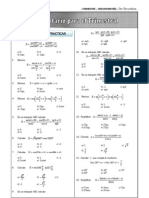
Formulario de Trigonometria
Diunggah oleh
tavito_12Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Formulario de Trigonometria
Diunggah oleh
tavito_12Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Prof. Julio C.
Cern Velsquez
37
53
3
5
4
45
45
1
1
2
30
60
1
2
3
30 60 45 37 53
1 3 2 3 4
sen
2 2 2 5 5
3 1 2 4 3
cos
2 2 2 5 5
3 3 4
tg 3 1
3 4 3
3 4 3
ctg 3 1
3 3 4
2 3 5 5
sec 2 2
3 4 3
2 3 5 5
csc 2 2
3 3 4
FORMULARIO DE TRIGONOMTRIA
TRIANGULOS NOTABLES
RAZONES TRIGONOMETRICAS DE
NGULOS NOTABLES
IDENTIDADES
TRIGONOMTRICAS
PITAGORICAS
x csc x ctg
x sec x tg
x cos x sen
2 2
2 2
2 2
1
1
1
= +
= +
= +
POR COCIENTE
RECPROCAS
senx.csc x 1
cos x. sec x 1
tgx.ctgx 1
=
=
=
1
csc x
senx
1
sec x
cos x
1
ctgx
tgx
=
=
=
IDENTIDADES AUXILIARES
IDENTIDADES PARA NGULOS
COMPUESTOS
senx.seny cosx.cosy = y) cos(x
cosx.seny senx.cosy = y) sen(x
tgy . tgx
tgy tgx
) y x ( tg
1
=
1
1
1
1
2 2
2 2
2 2
2 2
=
=
=
=
x ctg x csc
x tg x sec
x sen x cos
x cos x sen
x cos
senx
tgx =
senx
x cos
ctgx =
14
76
1
17
4
8
82
1
7
16
74
7
25
24
5 2
2 +1
17
28
62
8
17
15
1
31
59
3
5
17
45
2
31
75
53 37
15
5 4
1 1
2 3 6 +
2 2
10
2
6 - 2
127
2
153
2
Prof. Julio C. Cern Velsquez
IDENTIDADES AUXILIARES PARA COMPUESTOS
PROPIEDADES
1) asenxbcosx=
2 2
b a + .sen(xu) tal que:
y
2) x e R se cumple que:
-
2 2 2 2
b a bcosx asenx b a + s s +
(MINIMO) (MAXIMO)
IDENTIDADES AUXILIARES PARA TRES
ANGULOS
1) Si A + B + C = 180
Se cumple:
tgA+tgB+tgC = tgA.tgB.tgC
ctgA.ctgB+ctgA.ctgC+ctgB.ctgC=1
2) Si: A+B+C=90
Se cumple:
ctgA+ctgB+ctgC=ctgA.ctgB.ctgC
TgA.tgB+tgAtgC+tgB.tgC=1
IDENTIDADES PARA EL NGULO
DOBLE
sen2x=2senx.cosx
2 2
cos2x=cos x sen x
2
2tgx
tg2x=
1-tg x
Triangulo del ngulo doble
1 tg x
2
1
+
t
g
x
2
2 tg x
2x
sen2x=
1 + tg x
2
2tgx
cos2x=
1 + tg x
2
1 tg x
2
IDENTIDADES PARA EL NGULO
MITAD
AUXILIARES
Donde el signo depender del cuadrante en el que se
ubique
2
x
2 2
b a
b
sen
+
= u
2 2
b a
a
cos
+
= u
) y x ( tg y).tgx.tgy tg(x tgy tgx
seny . senx
) y x cos(
ctgy . ctgx
y cos . x cos
) y x cos(
tgy . tgx
seny . senx
) x y ( sen
ctgy ctgx
y cos . x cos
) y x ( sen
tgy tgx
y sen x cos y) - y).cos(x cos(x
y sen x sen y) - y).sen(x sen(x
=
=
= +
= +
1
1
2 2
2 2
2
2
cos2x=2cos x-1
cos2x=1 2sen x
2
x
tg = ctgx cscx
2
x
ctg = ctgx cscx
+
x cos
x cos
=
2
x
tg
x cos
=
2
x
cos
x cos
=
2
x
sen
+
1
1
2
1
2
1
AUXILIARES
2
2
2cos x 1 cos2x
2sen x 1-cos2x
ctgx tgx 2csc2x
ctgx tgx 2ctg2x
sec2x 1 tg2x.ctgx
sec2x 1 tg2x.tgx
= +
=
+ =
=
+ =
=
Prof. Julio C. Cern Velsquez
2 Senx Cosy = Sen(x + y) + Sen(x y)
2 Seny Cosx = Sen(x + y) Sen(x y)
2 Cosx Cosy = Cos(x + y) + Cos(x y)
2 Senx Seny = Cos(x y) Cos(x + y)
( )
( )
( )
nr
Sen
2
P U
Sen Sen( r) Sen( 2r) ..... Sen
2
r
Sen
n trminos
2
+
o + o + + o + + =
( )
( )
( )
nr
Sen
2
P U
Cos Cos ( r) Cos ( 2r) ..... Cos
2
r
Sen
n trminos
2
+
o + o + + o + + =
( ) ( ) ( )
3 5 1
Cos Cos Cos .... ntr minos
2n 1 2n 1 2n 1 2
t t t
+ + + =
+ + +
( ) ( ) ( )
2 4 6 1
Cos Cos Cos .... ntrminos
2n 1 2n 1 2n 1 2
t t t
+ + + =
+ + +
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
| +
=
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
| +
= +
|
.
|
\
| +
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
| +
= +
2
B A
en S
2
B A
Sen 2 CosA CosB
2
B A
Cos
2
B A
Cos 2 CosB CosA
2
B A
Cos
2
B A
Sen 2 SenB SenA
2
B A
Cos
2
B A
Sen 2 SenB SenA
IDENTIDADES PARA EL NGULO
TRIPLE
x 3tg - 1
x tg - 3tgx
= tg3x
3cosx - x 4cos = cos3x
x 4sen - 3senx = sen3x
2
3
3
3
AUXILIARES
TRANSFORMACIONES
TRIGONOMTRICAS
1. IDENTIDADES PARA LA SUMA Y PRODUCTO
DE SENOS Y/O COSENOS
CASO I : Para la suma o diferencia de dos Senos o Cosenos
a producto.
CASO II
Para el producto de dos trminos, Senos y/o Cosenos a suma
o diferencia.
Siendo : x > y
2. SERIES TRIGONOMETRICOS
Para la suma de Senos o Cosenos cuyos ngulos
estn en progresin aritmtica.
P : primer ngulo; U : ltimo ngulo
r = razn
3. SERIE ESPECIAL DE COSENOS
Propiedad
+
e Z n
Propiedad
+
e Z n
1 2cos2x
1 2cos2x
tgx = tg3x
1) x cosx(2cos2 = cos3x
1) x senx(2cos2 = sen3x
|
.
|
\
|
+
+
x tg ) x ( tg ) x ( tg tgx
x tg ) x ( tg ). x ( tg . tgx
x cos ) x cos( ). x cos( . x cos
x sen ) x ( sen ). x ( sen . senx
3 3 120 60
3 60 60
3 60 60 4
3 60 60 4
= + + + +
= +
= +
= +
Prof. Julio C. Cern Velsquez
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
A B
tg
2 a b
I. =
a + b A + B
tg
2
B C
tg
2 b c
II. =
b + c B + C
tg
2
A C
tg
2 a c
III. =
a + c A + C
tg
2
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
n
2n 1
2 3 n
Sen Sen Sen ....Sen
2n 1 2n 1 2n 1 2n 1
2
+
t t t t
=
+ + + +
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
n
2 3 n 1
Cos Cos Cos .... Cos
2n 1 2n 1 2n 1 2n 1
2
t t t t
=
+ + + +
A
A
C
C
B
B
b
a
c
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
2 3 n
Tg Tg Tg ... Tg 2n 1
2n 1 2n 1 2n 1 2n 1
t t t t
= +
+ + + +
2 2 2
2 2 2
2 2 2
a = b + c 2bc cos A
.......... (1)
b = a + c 2ac cos B .......... (2)
.......... (3) c = a + b 2ab cos C
a b c
= = = 2R
sen A sen B sen C
A C
B
b
A
a
c
2 2 2
b + c a
cos A =
2bc
A
B
O
C
c
a
b
R
a = 2R sen A
b = 2R sen B
c = 2R sen C
Tambin:
A
A
b cos A
c cos B
B
B
b
C
a
C
4. PRODUCTOS TRIGONOMETRICOS
RESOLUCION DE TRIANGULOS
OBLICUOS
1. TEOREMA DE SENOS
En todo tringulo ABC de circunradio R se verifica
(O: centro).
2. TEOREMA DE COSENOS
En todo tringulo ABC
Se cumple:
Si de (1) se despeja cos A obtenemos:
3. TEOREMA DE TANGENTES
Dado un tringulo ABC
Se cumple:
4. TEOREMA DE PROYECCIONES
Se cumple:
C = b cos A + c cos B
Tambien:
a = b cos C + c cos B
b = a cos C + c cos A
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Formulario2 111006101247 Phpapp01Dokumen4 halamanFormulario2 111006101247 Phpapp01Luisabel GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Trigonometria Semana 6,7,8,9,10,11,12Dokumen14 halamanTrigonometria Semana 6,7,8,9,10,11,12AndreeVillegasFarfan100% (1)
- Ángulo DobleDokumen9 halamanÁngulo Dobletavito_12Belum ada peringkat
- Semana 12Dokumen6 halamanSemana 12RODOLFO ANGEL CARRILLO VELASQUEZBelum ada peringkat
- Identidades Trigonometricas para El Angulo DobleDokumen9 halamanIdentidades Trigonometricas para El Angulo DobleRicardo BárcenaBelum ada peringkat
- Cap2 ResueltosDokumen14 halamanCap2 ResueltosOscar Salvador Soto ArenasBelum ada peringkat
- Cepuns 2013-II Semana 08Dokumen4 halamanCepuns 2013-II Semana 08boc_55Belum ada peringkat
- Solucionario Asignación de Identidades TrigonométricasDokumen12 halamanSolucionario Asignación de Identidades TrigonométricasCarlos Supo75% (8)
- Identidades Trigonométricas FundamentalesDokumen10 halamanIdentidades Trigonométricas Fundamentales5amv3l67% (3)
- 8 - Identidades Trigonométricas para Un Mismo ArcoDokumen10 halaman8 - Identidades Trigonométricas para Un Mismo ArcoPeter BBelum ada peringkat
- Semana 007raiDokumen4 halamanSemana 007raiJuan Aiquipa100% (1)
- Transformaciones TrigonométricasDokumen8 halamanTransformaciones Trigonométricastavito_12100% (1)
- Trigonometria PrepaDokumen9 halamanTrigonometria PrepaZOSIMO ZANABRIA OLARTEBelum ada peringkat
- 09 Identidades Trigonometricas de Angulos CompuestosDokumen9 halaman09 Identidades Trigonometricas de Angulos CompuestosOscar Pier Delgado PezoBelum ada peringkat
- IntegralDokumen30 halamanIntegralPedroanbu100% (1)
- Cepuns 2013-II Semana 10Dokumen4 halamanCepuns 2013-II Semana 10boc_55Belum ada peringkat
- Trigo.10 Ident. Trigon - Arc CompuestosDokumen4 halamanTrigo.10 Ident. Trigon - Arc CompuestosJulio César GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Cttrig5siii SRDokumen7 halamanCttrig5siii SRAnonymous 7za15o0Belum ada peringkat
- Formulario Productos NotablesDokumen5 halamanFormulario Productos NotablesHugo JhBelum ada peringkat
- Identidades Trigonométricas y Fórmulas Importantes en El Uso DelDokumen6 halamanIdentidades Trigonométricas y Fórmulas Importantes en El Uso DelAmIn20122Belum ada peringkat
- TRIGONOMETRIADokumen4 halamanTRIGONOMETRIAchristiancj34Belum ada peringkat
- Formula Rio en LaTexDokumen7 halamanFormula Rio en LaTexErikBelum ada peringkat
- Clase Práctica SolucionarioDokumen15 halamanClase Práctica SolucionarioAngélica VillavicencioBelum ada peringkat
- Todo Repaso74Dokumen2 halamanTodo Repaso74Miguel López TamargoBelum ada peringkat
- Cepuns 2013-II Semana 11Dokumen5 halamanCepuns 2013-II Semana 11boc_55Belum ada peringkat
- Secante, Cossecante e CotangenteDokumen5 halamanSecante, Cossecante e CotangenteMarcos Vinicius Oliveira RezendeBelum ada peringkat
- Cttrig5siii SRDokumen8 halamanCttrig5siii SRAdrian Sanchez0% (1)
- Formulario de Calculo IntegralDokumen3 halamanFormulario de Calculo Integralpiolin85Belum ada peringkat
- Formulario EDODokumen21 halamanFormulario EDOCok AlBelum ada peringkat
- Semana 10Dokumen5 halamanSemana 10Rodolfo Angel Carrillo VelasquezBelum ada peringkat
- Tarea 5 - Trigonometría - Vallejo BALOTARIODokumen2 halamanTarea 5 - Trigonometría - Vallejo BALOTARIO9100216606Belum ada peringkat
- Guia 4 TrigonometriaDokumen4 halamanGuia 4 TrigonometriamacarenaBelum ada peringkat
- Razones Trigonométricas de Ángulos CompuestosDokumen2 halamanRazones Trigonométricas de Ángulos Compuestoscarlos_kard032268889% (9)
- Ángulo DobleDokumen2 halamanÁngulo DobleCarlos SupoBelum ada peringkat
- Ecuaciones Trigonometricas PDFDokumen4 halamanEcuaciones Trigonometricas PDFJorge Abraham Trujillo FajardoBelum ada peringkat
- Taller de TrigonometriaDokumen9 halamanTaller de TrigonometriamillerBelum ada peringkat
- 2º Seminario de Trigonometría Preuniversitario-2013Dokumen11 halaman2º Seminario de Trigonometría Preuniversitario-2013Vane Taned100% (1)
- Cepuns 2013-II Semana 06Dokumen6 halamanCepuns 2013-II Semana 06boc_55Belum ada peringkat
- Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonometricasDokumen4 halamanPropiedades de Las Razones TrigonometricasAna Maria Atuncar Peña0% (1)
- Sintitul 2Dokumen22 halamanSintitul 2Lorraine JenkinsBelum ada peringkat
- La ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesDari EverandLa ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesBelum ada peringkat
- Métodos Matriciales para ingenieros con MATLABDari EverandMétodos Matriciales para ingenieros con MATLABPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Problemas resueltos de Hidráulica de CanalesDari EverandProblemas resueltos de Hidráulica de CanalesPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (7)
- Geometric modeling in computer: Aided geometric designDari EverandGeometric modeling in computer: Aided geometric designBelum ada peringkat
- Niñas rizadas: Patrón de amigurumi en ganchilloDari EverandNiñas rizadas: Patrón de amigurumi en ganchilloPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (6)
- Amiguitos Rechonchos, Patrón de Amigurumi a CrochetDari EverandAmiguitos Rechonchos, Patrón de Amigurumi a CrochetPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (2)
- Patrón de ganchillo Evie y Lilly, Muñecas con vestidosDari EverandPatrón de ganchillo Evie y Lilly, Muñecas con vestidosBelum ada peringkat
- Fisica Mru Mruv Teoria PracticaDokumen2 halamanFisica Mru Mruv Teoria PracticaRobin ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Sintitul 2Dokumen7 halamanSintitul 2tavito_12Belum ada peringkat
- Identidades Trigonometricas IIDokumen2 halamanIdentidades Trigonometricas IItavito_12100% (1)
- Preguntas PUCPDokumen5 halamanPreguntas PUCPtavito_12Belum ada peringkat
- Examen Talento Pucp - Preguntas de MatemDokumen9 halamanExamen Talento Pucp - Preguntas de MatemEdison SantiagoBelum ada peringkat
- 2º Seminario de Trigonometría Preuniversitario-2013Dokumen11 halaman2º Seminario de Trigonometría Preuniversitario-2013Vane Taned100% (1)
- Biologia Sem2 2010-IDokumen7 halamanBiologia Sem2 2010-Itavito_12Belum ada peringkat
- 29 HidrocarburosDokumen11 halaman29 Hidrocarburostavito_12Belum ada peringkat
- 2 Densidad y TemperaturaDokumen10 halaman2 Densidad y Temperaturatavito_12Belum ada peringkat
- 21 Masa y Gramo EquivalenteDokumen7 halaman21 Masa y Gramo Equivalentetavito_12Belum ada peringkat
- 6 Configuracion ElectronicaDokumen9 halaman6 Configuracion Electronicatavito_12Belum ada peringkat
- AritméticaDokumen156 halamanAritméticatavito_1250% (2)
- Ab1 2014 X 02Dokumen6 halamanAb1 2014 X 02Rosmeri Delgado GuerreroBelum ada peringkat