Kuliah 6 - Ratio Analysis
Diunggah oleh
Gembel Couvlac ElitHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Kuliah 6 - Ratio Analysis
Diunggah oleh
Gembel Couvlac ElitHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
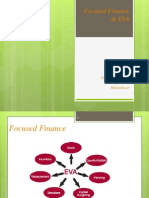
Ratio Analysis
Rini Novrianti Sutardjo Tui
Ratio Analysis
History
Examine trends
Budget
Compare actual with
expected values
Competition
Compare with other
firms
Categories of Ratios
Market
Value
Liquidity Asset
Mngt.
Debt
Mngt.
Profit
ability
Ratios
Illuminate some aspects
of how business is doing
Liquidity Ratios
Current Ratio
To ensure solvency the
current ratio has to exceed
1.0.
Quick Ratio
Measures liquidity without
considering inventory (the
firms least liquid current
asset).
s liabilitie Current
assets Current
Ratio Current
_
_
_ =
s liabilitie Current
Inventory assets Current
Ratio Quick
_
_
_
=
Asset Management Ratios
Inventory
Turnover
measures how
many times a
year the firm
uses up an
average stock of
goods.
Average
Collection Period
measures the
time it takes to
collect on credit
sales.
ACP
IT
FAT TAT
Total Asset
Turnover is
more widely
used than Fixed
Asset Turnover.
Fixed Asset
Turnover is
appropriate in
industries where
significant
equipment is
required to do
business.
sales daily Average
s receivable Account
ACP
_ _
_
=
Inventory
CoGS
Turnover Inventory = _
( )
( ) net assets Fixed
total Sales
FAT
_
=
( )
( ) total assets Fixed
total Sales
TAT
_
=
Debt Management Ratios
Times Interest Earned Debt-to-equity Ratio
Cash Coverage
Fixed Charge Coverage
Debt
Mngt.
equity Common
LTdebt
_
=
ense Interest
EBIT
exp _
=
ense Interest
on depreciati EBIT
exp _
+
=
payment lease ense Interest
payment lease EBIT
_ exp _
_
+
+
=
Profitability Ratios
ROS
Return on Sales represents a
fundamental indication of the overall
profitability of the business
ROA
Return on Assets measures the overall
ability of the firm to utilize the assets in
which it has invested to earn a profit.
ROE
Return on Equity measures the firms
ability to earn a return on the owners
invested capital.
Sales
income Net
ROS
_
=
assets Total
income Net
ROA
_
_
=
equity rs Stakeholde
income Net
ROE
'
_
=
Market Value Ratios
PE Ratio
Tells how much investors are
willing to pay for a dollar of
the firms earnings.
Market-to-book
Value Ratio
A healthy company is
expected to have a market
value greater than its book
value.
share per Earning
price stock Current
Ratio PE
_ _
_ _
_ =
share per value Book
price stock Current
ratio value book to Market
_ _ _
_ _
_ _ =
Rate of Return
C= 50
C= 500
C= 450
I= 50
I= 250
I= 200
I= 50
I= 250
I= 200
L= 50
L= 500
L= 450
0
0
0
1
1
1
5
5
5
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
5 , 5 ,
50 50 50 0
i i
F
P
A
P
PW Eq.
i=ROR
A
=100%, >i*= 15%
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
5 , 5 ,
500 250 500 0
i i
F
P
A
P
PW Eq.
i=ROR
B
=50%, >i*= 15%
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
5 , 5 ,
450 200 450 0
i i
F
P
A
P
PW Eq.
i=ROR
B-A
=44.4%, >i*= 15%
A
B
B-A
Net Value Analysis
C= 50
C= 500
C= 450
I= 50
I= 250
I= 200
I= 50
I= 250
I= 200
L= 50
L= 500
L= 450
0
0
0
1
1
1
5
5
5
A
B
B-A
50 . 286 $ 50 50 50
50 . 42 $ 50 50 50
50 . 142 $ 50 50 50
5 %, 15 5 %, 15
5 %, 15 5 %, 15
5 %, 15 5 %, 15
+ =
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
=
+ =
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
+ =
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
.
|
\
|
=
P
F
A
F
NFV
P
A
F
A
NAV
F
P
A
P
NPV
A
A
A
A B A B
A B A B
A B A B
NFV NFV NFV
NAV NAV NAV
NPV NPV NPV
=
=
=
Ratio Analysis
C= 50
C= 500
C= 450
I= 50
I= 250
I= 200
I= 50
I= 250
I= 200
L= 50
L= 500
L= 450
0
0
0
1
1
1
5
5
5
A
B
B-A
0 , 85 . 2
50
50 . 142
> = = =
Cost
A
A
PW
NPV
PVR
0 , 17 . 1
500
6 . 586
> = = =
Cost
B
B
PW
NPV
PVR
0 , 99 . 0
450
444
> = = =
Investment
A B
A B
PW
NPV
PVR
Cl i c k t o e d i t c o mp a n y s l o g a n .
A double pipe heat exchanger with steam in the shell is to be insulated to reduce
heat loss to surroundings. The thickness of insulation, initial cost and projected
annual cost of heat loss are given in the following table. If the minimum ROR is
20% before taxes, determine the optimumthickness of insulation for an insulation
life of 6 years with zero salvage value.
Insulation
Thickness (inch)
0
1
2
3
4
Initial Cost ($)
0
1,200
1,800
2,500
3,500
Annual Heat
Loss Cost ($)
1,400
800
600
500
400
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- CPA BEC Financial RatiosDokumen24 halamanCPA BEC Financial Ratiospambia200050% (2)
- Financial Statement Analysis 1Dokumen23 halamanFinancial Statement Analysis 1MedicareMinstun Project100% (1)
- Financial Statement Analysis 2 2Dokumen23 halamanFinancial Statement Analysis 2 2Denise Roque100% (1)
- Financial Statement Analysis 1Dokumen23 halamanFinancial Statement Analysis 1Theang ʚĩɞBelum ada peringkat
- Ratio Analysis: CC byDokumen39 halamanRatio Analysis: CC byrahul krishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Ratio AnalysisDokumen38 halamanRatio AnalysismdalakotiBelum ada peringkat
- FIN 3130 Chapter 14 StudentDokumen14 halamanFIN 3130 Chapter 14 StudentMitch FarrerBelum ada peringkat
- Session 2Dokumen39 halamanSession 2amanthi gunarathna95Belum ada peringkat
- Fatema NusratDokumen10 halamanFatema NusratFatema NusratBelum ada peringkat
- RATIO AnalysisDokumen4 halamanRATIO AnalysisDhaval PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Nalysis OF Inancial TatementsDokumen43 halamanNalysis OF Inancial TatementsBoo LeBelum ada peringkat
- FinMan Report On FS Analysis RATIODokumen31 halamanFinMan Report On FS Analysis RATIOMara LacsamanaBelum ada peringkat
- Ratio Analysis PresentationDokumen39 halamanRatio Analysis PresentationJeevan PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Control and Ratio AnalysisDokumen28 halamanFinancial Control and Ratio Analysismalavika100% (1)
- Financial Analysis 1Dokumen38 halamanFinancial Analysis 1Crestine Joyce Mirabel DelaCruzBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluating A Firm's Financial PerformanceDokumen45 halamanEvaluating A Firm's Financial PerformancemarediarameezBelum ada peringkat
- BusinessDokumen15 halamanBusinessEnes ErciyesBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Statement AnalysisDokumen39 halamanFinancial Statement AnalysisJoshua Naragdag ColladoBelum ada peringkat
- Liquidity Analysis RatiosDokumen7 halamanLiquidity Analysis RatiosGlessie DiñoBelum ada peringkat
- ProfitabilityDokumen30 halamanProfitabilitySumit KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Ratio Break Even AnalysisDokumen21 halamanRatio Break Even AnalysisAamirx64100% (1)
- Ratio Analysis - A2-Level-Level-Revision, Business-Studies, Accounting-Finance-Marketing, Ratio-Analysis - Revision WorldDokumen5 halamanRatio Analysis - A2-Level-Level-Revision, Business-Studies, Accounting-Finance-Marketing, Ratio-Analysis - Revision WorldFarzan SajwaniBelum ada peringkat
- BBC406 Fundamentals of Finance: Week 5 Analysis of Financial StatementsDokumen53 halamanBBC406 Fundamentals of Finance: Week 5 Analysis of Financial StatementsZhaslan HamzinBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis and Interpretation of Financial Statements 1Dokumen61 halamanAnalysis and Interpretation of Financial Statements 1Jeon Cyrone CuachonBelum ada peringkat
- Profitability Liquidity Ratio Analysis Investment AppraisalDokumen11 halamanProfitability Liquidity Ratio Analysis Investment AppraisalWILSON KosheyBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Ratio Analysis (Autosaved)Dokumen16 halamanIntroduction To Ratio Analysis (Autosaved)umarrizwan208Belum ada peringkat
- Narayana Engineering College Autonomous-Nellore: Prepared by M.Bhargav Charan 20711E0054Dokumen15 halamanNarayana Engineering College Autonomous-Nellore: Prepared by M.Bhargav Charan 20711E0054CH ANIL VARMABelum ada peringkat
- Valuation Methods Used in Mergers & Acquisition: Roshankumar S PimpalkarDokumen6 halamanValuation Methods Used in Mergers & Acquisition: Roshankumar S PimpalkarAmit GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Session 2 (Ratio Analsysis) SolutionDokumen14 halamanSession 2 (Ratio Analsysis) SolutionBintang David SusantoBelum ada peringkat
- Ratio Analysis 2.1Dokumen69 halamanRatio Analysis 2.1Sivaji AmmuBelum ada peringkat
- AE 24 Lesson 2-3Dokumen4 halamanAE 24 Lesson 2-3Keahlyn BoticarioBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 6 - Ratio AnalysisDokumen21 halamanLesson 6 - Ratio AnalysisLio MelBelum ada peringkat
- Ratio Analysis: An OverviewDokumen26 halamanRatio Analysis: An OverviewAnubhav Singhal0% (1)
- Current Ratio Liquidity Working CapitalDokumen2 halamanCurrent Ratio Liquidity Working CapitalThinagari JevataranBelum ada peringkat
- Ratio AnalysisDokumen37 halamanRatio AnalysisDebalina GhoshBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 13 Financial Statement AnalysisDokumen32 halamanTopic 13 Financial Statement AnalysisAbd AL Rahman Shah Bin Azlan ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Statement AnalysisDokumen20 halamanFinancial Statement AnalysisMary Gwyneth PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Ratio Analysis: Ratio Analysis Is The Process of Establishing and Interpreting Various RatiosDokumen26 halamanRatio Analysis: Ratio Analysis Is The Process of Establishing and Interpreting Various RatiosTarpan Mannan100% (2)
- Analysis of Financial StatementsDokumen17 halamanAnalysis of Financial StatementsShilpa RajuBelum ada peringkat
- Jamil Ahmed Assistant ProfessorDokumen29 halamanJamil Ahmed Assistant ProfessorParizad456Belum ada peringkat
- Profitability Ratio Analysis and Stock Price Calculation of 10 DSE Listed Company InbangladeshDokumen22 halamanProfitability Ratio Analysis and Stock Price Calculation of 10 DSE Listed Company InbangladeshMD. Hasan Al MamunBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Company AnalysisDokumen30 halamanChapter Company Analysisranbirkapoor8597Belum ada peringkat
- Financial Ratios - Complete List and Guide To All Financial RatiosDokumen6 halamanFinancial Ratios - Complete List and Guide To All Financial Ratiosayush_37100% (1)
- Focused Finance & Eva: Naina Adarsh Tanvi Chaudhary Pushpak Roy ManishwarDokumen23 halamanFocused Finance & Eva: Naina Adarsh Tanvi Chaudhary Pushpak Roy ManishwarNaina Singh AdarshBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluating A Firm's Financial Performance (Ratio Analysis)Dokumen64 halamanEvaluating A Firm's Financial Performance (Ratio Analysis)numlit1984Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Ratio AnalysisDokumen33 halamanIntroduction To Ratio AnalysisSayantan KhamruiBelum ada peringkat
- 2.3.2 Financial Ratios and Their Interpretation Table 2.3: Different Financial Ratios SL - No. Category Types of Ratio InterpretationDokumen8 halaman2.3.2 Financial Ratios and Their Interpretation Table 2.3: Different Financial Ratios SL - No. Category Types of Ratio InterpretationAnkur AroraBelum ada peringkat
- AccountDokumen16 halamanAccountMohamad AlifBelum ada peringkat
- FSA Chapter 8 NotesDokumen9 halamanFSA Chapter 8 NotesNadia ZahraBelum ada peringkat
- Financial RatiosDokumen15 halamanFinancial RatiosHojol100% (1)
- 16 Financial Ratios To Determine A Company's Strength and WeaknessesDokumen5 halaman16 Financial Ratios To Determine A Company's Strength and WeaknessesOld School Value88% (8)
- Chapter 13 Equity ValuationDokumen33 halamanChapter 13 Equity Valuationsharktale2828Belum ada peringkat
- Financial Analysis of Unilever PakistanDokumen7 halamanFinancial Analysis of Unilever Pakistanzainab malikBelum ada peringkat
- Figure 11.5: Operating Cash Flow and Sales VolumeDokumen7 halamanFigure 11.5: Operating Cash Flow and Sales VolumeAn DoBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Statement AnalysisDokumen3 halamanFinancial Statement AnalysisIeva Francheska AgustinBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Statement AnalysisDokumen3 halamanFinancial Statement AnalysisIeva Francheska AgustinBelum ada peringkat
- Finantial RatiosDokumen6 halamanFinantial RatiosGio RobakidzeBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Ratio Analysis FormulasDokumen4 halamanFinancial Ratio Analysis FormulasVaishali Jhaveri100% (1)
- Business Metrics and Tools; Reference for Professionals and StudentsDari EverandBusiness Metrics and Tools; Reference for Professionals and StudentsBelum ada peringkat
- Mining Investment AnalysisDokumen1 halamanMining Investment AnalysisBhathu Lha SheBelum ada peringkat
- GY403 Lecture1 IntroductionDokumen21 halamanGY403 Lecture1 IntroductionBhathu Lha SheBelum ada peringkat
- GY403 Lecture2 DescriptiveAnalysis BaseMapsDokumen17 halamanGY403 Lecture2 DescriptiveAnalysis BaseMapsBhathu Lha SheBelum ada peringkat
- 0c94c09453dfe07 EkDokumen12 halaman0c94c09453dfe07 EkBhathu Lha SheBelum ada peringkat
- GY403 Lecture2 DescriptiveAnalysis BaseMapsDokumen17 halamanGY403 Lecture2 DescriptiveAnalysis BaseMapsBhathu Lha SheBelum ada peringkat
- GY403 Lecture3 DescriptiveAnalysis PaceAndCompassDokumen14 halamanGY403 Lecture3 DescriptiveAnalysis PaceAndCompassBhathu Lha SheBelum ada peringkat
- GY403 Lecture3 DescriptiveAnalysis PaceAndCompassDokumen14 halamanGY403 Lecture3 DescriptiveAnalysis PaceAndCompassBhathu Lha SheBelum ada peringkat
- GY403 Lecture6 KinematicAnalysisDokumen10 halamanGY403 Lecture6 KinematicAnalysisBhathu Lha SheBelum ada peringkat
- 3Z03 2011-12 Course OutlineDokumen3 halaman3Z03 2011-12 Course OutlineBhathu Lha SheBelum ada peringkat
- AchievementDokumen1 halamanAchievementSafar Al InseBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Geological Site InvestigationsDokumen5 halamanEngineering Geological Site InvestigationsSafar Al InseBelum ada peringkat
- LAMPIRAN A (Data Curhuj) FixDokumen11 halamanLAMPIRAN A (Data Curhuj) FixBhathu Lha SheBelum ada peringkat
- 0c94c09453dfe07 EkDokumen12 halaman0c94c09453dfe07 EkBhathu Lha SheBelum ada peringkat
- MD 36 BDokumen4 halamanMD 36 Breski_minerzBelum ada peringkat