The Cost of Compressed Air
Diunggah oleh
Robert Barrett0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
768 tayangan2 halamanEffective management of the cost of compressed air is essential in today’s ultra competitive markets. There are two ways to define the cost of compressed air:
1. Unloaded cost
2. Loaded cost)
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniEffective management of the cost of compressed air is essential in today’s ultra competitive markets. There are two ways to define the cost of compressed air:
1. Unloaded cost
2. Loaded cost)
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
768 tayangan2 halamanThe Cost of Compressed Air
Diunggah oleh
Robert BarrettEffective management of the cost of compressed air is essential in today’s ultra competitive markets. There are two ways to define the cost of compressed air:
1. Unloaded cost
2. Loaded cost)
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
The Cost of Compressed Air
Effective management of the cost of compressed air is essential in
today’s ultra competitive markets. There are two ways to define the
cost of compressed air
1. Unloaded cost
2. Loaded cost
Unloaded cost is as follows:
H.P. x .746 x Hours x Rate
Power Cost (Dollars) = ------------------------------------------
Motor Efficiency
Hours - The number of hours of operation.
H.P. - The power used to drive the compressor
Rate - The power rate (cents per Kw).
Motor Efficiency - The motor efficiency.
This formula is acceptable as accurate for estimating and comparison
purposes. (Your actual power bill can be further affected positively or
negatively by such things as power factor, demand charges, etc.)
The Magnitude of Power Cost (Electric)
To see the magnitude of your potential expenditure in power cost,
calculate the power cost of a 100 h.p. air compressor:
The three components of steam quality at point of use are:
6000 hours a year
Rate of $.07/Kw
Motor efficiency .90
(100) (.746) (6000) (.07)
Power Cost (Dollars) = ------------------------------------------
.90
Power Cost = $34,800 per year
A 1000 h.p. air compressor would have a $350,000 per year power cost
Determining Loaded Costs of Compressed Air
The above cost is an unloaded cost, which means there is no additional
cost of producing the compressed air put into equation. Unfortunately,
this is not true cost.
When you as a consumer of a utility in your home; purchase water,
natural gas or electric, is this an unloaded cost? No, all associated cost
to produce, distribute and maintain utility are included into the cost. All
other utilities have cost calculated at the loaded values, and then why
not do the same with compressed air. What is the additional cost? The
plant additional cost will vary depending on the operation and
accounting procedures. Here are a few examples:
• Initial Cost of all components (compressor, air dryer, etc.)
• Water for compressors and aftercoolers
• Electrical (air dryers)
• Refrigerant (air dryers)
• Disposal costs for (refrigerant, desiccant)
• Desiccant cost (5 year change out)
• Compressor maintenance
• Dryer maintenance
• Filter maintenance
• Operational
The unloaded cost for a cfm, plus other associated cost will provide the
true cost of compressed air.
Every plant should have a document loaded cost for a CFM of
compressed air.
Typically the loaded costs are usually 1.7 to 3.1 times higher than the
unloaded cost.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Combustion TheoryDokumen74 halamanCombustion TheoryRobert Barrett100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Quantifying Steam QualityDokumen4 halamanQuantifying Steam QualityRobert BarrettBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Boiler Efficiency CalculationsDokumen6 halamanBoiler Efficiency CalculationsRobert BarrettBelum ada peringkat
- Reading Pump CurvesDokumen4 halamanReading Pump CurvesRobert Barrett100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Revision NotesDokumen16 halamanClass 10 Science Chapter 2 Revision NotesKriish RatnaniBelum ada peringkat
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Slide 1: No-Churn TelecomDokumen11 halamanSlide 1: No-Churn Telecomleongladxton100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Statistics Hand NotesDokumen16 halamanStatistics Hand NotesAtul VermaBelum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- SPACE GASS 12 ManualDokumen968 halamanSPACE GASS 12 Manualozbuild100% (3)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- UntitledDokumen33 halamanUntitledapi-235198167Belum ada peringkat
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Stock Price Prediction Using LSTMDokumen29 halamanStock Price Prediction Using LSTMKunal GargBelum ada peringkat
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Automotive Solutions: Setting The Pace For InnovationDokumen36 halamanAutomotive Solutions: Setting The Pace For InnovationAda TopanBelum ada peringkat
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Project Report On Modulation (Class 12)Dokumen14 halamanProject Report On Modulation (Class 12)Shivam Tripathi100% (9)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Alp - Sizer InfoDokumen13 halamanAlp - Sizer InfoLê Quang DuyBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Bluebeam Revu Keyboard Shortcuts 2017-UKDokumen8 halamanBluebeam Revu Keyboard Shortcuts 2017-UKStigBelum ada peringkat
- Parola A Do ZDokumen8 halamanParola A Do ZjovicaradBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Fpls 12 764103Dokumen10 halamanFpls 12 764103Pawan MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Eaton Xeffect Industrial Switchgear Range Catalog Ca003002en en UsDokumen379 halamanEaton Xeffect Industrial Switchgear Range Catalog Ca003002en en UsMAURIZIO MARINIBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Camber For Construction StageDokumen18 halamanCamber For Construction StageOanh PhanBelum ada peringkat
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- His To GramsDokumen15 halamanHis To GramsMaryam HasanBelum ada peringkat
- ScriptHookDotNet ReadmeDokumen8 halamanScriptHookDotNet ReadmeFajar Hari MuliaBelum ada peringkat
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- CAD-based Design of Three Phase Transformer and CoDokumen13 halamanCAD-based Design of Three Phase Transformer and CoM4gne7icBelum ada peringkat
- ManageEngine Application Manager Best PracticesDokumen12 halamanManageEngine Application Manager Best PracticesNghiêm Sỹ Tâm PhươngBelum ada peringkat
- Assignments CHSSCDokumen7 halamanAssignments CHSSCphani12_chem5672Belum ada peringkat
- Cisco Ccna Icnd PPT 2.0 OspfDokumen15 halamanCisco Ccna Icnd PPT 2.0 OspfAMIT RAJ KAUSHIKBelum ada peringkat
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Is 4031 Part 4 - ConsistencyDokumen4 halamanIs 4031 Part 4 - ConsistencyCrypto AbhishekBelum ada peringkat
- Quantum Computing: Exercise Sheet 1: Steven Herbert and Anuj DawarDokumen2 halamanQuantum Computing: Exercise Sheet 1: Steven Herbert and Anuj DawarJuan DiegoBelum ada peringkat
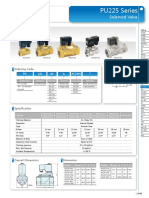
- PU225 Series: Solenoid ValveDokumen1 halamanPU225 Series: Solenoid Valveremus popescuBelum ada peringkat
- Virtual Memory & Demand PagingDokumen22 halamanVirtual Memory & Demand PagingAli AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Completation Inteligent RevistaDokumen9 halamanCompletation Inteligent RevistaGabriel Castellon HinojosaBelum ada peringkat
- Arthashastra: Citation NeededDokumen4 halamanArthashastra: Citation NeededtusharBelum ada peringkat
- Exam H13-611: IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way!Dokumen96 halamanExam H13-611: IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way!AdeyemiBelum ada peringkat
- TP 3017D Taman Angkasa Nuri - V01Dokumen25 halamanTP 3017D Taman Angkasa Nuri - V01Najwa AzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz 3 Basic ProbabilityDokumen38 halamanQuiz 3 Basic ProbabilityjacobtianBelum ada peringkat
- Flower-Visiting Insect Pollinators of Mustard (Brassica: Napus) in Jammu RegionDokumen7 halamanFlower-Visiting Insect Pollinators of Mustard (Brassica: Napus) in Jammu RegionMamata SubediBelum ada peringkat
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)