamanJournal of Paleontology/FossilsAngelina RandaBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Evolution Revision NotesDokumen23 halamanCBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Evolution Revision Noteskoredeadebayo2000Belum ada peringkat
- Braendle Et Al 2011 Chapter 1 PDFDokumen119 halamanBraendle Et Al 2011 Chapter 1 PDFFrederico HenningBelum ada peringkat
- Evolution, Science, and Society: Evolutionary Biology and The National Research AgendaDokumen75 halamanEvolution, Science, and Society: Evolutionary Biology and The National Research Agendaজুম্মা খানBelum ada peringkat
- Theories of Origin and Evolution of Life in <40 CharactersDokumen11 halamanTheories of Origin and Evolution of Life in <40 CharactersAnshika SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Bio ProjectDokumen17 halamanBio ProjectSpectra DragneelBelum ada peringkat
- Evolution Essays Research PapersDokumen8 halamanEvolution Essays Research Papersfyt18efe100% (1)
- Biological and Cultural Factors in Human EvolutionDokumen11 halamanBiological and Cultural Factors in Human Evolutionbalu42667% (9)
- Biology Project HUMAN EVOLUTIONDokumen12 halamanBiology Project HUMAN EVOLUTIONanonymous user 345Belum ada peringkat
- Torrey Botanical SocietyDokumen3 halamanTorrey Botanical SocietyXimena AlcántaraBelum ada peringkat
- Evolution and Extinction: Life's Changes Over Millions of YearsDokumen7 halamanEvolution and Extinction: Life's Changes Over Millions of YearsMarkdanielRamiterreBelum ada peringkat
- Giants of The Protozoa: Windows To The Deep ExplorationDokumen5 halamanGiants of The Protozoa: Windows To The Deep ExplorationcarlodolciBelum ada peringkat
- Fixity of SpeciesDokumen8 halamanFixity of Species'Lab Qou'Belum ada peringkat
- Evidences of EvolutionDokumen31 halamanEvidences of EvolutiondacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4 Feb 25th Class PresentationDokumen37 halamanUnit 4 Feb 25th Class Presentationapi-280153404Belum ada peringkat
- Evolution - Upto Homo and Analogous OrgansDokumen7 halamanEvolution - Upto Homo and Analogous Organsshreyavjha2020Belum ada peringkat
- ANA 316 Anthropology-1Dokumen23 halamanANA 316 Anthropology-1yahwehsbeloved001Belum ada peringkat
- Evolution Term Paper IdeasDokumen4 halamanEvolution Term Paper Ideasanhmbuwgf100% (1)
- Evolutionary Psychiatry Glossary 2Dokumen15 halamanEvolutionary Psychiatry Glossary 2Nenad MilosevicBelum ada peringkat
- Full TexthjbDokumen7 halamanFull TexthjbNailatul Izza HumammyBelum ada peringkat
- Gene To Protein Slides SultanyDokumen16 halamanGene To Protein Slides Sultanyapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
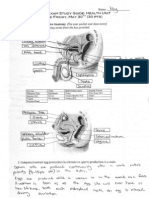
- 03 Skeleton SketchDokumen2 halaman03 Skeleton Sketchapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- 00-Intro Sci MetDokumen3 halaman00-Intro Sci Metapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Who Wants To Be A Great Scientist - Osmosis DiffusionDokumen34 halamanWho Wants To Be A Great Scientist - Osmosis Diffusionapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Bio Study Guide KeyDokumen8 halamanBio Study Guide Keyapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Fetal Pig Drawing AssignmentDokumen1 halamanFetal Pig Drawing Assignmentapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- 02-Types of Contraception Research SheetDokumen1 halaman02-Types of Contraception Research Sheetapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Sti SlidesDokumen18 halamanSti Slidesapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Health Study Guide KeyDokumen6 halamanHealth Study Guide Keyapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Respiratory System Study GuideDokumen2 halamanRespiratory System Study Guideapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- 02-Contraceptives Grid ActivityDokumen5 halaman02-Contraceptives Grid Activityapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Biology Final Exam Study GuideDokumen8 halamanBiology Final Exam Study Guideapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- 01-Dear Abby AssignmentDokumen2 halaman01-Dear Abby Assignmentapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Muscle TypesDokumen19 halamanMuscle Typesapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Muscle FatigueDokumen7 halamanMuscle Fatigueapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- CladisticsDokumen9 halamanCladisticsapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Darwin 2Dokumen1 halamanDarwin 2api-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment 5 EcDokumen2 halamanAssignment 5 Ecapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Darwin 3Dokumen2 halamanDarwin 3api-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Darwin AssignmentsDokumen1 halamanDarwin Assignmentsapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Population GeneticsDokumen12 halamanPopulation Geneticsapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment 4Dokumen2 halamanAssignment 4api-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Non Mendelian GeneticsDokumen10 halamanNon Mendelian Geneticsapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Mitosis ReadingDokumen4 halamanMitosis Readingapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Mitosis Flipbook ProjectDokumen1 halamanMitosis Flipbook Projectapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Mitosis SlidesDokumen14 halamanMitosis Slidesapi-236677776Belum ada peringkat
- Heredity and EvolutionDokumen4 halamanHeredity and EvolutionSneha GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- L22 Genome Evolution 15Dokumen31 halamanL22 Genome Evolution 15Juan RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- Biostratigraphy: Manalo, Tiarra Mojel F. 2014150275Dokumen20 halamanBiostratigraphy: Manalo, Tiarra Mojel F. 2014150275Tiarra Mojel100% (1)
- NG Ha Inv3 I-CheckDokumen4 halamanNG Ha Inv3 I-CheckHOANG DUONG KHONGBelum ada peringkat
- Ch. 23 Lecture Outline PDFDokumen15 halamanCh. 23 Lecture Outline PDFCSERM UNASBelum ada peringkat
- Allopatric SpeciationDokumen20 halamanAllopatric SpeciationPrincess CincoBelum ada peringkat
- 11.2 Natural Selection in PopulationsDokumen4 halaman11.2 Natural Selection in PopulationsOmar AlwaerBelum ada peringkat
- Phylogeny of UrochordatesDokumen2 halamanPhylogeny of UrochordatesPritam BhuteBelum ada peringkat
- Predicting inheritance outcomesDokumen30 halamanPredicting inheritance outcomesGrade12Ma.Bernadette SabarBelum ada peringkat
- Module 6: Genetic Change: OutcomesDokumen8 halamanModule 6: Genetic Change: OutcomesSorour KashbaBelum ada peringkat
- KladogramDokumen58 halamanKladogramDimo PratannaBelum ada peringkat
- Breed A Monster RubricDokumen1 halamanBreed A Monster Rubricapi-495151215Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1.introduction To SystematicsDokumen23 halamanLecture 1.introduction To SystematicsRia BalceBelum ada peringkat
- Evolution 1 - CladogramsDokumen2 halamanEvolution 1 - CladogramsJanelle-Janice Burgos100% (1)
- Organized by Jody Hey, Walter M. Fitch, and Francisco J. Ayala-Systematics and The Origin of Species. On Ernst Mayr's 100th AnniversaryDokumen127 halamanOrganized by Jody Hey, Walter M. Fitch, and Francisco J. Ayala-Systematics and The Origin of Species. On Ernst Mayr's 100th AnniversaryNathalia MelôBelum ada peringkat
- 10.2 Mendelian GeneticsDokumen11 halaman10.2 Mendelian GeneticsLiezl Cutchon CaguiatBelum ada peringkat
- Gizmo Natural Selection Artificial SelectionDokumen7 halamanGizmo Natural Selection Artificial SelectionAshley ClarkBelum ada peringkat
- GiraffeDokumen2 halamanGiraffeDogie FacdoBelum ada peringkat
- AP Biology Lab-02Dokumen27 halamanAP Biology Lab-02ldlewis0% (2)
- Class 12-Chapter 5 Principles of InheritanceDokumen5 halamanClass 12-Chapter 5 Principles of InheritanceSaransh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Evolution Inquiry Peppered MothsDokumen8 halamanEvolution Inquiry Peppered Mothsapi-394564312Belum ada peringkat
- Germ Plasm Theory: August WeismannDokumen2 halamanGerm Plasm Theory: August WeismannBiju Thomas100% (1)
- Peppered MothsDokumen3 halamanPeppered Mothsapi-320549212Belum ada peringkat
- JBS HALDANE FinalDokumen10 halamanJBS HALDANE FinalShruti Shree DashBelum ada peringkat
- Quantitative Genetics: Understanding Traits Through Genes and EnvironmentDokumen7 halamanQuantitative Genetics: Understanding Traits Through Genes and EnvironmentSource NatoBelum ada peringkat
- Sequence Alignment (Chapter 6) : The Biological ProblemDokumen44 halamanSequence Alignment (Chapter 6) : The Biological ProblemJahir HasanBelum ada peringkat
- Lamarck V DarwinDokumen2 halamanLamarck V Darwinapi-209631924Belum ada peringkat