Mutation Note PDF
Diunggah oleh
iki292Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Mutation Note PDF
Diunggah oleh
iki292Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
http://matriculation-biology.blogspot.
com
MUTATION
(4 hour)
Retold by:
Amran Md Said,
Matriculation College of Pahang.
Obecti!e. At the end of thi" to#ic, "tudent" "hould be able to:
$%#lain mutation
Cla""ify mutation
"tate ty#e" of mutation
define mutagen
"tate ty#e" of mutagen
e%#lain gene&#oint mutation
cla""ify gene mutation
de"cribe ba"e "ub"titution a" #oint mutation eng. Sic'le cell anemia
e%#lain frame"hift mutation
de"cribe ba"e in"ertion a" a frame"hift mutation
de"cribe ba"e deletion a" a frame"hif mutation
e%#lain chromo"omal mutation
cla""ify chromo"omal mutation
e%#lain chromo"omal aberration ("tructural change")
"tate and de"cribe ty#e of chromo"omal aberration
e%#lain alteration of chromo"ome number
"tate the ty#e" of the alteration
e%#lain aneu#loidy
de"cribe the cau"e and the affect aneu#loidy
e%#lain auto"omal abnormalitie" and their effect"
e%#lain "e% chromo"omal abnormalitie"
e%#lain eu#loidy
e%#lain #oly#loidy
What is mutation?
A mutation i" a change in the amount, arrangement or "tructure of the ()A of an organi"m.
Mutation" #roduce "udden and di"tinct difference" bet*een indi!idual" cau"e alternation of
chromo"ome.
Alteration of chromo"ome number or "tructure cau"e "ome genetic di"order" "uch a" Sic'le Cell
Anemia and (o*n Syndrome
Mutation can occurring in gamete cell" or "omatic cell".
i) gamete cell"
are inherited, +t #a""ed to "ub"e,uent generation" a" #art of the hereditary endo*ment of the
game" deri!ed from that cell.
ii) "omatic cell"
can only be inherited by daughter cell" #roduced by mito"i".
http://matriculation-biology.blogspot.com
A mutant i" an indi!idual or ne* genetic character ari"ing or re"ulting from an in"tance of mutation the
blue lob"ter i" an e%am#le of a mutant.
-y#e of mutation
i) "#ontaneou" mutation
. Mi"ta'e" ha##en "#ontaneou"ly during ()A re#lication, re#air and recombination
. eg. nondi"unction
ii) induced mutation
. Organi"m e%#o"ed to mutagen
What is mutagen ?
a mutagen (/atin, literally origin of change) i" a #hy"ical or chemical agent that change" the genetic
material
O#erate either by cau"ing change" in the ()A of the gene" or by cau"ing chromo"ome damage
ty#e of mutagen
i) Phy"ical agent
0ltra!iolet ray
+oni1ing radiation (2.ray, gamma ray, al#ha #article", neutron and electron)
ii) Chemical agent
eg. Colchicine (u"ually to treat rheumatic com#laint", e"#ecially gout)
$thidium bromide (i" an intercalating agent commonly u"ed a" a fluore"cent tag in laboratorie" for
techni,ue" "uch a" agaro"e gel electro#hore"i")
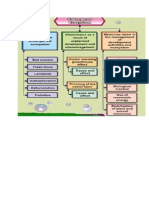
CLASSIFICATION OF MUTATION:
Cla""ify of mutation
i) gene & #oint mutation
ii) chromo"omal mutation
GENE MUTATION (POINT MUTATION) GENE MUTATION (POINT MUTATION)
Producing alteration" in the "e,uence of ()A nucleotide.
in!ol!e only one or a fe* ba"e #air in the coding "e,uence.
Ari"e due to "#ontaneou" #airing error" that occur during ()A re#lication,
Ari"e due to mutagen" li'e radiation or chemical" cau"e damage to the ()A.
A" a re"ult :
. Change the amino acid "e,uence and thu", change" the #rotein
. (ifferent #rotein #roduced a" the effect of mutation may not function a" normal
Cla""ify gene mutation
i) 3a"e "ub"titution
ii) 3a"e in"ertion
iii) 3a"e deletion
i!) 3a"e in!er"ion
mutation of ba"e deletion and in"ertion ma'e cau"e frame "hift mutation
Alteration of gene mutation cau"e "ome genetic di"order" "uch a" Sic'le Cell Anemia
Cassi!i"ation o! Gene Cassi!i"ation o! Gene mutation: mutation:
#ase su$stitution :
One or a fe* ba"e #air" in the nucleotide "e,uence" in gene" i" "ub"titute
Change" in ba"e "e,uence 4 re"ult" in change" of codon (0A0&050)
6 ba"e& nucleic acid 7 8 codon (coding for 8 amino acid)
Change" in codon:.
a) amino acid change" (mi""en"e mutation)
b) change" a codon to "to# codon (non"en"e mutation)
http://matriculation-biology.blogspot.com
Mi""en"e mutation" are tho"e that "till code for an amino acid but change the indicated amino acid eg.
Sic'le Cell Anemia.
)on"en"e mutation" c )on"en"e mutation" change an amino acid codon into a "to# codon, nearly al*ay" leading to a
nonfunctional #rotein.
Si"%e "e Anemia Si"%e "e Anemia
mutant 9b
"
cau"e defecti!e red blood cell. -he cell" are "ha#ed li'e a cre"cent or "ic'le
occur" more commonly in #eo#le region" *here malaria i" or *a" common. there i" a "ur!i!al !alue in
carrying only a "ingle "ic'le.cell gene -ho"e *ith only one of the t*o allele" of the "ic'le.cell di"ea"e are
more re"i"tant to malaria, "ince the infe"tation of the malaria #la"modium i" halted by the "ic'ling of the
cell" *hich it infe"t".
"ic'le "ha#e body #roduce" abnormally "ha#ed red blood cell".
9b
"
"tiff : tend to accumulate in "mall ca#illary, 9b i" not efficient of tran"#orting o%ygen
#oly#e#tide chain encode by different gen, cau"e differ one ba"e only
No&ma l Mutant
nucleotide - ba"e i" re#laced by A ba"e
()A chain C - - C A -
tran"cri#t
mR)A 5 A A 5 0 A
tran"lation
code of amino acid glutamic !aline
ty#e of #rotein 93 normal 93 S
A change in a "ingle nucleotide from - to A in the ()A tem#late lead" to an abnormal #rotein.
Amino acid !aline re#lace" glutamic acid at a "ingle #o"ition in the #rotein
#ase inse&tions
Addition of 8 or a fe* ba"e #air" in the nucleotide "e,uence" in gene"
mutation of ba"e in"ertion ma'e cau"e frame "hift mutation
http://matriculation-biology.blogspot.com
No&ma Mutant
additional nucleotide in"ertion *ith ba"e 5
()A chain A5A 5-C --C A5A 55- C--
tran"cri#t
mR)A 0C0 CA5 AA5 0C0 CCA 5AA
tran"lation
code of amino acid Ser 5ln /y" Ser Pro 5lu
frame."hift ha##en
#ase 'eetions
/o"" of 8 or a fe* ba"e #air" in the nucleotide "e,uence" in gene"
mutation of ba"e deletion ma'e cau"e frame "hift mutation
No&ma Mutant
lo"t of - ba"e during re#lication of ()A
()A chain A5A 5-C --C A5A 5C- -C5
tran"cri#t
mR)A 0C0 CA5 AA5 0C0 C5A A5C
tran"lation
code of amino acid Ser 5ln /y" Ser Arg Ser
frame."hift ha##en
#ase in(e&sion
; ba"e #air" or more are in!erted in nucleotide "e,uence
No&ma Mutant
in!erted in nucleotide "e,uence
()A chain A5A 5-C --C A5A -5C --C
tran"cri#t
mR)A 0C0 CA5 AA5 0C0 AC5 AA5
tran"lation
code of amino acid Ser 5ln /y" Ser -hr /y"
F&ame)shi!t Mutations F&ame)shi!t Mutations
+n!ol!e in"ertion&deletion of a ba"e #air or more into the nucleotide" "e,uence of ()A
Many of the"e deletion"&in"ertion "tart in the middle of a codon
Shifting the reading frame by one or t*o ba"e"
<rame "hift mutation" cau"e the gene to be read in the *rong three ba"e grou#" (codon)
<rom the mutation #oint,
+t abru#t the coding "e,uence of amino acid.
Change" in codon" re"ult" in change" in amino acid"
(ifferent #oly#e#tide i" #roduced
$ffect = u"ually harmful to human
$.g.: Maor -hala"emia (mutant homo1ygote allele")
http://matriculation-biology.blogspot.com
C9ROMOSOMA/ M0-A-+O)
(efinition: Abnormalitie" = in chromo"omal "tructure (chromo"ome aberration) : change" in
chromo"ome number (aneu#loidy & eu#loidy)
Chromo"omal mutation" ta'e #lace *hen the number of chromo"ome" change" or *hen "tructural
change" occur in the chromo"ome"
Cla""ification chromo"omal mutation
i) Chromo"omal aberration ("tructural of chromo"omal change)
ii) Chromo"omal number alteration
. Aneu#loidy
. $u#loidy (#oly#loidy)
Chromo"ome" aberration
Change" in the chromo"ome" "tructure, are mo"t fre,uently formed during mito"i" or meio"i"
Rearrangement a certain segment @ parts of chromosome
4 ty#e" of chromo"omal aberration
i) -ran"location
ii) (eletion ("egmental deletion)
iii) +n!er"ion
i!) (u#lication
Analogy of frame-shift mutation
one sentences
CAN YO !Y CA" #OR $%R &ON
after insertion only one alphabet ' A at CA" in the sentence'
CAN YO !Y ACA "#O R$% R&O N
(e can)t rea* that sentence
after *elete only one (or*' C at CA" in the sentence
CAN YO !Y A"# OR$ %R& ON
(e can)t rea* that sentence
+peringatan analogi ini untu, ,efahaman saha-a ianya ti*a, boleh *iguna,an *alam peperi,saan
http://matriculation-biology.blogspot.com
-ran"location
-ran"location : in!ol!e" a region of a chromo"ome brea'ing off and reoining either the other end of the "ame
chromo"ome or another non.homologou" chromo"ome
e.g. Robert"onian tran"location
Robert"onian tran"location in!ol!e" brea'" at the e%treme" end" of the "hort arm" of t*o
nonhomologou" chromo"ome" (86, 84, 8>, ;8 and ;;)
)amed after the American in"ect genetici"t ?.3.Robert"on
Al"o called *hole.arm tran"location or centric.fu"ion tran"location
(eletion
Deletion : the lost of 1 segment containing 1 or more genes
?hen the chromo"ome brea'" at t*o #lace" and lead to the lo"" of the middle "egment
-he "egment lo"t may contain one or more gene"
-he remaining end of chromo"ome *ill oin again and become "horten
5enetic di"ea"e: Cri du chat "yndrome (u"ually mentally retarded and crie" li'e a cat me*ing)
/o"" of a "mall #art of the "hort arm of chromo"ome >
Cri du chat i" a rare "yndrome (8 in >@,@@@ li!e birth") cau"ed by a deletion on the "hort arm of
chromo"ome >.
-he name of thi" "yndrome i" <rench for Acry of the cat,A referring to the di"tincti!e cry of children *ith
thi" di"order.
-he cry i" cau"ed by abnormal laryn% de!elo#ment, *hich become" normal *ithin a fe* *ee'" of birth.
+nfant" *ith cri du chat ha!e lo* birth *eight and may ha!e re"#iratory #roblem".
Some #eo#le *ith thi" di"order ha!e a "hortened life"#an, but mo"t ha!e a normal life e%#ectancy.
?here doe" the abnormal chromo"ome > come fromB +n C@ #ercent of the ca"e", the chromo"ome
carrying the deletion come" from the fatherD" "#erm.
http://matriculation-biology.blogspot.com
+n!er"ion
Inversion : a region of a chromosome breaks off and rotates through 180 before rejoining the
chromosome
(u#lication
Duplication : a region of a chromosome becomes duplicated; an additional set of genes exists
?hen a "ingle locu" or a large #iece of a chromo"ome i" #re"ent more than once in the genome
http://matriculation-biology.blogspot.com
Alteration of chromo"ome" number
-y#e of the alteration of chromo"omal number
i. aneu#loidy
ii. eu#loidy & #oly#loidy
9uman "omatic cell" containing a number of chromo"ome" *hich i" not a multi#le of ;6 are called
aneuploi*s
Aneu*oi'+
Aneu*oi'+ i" a condition in *hich the number of chromo"ome" i" abnormal due to e%tra or mi""ing
chromo"ome", in other *ord", it i" a chromo"omal "tate *here the number of chromo"ome" i" not a
multi#le of the ha#loid "et.
)ormal di#loid "#ecie" ha!e ;n chromo"ome", *here n i" the number in the ha#loid "et.
Aneu#loid indi!idual" *ould ha!e ;n.8 chromo"ome" (mono"omy), ;nE8 chromo"ome" (tri"omy), or
"ome other "uch arrangement.
A change in the number of chromo"ome" can lead to a chromo"omal di"order. Aneu#loidy i" common in
cancerou" cell".
Aneu#loidy occur" during cell di!i"ion *hen the chromo"ome" do not "e#arate #ro#erly bet*een the t*o
cell"
-y#e of aneu#loidy 5enome "ituation
Mono"omy ;n . 8
-ri"omy ;n E 8
-etra"omy ;n E ;
,is-un"tion: chromo"ome" "e#arated to the o##o"ite #ole" during meio"i"
Non 'is-un"tion : !ailure of #air of chromo"ome to "e#arate and to mo!e to the o##o"ite #ole"
both "et" of chromo"ome" #a"" to the "ame #ole of the cell
Cau"e of aneu#loidy
)ondi"unction in Ana#ha"e + : ++
http://matriculation-biology.blogspot.com
Non'is-un"tion in Ana*hase I an' II (meiosis)
9alf the daughter cell" #roduced ha!e an e%tra chromo"ome" (nE8) *hil"t the other half ha!e a
chromo"ome mi""ing (n.8)
<u"ion gamete" bet*een chromo"ome (nE8) and normal gamete (n), #roduced embryo *ith
chromo"ome (;nE8) : -ri"omyF eg. (o*nG" "yndrome
<u"ion gamete" bet*een chromo"ome (n.8) and normal gamete (n), #roduced embryo *ith
chromo"ome (;n.8) : Mono"omyF eg. -urner Syndrome
Auto"omal abnormalitie"
Mono"omy ;8
-ri"omy ;8 (do*n "yndrome)
Monosom+
http://matriculation-biology.blogspot.com
Monosom+ i" the #re"ence of only one chromo"ome from a #air in a cellD" nucleu".
Mono"omy in human !ery rare, the maority embryo" donDt be "ur!i!e, <or li!e infant re#orted in human,
the only of mono"omy 8;
Mono"omy ;8
-he "yndrome i" generally lethal and only "e!eral ca"e" of li!ing ne*born infant" ha!e been re#orted,
mo"t of *hom die bet*een 6 *ee'" and ;@ month" of life but "ome "ur!i!e into childhood.
Sym#tom":
. Short di"tance bet*een eye"
. /arge ear"
. Contracted mu"cle
. /arge no"e *ith a broad ba"e
. cleft li# and&or #alate
. Short nec'
. Short thora%
. Small hand" and feet, o!erla##ing and&or fle%ed finger" and toe",
. hy#eracti!e refle%e" (ner!ou" "y"tem)
-ri"omy
T&isom+ i" a #re"ence genetic abnormality in *hich there are three co#ie", in"tead of the normal t*o,
chromo"ome" of a #articular numbered ty#e in an organi"m
A tri"omy i" a ty#e of aneu#loidy (an abnormal number of chromo"ome")
.uman t&isom+ can occur *ith any chromo"ome. Mo"t tri"omie", li'e mo"t other abnormalitie" in
chromo"ome number, re"ult in di"tincti!e and "eriou" birth defect". Mo"t tri"omie" re"ult in "#ontaneou"
abortionF the mo"t common ty#e" that "ur!i!e to birth in human" are:
. -ri"omy ;8 ((o*n "yndrome)
. -ri"omy 8C ($d*ard" "yndrome)
. -ri"omy 86 (Patau "yndrome)
. -ri"omy H
. -ri"omy C (?ar'any "yndrome ;)
. -ri"omy 8I i" the mo"t common tri"omy in human", occurring in more than 8J of #regnancie". -hi"
condition, ho*e!er, u"ually re"ult" in "#ontaneou" mi"carriage in the fir"t trime"ter
http://matriculation-biology.blogspot.com
A t&isom+ i" the
-hu" the #re"ence of an e%tra chromo"ome ;8 i" called tri"omy ;8
Sym#tom" (o*n "yndrome & tri"omy ;8
Short "tature. A child often gro*" "lo*ly and, a" an adult, i" "horter than a!erage.
?ea' mu"cle" (hy#otonia) throughout the body. A child may "eem to ha!e le"" "trength than other
children of the "ame age.
A "hort, *ide nec' *ith e%ce"" fat and "'in. 0"ually, thi" trait i" le"" ob!iou" a" the child get" older.
Short, "toc'y arm" and leg". Some children al"o ha!e a *ide "#ace bet*een the big toe and "econd
toe.
Re"#iratory #roblem"
?here doe" the e%tra chromo"ome come fromB
+n H@J of -ri"omy ;8 ca"e", the additional chromo"ome come" from the motherD" egg.
-hi" 'aryoty#e i" an e%am#le of Don !"ndrome (tri"omy ;8), the mo"t common numerical
abnormality found in ne*born". +t i" characteri1ed by an e%tra chromo"ome ;8 and the 'aryoty#e i"
*ritten a": /01231456. -he 'ey to the 'aryoty#e de"cri#tion i" a" follo*":
/0: the total number of chromo"ome" (4I i" normal).
23: the "e% chromo"ome" (male).
456: de"ignate" the e%tra chromo"ome a" a ;8.
Se% chromo"omal abnormalitie"
Aneuploi*y' abnormalitie" in the "e% chromo"ome number
)on di"unction during "#ermatogene"i" dan oogene"i"
e.g. Klinefelter "yndrome (4L,22M) and -urner "yndrome (4>,2O)
http://matriculation-biology.blogspot.com
)on di"unction during "#ermatogene"i"
+f non di"unction during ana#ha"e + : ++
"#erm *ill ha!e the abnormal "e% chromo"ome : 2M, 22 N MM
Abnormal "#erm % o!um (2)
Klinefelter "yndrome (22M)
Su#er male "yndrome (2MM)
62 female (metafemale, 222)
)on di"unction during Oogene"i"
+f non di"unction ha##ened
Some o!um might not carry any chromo"ome 2 : "ome other" might carry ; chromo"ome 2
Abnormal o!um (O) % "#erm
-urner "yndrome (2O)
MO : dead
Abnormal o!um (22) % "#erm
Klinefelter "yndrome (22M)
62 female
Klinefelter "yndrome (4L,22M)
KlinefelterD" Syndrome i" a genetic di"order that ha##en" in 8 in e!ery >@@ to 8@@@ male birth".
+n"tead of the normal 2M chromo"ome", the"e indi!idual" ha!e and e%tra 2 chromo"ome ma'ing them
22M.
Male" *ith KlinefelterD" "yndrome ha!e t*o 2 chromo"ome" (4L.22M), -he 2.chromo"ome" carry
gene" in term" of de!elo#ment of te"ticle", "e% hormone #roduction and #hy"ical "e% de!elo#ment in
general a" *ell a" to a certain e%tent al"o height gro*th.
+t i" named after (r. 9arry Klinefelter, a medical re"earcher at Ma""achu"ett" 5eneral 9o"#ital, 3o"ton,
Ma""achu"ett", *ho fir"t de"cribed thi" condition in 8H4;.
Sym#tom"
. delayed "#eech
. "en"ory integration difficultie", including "en"iti!ity to noi"e
. hy#otonia or lo* mu"cle tone
. auditory #roce""ing #roblem"
. language.ba"ed learning di"abilitie", including reading difficultie"
. an%iety
. de#re""ion
. gynecoma"tia or "*elling of brea"t ti""ue during #uberty
http://matriculation-biology.blogspot.com
. <emini"ed male ("oft !oice
. Sterile male ("mall te"ti"), failed to #roduce "#erm
. long hand and leg
-urner "yndrome (4>,2O)
-urner "yndrome re"ult" from a chromo"omal abnormality in *hich a female infant i" born *ith only one
2 chromo"ome (in"tead of the u"ual t*o) or i" mi""ing #art of one 2 chromo"ome.
Sym#tom"
. "hort "tature
. A*ebbingA of the "'in of the nec' (e%tra fold" of "'in e%tending from the to#" of the "houlder" to the
"ide" of the nec')
. a lo* hairline at the bac' of the head
. lo*."et ear"
. abnormal eye feature", including droo#ing of the eyelid"
. abnormal bone de!elo#ment, e"#ecially the bone" of the hand" and elbo*"
. a lac' of brea"t de!elo#ment at the e%#ected age (u"ually by age 86)
. an ab"ence of men"truation (amenorrhea)
. a larger than u"ual number of mole" on the "'in
A$no&ma Phenot+*e
7ine!ete& S+n'&ome (223) : 5n46 (T&isom+)
Sterile male ("mall te"ti"), failed to #roduce "#erm
<emini"ed male ("oft !oice) : big brea"t, long hand and leg
)on di"unction during oogene"i"
Tu&ne& S+n'&ome (2O) : 5n)6 (Monosom+)
Sterile female (failed to o!ulate)
Small brea"t : unde!elo#ed o!ary
d*arf, deaf, abnormal heart : lo* +O
$u#loidy & Poly#loidy
cell of organi"m that ha" an e%act multi#le of the ha#loid number (n) of chromo"ome" in a nucleu".
5amete" fu"ion *ill #roduce cell *hich ha!e more than ; "et of chromo"ome, for e%am#le: di#loid (;n),
tri#loid (6n), and tetra#loid (4n) nuclei or cell are eu#loid
Occurred *hen a "et of chromo"ome did not "e#arate during gametogene"i"
Common in #lant" than in animal", cau"e gamete not occur in animal, *hile in #lant can #roduce
!egetati!e #ro#agate.
-ri#loid (6n) occur" *hen
i) a gamete (;n) occur non di"unction fu"ed *ith a normal gamete (n)
5amete A % AA (non di"unction gamete)
indi!idual of tri#loid AAA
ii) chromo"ome" di"able to "egregate during meio"i" to #roduce di#loid gamete
iii) gamete from tetra#loid organi"m (4n) fu"ed *ith di#loid organi"m gamete (;n).
e.g. #lant tri#loid i" a banana, lemon, ro"e, *atermelon ("eedle"") and cry"anthemum
-etra#loid #lant" can be #roduced by :
http://matriculation-biology.blogspot.com
8) Somatic du#lication of chromo"ome number
. du#lication of chromo"ome at callu" (ti#)
.
origin #lant : AA (;n)
((u#licate)
tetra#loid #lant AAAA (4n)
;) <u"ion of t*o di#loid gamete"
P : AA (;n) AA (;n)
5 : AA AA
<+: AAAA
; ty#e" of #oly#loidy
. Auto#oly#loidy
. Allo#oly#loidy
Auto*o+*oi'+ :
+" an indi!idual that ha" more than t*o chromo"ome "et", all deri!ed from a "ingle "#ecie"
-he chromo"ome" "et are homologou" *ith the #arent cell
+m#ortance in economic !alue *hich auto#oly#loid #lant" #roduce flo*er" and fruit" bigger than normal
di#loid #lant"
+n!ol!e #arent cell from one "#ecie" mean homologou" chromo"ome
P : AA (;n) AA (;n)
5 : AA % AA
<+: AAAA
Ao*o+*oi'+
A #oly#loid re"ulting from ; different "#ecie" (hybridi1ation) interbreeding and combining their
chromo"ome"
-he chromo"ome "et" are different to #arental cell mean non homologou" chromo"ome "et" in!ol!e
<8 hybrid" #roduced from different "#ecie" are u"ually "terile (ha#loid "et of chromo"ome from one
"#ecie" cannot #air during meio"i" *ith the ha#loid "et from the other "#ecie")
Chromo"ome number in a "terile hybrid become" doubled and #roduce" fertile hybrid" ("yna#"i" and
"egregation can occur and !iable gamete" can be #roduced)
http://matriculation-biology.blogspot.com
+m#ortance in #roducing ne* "#ecie"
e.g. #lant (*heat)
Triticum diccoccum (;n 7 4% 7 ;C) % Aegilops squarrosa (;n 7 ;% 7 84)
-etra#loid #lant
Triticum vulgare (;n 7 I% 7 4;)
9e%a#loid #lant
P : AA 33
5amete A % 3
9ybrid ( "terile ) A3
du#lication
AA33
5amete, ;n 7 ;% ( fertile ) A3
http://matriculation-biology.blogspot.com
Spartina anglica i" a "#e"ie" of cordgra"", +t i" an allo#oly#loid "#e"ie" deri!ed from the hybrid Spartina
x townsendii
P Spartina maritima ("mall cordgra"") % Spartina alterniflora ("mooth cordgra"")
9ybrid Spartina x townsendii
dublication
Spartina anglica
Retold by
Amran Md Said
Matriculation College of Pahang.
-he end.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Chap4 Mutation 120919212945 Phpapp02Dokumen85 halamanChap4 Mutation 120919212945 Phpapp02Rxjviie BodaBelum ada peringkat
- Telomerases: Chemistry, Biology, and Clinical ApplicationsDari EverandTelomerases: Chemistry, Biology, and Clinical ApplicationsNeal F. LueBelum ada peringkat
- Variation and Mutation Lecture 1Dokumen23 halamanVariation and Mutation Lecture 1Samuel BuakuBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 5 MutationsDokumen93 halamanLesson 5 Mutationsnathanielstanaj.mBelum ada peringkat
- MUTATIONSDokumen35 halamanMUTATIONSFrancis Bernard Malonzo100% (1)
- BBT317 T01Dokumen61 halamanBBT317 T01Sharmistha DebnathBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 6Dokumen60 halamanLecture 6Anthony FajardoBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Mutation2Dokumen21 halamanWhat Is Mutation2Deepsnehil Dubey100% (2)
- DNA Damage and RepairDokumen25 halamanDNA Damage and RepairKhyati GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Gene Mutations: Substitution, in Which One Base Is Substituted For AnotherDokumen75 halamanGene Mutations: Substitution, in Which One Base Is Substituted For Anotheramna saleemBelum ada peringkat
- MutationsDokumen29 halamanMutationsiariajay100% (1)
- Dna Mutation and Its Effect On IndividualDokumen7 halamanDna Mutation and Its Effect On IndividualFaye ViernesBelum ada peringkat
- Genetic MutationDokumen23 halamanGenetic MutationKylie GavinneBelum ada peringkat
- Mutations Power PointDokumen30 halamanMutations Power PointMonica NainBelum ada peringkat
- Types of MutationsDokumen64 halamanTypes of MutationsI'm Cracked100% (1)
- Topic 6Dokumen8 halamanTopic 6NURWARDINA ZUNBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 4 - Variation & EvolutionDokumen26 halamanLecture 4 - Variation & Evolutioncandy_fairy7Belum ada peringkat
- MutationDokumen25 halamanMutationRia PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Dnamutationfinal 151102140820 Lva1 App6891Dokumen125 halamanDnamutationfinal 151102140820 Lva1 App6891Dr.Noman AsgharBelum ada peringkat
- MutationDokumen28 halamanMutationdr_47839666Belum ada peringkat
- Mutations NotesDokumen8 halamanMutations NotesHarini anuBelum ada peringkat
- Gene MutationDokumen20 halamanGene Mutationdheeresh aggarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Cell DNA RNADokumen5 halamanCell DNA RNADerrick kinyaBelum ada peringkat
- Patterns of Inheritance & Mutations: Presented by S. Anita Mercy M. SC (N) I YearDokumen25 halamanPatterns of Inheritance & Mutations: Presented by S. Anita Mercy M. SC (N) I YearJennifer Dixon100% (1)
- MUTATIONDokumen30 halamanMUTATIONbam yeontanieBelum ada peringkat
- 7 Mutation SCDokumen54 halaman7 Mutation SCThivya SritharBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes Genetic Mutations and Applied GeneticsDokumen9 halamanLecture Notes Genetic Mutations and Applied GeneticsRia Gale AsiloBelum ada peringkat
- MutationDokumen11 halamanMutationNewsonBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Mutations 1Dokumen36 halamanTypes of Mutations 1Xan Dyre AcoyBelum ada peringkat
- MutationsDokumen18 halamanMutationsSushanthBelum ada peringkat
- Mutations PowerpointDokumen31 halamanMutations Powerpointabisantiago6131100% (1)
- BCH 405 Lecture 1Dokumen24 halamanBCH 405 Lecture 1idriscognitoleadsBelum ada peringkat
- Mutation: - Today? Mutation Refers To Changes That Occur Within GenesDokumen18 halamanMutation: - Today? Mutation Refers To Changes That Occur Within Genesapplemango93Belum ada peringkat
- Bio Score: Chapter 7: MutationDokumen16 halamanBio Score: Chapter 7: MutationROS EZRA HANNY A/P ROSLI MoeBelum ada peringkat
- MutationDokumen39 halamanMutationJanet BarcimoBelum ada peringkat
- DNA Mutation and Mutagen 2023Dokumen16 halamanDNA Mutation and Mutagen 2023endahh parahyanganBelum ada peringkat
- Mutation: Genome Mutations Chromosome Mutations Gene MutationsDokumen65 halamanMutation: Genome Mutations Chromosome Mutations Gene MutationsReza WirotamaBelum ada peringkat
- Utation: Big PictureDokumen2 halamanUtation: Big PicturehomamunfatBelum ada peringkat
- Dna MutationsDokumen27 halamanDna MutationslowellaBelum ada peringkat
- Gene Expression and Genetics: MutationDokumen23 halamanGene Expression and Genetics: Mutationprimal100% (1)
- DNA Mutation, DNA Repair and Transposable Elements: Micky VincentDokumen33 halamanDNA Mutation, DNA Repair and Transposable Elements: Micky VincentYasmin PrissyBelum ada peringkat
- Final DemonstrationDokumen33 halamanFinal DemonstrationJayla Mae MarcellanaBelum ada peringkat
- MutationDokumen62 halamanMutationAlan Syahputra100% (2)
- MutationDokumen40 halamanMutationapi-668571149Belum ada peringkat
- Types of MutationsDokumen25 halamanTypes of MutationsRoninBelum ada peringkat
- 13,3 MutationsDokumen6 halaman13,3 MutationsSanaa SamkoBelum ada peringkat
- AL Bio 2C-1 - Gene MutationDokumen18 halamanAL Bio 2C-1 - Gene MutationJyoti BarnwalBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Gene Mutations - UpravenéDokumen11 halaman3 Gene Mutations - Upravenéchurikovalexandr97Belum ada peringkat
- Gene Mutation: Presentated By: - Abida Khan - Shumaila Gull - Mehwish RahmanDokumen15 halamanGene Mutation: Presentated By: - Abida Khan - Shumaila Gull - Mehwish RahmanMehwish RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- 6.1.1 Gene MutationsDokumen43 halaman6.1.1 Gene Mutationsdylanyoung0511Belum ada peringkat
- Biotech. (Muleta Germa)Dokumen10 halamanBiotech. (Muleta Germa)Aman aman AbeyeBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 6 STPM Biology Form 6Dokumen11 halamanCHAPTER 6 STPM Biology Form 6Shereen Phang YcBelum ada peringkat
- LSM2107 Lect 4 How Do Variations Come About?Dokumen80 halamanLSM2107 Lect 4 How Do Variations Come About?Hey byeBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Mutation and MigrationDokumen68 halaman6 Mutation and MigrationtanesjoanalynBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7a - DNA Mutation and Repair: Mutation and Adaptation Types of Mutations DNA Repair MechanismsDokumen35 halamanChapter 7a - DNA Mutation and Repair: Mutation and Adaptation Types of Mutations DNA Repair MechanismsKelvin KhoaBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 8Dokumen14 halamanTopic 8Ciwan SahinBelum ada peringkat
- D1.3 Mutations and Gene EditingDokumen17 halamanD1.3 Mutations and Gene Editingatasay2024Belum ada peringkat
- 4.2 MutationDokumen28 halaman4.2 MutationAnika SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Human Genetic VariationDokumen35 halamanHuman Genetic VariationJeriz Marie GamboaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical BondDokumen7 halamanChemical BondAidah AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 - Endangered EcosystemDokumen9 halamanChapter 8 - Endangered EcosystemMohd Faisal NasronBelum ada peringkat
- Periodic TableDokumen10 halamanPeriodic TableAidah AmirBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 18 (Lesson21) - Group 14 Elements IIDokumen10 halamanCHAPTER 18 (Lesson21) - Group 14 Elements IIAidah AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Inorganic Chemistry: Period 3 ElementsDokumen5 halamanInorganic Chemistry: Period 3 ElementsAidah AmirBelum ada peringkat
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Dokumen18 halamanSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Aidah Amir100% (2)
- SPM BiologyDokumen12 halamanSPM BiologyAidah Amir100% (1)
- Cell Structure3Dokumen15 halamanCell Structure3MalaysiaBoleh100% (28)
- Bio Note 2Dokumen6 halamanBio Note 2Aidah AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Carbon CompoundDokumen16 halamanCarbon CompoundAidah AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Case-Kel.9 KEA is a privately-held, international home products retailer that sells flat pack furniture, accessories,and bathroom and kitchen items in their retail stores around the world. The company, which pioneered flat-pack design furniture at affordable prices, is now the world's largest furniture retailer.Dokumen16 halamanCase-Kel.9 KEA is a privately-held, international home products retailer that sells flat pack furniture, accessories,and bathroom and kitchen items in their retail stores around the world. The company, which pioneered flat-pack design furniture at affordable prices, is now the world's largest furniture retailer.Binh NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Radioactivity: Radioactive DecayDokumen1 halamanRadioactivity: Radioactive DecayAidah AmirBelum ada peringkat
- PD3 Nov13 Pre Released Case FV PRODokumen15 halamanPD3 Nov13 Pre Released Case FV PROEddieChenBelum ada peringkat
- Ikea Case StudyDokumen20 halamanIkea Case StudySaurabh Pansare100% (1)
- Introduction To Nondestructive TestingDokumen34 halamanIntroduction To Nondestructive TestingNanditha Mandava ChowdaryBelum ada peringkat
- FPCM8 24Dokumen9 halamanFPCM8 24Aidah AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Bio Note 1Dokumen11 halamanBio Note 1Aidah AmirBelum ada peringkat
- !fully Bioresorbable Scaffolds For Coronary Artery DiseaseDokumen70 halaman!fully Bioresorbable Scaffolds For Coronary Artery DiseaseAidah AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Light Reaction Electron PathwayDokumen5 halamanLight Reaction Electron PathwayAidah AmirBelum ada peringkat
- SPM BiologyDokumen12 halamanSPM BiologyAidah Amir100% (1)
- Physics STPM Past Year Questions With Answer 2007Dokumen0 halamanPhysics STPM Past Year Questions With Answer 2007Audra HendersonBelum ada peringkat
- !bioresorbable Vascular Scaffolds For Coronary Artery DiseaseDokumen25 halaman!bioresorbable Vascular Scaffolds For Coronary Artery DiseaseAidah AmirBelum ada peringkat
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Dokumen18 halamanSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Terminology and Concepts: Oxidation and Reduction (Part 1)Aidah Amir100% (2)
- Music LinesDokumen2 halamanMusic LinesAidah AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Carbon CompoundDokumen16 halamanCarbon CompoundAidah AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Nota Ringkas KimiaDokumen2 halamanNota Ringkas KimiaZulhilmil Zul100% (7)
- Fatigue of StructuresDokumen51 halamanFatigue of StructuresJ Guerhard GuerhardBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bond IIIDokumen4 halamanChemical Bond IIIMalaysiaBoleh100% (2)
- Inorganic Chemistry: Period 3 ElementsDokumen5 halamanInorganic Chemistry: Period 3 ElementsAidah AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Answer ExerciseDokumen9 halamanAnswer ExerciseSakinah SaadBelum ada peringkat
- L6-Steczina, Sonette BIOEN345 Lecture 20200415Dokumen22 halamanL6-Steczina, Sonette BIOEN345 Lecture 20200415asdfghjklBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 - Introduction To BiochemistryDokumen8 halamanUnit 2 - Introduction To BiochemistryWinrich Louise M. MontanoBelum ada peringkat
- Tarif Prodia 2020 Untuk EmailDokumen32 halamanTarif Prodia 2020 Untuk Emailklinik bhaksenatragia100% (2)
- Introduction To 16s RRNA Sequencing-CD GenomicsDokumen14 halamanIntroduction To 16s RRNA Sequencing-CD GenomicsSteven4654Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3Dokumen24 halamanChapter 3Dawlat Slama0% (1)
- T - 1437039951caipang 9Dokumen15 halamanT - 1437039951caipang 9Doge WoweBelum ada peringkat
- Browsing Genomes With Ensembl PDFDokumen105 halamanBrowsing Genomes With Ensembl PDFBiljana KiroskaBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Cell Biology Alberts 3rd Edition Test BankDokumen13 halamanEssential Cell Biology Alberts 3rd Edition Test Bankmeaganstephensonmdbapgcjfezt100% (45)
- hEGF Optimize E.coli 6387Dokumen7 halamanhEGF Optimize E.coli 6387Thuận NguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- Why Johnny Can't Clone: Common Pitfalls and Not So Common SolutionsDokumen10 halamanWhy Johnny Can't Clone: Common Pitfalls and Not So Common SolutionsGanesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Panicker 2008Dokumen9 halamanPanicker 2008Tanzeel Rehman JaniiBelum ada peringkat
- ScienxeDokumen35 halamanScienxeBloom rachBelum ada peringkat
- Bio 112 UBC MT2 Practice Exam Qs - Oct25th2013Dokumen13 halamanBio 112 UBC MT2 Practice Exam Qs - Oct25th2013Cherica Oñate0% (1)
- Animal Trans Genesis and CloningDokumen230 halamanAnimal Trans Genesis and CloningJanapareddi VenkataramanaBelum ada peringkat
- Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Mechanisms of Heat Stress PDFDokumen42 halamanPhysiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Mechanisms of Heat Stress PDFkuangBelum ada peringkat
- Immunology and Immunochemistry 3 PDFDokumen7 halamanImmunology and Immunochemistry 3 PDFboatcomBelum ada peringkat
- 2021 Article 4246Dokumen40 halaman2021 Article 4246Sobek1789Belum ada peringkat
- Aqib McqsDokumen62 halamanAqib McqsMUn EEb100% (1)
- Molecular Biology of The Cell 6Th Edition Bruce Alberts Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokumen67 halamanMolecular Biology of The Cell 6Th Edition Bruce Alberts Test Bank Full Chapter PDFrorybridgetewe100% (10)
- Cell Division WorksheetDokumen4 halamanCell Division WorksheetIndah SaputriBelum ada peringkat
- Antibody Source Book EURDokumen66 halamanAntibody Source Book EURchristina_finkeBelum ada peringkat
- Review: Mitochondria: in Sickness and in HealthDokumen15 halamanReview: Mitochondria: in Sickness and in HealthPetra JobovaBelum ada peringkat
- Redox Signaling (Wikipedia)Dokumen5 halamanRedox Signaling (Wikipedia)gotglutBelum ada peringkat
- Emini Surface Accessibility Prediction ResultsDokumen117 halamanEmini Surface Accessibility Prediction ResultsFernando GranzottoBelum ada peringkat
- Science 113 - Laboratory Course Guide in BiochemistryDokumen3 halamanScience 113 - Laboratory Course Guide in BiochemistryYvonne De Venecia Malicdem100% (1)
- 10 3389@fmicb 2020 01423Dokumen10 halaman10 3389@fmicb 2020 01423gusti ningsihBelum ada peringkat
- BIOL100, Prof Adrienne Alaie: Fall 2010Dokumen118 halamanBIOL100, Prof Adrienne Alaie: Fall 2010Barukh B. Rohde0% (1)
- Hmm202 Practical 1 WorksheetDokumen7 halamanHmm202 Practical 1 WorksheetWafaa AdamBelum ada peringkat
- Coagulation Cascade (Hema)Dokumen4 halamanCoagulation Cascade (Hema)MarjoBelum ada peringkat
- ForteBio App Note 1Dokumen2 halamanForteBio App Note 1Fernando OviedoBelum ada peringkat
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDari EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (81)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDari EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (6)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDari EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (404)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDDari EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDari EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (29)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDari EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BePenilaian: 2 dari 5 bintang2/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsDari EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsBelum ada peringkat
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Dari EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Penilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDari EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDari EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (42)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDari EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDari EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (3)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDari EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDari EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Dari EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (110)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDari EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (328)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearDari EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (23)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningDari EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsDari EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (170)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDari EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Empath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainDari EverandEmpath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (95)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDari EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (8)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsDari EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (6)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlDari EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (59)