The LNG Process
Diunggah oleh
aby_abraham5005Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
The LNG Process
Diunggah oleh
aby_abraham5005Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
The LNG Process
1. Sulfinol absorber columns. Raw gas enters the column where it mixes with a
solvent (Sulfinol) that removes CO2 from the gas
2. Sulfinol regeneration: Solvent from the Sulfinol absorber is stripped of CO2 for re-
use in the absorber column
3. Mercury removal unit: Any mercury in the gas is removed to protect the main
cryogenic heat exchanger which is made of aluminium
4. Gas dehydration units: Gas leaving the Sulfinol unit has saturated water removed
and cooled to 210C.
5. Air-fin coolers: The banks of coolers provide cooling for the propane refrigerant
cycle and some cooling for the mixed refrigerant cycle
6. Exhaust stacks for gas turbine compressors: These are for the propane and
mixed refrigerant compressors
7. Refrigerant (propane) heat exchangers: Propane chills the gas to -350C before
entering the main cryogenic heat exchanger
8. Scrub column: Heavy components of the gas (pentanes and heavier) are removed
to produce ethane and propane for the refrigerant cycles
9. Mixed refrigerant heat exchanger: Refrigerant is cooled to -350C before its use in
the main cryogenic heat exchanger
10. Exhaust stacks for mixed refrigerant compressors: These are for the mixed
refrigerant compressors
11. Main cryogenic heat exchangers: The heart of the liquefaction process where
gas is cooled again mixed refrigerant to minus 1380C and becomes liquid
12. High and low pressure LNG flash vessels: Final cooling achieved by expanding
liquefied gas to close to atmospheric pressure. As the liquid expands it cools to -
1610C, ready for piping to the LNG storage tanks
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Ethylene UnitsDokumen20 halamanEthylene UnitsLindah Turson100% (3)
- H2 Production ProcessDokumen3 halamanH2 Production ProcessJulianto TobingBelum ada peringkat
- ASU - Air Separation UnitDokumen2 halamanASU - Air Separation Unitsajalkk25Belum ada peringkat
- ME432 Unit4 Ch2-VAPOUR COMPRESSION REFRIGERATIONDokumen32 halamanME432 Unit4 Ch2-VAPOUR COMPRESSION REFRIGERATIONJOHN ROHAAN R 1961430Belum ada peringkat
- National Fertilizers Limited Nan Gal PunjabDokumen3 halamanNational Fertilizers Limited Nan Gal PunjabNirmanyu JamwalBelum ada peringkat
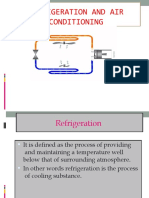
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDokumen102 halamanRefrigeration and Air ConditioningYuvaperiyasamy MayilsamyBelum ada peringkat
- Cryogenic SystemsDokumen9 halamanCryogenic SystemsGanesh ThoratBelum ada peringkat
- Auto Thermal Reactor:: Secondary ReformerDokumen6 halamanAuto Thermal Reactor:: Secondary ReformerAtif MehfoozBelum ada peringkat
- Gasifier ProcessDokumen4 halamanGasifier ProcessHenry ArenasBelum ada peringkat
- Descriptions Example Process Flowsheets: Appendix 2.1Dokumen5 halamanDescriptions Example Process Flowsheets: Appendix 2.1Kevin Alberto Tejera PereiraBelum ada peringkat
- The Definitive Guide To Cryogenic EngineeringDokumen21 halamanThe Definitive Guide To Cryogenic EngineeringSamanthaPereraBelum ada peringkat
- NOTES 5 - RefrigerationDokumen20 halamanNOTES 5 - RefrigerationMakoya_malumeBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6Dokumen7 halamanChapter 6esraaoraby24Belum ada peringkat
- Refrigeration and Liquefaction: Instructor: Engr. Caressa Marie Frial-De JesusDokumen22 halamanRefrigeration and Liquefaction: Instructor: Engr. Caressa Marie Frial-De JesusEmmanuel PlazaBelum ada peringkat
- 5 LNGDokumen32 halaman5 LNGOliverTumbayBelum ada peringkat
- Cryogenic UnitDokumen7 halamanCryogenic UnitAhmed ElShoraBelum ada peringkat
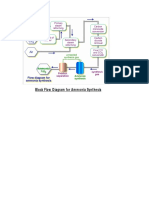
- Block Flow Diagram For Ammonia SynthesisDokumen2 halamanBlock Flow Diagram For Ammonia SynthesisK.R Technosafe EngineersBelum ada peringkat
- RefrigerationDokumen7 halamanRefrigerationhitesh bhoiBelum ada peringkat
- Deisel Hydrotreating UnitDokumen9 halamanDeisel Hydrotreating UnitRittu Paul100% (1)
- SAPDokumen16 halamanSAPsourav84Belum ada peringkat
- Ammonia Process DescriptionDokumen7 halamanAmmonia Process DescriptionAnanda BalaBelum ada peringkat
- Cpe 601 Mini ProjectDokumen9 halamanCpe 601 Mini ProjectSchaieraBelum ada peringkat
- Process SelectionDokumen8 halamanProcess SelectionSwathi SBelum ada peringkat
- Refrigeration Cycles: Wan Rosli Wan SulaimanDokumen21 halamanRefrigeration Cycles: Wan Rosli Wan Sulaimanعبدالله عمرBelum ada peringkat
- PRE - Ppt-Thermal Cracking DesignDokumen16 halamanPRE - Ppt-Thermal Cracking DesignnikhilBelum ada peringkat
- Process DescriptionDokumen5 halamanProcess DescriptionGurunath EpiliBelum ada peringkat
- PSH AaaaaaaaaaaaDokumen7 halamanPSH AaaaaaaaaaaaEdris SalamBelum ada peringkat
- Handbook of LNGDokumen3 halamanHandbook of LNGBorisvc8Belum ada peringkat
- By Product PlantDokumen6 halamanBy Product PlantRajan BhandariBelum ada peringkat
- NH3 Process DescriptionDokumen8 halamanNH3 Process DescriptionMusa KaleemBelum ada peringkat
- Steam Uses of Steam On The ShipDokumen3 halamanSteam Uses of Steam On The ShipMeghanath AdkonkarBelum ada peringkat
- GTL and GTSDokumen21 halamanGTL and GTSNicolaBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 4 - REFRIGERATION CYCLE - Oct 2015Dokumen58 halamanChap 4 - REFRIGERATION CYCLE - Oct 2015FaizMuhamadZain50% (2)
- Process Flow Diagram For Ammonia SynthesisDokumen6 halamanProcess Flow Diagram For Ammonia SynthesisHanan Ahmed Ibrahim100% (1)
- Process Description1Dokumen2 halamanProcess Description1Ismail IdrisBelum ada peringkat
- A New Method For Co2 CaptureDokumen6 halamanA New Method For Co2 CaptureAbul HassanBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 2Dokumen12 halamanLecture 2Eyad EmadBelum ada peringkat
- Low-Temperature ProcessingDokumen5 halamanLow-Temperature ProcessingAlberto Fonseca UribeBelum ada peringkat
- CF BraunDokumen4 halamanCF BraunTito EcheverriaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 11Dokumen21 halamanChapter 11Jomar HefiBelum ada peringkat
- Refrigeration Systems Are Common in The Natural Gas Processing Industry and Processes Related To The Petroleum RefiningDokumen15 halamanRefrigeration Systems Are Common in The Natural Gas Processing Industry and Processes Related To The Petroleum RefiningMahmoud ElarabyBelum ada peringkat
- MODULE I Introduction To Refrigeration SystemsDokumen3 halamanMODULE I Introduction To Refrigeration SystemsNELMIDA AIRISH JOY N.Belum ada peringkat
- Byproduct Operations and ProcessDokumen8 halamanByproduct Operations and ProcessAbhaySnghBelum ada peringkat
- Vapor Compression Refrigeration Test Rig Lab Manual LatestDokumen12 halamanVapor Compression Refrigeration Test Rig Lab Manual LatestAshish VermaBelum ada peringkat
- Refrigeration CyclesDokumen10 halamanRefrigeration Cyclesaravoof84Belum ada peringkat
- Ammonia ProductionDokumen28 halamanAmmonia ProductionMuhammad Ali HashmiBelum ada peringkat
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDokumen9 halamanRefrigeration and Air ConditioningLuis Enrique Cervantes DominguezBelum ada peringkat
- RefrigerationDokumen21 halamanRefrigerationAbdul Hannan0% (1)
- Nitric Acid Design Project: Shivam PandyaDokumen15 halamanNitric Acid Design Project: Shivam PandyaShivam PandyaBelum ada peringkat
- Process Description Sulphuric AcidDokumen2 halamanProcess Description Sulphuric AcidAbdul QayyumBelum ada peringkat
- Precooling Strategies For Efficient Natural Gas Liquefaction - Gas Processing & LNGDokumen20 halamanPrecooling Strategies For Efficient Natural Gas Liquefaction - Gas Processing & LNGMuhammad ImranBelum ada peringkat
- Treatment of Ethane-Propane in A Petrochemical Complex: Apoorva Vinayak RudraDokumen5 halamanTreatment of Ethane-Propane in A Petrochemical Complex: Apoorva Vinayak RudraEditorijer IjerBelum ada peringkat
- Crude Oil DistillationDokumen34 halamanCrude Oil Distillationfathi100% (2)
- 1.2 Steady State Simulation: 1.2.1 Process DescriptionDokumen1 halaman1.2 Steady State Simulation: 1.2.1 Process Descriptionengr_usman7353933Belum ada peringkat
- Liquified Natural Gas TechnologyDokumen14 halamanLiquified Natural Gas Technologyabkafaru67% (3)
- 1553003659-ABB - DCU - Module 2 - PDFsDokumen32 halaman1553003659-ABB - DCU - Module 2 - PDFsAhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Lcture 1 R&ACDokumen95 halamanLcture 1 R&ACzetseatBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesDari EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesBelum ada peringkat
- Astm D 422: Tolunay-Wong Engineers, Inc. Houston, TexasDokumen1 halamanAstm D 422: Tolunay-Wong Engineers, Inc. Houston, Texasaby_abraham5005Belum ada peringkat
- Questions and Clarification For Al Zour Refinery ProjectDokumen2 halamanQuestions and Clarification For Al Zour Refinery Projectaby_abraham5005Belum ada peringkat
- Consolidation Test Report: Tolunay-Wong Engineers, Inc. Houston, TexasDokumen10 halamanConsolidation Test Report: Tolunay-Wong Engineers, Inc. Houston, Texasaby_abraham5005Belum ada peringkat
- Pavement DesignDokumen598 halamanPavement Designaby_abraham5005100% (4)
- River Water Intake TOC: +652 BOC: +608 Use BH-4, 5 &6Dokumen1 halamanRiver Water Intake TOC: +652 BOC: +608 Use BH-4, 5 &6aby_abraham5005Belum ada peringkat
- STF 05530Dokumen13 halamanSTF 05530aby_abraham5005Belum ada peringkat
- CBI LNG Journal JanFeb05-LoresDokumen3 halamanCBI LNG Journal JanFeb05-Loresaby_abraham5005Belum ada peringkat
- Off Project Work Authorization: Escondida Water Supply ProjectDokumen1 halamanOff Project Work Authorization: Escondida Water Supply Projectaby_abraham5005Belum ada peringkat
- API 650 OutputDokumen88 halamanAPI 650 Outputaby_abraham50050% (1)