Hiperemesis Gravidarum
Diunggah oleh
Febrina Utami Putri0%(1)0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
63 tayangan5 halamanhiperemesis gravidarum
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inihiperemesis gravidarum
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0%(1)0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
63 tayangan5 halamanHiperemesis Gravidarum
Diunggah oleh
Febrina Utami Putrihiperemesis gravidarum
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPTX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 5
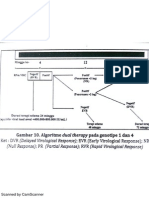
Management
Multimodal treatment: Medical, Dietary, and
Psychological Support
Dietary management:
Eat more frequently in small portions + snacks
High carbohydrate and protein, low fat and acid
Drinks that contain electrolytes and other
supplements
Food abstinence Total Parenteral Nutrition
until symptoms can be managed
IV fluids : Normal saline or Hartmann solution
are suitable solutions; potassium chloride can be
added as needed
Management
Medications:
American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
Guidelines (2004) : dimenhydrinate, metoclopramide, or
promethazine
Anti-emetics: dopamin antagonists, phenothiazine, 5-HT3
antagonists
Steroids : IV hydrocortisone
Ginger
Antacids and H2-blockers or Proton Pump Inhibitors
Supplementary:
Pyridoxine
Thiamine
Vitamin C
Iron
Management
Patients with depressive and psychotic
symptoms Psychiatric counseling +
medication
Hypnotic-sedatives: Midazolam or Diazepam
Education:
Avoid stressful conditions
Family members provide physical and
emotional support
References
Siddik D. Kelainan Gastrointestinal. Di dalam:
Saifuddin AB, editor. Ilmu Kebidanan. Ed ke-
4. Jakarta: PT. Bina Pustaka Sarwono
Prawirohardjo; 2010. hlm 815-818.
JK Jueckstock, R Kaestner, I Mylonas.
Managing hyperemesis gravidarum: a
multimodal challenge. BMC Medicine. 2010;
8:46. Downloaded from
http://www.biomedcentral.com/1741-
7015/8/46
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- NewDokumen1 halamanNewFebrina Utami PutriBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- New Doc 1Dokumen1 halamanNew Doc 1Febrina Utami PutriBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Does Bacterial Biofilms Have A Role in The Development of Human Chronic Rhinosinusitis?Dokumen4 halamanDoes Bacterial Biofilms Have A Role in The Development of Human Chronic Rhinosinusitis?Febrina Utami PutriBelum ada peringkat
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Neonatal AnemiaDokumen22 halamanNeonatal AnemiaFebrina Utami Putri100% (4)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)