Pre-Anaesthetic Assessment For General Anaesthesia
Diunggah oleh
Haffie HafiziJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Pre-Anaesthetic Assessment For General Anaesthesia
Diunggah oleh
Haffie HafiziHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Pre-anaesthetic assessment for
general anaesthesia
If a patient has complex medical problems, a preoperative anaesthetic
assessment may be required as a separate consultation prior to the day of
surgery. The anaesthetist will particularly want to be aware of:
Behavioural issues, e.g. autism, developmental delay, extreme anxiety and needlephobia.
Syndromes, e.g. Down syndrome, velocardiofacial syndrome.
Cardiac disease, heart murmurs, previous surgery for congenital defects.
Respiratory disease, e.g. Asthma.
Airway problems, e.g. history of croup, cleft palate, micrognathia, previous tracheostomy,known history of
intubation difficulties, sleep apnoea.
Neurological disease, e.g. epilepsy, previous brain injuries, cerebral palsy.
Endocrine and metabolic disorders, e.g. diabetes, genetic metabolic disorders.
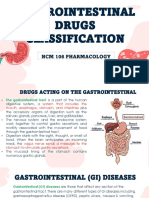
Gastrointestinal problems, e.g. reflux, difficulty swallowing or feeding.
Haematological, e.g. haemophilia, thrombocytopenia, haemoglobinopathies.
Neuromuscular disorders, e.g. muscular dystrophy.
Allergic Reactions
Latex allergy accounts for 19% of allergic
reaction in children and the most common
cause of intra-operative anaphylaxis
Medications
Most medications should be continued untilthe
time of anaesthesia unless there is a clear reason
to withhold (e.g. with anticoagulants or insulin).
Consultation with the primary physician should
be made before warfarin or aspirin is ceased to
make an assessment of the risk or benefit of
ceasing these drugs.
Management of diabetic patients will require
consultation with the patients endocrinologist.
Upper respiratory tract infection
It may be appropriate to delay elective anaesthesia for
23 weeks until the infection is treated.
The efficacy of GA will be lower in Patient with urti
However ,this decision can be balanced against
economic and social issues and patient factors such as
the childs age, urgency of treatment, severity of the
infection and any other medical problems the child
may have. Ultimately, the decision to cancel or proceed
is up to the anaesthetist.
Types of Adminstration of GA
Nitrous oxide
inhalation
Oral
induction
Rectal
induction
Intramuscular
induction
Intravenous
induction
Larry D. Trapp Techniques for Induction of General
Anesthesia in the Pediatric Dental Patient
Anesth Prog 39:138-141 1992
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Medical History TakingDokumen19 halamanMedical History TakingPHARMACY 2021100% (1)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesDari EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- Pre-Operative AssessmentDokumen62 halamanPre-Operative AssessmentRochelle BaileyBelum ada peringkat
- Preoperative PreparationsDokumen26 halamanPreoperative PreparationsReda IsmaeelBelum ada peringkat
- 1 PreoperativeDokumen67 halaman1 PreoperativeMoayad NawaflehBelum ada peringkat
- Epilepsy Presentation1Dokumen19 halamanEpilepsy Presentation1Daneshwari SahuBelum ada peringkat
- 2022 Preoperative Assessment Premedication Perioperative DocumentationDokumen38 halaman2022 Preoperative Assessment Premedication Perioperative DocumentationMohmmed Mousa100% (1)
- Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDokumen11 halamanSystemic Lupus Erythematosusneu_gluhenBelum ada peringkat
- NSBO22 General NotesDokumen72 halamanNSBO22 General Notesjunxicooper100% (1)
- PreoperativeDokumen34 halamanPreoperativeTasha NurfitrianiBelum ada peringkat
- Epilepsy GuidelinesDokumen8 halamanEpilepsy GuidelinesSivaraj Raman100% (1)
- Prescribing Guidelines For Geriatric PatientsDokumen17 halamanPrescribing Guidelines For Geriatric PatientsDrVinod Kumar Goud Vemula100% (1)
- PreOperative CareDokumen9 halamanPreOperative CareYana Pot100% (2)
- Patient History: Prof. Hoda ElguindyDokumen14 halamanPatient History: Prof. Hoda Elguindyyahia salah100% (1)
- Preoperative EvaluationDokumen4 halamanPreoperative EvaluationFadly Setiawirawan100% (1)
- Preoperative Evaluation and Considerations in ChildrenDokumen24 halamanPreoperative Evaluation and Considerations in ChildrenArshan AliBelum ada peringkat
- Preoperative Evaluation: Ian Magonigal, M.DDokumen49 halamanPreoperative Evaluation: Ian Magonigal, M.DGeeta KulkarniBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 42: Nursing Management: Upper Gastrointestinal ProblemsDokumen10 halamanChapter 42: Nursing Management: Upper Gastrointestinal ProblemsjefrocBelum ada peringkat
- Care of The Patient in The Perioperative PeriodDokumen20 halamanCare of The Patient in The Perioperative PeriodMohammed FaragBelum ada peringkat
- Preop - Evaluation and Risk AssessmentDokumen35 halamanPreop - Evaluation and Risk AssessmentReslan ReslanBelum ada peringkat
- Delirium in The Geriatric Patient: Risk Factors For DeliriumDokumen5 halamanDelirium in The Geriatric Patient: Risk Factors For DeliriumDenyBelum ada peringkat
- Criterii de Trimitere ImunologieDokumen7 halamanCriterii de Trimitere ImunologieRoxana HuțanuBelum ada peringkat
- Anaesthesia Clerkship HandbookDokumen12 halamanAnaesthesia Clerkship HandbookKay BristolBelum ada peringkat
- Preoperative & Postoperative EvaluationDokumen61 halamanPreoperative & Postoperative EvaluationSonntagsschule St. Antonius Kloster in KröffelbachBelum ada peringkat
- GIIIIDokumen1 halamanGIIIISamantha QuintoBelum ada peringkat
- Preoperative Nursing CareDokumen42 halamanPreoperative Nursing Careakoeljames8543Belum ada peringkat
- Preop Assess in AnesthesiaDokumen32 halamanPreop Assess in AnesthesiaEva PerdanaBelum ada peringkat
- Nausea in AdultsDokumen13 halamanNausea in AdultsSadaf N. HudaBelum ada peringkat
- Epilepsies in Children, Young People, and Adults: Summary of Updated NICE GuidanceDokumen13 halamanEpilepsies in Children, Young People, and Adults: Summary of Updated NICE GuidanceANDREWBelum ada peringkat
- Access To Special Care Dentistry, Part 5. Safety: A. Dougall and J. FiskeDokumen14 halamanAccess To Special Care Dentistry, Part 5. Safety: A. Dougall and J. FiskeMostafa FayadBelum ada peringkat
- Radiation TherapyDokumen48 halamanRadiation TherapyajhaytidongBelum ada peringkat
- Preoperative AssessmentDokumen17 halamanPreoperative AssessmentJun 27Belum ada peringkat
- Dental Treatment of Medical Compromised PatientsDokumen50 halamanDental Treatment of Medical Compromised PatientssrinivasBelum ada peringkat
- The Preoperative EvaluationDokumen25 halamanThe Preoperative Evaluationnormie littlemonsterBelum ada peringkat
- Preoperative PreparationDokumen53 halamanPreoperative PreparationBir Mohammad Sonet0% (1)
- Medically Compromised PatientsVoiceDokumen30 halamanMedically Compromised PatientsVoiceGeorge CharchBelum ada peringkat
- Preoperative PhaseDokumen13 halamanPreoperative PhaseNick RealinoBelum ada peringkat
- SS Hour - Pre-Operative Care - 1670891305Dokumen51 halamanSS Hour - Pre-Operative Care - 1670891305Pediatrics SLCM-WHQMBelum ada peringkat
- Cns الجديدةDokumen9 halamanCns الجديدةlyli Star AngeloBelum ada peringkat
- Preoperative and Postoperative Care of Surgical Patient ModifiedDokumen68 halamanPreoperative and Postoperative Care of Surgical Patient ModifiedJohn Wesley OmbogoBelum ada peringkat
- Preoperative Assessment and PremedicationDokumen10 halamanPreoperative Assessment and PremedicationHelene AlawamiBelum ada peringkat
- Managementofepilepticpat 170421211033Dokumen50 halamanManagementofepilepticpat 170421211033hassonamonaBelum ada peringkat
- Points MRCP 2Dokumen6 halamanPoints MRCP 2safi abroBelum ada peringkat
- Treating The Medically Compromised Patient - American Association of EndodontistsDokumen2 halamanTreating The Medically Compromised Patient - American Association of Endodontistsdent79Belum ada peringkat
- PREDNISONEDokumen4 halamanPREDNISONECay SevillaBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Patient NeedsDokumen15 halamanBasic Patient NeedsMarggie SalaoBelum ada peringkat
- Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryDokumen6 halamanOral and Maxillofacial Surgerysunaina chopraBelum ada peringkat
- Gastrointestinal DrugDokumen29 halamanGastrointestinal DrugJeneyse Ajap BalcenaBelum ada peringkat
- General Anesthesia in Neonates and Children - Agents and Techniques - UpToDateDokumen51 halamanGeneral Anesthesia in Neonates and Children - Agents and Techniques - UpToDateAnaid MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- AlzhemiersDokumen19 halamanAlzhemiersprembarnabasBelum ada peringkat
- Alzheimer'S DiseaseDokumen14 halamanAlzheimer'S DiseaseIrfan AuliaBelum ada peringkat
- CTC 72017Dokumen1.662 halamanCTC 72017Dilan GalaryBelum ada peringkat
- Diclofenacsandoztab AdjustmentDokumen14 halamanDiclofenacsandoztab AdjustmentShafira TamaraBelum ada peringkat
- Anxiolytics & AntidepressantsDokumen34 halamanAnxiolytics & AntidepressantsIconMaicoBelum ada peringkat
- Perioperative Care of A Pediatric Surgical PatientDokumen60 halamanPerioperative Care of A Pediatric Surgical Patienthabtsh habshaBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar On SEDokumen49 halamanSeminar On SEmubarak abdulkadirBelum ada peringkat
- Anaesthesia For Infants and ChildrenDokumen9 halamanAnaesthesia For Infants and Childrenapi-142637023Belum ada peringkat
- Vaishali Syal Moderator - Prof. J. R. ThakurDokumen34 halamanVaishali Syal Moderator - Prof. J. R. ThakurTasha NurfitrianiBelum ada peringkat
- Study Notes PediatricsDokumen64 halamanStudy Notes PediatricsSteam LcBelum ada peringkat
- Management of Ectopic TeethDokumen21 halamanManagement of Ectopic TeethHaffie HafiziBelum ada peringkat
- History of Composite Resin: Kenneth.J.Anusavice, 2009.phillips' Science of DentalDokumen3 halamanHistory of Composite Resin: Kenneth.J.Anusavice, 2009.phillips' Science of DentalHaffie HafiziBelum ada peringkat
- Late Lower Incisor CrowdingDokumen18 halamanLate Lower Incisor CrowdingHaffie HafiziBelum ada peringkat
- Addition Polymerisation of Dental MaterialDokumen17 halamanAddition Polymerisation of Dental MaterialHaffie HafiziBelum ada peringkat
- Anomalies DentinDokumen19 halamanAnomalies DentinHaffie HafiziBelum ada peringkat
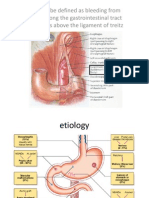
- Upper Gastrointestinal BleedingDokumen11 halamanUpper Gastrointestinal BleedingHaffie HafiziBelum ada peringkat
- PostOp Extraction InstructionDokumen2 halamanPostOp Extraction InstructionHaffie HafiziBelum ada peringkat