1017mm in Hogging Region 2304mm in Sagging Region: C S CT
Diunggah oleh
aurea_yansikuJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1017mm in Hogging Region 2304mm in Sagging Region: C S CT
Diunggah oleh
aurea_yansikuHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
1
Tutorial 1 serviceability (due Friday August 15
th
by 5pm)
Only online submissions will be marked.
Marked question
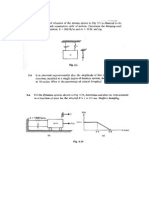
1. The beam shown in Figure 1 forms part of the floor system of an RC building designed to
carry a calculated dead load of 24kN/m and a service live load of 48kN/m. Of the total live
load 20% is sustained in nature and 80% is applied only intermittently over the structures
lifetime.
The beam will support non-structural partitions which that will be damaged if large
deflections were to take place. The partitions will be installed shortly after construction
shoring is removed and dead loads take effect, but before significant creep takes place.
Calculate the total deflection that would adversely affect the partitions, i.e. the sum of the
long-term deflection due to the dead and partial live load, plus the immediate deflection due
to the non-sustained part of the live load.
HINT: Consider the long and short term components of the dead and live load and their
influence on the deflection when the partition is in place.
Short term dead load occurs before partition is in place because shoring is
removed before partition construction, i.e. no influence on partition
Long term dead load occurs after partition is in place i.e. influences partitions
Short and long term live load occur after partition is in place i.e. influences
partitions.
NOTE: As the shrinkage strain is not known take the cracking moment as
Figure 1
1017mm in hogging region
2304mm in sagging region
2
2
1900mm
E =25000MPa
c
7600mm
360mm
130mm
620mm
60mm
60mm
E =200GPa
s
f =3.3MPa
ct
2
Additional study problems
2. Determine the immediate and long-term deflections of the beam in Figure 2. The beams are
spaced at 8m centres. The total dead load, including the weight of the beam is 6.3kPa
including the weight of the beam and the live load is 4.8kPa of which 20% is sustained.
Figure 2
3. Given a short term service load of 50kN/m and a sustained service load of 48kN/m is applied
to the beam in Figure 3 determine:
a. The immediate and long term deflection at the free end of cantilever AB
b. The immediate and long term deflection at the mid-span of BC
Figure 3
9N24 920mm
560mm
E=24000MPa
c
cover from centre
of reinforcement
60mm
E =200GPa
s
10m
4800mm
2
3400mm
2
2600mm
E =25000
c
4000mm 14000mm
A B C
400mm
140mm
700mm
E=24000MPa
c
cover from centre
of reinforcement
60mm
E =200GPa
s
3
4. Calculate the maximum crack width for the beam in Figure 4 for a sagging moment of
350kNm.
Figure 4
Foundation skills practice (problems from 2
nd
year structural design)
Determine the flexural rigidity of the uncracked and cracked sections in Figure 5.
Figure 5
300mm
120mm
800mm
E=30100MPa
c
e* =600E-6
f =2.8MPa
cs
ct
E =200GPa
s
A = 3720mm
(6N28)
st
2
1000mm
60mm
30mm
90mm
A = 2170mm
(7N20)
st
2
300mm
150mm
650mm
E=20000MPa
c
cover from centre
of reinforcement
50mm
E =200GPa
s
A = 3000mm
st
2
25mm
250mm
150mm
300mm
A = 602mm
A = 300mm
E =26250MPa
E =210GPa
st
sc
c
s
2
2
1000mm
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- 04a QUTStudentBeam PDFDokumen25 halaman04a QUTStudentBeam PDFaurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Critical ReviewDokumen4 halamanCritical ReviewChendie ChantiqueBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- CONTOH Critical ReviewsDokumen10 halamanCONTOH Critical ReviewsFadhlina IshakBelum ada peringkat
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- HW Solution w1 Jan8-Jan10Dokumen6 halamanHW Solution w1 Jan8-Jan10patyBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Microstran 2013 v8 11 130225Dokumen1 halamanMicrostran 2013 v8 11 130225aurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- RR 405Dokumen80 halamanRR 405aurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- 018 PDFDokumen6 halaman018 PDFaurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Tutorial 1Dokumen2 halamanTutorial 1aurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Lecture Note Blast2015Dokumen97 halamanLecture Note Blast2015aurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- HW Solution w1 Jan8-Jan10Dokumen6 halamanHW Solution w1 Jan8-Jan10patyBelum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Tutorial 3 2015Dokumen2 halamanTutorial 3 2015aurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- 4100 1998 PDFDokumen11 halaman4100 1998 PDFaurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- 018 PDFDokumen6 halaman018 PDFaurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Report To ITEM NO. 2.6 Meeting Date Subject Southern Peninsula Aquatic Centre Geotechnical Investigation Prepared by Authorised by Attachment (S)Dokumen3 halamanReport To ITEM NO. 2.6 Meeting Date Subject Southern Peninsula Aquatic Centre Geotechnical Investigation Prepared by Authorised by Attachment (S)aurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- SeismicDokumen23 halamanSeismicHassan Anis Yamout100% (2)
- Lab 3 - Masonry Laboratory Operations - Determine Bond StrengthDokumen2 halamanLab 3 - Masonry Laboratory Operations - Determine Bond Strengthaurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- 01 - Solution To in Class ProblemDokumen4 halaman01 - Solution To in Class Problemaurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Solutions To Question 3,5,6Dokumen8 halamanSolutions To Question 3,5,6aurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Tute 2Dokumen2 halamanTute 2aurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Tute 1Dokumen3 halamanTute 1aurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- TEST1 SolutionsDokumen9 halamanTEST1 Solutionsaurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- Diagonal Shear Strength of Unreinforced Masonry Wallettes Retrofitted Using Twisted Steel BarsDokumen23 halamanDiagonal Shear Strength of Unreinforced Masonry Wallettes Retrofitted Using Twisted Steel Barsaurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- Lifestyles Life, Leisure LifeDokumen4 halamanLifestyles Life, Leisure Lifeaurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- Recent Developments in The Design and Construction of Concrete Structures Incorporating Low-Ductility Steel ReinforcementDokumen10 halamanRecent Developments in The Design and Construction of Concrete Structures Incorporating Low-Ductility Steel Reinforcementaurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- The Master of EngineeringDokumen17 halamanThe Master of Engineeringaurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- Keeping Fit IinDokumen7 halamanKeeping Fit Iinaurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- Fulbright-Dikti Scholarship Programs Preliminary Application FormDokumen6 halamanFulbright-Dikti Scholarship Programs Preliminary Application Formaurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (120)
- Japanese SubcultureDokumen2 halamanJapanese Subcultureaurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- JourneyDokumen1 halamanJourneyaurea_yansikuBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ Cell InjuryDokumen19 halamanMCQ Cell InjuryMoaz EbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- Uric Acid Mono SL: Clinical SignificanceDokumen2 halamanUric Acid Mono SL: Clinical SignificancexlkoBelum ada peringkat
- Ott OTT Ecolog 1000 Water Level LoggerDokumen3 halamanOtt OTT Ecolog 1000 Water Level LoggerNedimZ1Belum ada peringkat
- Employee Leave PolicyDokumen3 halamanEmployee Leave Policyladdu30Belum ada peringkat
- Week 4 (Theories)Dokumen15 halamanWeek 4 (Theories)Erica Velasco100% (1)
- Coiled Tubing Safety Impact Firing Head (HP) - by DynaDokumen16 halamanCoiled Tubing Safety Impact Firing Head (HP) - by DynamahsaBelum ada peringkat
- Full Download Small Animal Care and Management 4th Edition Warren Test BankDokumen35 halamanFull Download Small Animal Care and Management 4th Edition Warren Test Bankkrzyszhugvik6100% (20)
- Purpose in Life Is A Robust Protective Factor of Reported Cognitive Decline Among Late Middle-Aged Adults: The Emory Healthy Aging StudyDokumen8 halamanPurpose in Life Is A Robust Protective Factor of Reported Cognitive Decline Among Late Middle-Aged Adults: The Emory Healthy Aging StudyRaúl AñariBelum ada peringkat
- T103 InstructionsDokumen1 halamanT103 Instructionsjtcool74Belum ada peringkat
- Project Report On MKT Segmentation of Lux SoapDokumen25 halamanProject Report On MKT Segmentation of Lux Soapsonu sahBelum ada peringkat
- Consolidation of ClayDokumen17 halamanConsolidation of ClayMD Anan MorshedBelum ada peringkat
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Air MassesDokumen22 halamanAir MassesPrince MpofuBelum ada peringkat
- Supply ForecastingDokumen17 halamanSupply ForecastingBhavesh RahamatkarBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd Term Biology Ss3Dokumen20 halaman2nd Term Biology Ss3Wisdom Lawal (Wizywise)Belum ada peringkat
- Respiratory Examination - Protected 1Dokumen4 halamanRespiratory Examination - Protected 1anirudh811100% (1)
- Science Form 3 2020 (Notes, PBD, Exercise) : Chapter: 8 RadioactivityDokumen19 halamanScience Form 3 2020 (Notes, PBD, Exercise) : Chapter: 8 Radioactivitysakinah100% (1)
- Lpalmer ResumeDokumen4 halamanLpalmer Resumeapi-216019096Belum ada peringkat
- Red Bank Squadron - 01/22/1942Dokumen28 halamanRed Bank Squadron - 01/22/1942CAP History LibraryBelum ada peringkat
- CGMP Training ToolDokumen21 halamanCGMP Training Toolbabusure99Belum ada peringkat
- Tarot Cards: Cheat SheetDokumen1 halamanTarot Cards: Cheat SheetDipti100% (7)
- DM - BienAir - CHIROPRO 980 - EngDokumen8 halamanDM - BienAir - CHIROPRO 980 - Engfomed_twBelum ada peringkat
- Cough: A Rapid Expulsion of Air FromDokumen2 halamanCough: A Rapid Expulsion of Air FromaubyangBelum ada peringkat
- 4.section 3 - Routine MaintenanceDokumen96 halaman4.section 3 - Routine MaintenanceMyo minBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluation of Whole-Body Vibration (WBV) On Ready Mixed Concrete Truck DriversDokumen8 halamanEvaluation of Whole-Body Vibration (WBV) On Ready Mixed Concrete Truck DriversmariaBelum ada peringkat
- Maxs AdultDokumen1 halamanMaxs Adultclark lopezBelum ada peringkat
- Installation and Operation Manual: Proact™ Ii Electric Powered Actuator and DriverDokumen32 halamanInstallation and Operation Manual: Proact™ Ii Electric Powered Actuator and DriverDjebali MouradBelum ada peringkat
- LivingScience CBSE CompanionDokumen56 halamanLivingScience CBSE Companionnjlenovo95% (19)
- 2012 U.S. History End-of-Course (EOC) Assessment Field Test Fact SheetDokumen2 halaman2012 U.S. History End-of-Course (EOC) Assessment Field Test Fact SheetswainanjanBelum ada peringkat
- Epidemiology of Injury in Powerlifting: Retrospective ResultsDokumen2 halamanEpidemiology of Injury in Powerlifting: Retrospective ResultsJavier Estelles MuñozBelum ada peringkat
- Mcdes 1Dokumen7 halamanMcdes 1JerdBelum ada peringkat