Gangguan Gerak
Diunggah oleh
Farah MuthiaDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Gangguan Gerak
Diunggah oleh
Farah MuthiaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1/13/2013
1
Movement Disorders
General Overview
1/13/2013
2
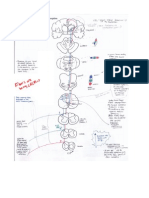
BASAL GANGLIA CIRCUITRY
1/13/2013
3
Hypokinesias
Parkinsonism
Akinesia/Bradykinesia
Rigidity
Motor Freezing
Spasticity
Apraxias
Tics (Blocking & Holding Tics, Obsessional Tics)
Psychiatric
Catatonia
Psychomotor Depression
Psychogenic Parkinsonism
Cataplexy/Drop Attacks
Hypothyroidism or other Endocrinologic
Disorders
Hesitant Gait of the Elderly
1/13/2013
4
Hyperkinesias and Dyskinesias
Tremor
Chorea
Dystonia
Myoclonus
Ataxia and Dysmetria
Stereotypies and Tics
Akathisia
Myokymia and Synkinesias
Restless Legs
Periodic Hypnogogic Movements (PLMS)
1/13/2013
5
Movement Disorders --
Parkinsonisms
Parkinsons Disease
Diffuse Lewy Body Disease
Multiple Systems Atrophy (+/- Ataxia)
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
Corticobasal Degeneration
Vascular Parkinsonism
Post Traumatic Parkinsonism
Secondary (Toxin, Medication, Metabolic)
1/13/2013
6
PARKINSONISMS
1/13/2013
7
Idiopathic Parkinsons Disease
Usually Asymmetric
Cardinal Signs
Tremor
Rigidity
Bradykinesia
Levodopa Responsive
Later Findings
Postural Instability
Levodopa-unresponsive gait disorder
Non Motor Features (Depression, Sexual
Dysfunction, Cognitive Dysfunction of
Variable Severity)
1/13/2013
8
Diffuse Lewy Body Disease
Unlike PD, Lewy Bodies rapidly spready
throughout the brain, including the
cerebral cortex
Levodopa Responsive Parkinsonism
Rapidly Progressive Dementia
Hallucinations
1/13/2013
9
Multiple Systems Atrophy
Cardinal Findings
Parkinsonism that is poorly responsive to Levodopa
Autonomic Failure (Low Blood Pressure)
Cerebellar Signs
Long Tract Signs (Spasticity)
Striato-Nigral Type (Parkinsonism First)
Shy-Drager Syndrome (Autonomic Failure First)
Olivo-ponto-cerebellar Type (OPCA Ataxia
First)
1/13/2013
10
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
Early Postural Instability and Falls
Parkinsonism (Unresponsive to
Levodopa)
Stone Face
Dementia
Ocular Signs
1/13/2013
11
Corticobasal Degeneration
Asymmetric Parkinsonism with Poor
Response to Levodopa
Apraxia and Alien Limb
Spasticity, Rigidity, Dystonia
Gait and Balance Problems
Dementia always occurs, but may be a
late feature
1/13/2013
12
Drug Related Parkinsonism
Haldol and other antipsychotic
medications cause symmetric findings
that are indistinguishable at times from
Idiopathic Parkinsons Disease
Reglan is a dopamine blocker and is an
important cause of Parkinsonism in elderly
patients (currently used as an anti-nausea
medication)
1/13/2013
13
HYPERKINESIAS
1/13/2013
14
Movement Disorders -- Tremor
Essential Tremor
Limbs, Head, Voice
Dystonic Tremor
Task Specific Tremors
Midbrain Outflow Tremors
Cerebellar Tremor
Rubral Tremor
Rest Tremor (Parkinsonism)
Orthostatic Tremor
Exaggerated Physiologic Tremor
Caffiene, Medication Withdrawal
Other (Drug Related Tremor)
1/13/2013
15
Essential Tremor
Common
Upper Extremity Tremor with Posture and/or
Action
Bilateral, usually roughly symmetric
Typically of Long-Standing Duration
Other Areas May Be Involved
Head or Jaw
Voice
Lower Extremities
Tremor may produce disability, but often
doesnt
No clear association with other diseases or
disorders
1/13/2013
16
Myoclonus
Not a Tremor
Sudden, shock-like muscle contractions
Focal, Multifocal, or Generalized
May be regular and rythmic, but usually
irregular and jerky
Epileptic or Non-Epileptic
Cortical (Epileptic)
Brainstem or Spinal Segmental (Non-
Epileptic)
1/13/2013
17
Chorea
Excessive Spontaneous Movements
Irregular, Random, Brief and Abrupt
Non-repetitive
Distal Predominance
Flitting randomly from one body part to
another
Purposeless, but may be disguised
(parakinesias)
Facial grimacing and abnormal
respiratory sounds
1/13/2013
18
Chorea -- Causes
MEDICATIONS (e.g. tardive dyskinesia)
Haldol, other antipsychotics
Reglan is an important cause of tardive
dyskinesia
Huntingtons Disease
Hemiballism (Stroke)
Post-Infectious (Strep Infection)
Pregnancy
Other Disorders
1/13/2013
19
Tics
Semi-voluntary (e.g. suppressible),
rapid,non-rythmic movements or sounds
Background of normal activity
Associated Compulsions
May be associated with OCD
Occasionally tics are disabling, but the
OCD is usually the more disabling
condition, if it exists
1/13/2013
20
Akathisia
Motor restlessness with a desire to move
Difficult for patients to describe
I feel like Im always crawling out of my
skin
Often with associated vocalizations and
grunting
Often very disabling
Cause: MEDICATIONS antipsychotics
and Metoclopromide (Reglan)
1/13/2013
21
Dystonia
Sustained, patterned muscle contractions
Agonists and Antagonists
Clinical Findings
Repetitive Twisting or Squeezing Movements
Fixed Postures
Localization
Focal
Face (Blepharospasm and Meige Syndrome)
Neck (Cervical Dystonia)
Limbs (Task Specific Dystonias)
Segmental
Generalized
1/13/2013
22
Causes of Dystonia
Idiopathic (Most Cases)
DRUG RELATED
Antipsychotics and Reglan
Genetic (DYT-1 Gene)
Structural
Trauma
Stroke
Multiple Rare Diseases
1/13/2013
23
Ataxia
Symptomatic Interruption of the
Cerebellar Pathways
Dysmetria (Poor targeting of planned
movements)
Dysdiadochokinesia (Poor sequencing of
planned movements)
Intention Tremor (Past Pointing)
Gait Abnormalities
Wide based gait
Poor balance
Drunken Sailors Walk
1/13/2013
24
Causes of Ataxia
Lesion in the following areas of the brain
Cerebellum
Pons
Midbrain (Red Nucleus)
Olivary Nucleus
Thalamus (Cerebellar Inflow Nucleus)
1/13/2013
25
Causes of Ataxia
Acute intoxication (Alcohol, Dilantin, others)
Chronic Substance Abuse (including Alcohol)
Stroke
Multiple Sclerosis
Brain Tumors
Genetic Ataxias
Autosomal Dominant Ataxias
Autosomal Recessive Ataxias
Metabolic
Vitamin E, Thiamine,
Multiple Systems Atrophy
1/13/2013
26
Restless Legs
Bothersome urge to move legs at night
Prevents sleep
1/13/2013
27
Treatment of Parkinsons
Disease
Levodopa and Dopamine Agonists
Amantidine, MAO-B Inhibitors
Deep Brain Stimulation (Subthalamic Nucleus,
Globus Pallidus Interna)
1/13/2013
28
Treatment of Dystonia
Artane, Valium, occasionally Baclofen
Botulinum Toxin Injection
Deep Brain Stimulation (Globus Pallidus
Interna)
1/13/2013
29
Treatment of Essential Tremor
Primidone
Propanolol and other Beta Blockers
Deep Brain Stimulation (Thalamus)
Tremors of some patients are quite
responsive to alcohol, and patients
may self-medicate
1/13/2013
30
Treatment of Tardive (Post
Dopamine-Blockade) Movement
Disorders
PREVENTION
Dopamine Depleting Agents (Difficult to
Obtain in the U.S.)
Ramp up dopamine blockade (often
worsens the underlying pathologic process)
Life Long Botulinum Toxin Injections
Deep Brain Stimulation
1/13/2013
31
Complications of Dopamine
Blocking Agents
Reversible? Sequelae Include
Tremor
Parkinsonism
Permanent and Difficult to Treat Sequelae
Include
Tardive Dyskinesia (Chorea-like syndrome)
Tardive Akathisia
Tardive Dystonia (Long Term Botox, may
need DBS)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Purves Neuroscience Website Questions CH 7 AnswersDokumen4 halamanPurves Neuroscience Website Questions CH 7 AnswersPK32145987100% (1)
- CRPS and Compartment SyndromeDokumen19 halamanCRPS and Compartment Syndromegbc1989Belum ada peringkat
- 3 AttentionDokumen53 halaman3 AttentionSanjeev Kumar100% (2)
- Lecture Notes On PsychiatryDokumen38 halamanLecture Notes On PsychiatryMing Wang50% (6)
- Lecture On MovementDokumen29 halamanLecture On MovementHassen Kavi Isse100% (1)
- Randa Al-Harizy Prof of Internal MedicineDokumen40 halamanRanda Al-Harizy Prof of Internal MedicinerafikaBelum ada peringkat
- Parkinson'S Disease: DR M Tariq (PT)Dokumen29 halamanParkinson'S Disease: DR M Tariq (PT)syge zwvuBelum ada peringkat
- Movement Disorders Include:: and Lower Lip)Dokumen7 halamanMovement Disorders Include:: and Lower Lip)mainehoonaBelum ada peringkat
- KP 3-1-15 Movement DisorderDokumen37 halamanKP 3-1-15 Movement DisorderShintia Surya PutriBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Dystonia: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDokumen40 halamanUnderstanding Dystonia: Causes, Symptoms and Treatmentdrkish81100% (1)
- Progressive Supra Nuclear PalsyDokumen4 halamanProgressive Supra Nuclear PalsyabbifinniBelum ada peringkat
- Parkinsons DiseaseDokumen58 halamanParkinsons DiseasemuthuuBelum ada peringkat
- TMP - 6100-Tardive PGMay04Article3Dokumen7 halamanTMP - 6100-Tardive PGMay04Article3ajescoolBelum ada peringkat
- Dementia Conversion DisordersDokumen28 halamanDementia Conversion DisordersAYO NELSON100% (1)
- Parkinson's Disease SymptomsDokumen13 halamanParkinson's Disease SymptomsAnastasia Widha SylvianiBelum ada peringkat
- Extrapyramidal DisorderDokumen35 halamanExtrapyramidal DisorderFerdy SetiawanBelum ada peringkat
- Disorders of The Nervous System: Vascular DisorderDokumen3 halamanDisorders of The Nervous System: Vascular DisorderHetty100% (1)
- Movement Disorders GuideDokumen23 halamanMovement Disorders GuideBrendan O'HareBelum ada peringkat
- SDL 23 Parkinson's Disease BMS16091064Dokumen8 halamanSDL 23 Parkinson's Disease BMS16091064Jonathan YeohBelum ada peringkat
- Movement Disorders: Prof. DR Taha Kamel Alloush MD NeurologyDokumen68 halamanMovement Disorders: Prof. DR Taha Kamel Alloush MD NeurologyKhaled OssamaBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System Diseases GuideDokumen52 halamanNervous System Diseases GuideAhmed Adel SaadBelum ada peringkat
- Basal Ganglia DisordrsDokumen50 halamanBasal Ganglia DisordrsPhysiology by Dr Raghuveer100% (1)
- Movement Disorders: AtaxiaDokumen7 halamanMovement Disorders: AtaxiaChakram SundarBelum ada peringkat
- Running Head: (GAGTAN, ANDREI RAPHAEL L.)Dokumen7 halamanRunning Head: (GAGTAN, ANDREI RAPHAEL L.)Edmarkmoises ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Huntington's Disease: Liver Disease Dystonia VomitingDokumen5 halamanHuntington's Disease: Liver Disease Dystonia VomitingmainehoonaBelum ada peringkat
- EpilepsyDokumen6 halamanEpilepsyDeenah ElwaihidiBelum ada peringkat
- Parkinson's Disease GuideDokumen2 halamanParkinson's Disease GuiderajeevkeyarBelum ada peringkat
- Parkinson Disease & Other Movement Disorders: Cherian Abraham Karunapuzha, M.DDokumen40 halamanParkinson Disease & Other Movement Disorders: Cherian Abraham Karunapuzha, M.DsafiraBelum ada peringkat
- Parkinson DiseaseDokumen17 halamanParkinson Diseasewinda lestariBelum ada peringkat
- Movement Disorders: Akinetic-Rigid SyndromesDokumen8 halamanMovement Disorders: Akinetic-Rigid SyndromesMarwan M.Belum ada peringkat
- Understanding Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALSDokumen17 halamanUnderstanding Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALSJoel Andrew Java Daga100% (2)
- AtaxiaDokumen8 halamanAtaxiaDivya Gupta0% (1)
- Gait Abnormalities Assessment and CausesDokumen12 halamanGait Abnormalities Assessment and CausesMudassar SattarBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Parkinson's DiseaseDokumen52 halamanUnderstanding Parkinson's Diseasetorr123Belum ada peringkat
- Dystonia Fact Sheet: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentsDokumen7 halamanDystonia Fact Sheet: Causes, Symptoms & Treatmentsepiipo91Belum ada peringkat
- The Cerebellum: Clinical ExaminationDokumen70 halamanThe Cerebellum: Clinical ExaminationTarun MathurBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 14 Neurologic Disorders Study Guide Outline #2Dokumen12 halamanChapter 14 Neurologic Disorders Study Guide Outline #2Del Delgado100% (1)
- PARKINSON’S DISEASEDokumen7 halamanPARKINSON’S DISEASEKarthikBelum ada peringkat
- Epilpesy: Yul Orozco MoralesDokumen15 halamanEpilpesy: Yul Orozco MoralesYul OrozcoBelum ada peringkat
- Motor Neuron DiseaseDokumen8 halamanMotor Neuron DiseaseyigoBelum ada peringkat
- Anti-Parkinsonism Drugs PDFDokumen75 halamanAnti-Parkinsonism Drugs PDFSayan NagBelum ada peringkat
- Movement DisorderDokumen37 halamanMovement DisorderFalcon DarkBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Alzheimer's Disease and Other DementiasDokumen41 halamanUnderstanding Alzheimer's Disease and Other DementiasHeyBelum ada peringkat
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDokumen34 halamanCerebrovascular AccidentAustin Dominic Dela ResmaBelum ada peringkat
- Neurological Impairment After Stroke....Dokumen5 halamanNeurological Impairment After Stroke....OGU CourageBelum ada peringkat
- Parkinson's DiseaseDokumen25 halamanParkinson's DiseaseJonah reiBelum ada peringkat
- Parkinson Disease Guide: Symptoms, Treatments & MoreDokumen11 halamanParkinson Disease Guide: Symptoms, Treatments & MoreasihsuciBelum ada peringkat
- Involuntary MovementDokumen26 halamanInvoluntary MovementMustafa Abd-Al SahibBelum ada peringkat
- Autism to ALS: OT InterventionsDokumen34 halamanAutism to ALS: OT InterventionsAnAs Al ArjanBelum ada peringkat
- Movement Disorders II "Dyskinesias": Nasser HospitalDokumen30 halamanMovement Disorders II "Dyskinesias": Nasser HospitalMahmoud Abu Al AmrainBelum ada peringkat
- PimozideDokumen5 halamanPimozideMega AnandaBelum ada peringkat
- Memory Loss Dementia Seizures Coma: What Causes Encephalopathy?Dokumen16 halamanMemory Loss Dementia Seizures Coma: What Causes Encephalopathy?drdewdewBelum ada peringkat
- Multiple System AtrophyDokumen6 halamanMultiple System AtrophyAllan de Souza100% (1)
- Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisDokumen15 halamanAmyotrophic Lateral SclerosisYakan AbdulrahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Guide to Postural Tachycardia Syndrome (PoTSDokumen12 halamanMedical Guide to Postural Tachycardia Syndrome (PoTSAttis PhrygiaBelum ada peringkat
- Ohtahara Syndrome: Corticosteroids (Prednisolone or ACTH) Are Occasionally HelpfulDokumen2 halamanOhtahara Syndrome: Corticosteroids (Prednisolone or ACTH) Are Occasionally HelpfulidscribddotcomBelum ada peringkat
- Parkinson S Disease Epidemiology,.9Dokumen5 halamanParkinson S Disease Epidemiology,.9bacharelado2010Belum ada peringkat
- Parkinson's Disease (Parkinsonism) : Degenerative Diseases of The CNS IncludeDokumen4 halamanParkinson's Disease (Parkinsonism) : Degenerative Diseases of The CNS IncludeThyia OwBelum ada peringkat
- Delirium, Dementia, and Amnestic and Other Cognitive DisordersDokumen78 halamanDelirium, Dementia, and Amnestic and Other Cognitive DisordersjashchiruBelum ada peringkat
- Delirium, Dementia, and Amnestic and Other Cognitive DisordersDokumen78 halamanDelirium, Dementia, and Amnestic and Other Cognitive DisordersrashidBelum ada peringkat
- Physiotherapy Study MaterialsDokumen113 halamanPhysiotherapy Study MaterialsLove & HumanityBelum ada peringkat
- Movement Disorders Types - Mayo ClinicDokumen1 halamanMovement Disorders Types - Mayo ClinicdrrajmptnBelum ada peringkat
- Homoeopathic Treatment of Parkinson DieseDokumen23 halamanHomoeopathic Treatment of Parkinson DieseNidhi SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Autonomic and Mitochondrial Disorders: Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment for Mind-Body WellnessDari EverandClinical Autonomic and Mitochondrial Disorders: Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment for Mind-Body WellnessBelum ada peringkat
- NeuroDokumen51 halamanNeuroSwiny AnnizaBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar PustakaDokumen1 halamanDaftar PustakaFarah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- Amiodaron Sebagai Obat Anti Aritmia Dan Pengaruhnya Terhadap Fungsi TiroidDokumen11 halamanAmiodaron Sebagai Obat Anti Aritmia Dan Pengaruhnya Terhadap Fungsi TiroidFarah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- 574Dokumen3 halaman574Farah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- 05 - DR - Dominicus - PELATIHAN DIFTERI TANGERANG 07 Jan 2018 - Tatalaksana - SharedDokumen48 halaman05 - DR - Dominicus - PELATIHAN DIFTERI TANGERANG 07 Jan 2018 - Tatalaksana - SharedArainy TikaBelum ada peringkat
- Marijuana and The Psychiatric Patient - Page 1 of 2 - PsychiatricDokumen4 halamanMarijuana and The Psychiatric Patient - Page 1 of 2 - PsychiatricFarah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- Wilcoxon Film: RanksDokumen2 halamanWilcoxon Film: RanksFarah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar PustakaDokumen1 halamanDaftar PustakaFarah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- Amiodaron Sebagai Obat Anti Aritmia Dan Pengaruhnya Terhadap Fungsi TiroidDokumen11 halamanAmiodaron Sebagai Obat Anti Aritmia Dan Pengaruhnya Terhadap Fungsi TiroidFarah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- Hybrid Rhythm Control Therapy: 12.1 Combining Antiarrhythmic Drugs and Catheter AblationDokumen14 halamanHybrid Rhythm Control Therapy: 12.1 Combining Antiarrhythmic Drugs and Catheter AblationFarah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- 574Dokumen3 halaman574Farah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- Marijuana in The Workplace: Guidance For Occupational Health Professionals and EmployersDokumen7 halamanMarijuana in The Workplace: Guidance For Occupational Health Professionals and EmployersFarah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- Cannabis and ShizoDokumen2 halamanCannabis and ShizoFarah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- Ijms 18 01689Dokumen14 halamanIjms 18 01689Farah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- Persepsi Mahasiswa Dan Mahasiswi Akuntan PDFDokumen17 halamanPersepsi Mahasiswa Dan Mahasiswi Akuntan PDFFarah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- Nutritional Management of A Critically Injured Patient: SASPEN Case StudyDokumen4 halamanNutritional Management of A Critically Injured Patient: SASPEN Case StudyCitra KristiBelum ada peringkat
- 20 60 1 PB PDFDokumen11 halaman20 60 1 PB PDFFarah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- 14 Bold ContrastDokumen2 halaman14 Bold ContrastFarah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- Uji Wilcoxon FarahDokumen2 halamanUji Wilcoxon FarahFarah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- 4-InTOSAI S Comments On Revised COSODokumen6 halaman4-InTOSAI S Comments On Revised COSOFarah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- DISFAGIA, Inkontinen Dan Konstipasi, Kuliah UntanDokumen84 halamanDISFAGIA, Inkontinen Dan Konstipasi, Kuliah UntanFarah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- 4-InTOSAI S Comments On Revised COSODokumen6 halaman4-InTOSAI S Comments On Revised COSOFarah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- Neurofisiologi 2 Handout 1Dokumen6 halamanNeurofisiologi 2 Handout 1Farah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- Latihan Tpa SNMPTN 2011 KunciDokumen1 halamanLatihan Tpa SNMPTN 2011 KunciRoland LambaBelum ada peringkat
- Neuroanatomi 2011Dokumen51 halamanNeuroanatomi 2011Farah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- Ciri-Ciri Media Cetak (Jurnal)Dokumen2 halamanCiri-Ciri Media Cetak (Jurnal)Farah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- Molecular Diagnostic1Dokumen60 halamanMolecular Diagnostic1Farah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- Ciri-Ciri Media Cetak (Jurnal)Dokumen2 halamanCiri-Ciri Media Cetak (Jurnal)Farah MuthiaBelum ada peringkat
- Neuroplasticity: Presented By: Advincula, Arnina Fortus, Jacyrone Pitpit, MarcusDokumen17 halamanNeuroplasticity: Presented By: Advincula, Arnina Fortus, Jacyrone Pitpit, MarcusCLAIRE DENISSE DEVISBelum ada peringkat
- Danielle S. Bassett, PH.D.: Academic EmploymentDokumen41 halamanDanielle S. Bassett, PH.D.: Academic EmploymentConstantin Von TsirlenBelum ada peringkat
- VertigoDokumen41 halamanVertigoAnonymous 4Oe8clFY100% (1)
- Ieee AUTOMATIC NUMBER-PLATE RECOGNITION VNIS.1994.396858-NEURAL NETWORK APPROACHDokumen3 halamanIeee AUTOMATIC NUMBER-PLATE RECOGNITION VNIS.1994.396858-NEURAL NETWORK APPROACHEdikan AkpanBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of The EarDokumen8 halamanAnatomy of The EarDarkAngelBelum ada peringkat
- Pinocchio SyndromeDokumen1 halamanPinocchio SyndromeTakeshi ClairBelum ada peringkat
- Febrile SeizureDokumen32 halamanFebrile SeizureShiva Valeska ArdhaniswariBelum ada peringkat
- Symptoms: SchizophreniaDokumen5 halamanSymptoms: SchizophreniaPugsley AddamsBelum ada peringkat
- Topographic Anatomy of Basal NucleiDokumen44 halamanTopographic Anatomy of Basal NucleiRafique AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Neurological Channelopathies: ReviewDokumen14 halamanNeurological Channelopathies: ReviewPanduRespatiBelum ada peringkat
- Brain Fog PDFDokumen1 halamanBrain Fog PDFRomina Faur CapparelliBelum ada peringkat
- FOUR Score Coma ScaleDokumen32 halamanFOUR Score Coma ScaleAndriawan BramBelum ada peringkat
- Ischialgia 4yuli FixDokumen20 halamanIschialgia 4yuli FixLindapratama SaifuddinBelum ada peringkat
- The 7 Main Outer Organs of the Human BodyDokumen17 halamanThe 7 Main Outer Organs of the Human BodySalsabilaBelum ada peringkat
- Spinal Tracts (Ascending & Descending)Dokumen9 halamanSpinal Tracts (Ascending & Descending)jcee90210Belum ada peringkat
- Corticospinal Tract Practice QuestionsDokumen2 halamanCorticospinal Tract Practice QuestionsAlexaBelum ada peringkat
- Factors influencing creativity and innovation--- creativityDokumen19 halamanFactors influencing creativity and innovation--- creativityvlkanteti5258Belum ada peringkat
- Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) "Stroke": Ma. Tosca Cybil A. Torres, RN, MANDokumen53 halamanCerebrovascular Accident (CVA) "Stroke": Ma. Tosca Cybil A. Torres, RN, MANMa Tosca Cybil TorresBelum ada peringkat
- The Central ner-WPS OfficeDokumen2 halamanThe Central ner-WPS OfficeMargareth Bonita PasaribuBelum ada peringkat
- Ice TherapyDokumen5 halamanIce TherapyDiane CastillonBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous Tissue P PXDokumen13 halamanNervous Tissue P PXAbet SiaBelum ada peringkat
- PhysiocoursesDokumen5 halamanPhysiocoursesasdar fajrinBelum ada peringkat
- Brain 1963 PENFIELD 595 696Dokumen102 halamanBrain 1963 PENFIELD 595 696Leroy FinkleBelum ada peringkat
- Visual Pathway - Neurology - Medbullets Step 1Dokumen5 halamanVisual Pathway - Neurology - Medbullets Step 1Andi.Roem_97Belum ada peringkat
- Topografska anatomija moždane kore i limbičkih područjaDokumen194 halamanTopografska anatomija moždane kore i limbičkih područjaGoran SimicBelum ada peringkat
- Brain-Based Models of Developmental Language DisordersDokumen19 halamanBrain-Based Models of Developmental Language DisordersЈован Д. РадовановићBelum ada peringkat