Cell Structure Function Worksheet With Hints
Diunggah oleh
api-249772989Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Cell Structure Function Worksheet With Hints
Diunggah oleh
api-249772989Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Thought questions to help you understand cell structure and function Biology I Hillis Chapter 4: Cells
(with hints)
Each learning team will have 15 minutes to answer questions 1 through 7. If you finish early, start to work on other questions. Then we will share answers. For up to 5 points extra credit and part of studying for Exam 2, answer the rest of the questions. Extra credit is due by Wednesday, October 16, at the beginning of class. 1. How are prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells similar? List as many structural and functional similarities as you can.
2. How are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells different? List as many structural and functional differences as you can.
3. What problems do larger cells encounter that limit cell size? Eukaryotic cells are, in general, much larger than prokaryotic cells. How have eukaryotic cells overcome some of the problems that limit cell size? See pp 57-58 and http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2rihCCBzqMc
4. Describe the structure of ribosomes. Where are ribosomes located in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? What is the function of ribosomes? p. 64
5. Compare and contrast prokaryotic (p. 60) and eukaryotic (p. 73 for plants) cell walls. How are they similar? How are they different?
6. Compare and contrast eukaryotic and prokaryotic flagella. How are they similar? How are they different?
pp. 70-72 (eukaryotes) and p. 61 (prokaryotes)
7. How are Archaea different from Bacteria? Answer in one sentence. (Hint: the long answer is in Chapter 19, but the short answer is in Chapter 1.)
8. Eukaryotic cells have several membrane-bound organelles. Membranes segregate space within the cell into different compartments in which significantly different conditions can exist. Why is cellular compartmentalization adaptive? Use real examples of subcellular compartments in your answer. This video explains the importance of compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells, including examples of functions of specific subcellular compartments: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2rihCCBzqMc
9. Describe the structure of the nuclear membranes. How do things enter and exit the nucleus and why is this important? What occurs within the nucleus? What is stored and accessed within the nucleus? Why might it be advantageous to separate this from the rest of the cell?
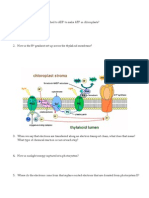
10. What organelles make up the endomembrane system? How are they linked structurally? How are they related functionally? Hillis Figure 4.8 and pp. 64-67
11. Compare and contrast the rough ER and smooth ER. How are they similar? How are they different? pp. 65-66
12. The Golgi apparatus has sometimes been compared to the FedEx distribution center in Atlanta, GA. Why does this comparison make sense? All FedEx packages go to Atlanta, then are sorted and sent to their destinations. This is easier than trying to work out various distribution patterns among all possible locations where people ship and receive packages. See also Animated Tutorial 4.2 on the Hillis website.
13. Read the Apply the Concept box on page 67 and answer the two questions.
The experiment describes a method for pulse labeling lipase protein. The location of the labeled protein is then identified at various time points (in minutes) after the pulse labeling.
14. How do vesicles move between the ER, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes or the plasma membrane? Compare this movement to the shipping of goods by train. This video shows how the protein kinesin moves along microtubules: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lLxlBB9ZBj4. Another protein, dyenin, moves the other direction along microtubules and can tow organelles or vesicles. Myosin dimers (the same molecule we met in muscles) can move along actin filaments and tow organelles or vesicles.
15. Which two eukaryotic organelles, besides the nucleus, contain DNA? How are the functions of these organelles similar? p. 68
16. Make a table listing the structures and functions of the three types of cytoskeletal filaments. Which of these is also present in a rudimentary form in prokaryotic cells? Fig. 4.10 and pp. 69-72 (eukaryotes) and p. 61 (prokaryotes)
17. Compare a eukaryotic cell wall to a eukaryotic extracellular matrix. How are they similar? How are they different? Summarize the functions of each. pp. 73-74
18. Describe the structures and functions of the three animal cell junctions. How is one of these like plasmodesmata of plants? pp. 74-75 and Activity 4.3 on the Hillis website
See this very cool animation from Harvard U. to see various parts of a eukaryotic cell (a white blood cell) in action: http://multimedia.mcb.harvard.edu/anim_innerlife.html Next time Cell Jeopardy: Will your learning team win? 7
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Cells HW PacketDokumen11 halamanCells HW PacketSandy Tana100% (2)
- What's in A Cell - Worksheet & ColoringDokumen2 halamanWhat's in A Cell - Worksheet & ColoringNuria Tarancon0% (1)
- Chapter Outline: ELL Tructure and UnctionDokumen5 halamanChapter Outline: ELL Tructure and Unctionrommel benamir100% (1)
- Evol RelationshipsDokumen15 halamanEvol RelationshipsCarla BanzuelaBelum ada peringkat
- Circulatory Lesson PlansDokumen4 halamanCirculatory Lesson Plansapi-281424654Belum ada peringkat
- Bio 150 Syllabus 2011Dokumen3 halamanBio 150 Syllabus 2011Jolaine ValloBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure and IonDokumen14 halamanCell Structure and IonNur NaNa100% (1)
- High School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Cell & Molecular BiologyDari EverandHigh School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Cell & Molecular BiologyBelum ada peringkat
- Evolution Review Packet Key EditableDokumen4 halamanEvolution Review Packet Key EditableMiljoy Delegado100% (1)
- Cell Composition, Structures and Cell As ReactorsDokumen10 halamanCell Composition, Structures and Cell As ReactorsFirdaus Asha'riBelum ada peringkat
- 5.3 Understanding Genes and ChromosomesDokumen11 halaman5.3 Understanding Genes and ChromosomesNoor Hidayah SambliBelum ada peringkat
- Prokaryotic Cells: Cell Membrane Cell Wall Capsule Pili Plasmid Flagella Nucleoid Region Ribosomes CytoplasmDokumen3 halamanProkaryotic Cells: Cell Membrane Cell Wall Capsule Pili Plasmid Flagella Nucleoid Region Ribosomes CytoplasmErvin WilliamsBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet As Level Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis 1Dokumen4 halamanWorksheet As Level Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis 1AreebBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Chapter 4 Study Guide AnswersDokumen3 halamanBiology Chapter 4 Study Guide AnswersEmma Frasier50% (2)
- 10th Life Science Carol Lilliam Muñoz Avila 2: Identify Desired Results (Stage 1)Dokumen8 halaman10th Life Science Carol Lilliam Muñoz Avila 2: Identify Desired Results (Stage 1)Carol LilliamBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Plan Cells and Micro k5 CellDokumen7 halamanUnit Plan Cells and Micro k5 Cellapi-371640211Belum ada peringkat
- Mitosis and Meiosis ActivityDokumen8 halamanMitosis and Meiosis ActivityTamicka BonnickBelum ada peringkat
- Eukaryotic Cell Lecture PDFDokumen49 halamanEukaryotic Cell Lecture PDFDaezel Deux100% (1)
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet: 1. Filling The BlanksDokumen3 halamanProtein Synthesis Worksheet: 1. Filling The BlanksFelix SimsungBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus v9 - Fall 2002 - Cell & Molecular BiologyDokumen4 halamanSyllabus v9 - Fall 2002 - Cell & Molecular Biologyogangurel100% (2)
- 6th Grade Science Scope and SequenceDokumen5 halaman6th Grade Science Scope and Sequenceapi-261880769Belum ada peringkat
- Plant and Animal TissuesDokumen9 halamanPlant and Animal TissuesfranciscocyrilleBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz Cell MembraneDokumen4 halamanQuiz Cell MembraneDeepan Chakkaravarthi100% (1)
- Nervous System WorksheetDokumen2 halamanNervous System WorksheetMcLargoBelum ada peringkat
- BiochemistryDokumen9 halamanBiochemistryClarissa IsuriñaBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Organelles Review ActivityDokumen5 halamanCell Organelles Review ActivityAngelica PantaleonBelum ada peringkat
- Cell StructuresDokumen3 halamanCell StructuresKatherine DenisBelum ada peringkat
- Mendelian WorksheetsDokumen17 halamanMendelian WorksheetsLesley AntojadoBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Unit PlanDokumen10 halamanBiology Unit Planapi-246097943Belum ada peringkat
- 6 Kingdoms of Life Lecture NotesDokumen82 halaman6 Kingdoms of Life Lecture NotesEvangelene Esquillo SanaBelum ada peringkat
- Taxonomy - Classification and Hierarchy of OrganismsDokumen16 halamanTaxonomy - Classification and Hierarchy of OrganismsBobbiRedBelum ada peringkat
- CloningDokumen6 halamanCloningkikkabuttigieg1466Belum ada peringkat
- Cell DifferentiationDokumen16 halamanCell DifferentiationHarika KeshavBelum ada peringkat
- Cladogram WsDokumen4 halamanCladogram Wsjeffery thomasBelum ada peringkat
- MeiosisDokumen24 halamanMeiosisMuhammad HamzaBelum ada peringkat
- Pond WaterDokumen4 halamanPond Waterapi-264011999Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 A Tour of The CellDokumen4 halamanChapter 4 A Tour of The Cellmzunl254760% (1)
- BIO 127 General Microbiology:: Course Description and ObjectivesDokumen24 halamanBIO 127 General Microbiology:: Course Description and Objectivescheramae ancesBelum ada peringkat
- Student Guide To Vce Unit 1 BiologyDokumen8 halamanStudent Guide To Vce Unit 1 Biologyapi-348068677Belum ada peringkat
- Plant CellDokumen112 halamanPlant CellAlfonso PlantillaBelum ada peringkat
- BLG 230 SyllabusDokumen6 halamanBLG 230 Syllabusjulliee112Belum ada peringkat
- Organelles - Presentation With GraphicsDokumen34 halamanOrganelles - Presentation With GraphicsFrederick LoganBelum ada peringkat
- STK1211 Practical Analytical ChemistryDokumen39 halamanSTK1211 Practical Analytical Chemistrylox agencyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3: Movement of Substance Across The Plasma MembraneDokumen13 halamanChapter 3: Movement of Substance Across The Plasma MembraneEma FatimahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plans - Biology 20 Unit D - Circulatory SystemDokumen4 halamanLesson Plans - Biology 20 Unit D - Circulatory Systemapi-337955718Belum ada peringkat
- (Preferred) Plant and Animal TissuesDokumen20 halaman(Preferred) Plant and Animal TissuesHannah CenaBelum ada peringkat
- 3.46B1 Blood Worksheet 1Dokumen4 halaman3.46B1 Blood Worksheet 1Nakeisha Joseph100% (1)
- Intro. Gen ZooDokumen49 halamanIntro. Gen ZooEdward Ashley ArcillaBelum ada peringkat
- Human Reproductive System To BirthDokumen11 halamanHuman Reproductive System To BirthDEEBANBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Test PracticeDokumen7 halamanCell Test Practiceapi-240396878Belum ada peringkat
- Day 4. Warm-Up. STAAR® Blitz. Science. BiologyDokumen2 halamanDay 4. Warm-Up. STAAR® Blitz. Science. BiologyRaul Ramirez RangelBelum ada peringkat
- DNA Molecule & Central DogmaDokumen43 halamanDNA Molecule & Central DogmaJoanna Ruth SeproBelum ada peringkat
- Science 10 Unit C PlanDokumen10 halamanScience 10 Unit C Planapi-242289205Belum ada peringkat
- Biology Paper 2 (Question) LDokumen15 halamanBiology Paper 2 (Question) Lhasimahazit75% (8)
- LAB Plant and Animal Cells WorksheetDokumen3 halamanLAB Plant and Animal Cells WorksheetKyle UyBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Grade 7Dokumen5 halamanBiology Grade 7Gunawan MuhammadBelum ada peringkat
- Ch. 2 (Systematics)Dokumen26 halamanCh. 2 (Systematics)ElsieCachoBelum ada peringkat
- Sex Chromosomes, Sex-Linked Genes and DNADokumen4 halamanSex Chromosomes, Sex-Linked Genes and DNAAlyn Mondrano AlonzoBelum ada peringkat
- Topic Study #9: CellsDokumen1 halamanTopic Study #9: CellsEstrella CoronaBelum ada peringkat
- Kenzie Fenske Thanks EmailDokumen1 halamanKenzie Fenske Thanks Emailapi-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Faceva Gollery May2010Dokumen7 halamanFaceva Gollery May2010api-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Faculty Eval Gollery April 2013Dokumen13 halamanFaculty Eval Gollery April 2013api-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Facultyeval Gollery June 2011Dokumen6 halamanFacultyeval Gollery June 2011api-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Facevalform Suzannegollery 08-09Dokumen2 halamanFacevalform Suzannegollery 08-09api-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Suzanne Gollery Professor RankDokumen2 halamanSuzanne Gollery Professor Rankapi-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Gollery 12-13 Eval Supervisor ResponseDokumen3 halamanGollery 12-13 Eval Supervisor Responseapi-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Lynns Annual Evaluation For Suzanne Gollery 2010Dokumen1 halamanLynns Annual Evaluation For Suzanne Gollery 2010api-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Gollery Suzanne Biol 101 Fall 2013Dokumen62 halamanGollery Suzanne Biol 101 Fall 2013api-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Exam 2 Cells Membranes Energy Metabolism Biol101 f13Dokumen8 halamanExam 2 Cells Membranes Energy Metabolism Biol101 f13api-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- First Page 2 of My Research PapersDokumen2 halamanFirst Page 2 of My Research Papersapi-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Gollery Suzanne Biol 101 Fall 12Dokumen64 halamanGollery Suzanne Biol 101 Fall 12api-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Faculty Self EvaluationDokumen14 halamanFaculty Self Evaluationapi-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Biology I 2013 ExamDokumen7 halamanBiology I 2013 Examapi-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Class Preparation Questions Biol101 f13Dokumen16 halamanClass Preparation Questions Biol101 f13api-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Exam 2 Review Bioli f13Dokumen4 halamanExam 2 Review Bioli f13api-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Molecular Structures Water and PH LabDokumen13 halamanMolecular Structures Water and PH Labapi-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Inquiry Respiration Lab Biol105Dokumen6 halamanInquiry Respiration Lab Biol105api-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Photosynthesis WorksheetDokumen2 halamanPhotosynthesis Worksheetapi-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Question StemsDokumen1 halamanQuestion Stemsapi-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Jack-O-Lantern Inheritance LabDokumen1 halamanJack-O-Lantern Inheritance Labapi-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Cattell Cpa 1 15Dokumen2 halamanCattell Cpa 1 15api-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Cpa 1 Caroline Parkhill 15Dokumen2 halamanCpa 1 Caroline Parkhill 15api-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- PhotosynthesisDokumen18 halamanPhotosynthesisapi-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Biology I Problem Solving ActivityDokumen6 halamanBiology I Problem Solving Activityapi-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Ap II Extra Credit Clinical Topic EssayDokumen3 halamanAp II Extra Credit Clinical Topic Essayapi-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Cell Cycle Cell DivisionDokumen14 halamanCell Cycle Cell Divisionapi-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Cells JeopardyDokumen22 halamanCells Jeopardyapi-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- Extra Credit PhilosophyDokumen1 halamanExtra Credit Philosophyapi-249772989Belum ada peringkat
- BiomedicalDokumen3 halamanBiomedicalreshmibiotechBelum ada peringkat
- SPREad PlateDokumen7 halamanSPREad PlateJermeLou BaoBelum ada peringkat
- Raman Spectroscopy As A Process Analytical Technology For Pharmaceutical Manufacturing and BioprocessingDokumen13 halamanRaman Spectroscopy As A Process Analytical Technology For Pharmaceutical Manufacturing and BioprocessingJian JinBelum ada peringkat
- Botany LAB Plant and Animal CellsDokumen7 halamanBotany LAB Plant and Animal CellsJasmine SandroBelum ada peringkat
- Agilent Catalogue 2011 12Dokumen1.349 halamanAgilent Catalogue 2011 12framezany100% (1)
- Pewarnaan HistologiDokumen16 halamanPewarnaan HistologiStnrhalizaBelum ada peringkat
- Laser DissertationDokumen7 halamanLaser DissertationPayForAPaperCanada100% (1)
- Histology Lecture #2Dokumen9 halamanHistology Lecture #2رشيد عليانBelum ada peringkat
- Microscope ObservationDokumen18 halamanMicroscope ObservationYUSNIRABelum ada peringkat
- Vector Simulations of Dark Beam InteractionDokumen11 halamanVector Simulations of Dark Beam InteractiongremlindemlinBelum ada peringkat
- Biophysical TechniquesDokumen12 halamanBiophysical TechniquesKaren Joy ReasBelum ada peringkat
- MNL46 - Metallographic and Materialographic Specimen Preparation, Light Microscopy, Image Analysis and Hardness Testing 2007Dokumen761 halamanMNL46 - Metallographic and Materialographic Specimen Preparation, Light Microscopy, Image Analysis and Hardness Testing 2007Miguel AngelBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 3: Cell Structure and Function Chapter 8: Cell: The Unit of LifeDokumen4 halamanUnit 3: Cell Structure and Function Chapter 8: Cell: The Unit of Lifevoice for islamBelum ada peringkat
- Sperm MorphologyDokumen4 halamanSperm MorphologyDr.Jignesh chaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Ch-8, Cell Class - 8, Science Textbook QuestionsDokumen5 halamanCh-8, Cell Class - 8, Science Textbook Questionsbucks GamingBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 5Dokumen5 halamanExperiment 5Nipuni Saubhagya RathnayakeBelum ada peringkat
- Flotation BathDokumen3 halamanFlotation Bathnurul fatinajihahBelum ada peringkat
- Science 7 q2 Week 4Dokumen28 halamanScience 7 q2 Week 4Galang Alpha100% (2)
- Course Syllabus Exam Micro paraDokumen18 halamanCourse Syllabus Exam Micro paralanie_jecielBelum ada peringkat
- Coll OidDokumen8 halamanColl OidAlvian VianBelum ada peringkat
- BioSelMol - Pertautan Antar SelDokumen22 halamanBioSelMol - Pertautan Antar SelBrillian AlfiBelum ada peringkat
- Eraser Treatmenty On PaperDokumen13 halamanEraser Treatmenty On Papergomez.teran.ximenaBelum ada peringkat
- Catalyst Characterization TechniquesDokumen8 halamanCatalyst Characterization TechniquesDaniel DadzieBelum ada peringkat
- Lab. Activity No. 2 MicroscopeDokumen4 halamanLab. Activity No. 2 MicroscopeBlack RoseBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 11 - Life Science - Revision Questions - Micro-OrganismsDokumen5 halamanGrade 11 - Life Science - Revision Questions - Micro-OrganismsJustinCase1991100% (1)
- Pauline Mary La Corda - 3 Transfer of CulturesDokumen3 halamanPauline Mary La Corda - 3 Transfer of CulturesPauline MaryBelum ada peringkat
- Chatelaine, Aug 2011Dokumen4 halamanChatelaine, Aug 2011emediageBelum ada peringkat
- 1) Introduction To Microbiology - HistoryDokumen37 halaman1) Introduction To Microbiology - HistoryJustin Dave ManantanBelum ada peringkat
- Structural Organisation in Animals - IDokumen49 halamanStructural Organisation in Animals - IPukazhvanthen ParamanandhanBelum ada peringkat
- O Level'S: BIOLOGY (5090)Dokumen59 halamanO Level'S: BIOLOGY (5090)Maryyam ShahzadBelum ada peringkat