Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Diunggah oleh
karenkaren09Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Diunggah oleh
karenkaren09Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
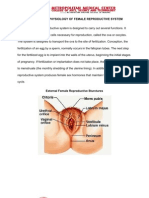
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women is a major cause of sterility (infertility).
An infection of the uterine tubes, PID affects an estimated 850,000 women each year in the United States. In many cases, sexually transmitted pathogens are involved. As much as 5080 percent of all first cases may be due to infection by Neisseria gonorrhoeae , the organism responsible for symptoms of gonorrhea, a sexually transmitted disease. Invasion of the region by bacteria that normally reside in the vagina can also cause PID. Recently, another sexually transmitted bacterium, belonging to the genus Chlamydia , has been identified as the probable cause of up to 50 percent of all cases of PID. Despite the fact that women with this infection may develop few, if any, symptoms, scarring of the uterine tubes can still produce infertility. The Uterus provides mechanical protection, nutritional support, and waste removal for the developing embryo (weeks 18) and fetus (from week 9 to delivery). In addition, contractions in the muscular wall of the uterus are important in ejecting the fetus at the time of birth. The uterus is a small, pearshaped organ about 7.5 cm (3 in.) long with a maximum diameter of 5 cm (2 in.). It weighs 3040 g (11.4 oz). In its normal position, the uterus bends anteriorly near its base, a condition known as anteflexion. In this position, the uterus tilts anteriorly, covering the superior and posterior surfaces of the urinary bladder. Suspensory Ligaments of the Uterus In addition to the broad ligament, three pairs of suspensory ligaments stabilize the position of the uterus and limit its range of movement.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- About VaginaDokumen13 halamanAbout VaginaRazend Muhd0% (1)
- Mechanism of LaborDokumen3 halamanMechanism of Laborkarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- Ectopic Pregnancy1Dokumen89 halamanEctopic Pregnancy1Muhammad AbeeshBelum ada peringkat
- Female Reproductive SystemDokumen42 halamanFemale Reproductive SystemAhmie MarcosBelum ada peringkat
- Ovarian New Growth CASE REPORTDokumen53 halamanOvarian New Growth CASE REPORTAbbey Jane Ayro69% (13)
- FNCPDokumen3 halamanFNCPkarenkaren09100% (1)
- Human Reproductive SystemDokumen23 halamanHuman Reproductive SystemQuennie AceronBelum ada peringkat
- Case Pres TahbsoDokumen19 halamanCase Pres TahbsoHazel Endaya0% (1)
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive SystemDokumen7 halamanAnatomy of Female Reproductive SystemseongeokBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study 3D FinaaaalDokumen34 halamanCase Study 3D FinaaaalPaul AnteBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen14 halamanAnatomy and PhysiologyIvee BustaBelum ada peringkat
- Operative Review TAHBSODokumen22 halamanOperative Review TAHBSOGinger Enireht HTaibBelum ada peringkat
- Review of Ovulation and Induction Protocolesal2Dokumen284 halamanReview of Ovulation and Induction Protocolesal2Hossamaldin Hussein Kamel SalemBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study: MicrobiologyDokumen13 halamanCase Study: MicrobiologywellYONGBelum ada peringkat
- Documemt Fo ReprashingDokumen10 halamanDocumemt Fo ReprashingMarvellous OkonobohBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction of Obstetrc UOHDokumen95 halamanIntroduction of Obstetrc UOHCaamir Dek HaybeBelum ada peringkat
- Uterus AnatomyDokumen7 halamanUterus AnatomyJoseph RadislaoBelum ada peringkat
- Lague - Case Analysis ReportDokumen43 halamanLague - Case Analysis Reportinah krizia lagueBelum ada peringkat
- Adebayo M.O. Care Study On Ovarian CystectomyDokumen47 halamanAdebayo M.O. Care Study On Ovarian CystectomyDamilola Olowolabi AdebayoBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and PathophysiologyDokumen6 halamanAnatomy and PathophysiologyRaymond EscuzarBelum ada peringkat
- 3 - Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis - Female Internal Genitals - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDokumen10 halaman3 - Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis - Female Internal Genitals - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfmimatechcontabilidadBelum ada peringkat
- Vaginal HysterectomyDokumen43 halamanVaginal HysterectomyKristine BillonesBelum ada peringkat
- Female Reproductive SystemDokumen48 halamanFemale Reproductive SystemLarry MagwegweBelum ada peringkat
- The Female Reproductive SystemDokumen25 halamanThe Female Reproductive SystemIan Mizzel A. Dulfina100% (1)
- IGCSE Biology Chapter #17 Human ReproductionDokumen18 halamanIGCSE Biology Chapter #17 Human ReproductionAazif JafriBelum ada peringkat
- Pathology and Management of Benign Breast Diseases: DR Bashiruaminu Moderator Prof LMD YusufDokumen58 halamanPathology and Management of Benign Breast Diseases: DR Bashiruaminu Moderator Prof LMD YusufisuhuBelum ada peringkat
- Female Reproductive SystemDokumen7 halamanFemale Reproductive SystemAbdallah AlasalBelum ada peringkat
- Anaphysio (Case Pres)Dokumen7 halamanAnaphysio (Case Pres)Ralph_John_Pac_8337Belum ada peringkat
- Case Study - Repeat LtcsDokumen9 halamanCase Study - Repeat LtcsAnna SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Female Reproductive System2Dokumen41 halamanFemale Reproductive System2joel1414Belum ada peringkat
- Ovarian CancerDokumen4 halamanOvarian CancerJuan Miguel Caspe MangayaBelum ada peringkat
- MCN NotesDokumen16 halamanMCN NotesKarla GiorlaBelum ada peringkat
- EndometritisDokumen2 halamanEndometritisMordao PantilaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive System:: VaginaDokumen5 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive System:: VaginaphallicBelum ada peringkat
- Head NursingDokumen16 halamanHead Nursingjayjay_simbulanBelum ada peringkat
- X. Anatomy & Physiology Cervix: VaginaDokumen8 halamanX. Anatomy & Physiology Cervix: VaginaNicaMariannePañaBelum ada peringkat
- Female Reproductive System DiseasesDokumen2 halamanFemale Reproductive System DiseasesRichard Bueta0% (1)
- Female Reproductive System (Human)Dokumen21 halamanFemale Reproductive System (Human)RiazAhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Placenta Accreta2Dokumen16 halamanPlacenta Accreta2Demi Rose BolivarBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Female Reproductive SystemDokumen39 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of The Female Reproductive SystemDevi Arine KusumawardaniBelum ada peringkat
- Powerpoint Case Study of MiscarriageDokumen25 halamanPowerpoint Case Study of MiscarriageAngel CauilanBelum ada peringkat
- Reproductive Physiology and Anatomy of The Sow PDFDokumen4 halamanReproductive Physiology and Anatomy of The Sow PDFCarol OrequesBelum ada peringkat
- GENERAL BIOLOGY 2 Notes - 073143Dokumen8 halamanGENERAL BIOLOGY 2 Notes - 073143John Axel CosmodBelum ada peringkat
- Procreative Health Is The Moral Obligation of Parents To Have The Healthiest Children Through All Natural and Artificial Means AvailableDokumen11 halamanProcreative Health Is The Moral Obligation of Parents To Have The Healthiest Children Through All Natural and Artificial Means AvailableFrankie Macabada0% (2)
- Student Name: ALI HASSAN RAZA STUDENT I D: 2018304027Dokumen6 halamanStudent Name: ALI HASSAN RAZA STUDENT I D: 2018304027Sayed AsifBelum ada peringkat
- Normal Spontaneous Delivery With Newborn Care: Nazarenus College and Hospital Foundation IncDokumen6 halamanNormal Spontaneous Delivery With Newborn Care: Nazarenus College and Hospital Foundation IncJc GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- LESSON 10 Intestinal ParasitesDokumen17 halamanLESSON 10 Intestinal Parasitesgimel tenorioBelum ada peringkat
- LP Prolpase Uterin - Id.en InggrisDokumen13 halamanLP Prolpase Uterin - Id.en InggrisNajahBelum ada peringkat
- Rle FinalsDokumen31 halamanRle FinalsMae Arra Lecobu-anBelum ada peringkat
- Female Genital Tract and The Pelvic BonesDokumen37 halamanFemale Genital Tract and The Pelvic Bonesعبد الله الحربيBelum ada peringkat
- What Is The Female Reproductive System?Dokumen11 halamanWhat Is The Female Reproductive System?MarianaBelum ada peringkat
- Female ReproductiveDokumen4 halamanFemale ReproductiveperaltajhynBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes On The Parts and Functions of The Female Reproductive System by Madel May EgeraDokumen5 halamanLecture Notes On The Parts and Functions of The Female Reproductive System by Madel May EgeraMadel May D EgeraBelum ada peringkat
- Local Media7887757728146616486Dokumen13 halamanLocal Media7887757728146616486IRA MONIQUE CABADENBelum ada peringkat
- IDL Ectopic PregnancyDokumen7 halamanIDL Ectopic Pregnancyرامي الشلاحيBelum ada peringkat
- Science 10 Quarter 3 ReviewerDokumen18 halamanScience 10 Quarter 3 ReviewerAntonBelum ada peringkat
- BookDokumen33 halamanBookObiogwu MichaelBelum ada peringkat
- Female Urinary Tract Infections in Clinical PracticeDari EverandFemale Urinary Tract Infections in Clinical PracticeBob YangBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Cancer Is A Malignant, Metastasizing Cancer of The Mammary Gland. It Is TheDokumen1 halamanBreast Cancer Is A Malignant, Metastasizing Cancer of The Mammary Gland. It Is Thekarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- Age and Oogenesis: The Uterine TubesDokumen1 halamanAge and Oogenesis: The Uterine Tubeskarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- HTTPDokumen2 halamanHTTPkarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- The Secretory PhaseDokumen3 halamanThe Secretory Phasekarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- Generic Name MetronidazoleDokumen1 halamanGeneric Name Metronidazolekarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- Internal Anatomy of The UterusDokumen1 halamanInternal Anatomy of The Uteruskarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- As Layers of Granulosa Cells Develop Around The Primary OocyteDokumen2 halamanAs Layers of Granulosa Cells Develop Around The Primary Oocytekarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- Cervical CancerDokumen1 halamanCervical Cancerkarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- Apgar: Email This Page To A Friendshare On Facebookshare On Twitterbookmark & Shareprinter-Friendly VersionDokumen2 halamanApgar: Email This Page To A Friendshare On Facebookshare On Twitterbookmark & Shareprinter-Friendly Versionkarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- Surgical TeamDokumen9 halamanSurgical Teamkarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen8 halamanDrug Studykarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- AddisonDokumen14 halamanAddisonkarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- NegerdDokumen1 halamanNegerdkarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- A Typical Ovary Is A Flattened Oval About 5 CM in LengthDokumen1 halamanA Typical Ovary Is A Flattened Oval About 5 CM in Lengthkarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen8 halamanDrug Studykarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- CoolDokumen12 halamanCoolkarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- ElectDokumen11 halamanElectkarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- AntibioticsDokumen11 halamanAntibioticskarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- AntibioticsDokumen11 halamanAntibioticskarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- Surgical TeamDokumen9 halamanSurgical Teamkarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- Table of ContntsDokumen6 halamanTable of Contntskarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- Letter of Guest SpeakerDokumen2 halamanLetter of Guest Speakerkarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- NR Final!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Dokumen1 halamanNR Final!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!karenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- Recommendation Final!!!!!!!!!!!!Dokumen1 halamanRecommendation Final!!!!!!!!!!!!karenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- Table BaliwasanDokumen3 halamanTable Baliwasankarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- Sta. Catalina Before After Brand No. of Sticks AMT Ways Brand No. of Sticks AMT WaysDokumen4 halamanSta. Catalina Before After Brand No. of Sticks AMT Ways Brand No. of Sticks AMT Wayskarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat
- Fo AbsractDokumen1 halamanFo Absractkarenkaren09Belum ada peringkat