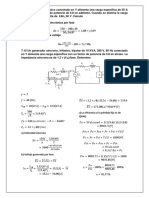
Construcción de Un Panel Solar Basico
Diunggah oleh
traoken0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
32 tayangan9 halamanHak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
32 tayangan9 halamanConstrucción de Un Panel Solar Basico
Diunggah oleh
traokenHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 9
Manual para la Construccin de Paneles Solares
Solar Panel Construction Manual
Aaron Smith
1 CONOCIMIENTOS BSICOS DE LOS SISTEMAS SOLARES
1 SOLAR SYSTEM BASICS
Fig. 1.1: Los componentes bsicos de sistemas solares.
Fig. 1.1: The basic components for a solar energy system.
Los sistemas solares tpicos tienen un panel solar, un controlador de carga, un breaker, una batera, lmparas
compactas, interruptores, porta lmparas y alambre. (ver Fig. 1.1)
El panel solar convierte la energa sol en electricidad para luego almacenar en la batera. Mientras est
cargando es controlado por un controlador de carga. El controlador de carga hace dos funciones, previene
carga demasiado de la batera y previene carga baja de la batera a travs del panel solar en la noche. La
batera es necesaria porque necesita tener energa cuando no hay suficiente sol o cuando est muy nublado.
Typical solar systems that Grupo Fenix sells consist of a solar panel, charge controller, circuit breaker, deep-
cycle battery and light bulbs, sockets, switches and wire. (see Fig. 1.1)
The solar panel converts solar energy into electricity and charges the battery. This charging is controlled by a
device called a charge controller. The charge controller has two principal functions, it prevents overcharging of
the battery and it prevents the battery from discharging through the solar panel at night. The battery is necessary
because it stores electricity for the times when there is not sufficient sunlight or not any sunlight at all.
2 CONOCIMIENTOS BSICOS DE LOS PANELES SOLARES
2 SOLAR PANEL BASICS
Un panel solar fotovoltaico es un mecanismo para convertir energa del sol a electricidad. La electricidad
producida es corriente directa (CD) para cargar bateras, este es diferente de corriente alterna (CA), electricidad
normalmente usada en casas.
Los paneles solares consisten en una capa de silicn, celdas solares conectadas para tener un voltaje deseado
(V) y corriente (A). Por lo comn, los paneles solares son usados para cargar bateras de 12V, por lo tanto son
A photovoltaic solar panel is a device used to convert energy from the sun into electricity. The electricity
produced is direct current (DC) electricity to charge batteries, as opposed to alternating current (AC), the type of
electricity commonly used in homes.
These solar panels consist of a string of silicon solar cells connected to create a desired voltage (V) and current
(A). Solar panels are commonly used to charge 12V batteries therefore they are designed to produce more
Batera (Battery)
Controlador (Controller)
Panel Solar (Solar Panel)
Breaker (Circuit Breaker)
Lmpara (Light bulb)
| Pgina 3 de 17 |
diseados para producir ms de 12V, normalmente 18V. Cada celda puede producir alrededor de 0.5V no
importa el rea de la superficie, la corriente cambia con el rea de la superficie. Por ejemplo, si usted rompe una
celda de 0.5 V, 3A en dos partes iguales, tiene dos celdas de 0.5 V, 1.5A.
Para obtener 18 V, 36 celdas son conectadas en serie. (ver Fig. 2.1) La diferencia entre un panel de 20W y un
panel de 100 W es el tamao de las celdas. Ambos tienen las 36 celdas requeridas pero las celdas ms
grandes producen ms corriente y ms potencia.
than 12V, usually about 18V to allow charging. Each cell produces about 0.5V no matter the surface area, the
current changes with surface area. For example, if you break one 0.5V, 3A cell in half you will have two 0.5V,
1.5A cells.
To get the desired 18V, 36 cells are connected in series. (see Fig 2.1) The difference between a 20W panel and
a 100W panel is the size of the cells. They both contain the required 36 cells to produce 18 volts but larger cells
produce more current and more power.
Fig. 2.1: (a) Seis celdas en series. (b) Treinta y seis celdas en series.
Fig. 2.1: (a) Six cells in series. (b) Thirty-six cells in series.
3 CONSTRUCCIN DE UN PANEL SOLAR
3 CONSTRUCTION OF A SOLAR PANEL
Tabla 3.1: Herramientas
Table 3.1: Tools
Herramientas
Tools
Cautn
Taladro
Brocas (3/16", 5/32")
Cortador de Aluminio, mano o elctrico
Lima
Soldering Iron
Drill
Drill Bits (3/16", 5/32")
Manual or electric saw for Aluminum
File
(a)
(b)
| Pgina 4 de 17 |
Escuadra
Remachadora
Cinta Mtrica
Lpiz
Marcadores
Navaja
Pistola
Square
Rivet gun
Tape Measure
Pencil
Marker
Knife
Silicone gun
4 MATERIALES
4 MATERIALS
Muchos de los materiales pueden ser comprados en ferreteras en todo el mundo. Los materiales problemticos
son el Sylgard 184 silicone, cinta metlica y celdas solares. En Nicaragua, importamos estos materiales desde
los Estados Unidos. La cinta y el silicn son fciles de obtener pero ahora hay un dficit de celdas solares en el
mundo. Tambin, nosotros tratamos de conseguir "segundas" porque son mas baratas pero es ms difcil de
obtener sistemas de calidad.
La tabla siguiente tiene los materiales requeridos para un panel de 75 W.
Most of the required materials can be purchased in a small town hardware store almost everywhere in the world.
The problematic materials are the Sylgard 184 silicone, ribbon and solar cells. In Nicaragua, we import these
materials from the United States. The ribbon and silicone are readily available for import but at the time of writing
there was a world shortage of solar cells. On top of the shortage we try and get "seconds" since they are
cheaper making the task that much more difficult.
The following table has the materials required for a 75W panel.
Tabla 4.1: Materiales
Table 4.1: Materials
Materiales
Materials
Medida/Size
Cant./Qty.
Marco:
Aluminio lateral
Aluminio angular
Remaches
Vidrio
Celdas solares
Silicn (Arbo 1200)
Silicn (Sylgard 184)
Conductor elctrico
Cinta metlica
Aluminio angular pesado Lona plstica
Caja electrnica (Plexo)
Estao
Papel bon*
3/4" poroplas
Frame:
Aluminum framing
Aluminum angle
Pop rivets
Glass
Solar cells
Silicone (Arbo 1200)
Silicone (Sylgard 184)
Wire
Metal ribbon
Angle aluminum
Plastic canvas
Electrical box
Soldier
White paper*
3/4" foam
1" x 1"
1.5" x 1.5"
5/32" x 1/2"
4mm
3.5 Amp
Tubo/Tube
Tub
#18
2mm
3/4"
600x1300mm
80x80x40mm
0.8mm
560x1200mm
560x1200mm
3800mm
100mm
16
500x1040mm
36
de tubo/tube
500ml
200mm
8000mm
3600mm
1
1
1
1
* - Required for constructing panels with fragile cells, i.e. with Evergreen Solar Cells.
5 CONSEJOS TILES
5 USEFUL TIPS
Para Soldar
Soldering
Limpiar la punta del cautn regulada. Usar una herramienta de metal para limpiar el carbn,
Make sure that the soldering iron has a clean tip. You can use a file to clean off carbon
| Pgina 5 de 17 |
poner la punta en pasta de soldar y limpiar la pasta en un trapo/esponja mojada/peridico.
deposits and then dip the iron in soldering paste and wipe the paste off with a rag/wet sponge/newspaper.
Haciendo "Cinta Doble"
Making "Double Ribbon"
Para conectar dos filas de celdas se necesita usar dos trozos de cinta, como cuando se conectan dos celdas.
Para hacer esto, poner dos trozos de cinta al lado de la otra y soldarla de un extremo a otro.
To connect rows of cells you need to use two pieces of ribbon, just like you do when you connect individual cells.
To make this, lie two pieces of ribbon beside each other and apply soldier all along the length of the strips to
connect them.
Probando Paneles
Testing Panels
Necesita probar los paneles a ver si producen la corriente apropiada y voltaje. Trae el panel afuera y ponerlo en
el sol. La produccin de corriente y voltaje depende del ngulo del sol, la distancia y las condiciones climticas.
Las celdas solares de silicn producen de 0.5 0.65 (circuito-abierto) voltios y la corriente depende del tamao
de la celda. Las celdas de Evergreen tienen un rea de 15 cm x 8 cm y su produccin es de 3.5 4.5 A.
Entonces un panel con 36 de estas celdas produce mas o menos 4 A (circuito-bajo) y 20 V (circuito-abierto). La
potencia mxima que produce el panel no es 80 W (4 A x 20 V),es un poco menos porque a la corriente circuito-
bajo el voltaje es cero y al voltaje circuito-abierto, la corriente es cero. Ver la grfica en la figura 5.1.
Usa un multmetro a probar la corriente y voltaje que produce. Si su resultado no cae entre los requerimientos
especficos, necesita investigar cul es el problema. Debe de probar cada fila y despus cada celda, si en
algunas de las filas no nos da la cantidad que percibimos necesitamos encontrar las fallas. Los problemas
comunes son celdas rotas y conexiones mal soldadas por el fabricante.
In testing panels you want to make sure that the cells are producing proper current and voltage. Bring the panel
outside and face it toward the sun. The output will depend on the angle that the panel is with the sun, the height
of the sun and the amount of clouds. All silicon cells should produce between 0.5 and 0.65 (open circuit) volts
and the current depends on the size of the cell. Our 15 cm x 8 cm Evergreen cells produce about 3.5 4.5 (short
circuit) Amps. Therefore a panel with 36 of these cells in series will produce about 4 (short circuit) Amps and 20
V (open circuit). The maximum power produced by the panel will not be 80W (4 A x 20 V) though, the maximum
is slightly less than this because at the short-circuit current the voltage is zero and at the open-circuit voltage the
current is zero. See the graph in Figure 5.1.
Using a multimeter check the current and voltage produced. If your results do not fall within the specified
requirements you must find where the problem lies. You should check each row of cells to find the bad row first
then each cell in that row. Common problems are cracked cells and bad solder connections.
| Pgina 6 de 17 |
Fig. 5.1: Relacin Corriente-Voltaje con celdas solar de silicn.
Fig. 5.1: Current-Voltage relationship with silicone solar cells. (Practical Photovoltaics)
6 INSTRUCCIONES PARA
CONSTRUIR UN PANEL
SOLAR
6 INSTRUCTIONS FOR
CONSTRUCTING A SOLAR
PANEL
Para construir el Marco Constructing the Frame
1) Poner las celdas encima de una mesa para
determinar las dimensiones del vidrio.
Necesita 2-5mm entre las celdas y 2cm
alrededor del exterior. Usando estas
dimensiones, puede construir el marco. Cortar
las cuatro piezas de aluminio con ngulos de
45. Es ms fcil de cortar estos ngulos con
un cortador elctrico. Nuestras piezas son de
560mm y 1105mm. Cortar cuatro piezas de
1.5" ngulo aproximadamente 100 mm de
largo para meterlo dentro del marco. (ver Fig.
6.1)
1) Lay the cells out on a table to determine the
required dimensions of glass. You should have
about 2-5 mm between cells and an extra
about 2 cm around the perimeter. Based on
the dimensions of the glass you can construct
the frame. Cut the four pieces of Aluminum at
45 angles. A chop saw makes this task much
easier. Our pieces are 560 and 1105mm long.
Cut four more pieces of 1.5" angle about
100mm long to snugly fit into the frame. (see
Fig. 6.1)
VCA (VOC) V, Voltaje (Voltage)
Grupo Fenix
Universidad Nacional de Ingeniera (UNI),
Managua, Nicaragua, www.grupofenix.org
Manual para la Construccin de Paneles Solar Panel Construction Manual
Corriente (Current), I
Pmax = Imax x Vmax
Corriente Circuito-Bajo
(Short-Circuit Current)
Grupo Fenix
Universidad Nacional de Ingeniera (UNI),
Managua, Nicaragua, www.grupofenix.org
Manual para la Construccin de Paneles Solares
Solar Panel Construction Manual
Aaron Smith
smithaaronr@hotmail.com
Voluntario a Grupo Fenix, Noviembre 2005 Marzo 2006
Ponto Potencia Mxima
(Maximum Power Point)
Voltaje Circuito-Abierto
(Open-Circuit Voltage)
Grupo Fenix
Universidad Nacional de Ingeniera Managua, Nicaragua, www.grupofenix.Manual para la
Construccin de Paneles Solar Panel Construction Manual
ISC
(ISC)
Grupo Fenix
Universidad Nacional de Ingeniera (UNI),
Managua, Nicaragua, www.grupofenix.org
Manual para la Construccin de Paneles Solares
Solar Panel Construction Manual
Aaron Smith
smithaaronr@hotmail.com
Voluntario a Grupo Fenix, Noviembre 2005 Marzo 2006
| Pgina 7 de 17 |
Fig. 6.1: Materiales para el marco.
Fig. 6.1: Frame materials.
2) Cheque los ngulos con una escuadra y lima si es necesario. (ver Fig. 6.2)
2) Use a square to check the angles and file the edges as needed. (see Fig. 6.2)
Fig. 6.2: Cheque el ngulo de 45
Fig. 6.2: Check the 45 angle.
3) Usar una pieza de madera dentro del ngulo del marco y taladrar dos hoyos de 5/32" en el marco y el ngulo.
(ver Fig. 6.3)
3) Use a piece of wood to wedge the angle into the frame and drill two 5/32" holes through the frame and the
angle. (see Fig. 6.3)
| Pgina 8 de 17 |
Fig. 6.3: Use madera para sujetar el ngulo dentro de el marco.
Fig. 6.3: Use a piece of wood to hold the angle in place inside the frame.
4) Remache el ngulo dentro del marco. (ver Fig. 6.4)
4) Rivet the angle to the frame. (see Fig. 6.4)
Fig. 6.4: Remache la esquinas del marco.
Fig. 6.4: Rivet the corners of the frame.
5) Use la madera para taladrar ms agujero en el otro lado de la esquina. Remache por completo la esquina.
(ver Fig. 6.5)
5) Use the piece of wood again to drill holes through the frame in the other side of the corner. Remove the wood
and rivet the angle to the frame to complete the corner. (see Fig 6.5)
| Pgina 9 de 17 |
Fig. 6.5: Esquina completa.
Fig. 6.5: Completed corner.
7) Repetir pasos 11 y 12 para las otra tres esquinas.
6) Repeat Steps 11 and 12 for the other three corners.
Hay dos formas de encapsular las celdas solares. Si las celdas son muy frgiles, poner las celdas con la cara
hacia arriba o sea la parte negativa y echar el silicones encima y despus poner el vidrio encima de las celdas.
Si las celdas son mas fuertes puede echar el silicn encima del vidrio ya en el marco de aluminio y luego poner
las celdas dentro del silicn con la parte negativa hacia abajo contra el vidrio.
There are two ways of encapsulating the solar cells. If the cells are very fragile, it is better to lie the cells face up
and pour the silicone on top then lie the glass overtop of that. Otherwise, with more durable cells you can pour
the silicone on the glass and push the cells into the silicone face down.
Para encapsular Celdas Frgiles (Evergreen)
Encapsulating Fragile (Evergreen) Cells
1) La primera cosa es soldar las celdas juntas. Normalmente, las celdas se colocan en 3 filas de 12 celdas o 4
filas de 9. Si no hay cinta metlica en el frente de las celdas (lado azl), necesita soldar la cinta all primero y
limpiar cerca de la unin. Poner las celdas cara abajo y soldar la superficie de la capa de una al fondo de la
siguiente. (ver Fig. 6.6)
NOTA: Necesita poner otra pareja de cinta en los extremos de las filas.
1) The first step is to soldier the cells together. The cells are usually orientated in 3 rows of 12 or 4 rows of 9. If
there is no metallic ribbon on the front (blue side) of the cells, ribbon should be soldiered on here first and then
the area can be cleaned around the joint. Next lie the cells face down and soldier the top of one cell to the
bottom the next. (see Fig. 6.6)
NOTE: You need to add on an extra pair of ribbon on the ends of each row.
| Pgina 10 de 17 |
Fig. 6.6: Soldar la superficie de la capa de una al fondo de la siguiente.
Fig. 6.6: Solder the bottom of one to the top of the next.
2) Poner una hoja de papel grande encima del poroplas. Poner las cadenas de las celdas cara arriba encima de
la hoja de papel. (ver Fig. 6.7)
2) Lie a large sheet of white paper on top of 3/4" foam. Lie the long rows of cells face up on top of the sheet of
paper. (see Fig. 6.7)
Fig. 6.7: Poner las celdas encima del papel.
Fig. 6.7: Lay the cells on the paper.
3) Conectar las cadenas para hacer una sola serie de 36 celdas. Necesita soldar dos pedazos de cintas juntas
porque hay dos pedazos de cinta para cada celda. (ver Fig. 6.8)
NOTA: Recuerda conectar la superficie de una celda al fondo de la siguiente.
3) Connect the three or four rows of cells to make one long string of 36 cells. You need to soldier two strips of
ribbon together as you are connecting two pieces of ribbon from each cell. (see Fig. 6.8)
NOTE: Make sure that you connect the cells on the ends of the rows top to bottom like the rest of the cells.
| Pgina 11 de 17 |
Fig. 6.8: Conectar las filas para hacer una serie de 36 celdas.
Fig. 6.8: Connect the rows of cells to make a string of 36 cells.
4) Empujar las cintas entre los extremos del papel (una pareja de positivo y negativo).
4) Poke the free ends (a pair of positive, a pair of negative) through the paper.
5) Mezcla aproximadamente 250 ml de Sylguard 184 silicn. Mezclar con catalizador hasta agitarlo lo ms
posible Echar media cucharada encima de cada celda. (ver Fig. 6.9) Esperar una hora aproximadamente para
que el silicn cubra todas las celdas y el papel. Echar ms silicones alrededor de las celdas si necesita.
5) Mix about 250 ml of Slygard 184 silicone. Stir the mixture until white bubbles forming the liquid. Pour about
half a spoonful of silicone on each cell. (see Fig 6.9) Allow about an hour for the silicone to spread out and cover
the whole surface of the cells. Add more silicone if needed to the outside edges of the cells of the white paper
between the cells.
Fig. 6.9: Echar media cucharada de silicn encima de cada celda.
Fig. 6.9: Pour about half a spoonful of silicone on each cell.
6) Poner la hoja de vidrio encima de las celdas. Esperar aproximadamente hora para que el silicn se seque.
Empujar hacia abajo el vidrio para mover las burbujas hacia fuera y a la orilla
6) Lie the sheet of glass on top of the cells. Wait about hour for the silicone to dry more. Push down on the
glass with your hands to try and move the bubbles from on top of the cells
| Pgina 12 de 17 |
del vidrio. Poner poroplas encima del vidrio y poner peso encima del poroplas, i.e. dos bateras de 50 lb.
Esperar 6-8 horas y cortar papel adicional. (ver Fig. 6.10)
to the outside of the glass. Lie more foam on top of the glass and some weight on top of the foam, i.e. two 50 lb.
batteries. Wait about 6-8 hours then cut off excess paper. (See Fig. 6.10)
Fig. 6.10: Poner peso encima del vidrio y poroplas
Fig. 6.10: Put weight on top of the glass and foam.
13) Poner el silicn de tubo alrededor del borde dentro del marco. (ver Fig. 6.11)
13) Put silicone around the inside lip of the frame to form a seal between the glass and frame. (see Fig. 6.11)
Fig. 6.11: Poner el silicn alrededor del borde adentro del marco.
Fig. 6.11: Put silicone around the inside lip of the frame.
14) Poner el vidrio en el marco y poner presin en los bordes del vidrio.
14) Lie the glass into the frame applying a bit of pressure to the glass around the edges.
15) Continuar "Completando el Panel".
15) Continue at "Completing the Panel".
| Pgina 13 de 17 |
Encapsulando Otras celdas (Astropower)
Encapsulating other (Astropower) Cells
1) El primer paso es soldar las celdas juntas. Normalmente, las celdas son colocadas en 3 filas de 12 celdas o 4
filas de 9. Si no hay cinta metlica en el frente de las celdas (lado azul), necesita soldar la cinta all
primeramente y limpiar cerca de la unin. Poner las celdas cara abajo y soldar la superficie de la capa de una al
fondo de la siguiente. (ver Fig. 6.12)
NOTA: Necesita a poner otra pareja de cinta en los extremos de las filas.
1) The first step is to soldier the cells together. The cells are usually orientated in 3 rows of 12 or 4 rows of 9. If
there is no metallic ribbon on the front (blue side) of the cells, ribbon should be soldiered on here first and then
the area can be cleaned around the joint. Next lie the cells face down and soldier ribbon from the top of one to
the bottom of the next. (see Fig. 6.12)
NOTE: You need to add on an extra pair of ribbon on the ends of each row.
Fig. 6.12: Soldar la superficie de la capa de una al fondo de la siguiente.
Fig. 6.12: Solder the bottom of one to the top of the next.
2) Poner silicn alrededor del borde, dentro del marco. (ver Fig. 6.11)
2) Put silicone around the inside lip of the frame. (see Fig. 6.11)
Fig. 6.13
| Pgina 14 de 17 |
3) Poner el vidrio encima del marco y poner presin en los extremos del vidrio.
3) Lie the glass into the frame applying a bit of pressure to the glass around the edges.
4) Mezclar aproximadamente 250 ml de Sylguard 184 silicn lquido con catalizador y agitarlo lo ms posible.
Echar media cucharada encima de cada celda. (ver Fig. 6.9) Esperar una hora para que el silicn cubra todas
las celdas y el papel. Echar ms silicn alrededor de las celdas si necesita.
4) Mix about 250 ml of Slygard 184 silicone. Stir the mixture until white bubbles forming the liquid. Pour the
silicone evenly overtop of the glass. Allow about an hour for the silicone to spread out and cover the whole
surface of the glass. Add more silicone if needed to the outside edges of the glass.
5) Poner las filas de celdas una por una encima del silicn. (ver Fig. 6.14)
NOTA: Dejar la cinta de los extremos fuera del silicn.
5) Lie the rows of cells, one at a time on top of the silicone. (see Fig. 6.14)
NOTE: Leave the ribbon at each end of the rows up out of the silicone.
Fig. 6.14: Poner las filas de celdas una por una encima del silicn.
Fig. 6.14: Lie the cells, one row at a time on the silicone.
7) Suavemente empujar las celdas para abajo para quitar las burbujas. Mezclar ms silicn (tal vez 100 ml) para
tapar las celdas. Esperar de 6 a 8 horas hasta que el silicn se seque.
6) Gently push down on the cells to try and remove bubbles from underneath. Mix up more silicone (maybe
about 100ml) to cover the tops of the cells. Allow the silicone to dry for about 6-8 hours.
7) Soldar las filas junto con las "cintas dobles" as se forma una cuerda de 36 celdas. (ver Fig. 6.15)
7) Solder rows together with "double ribbon" so that you get one long string of 36 cells. (see Fig. 6.15)
| Pgina 15 de 17 |
Fig. 6.15: Soldar las filas juntas con las "cintas dobles".
Fig. 6.15: Solder rows together with "double ribbon".
Completando el Panel
Completing the Panel
1) Si tiene un nmero impar de filas, necesita poner un alambre de un extremo al otro, as tiene el positivo y
negativo en un extremo.
1) If you have an odd number of rows you are going to have to run a wire along the whole length of the panel so
that the positive and negative can exit the panel at the same location.
2) Ahora necesita probar el panel. Ver la seccin probando paneles.
2) The panel can now be tested before the back is sealed up. See the section on testing panels.
3) Poner silicn (tubo de RTV) en todo el espaldar del panel. Untar el silicn con sus dedos en todo el panel.
3) Apply silicone (RTV tube) to the back of the cells and spread it out with your fingers to have a thin coating
over the whole surface.
4) Poner el plstico blanco encima del silicn.
4) Lie the white plastic over the silicone.
5) Cortar ngulo 3/4" para alcanzar dentro del marco y taladrar un agujero en el ngulo donde sale el alambre
del panel. (ver fig. 6.16)
5) Cut the " angle to fit the insides of the frame and drill a hole in the angle where the wire exits the panel. (see
fig. 6.16)
| Pgina 16 de 17 |
Fig. 6.16
Fig. 6.16
6) Taladrar agujeros 5/32" en el ngulo y el marco. Remachar el ngulo del marco para sujetar el vidrio.
6) Drill 5/32" holes through the angle and frame. Pop rivet the angle to the frame to hold the glass in place.
7) Poner silicn en la parte trasera de la caja elctrica y ponerla en la parte trasera del panel donde sale el
alambre.
7) Apply silicone to the bottom of the electrical box and stick it to the back of the panel where the wire exits.
8) El panel est terminado! pero debera de probar el panel una vez ms antes de la instalacin.
8) The panel is complete! but you should test the panel once again before installation.
7 GLOSARIO
7 GLOSSARY
Corriente Alterna, CA
Alternating Current, AC
Electricidad que retrocede su direccin de flujo.
Este tipo de electricidad es normalmente usado en casa.
Electrical current that reverses its direction of flow. This type of electricity is normally used in homes.
Ampere, Amp., A
Ampere, Amp., A
La unidad usada para medir corriente.
The unit used to measure current.
Corriente Directa, CD
Direct Current, DC
El tipo de electricidad que es producida por celdas solares y es almacenada en bateras.
The type of electricity that solar cells produce and is stored in batteries.
Inversor
Inverter
Un mecanismo para convertir DC a AC.
A device used to convert DC electricity into AC electricity.
Circuito Abierto Voltaje
Open Circuit Voltage, VOC
Es el voltaje producido cuando el circuito est abierto, cuando no hay conexin en la batera con el panel
The voltage produced when the circuit is open, i.e. when there is no load (battery) attached to the panel.
| Pgina 17 de 17 |
Paralelo
Parallel
Es una forma de conectar una celda para obtener ms corriente y manteniendo el mismo voltaje. Es igual con
las batera cuando estn conectadas en paralelo aumentan la capacidad de almacenaje mientras mantiene el
mismo voltaje.
A way of connecting cells so that you produce a higher current while keeping the same voltage. The back of one
is connected to the back of the next. Batteries are connected in parallel to increase storage capacity while
keeping the same voltage.
Potencia, P
Power, P
Es la energa producida a travs de un perodo de tiempo.
La potencia est calculada multiplicando la corriente por el voltaje ,P=IV
The energy produced over a period of time. Power is calculated by multiplying the current by the voltage, P=IV.
Serie
Series
Es una forma de conectar la celda para aumentar voltaje mientras se mantiene la corriente estable.
Estn interconectada de negativo a positivo hasta conseguir el voltaje que queremos.
A way of connecting cells so that you increase the voltage while keeping the current constant. The top of one
cell is connected to the bottom of the next.
Circuito Bajo Corriente
Short Circuit Current, ISC
Es la mxima cantidad de corriente que puede ser producida por la celda segn su eficiencia.
The maximum amount of current that can be produced by the cell(s).
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Calculo de Energia de Un AerogeneradorDokumen5 halamanCalculo de Energia de Un AerogeneradorBony Diazg100% (2)
- TemarioDokumen4 halamanTemarioAndrés MorenoBelum ada peringkat
- Ejer Cici OsDokumen13 halamanEjer Cici OsJairo Aguilar Romero100% (1)
- Calculo Mecanico de Tuberia EnterradaDokumen1 halamanCalculo Mecanico de Tuberia EnterradatraokenBelum ada peringkat
- Sistema de Tierras RackDokumen2 halamanSistema de Tierras RacktraokenBelum ada peringkat
- Calculo Mecanico de Tuberia EnterradaDokumen1 halamanCalculo Mecanico de Tuberia EnterradatraokenBelum ada peringkat
- Diseño Soldaduras AWSDokumen9 halamanDiseño Soldaduras AWSVictor TitoBelum ada peringkat
- CATALOGO FOSAS Vivian 2Dokumen14 halamanCATALOGO FOSAS Vivian 2traokenBelum ada peringkat
- Tuberia Conduit Embebida Generador G-7210Dokumen3 halamanTuberia Conduit Embebida Generador G-7210traokenBelum ada peringkat
- PDFDokumen25 halamanPDFLuis GutierrezBelum ada peringkat
- Etapas de Revision y EntregaDokumen5 halamanEtapas de Revision y EntregatraokenBelum ada peringkat
- Planeacion de Servicios y SoportesDokumen4 halamanPlaneacion de Servicios y SoportestraokenBelum ada peringkat
- Boletin Ventanas para DeptosDokumen1 halamanBoletin Ventanas para DeptostraokenBelum ada peringkat
- Programacion de La ConstruccionDokumen5 halamanProgramacion de La ConstrucciontraokenBelum ada peringkat
- Mayonesa y CaféDokumen1 halamanMayonesa y CaféMaru RiverosBelum ada peringkat
- Programacion de La ConstruccionDokumen5 halamanProgramacion de La ConstrucciontraokenBelum ada peringkat
- Manual de Construcción de Viviendas de MaderaDokumen102 halamanManual de Construcción de Viviendas de MaderaManuales de Interes94% (16)
- Numeros Parese ImparesDokumen1 halamanNumeros Parese ImparestraokenBelum ada peringkat
- Guia MiaDokumen8 halamanGuia MiatraokenBelum ada peringkat
- Manual de Crianza de PatosDokumen84 halamanManual de Crianza de Patosnoriegatrejoroy100% (4)
- Los Numeros Romanos Del 1 Al 1000Dokumen1 halamanLos Numeros Romanos Del 1 Al 1000traoken100% (1)
- Rutinas Diarias HorasDokumen1 halamanRutinas Diarias HorastraokenBelum ada peringkat
- Tarjetas de Segmentacion en Silabas 2 3 4 SílabasDokumen8 halamanTarjetas de Segmentacion en Silabas 2 3 4 SílabastraokenBelum ada peringkat
- Teoría Del Ultimo PlanificadorDokumen19 halamanTeoría Del Ultimo Planificadortraoken100% (1)
- Hoja Excel para El Cálculo Del Costo de Horas Hombre (Ing. Jorge Blanco)Dokumen17 halamanHoja Excel para El Cálculo Del Costo de Horas Hombre (Ing. Jorge Blanco)Angel Casilla ParedesBelum ada peringkat
- 100 Libros LaboratorioTI PDFDokumen123 halaman100 Libros LaboratorioTI PDFGUSTAVO100% (1)
- Analisis Planificacion Financiera EstrategicaDokumen40 halamanAnalisis Planificacion Financiera EstrategicatraokenBelum ada peringkat
- Ayudar A RazonarDokumen5 halamanAyudar A RazonartraokenBelum ada peringkat
- Cómo Crear UnDokumen18 halamanCómo Crear UntraokenBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Explicativo Ecotecnoligas InfonavitDokumen81 halamanManual Explicativo Ecotecnoligas InfonavittraokenBelum ada peringkat
- Clasificación de Suelos AASHTODokumen2 halamanClasificación de Suelos AASHTOtraokenBelum ada peringkat
- Balanced ScorecardDokumen6 halamanBalanced ScorecardtraokenBelum ada peringkat
- Diagtrama Del Pozo San RoqueDokumen1 halamanDiagtrama Del Pozo San RoquefernandoBelum ada peringkat
- Planos Planta BiodieselDokumen8 halamanPlanos Planta BiodieselAndy EscalanteBelum ada peringkat
- Conformidad FormatoDokumen4 halamanConformidad Formatoharold santtosBelum ada peringkat
- Conexión SteinmetzDokumen4 halamanConexión Steinmetzramos valdan murcielagoBelum ada peringkat
- Enunciados de Otros Ejercicios de Motores EléctricosDokumen1 halamanEnunciados de Otros Ejercicios de Motores EléctricoscolhonsBelum ada peringkat
- Actividad #1Dokumen4 halamanActividad #1NELSONBelum ada peringkat
- Ensayos en Transformadores MonofasicoDokumen5 halamanEnsayos en Transformadores MonofasicoJose Daza GuzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Norma de AcometidaDokumen7 halamanNorma de AcometidaAbisaiBelum ada peringkat
- Calculo y Selección ArrancadoresDokumen1 halamanCalculo y Selección ArrancadoresNatali AstudilloBelum ada peringkat
- Tema 5 S2 Interpretacion - Planos - EsquemasDokumen36 halamanTema 5 S2 Interpretacion - Planos - EsquemasViktor StarkBelum ada peringkat
- Electrólisis de AguaDokumen4 halamanElectrólisis de AguaEsperanza TvnBelum ada peringkat
- Terminado Lab 2Dokumen17 halamanTerminado Lab 2Andrés NogueraBelum ada peringkat
- Centrales Eléctricas de Honduras 2015Dokumen5 halamanCentrales Eléctricas de Honduras 2015Juan Fernando RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- Certificado de Instalacion. RITE MEMORIADokumen2 halamanCertificado de Instalacion. RITE MEMORIAnachoxxiBelum ada peringkat
- Capitulo 6 - Componentes Simetricas SEP 2016Dokumen44 halamanCapitulo 6 - Componentes Simetricas SEP 2016FelipeBarreraAlvarezBelum ada peringkat
- Potencia en Motores A.CDokumen12 halamanPotencia en Motores A.CEdisonWillisBelum ada peringkat
- CaratulaDokumen17 halamanCaratulaCarmen Rosa Huanca ApazaBelum ada peringkat
- Tarifas Energia Codensa Junio 2012Dokumen1 halamanTarifas Energia Codensa Junio 2012blogvillapinzonBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz 1 - Fisica ElectronicaDokumen3 halamanQuiz 1 - Fisica ElectronicamarielaecheverriaBelum ada peringkat
- Cocina SolarDokumen5 halamanCocina SolarHernan CharañaBelum ada peringkat
- Diagrama EdtDokumen3 halamanDiagrama EdtJose CuencaBelum ada peringkat
- Energia SolarDokumen33 halamanEnergia Solaribericadelcalor100% (5)
- El TransformadorDokumen2 halamanEl TransformadorMarcos Alexander Argueta mendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Semaforización Con Panel SolarDokumen6 halamanSemaforización Con Panel SolarAnonymous CRPY3d6Belum ada peringkat
- Calculo de AlimentadoresDokumen35 halamanCalculo de AlimentadoresJohn RangelBelum ada peringkat
- Manual T25S RDokumen21 halamanManual T25S RJorge Santiago MontielBelum ada peringkat
- Sem 17 EeidDokumen17 halamanSem 17 EeidVictors Palomino AsencioBelum ada peringkat