Tri-Fold Template-1
Diunggah oleh
api-260947636Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Tri-Fold Template-1
Diunggah oleh
api-260947636Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Mitosis
VS
Meiosis
how mitosis and meiosis
are diferent
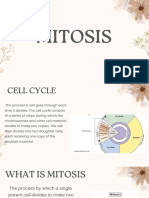
Cells divide and reproduce in two ways:
mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is a process of
cell division that results in two genetically
identical daughter cells developing from a
single parent cell. Meiosis, on the other
hand, is the division of a germ cell involving
two fssions of the nucleus and giving rise
to four gametes, or sex cells, each possess-
ing half the number of chromosomes of the
original cell.
Mitosis is used by single-celled organisms
to reproduce; it is also used for the organic
growth of tissues, fbers, and membranes.
Meiosis is found in sexual reproduction of
organisms. The male and female sex cells
(i.e., egg and sperm) combine to create
new, genetically diferent ofspring.
Citations
http://whttp://www.difen.com/difer-
ence/Meiosis_vs_Mitosis
www.upt.pitt.edu/ntress/Bio1_Lab_Man-
ual_New/mitosis_and_meiosis.htm
Function of mitosis
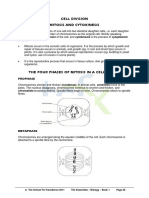
Mitosis have 4 main phases it goes through called , prophase -During prophase, the frst phase of mitosis, the chromosomes condense (shorten) and become
visible when stained and viewed under a microscope. During the latter part of prophase, the nuclear membrane disappears and the newly formed spindle
fbers attach to a region of the centromere called the kinetochore.
Metaphase -During metaphase, the spindle fbers move the replicated chromosomes to the middle of the cell where they line up in single fle along the equa-
torial plane.
Anaphase -During anaphase, the sister chromatids are "pulled" apart (separated) and move towards opposite poles of the cell. The separated chromatids are
now called daughter
chromosomes. Telophase -During telophase, the last phase of mitosis, the spindle apparatus disappears and nuclei reform around each set of daughter chro-
mosomes. Cytokinesis also occurs during telophase. In animal cells, a cleavage furrow forms and eventually divides the cytoplasm in half among the two
daughter cells. In vplant cells, cytokinesis is accomplished with the formation of the cell plate.
Function of meiosis
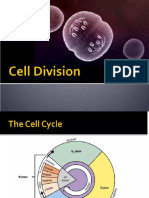
Prior to the initiation of mitosis or meiosis, the cell must duplicate its chromosomes and manufacture the materials needed for cell division. This is accom-
plished in a phase that precedes cell division known as interphase. Interphase can be divided into three phases. In the frst, called the Gl phase, the cell carries
out its basic functions and performs specialized activities. In the second period of interphase, the S phase, each chromosome in the nucleus is replicated so that
there are now two identical copies of each chromosome. Identical chromosomes are attached to each other by way of a centromere. When attached by their
centromeres, chromosomes are referred to as chromatids. In plants, the mitotic spindle is also formed during the S phase. In animal cells, a pair of centrioles
duplicates to form two pairs of centrioles. Like the mitotic spindle in plants, the centrioles will form spindle fbers. Spindle fbers are composed of microtubules
and are used to pull the duplicated chromosomes apart during cell division. In the third period of interphase, the G2 phase, proteins and structures that will be
used during mitosis or meiosis, are synthesized. After the G2 phase has been completed, the cell can then undergo mitosis or meiosis.
What is mitosis & meiosis ?
According to the Cell Theory, all living cells arise from preexisting cells. The process whereby new cells are formed is called cell division or
mitosis, which involves the division of the cell's nucleus (karyokinesis) and the cytoplasm (cytokinesis). Mitosis results in the production of two
genetically identical daughter cells. Formation of an adult organism from a fertilized egg, regeneration, and the repair of tissues are all accom-
plished by mitosis. Meiosis
In animals that reproduce sexually, the production of sex cells or gametes (i.e., eggs and sperm), requires that each parent's chromosomes be
reduced by one half the normal number. Reducing the parent's chromosome number from the diploid (2n) number (46 in humans) to the haploid
(n) number (23 in humans) is accomplished by a type of cell division known as meiosis.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Week 5 Mitosis and MiosisDokumen11 halamanWeek 5 Mitosis and MiosisEarl RénzBelum ada peringkat
- Bio 001 Cell DivisionDokumen8 halamanBio 001 Cell DivisionKnick KnackBelum ada peringkat
- mitosis-WPS OfficeDokumen5 halamanmitosis-WPS OfficeSheila Mae AramanBelum ada peringkat
- Mitosis and Meiosis: TranscriptDokumen2 halamanMitosis and Meiosis: TranscriptKareem AghaBelum ada peringkat
- HDTD-B-7 - Cell DivisionsDokumen43 halamanHDTD-B-7 - Cell DivisionsMariam QaisBelum ada peringkat
- SZL B206 Principles of GeneticsDokumen28 halamanSZL B206 Principles of Geneticsawuors249Belum ada peringkat
- Folio Kerja Kursus Biology SPMDokumen29 halamanFolio Kerja Kursus Biology SPMzam_ir100% (2)
- Cell Division - Key PointsDokumen10 halamanCell Division - Key PointssivarajeshwarBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Cell Cycle, Mitosis and MeiosisDokumen55 halaman3 Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosisapi-19641337Belum ada peringkat
- Cell DivisionDokumen6 halamanCell DivisionAbdallah AlasalBelum ada peringkat
- Cell DivisionDokumen2 halamanCell DivisionedukahonBelum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen1 halamanUntitledsuckamaBelum ada peringkat
- Mitosis DefinitionDokumen19 halamanMitosis DefinitionMar Delos ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- MITOSISDokumen18 halamanMITOSISEdryan LambiquitBelum ada peringkat
- Science 8 Q4 L2Dokumen5 halamanScience 8 Q4 L2Sheila mae CadiaoBelum ada peringkat
- The Cell Cycle-TRFDokumen8 halamanThe Cell Cycle-TRFmaniiiiiiiiBelum ada peringkat
- Module 2 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDokumen9 halamanModule 2 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionBalolot RalphBelum ada peringkat
- Cell DivisionDokumen17 halamanCell DivisionGenevieve GanubBelum ada peringkat
- Misconceptions On Mitosis and MeiosisDokumen2 halamanMisconceptions On Mitosis and MeiosisEdcademiaBelum ada peringkat
- Biosciweek6 11Dokumen43 halamanBiosciweek6 11Jesalyn AbrinicaBelum ada peringkat
- Science8 Q4 M2Dokumen6 halamanScience8 Q4 M2Arabella BaldonadoBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Cycle LectureDokumen3 halamanCell Cycle LectureR Jay LagdaminBelum ada peringkat
- WEEK7 ModuleLec&LabDokumen17 halamanWEEK7 ModuleLec&LabMaricris GatdulaBelum ada peringkat
- B.SC., 2 Year, 3 Semester Paper-III: Cell Biology, Genetics and Immunology Cell DivisionDokumen24 halamanB.SC., 2 Year, 3 Semester Paper-III: Cell Biology, Genetics and Immunology Cell DivisionLAZY I LEoPARDBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Division LessonDokumen9 halamanCell Division LessonGerry100% (1)
- CELL DIVISION-MitosisDokumen28 halamanCELL DIVISION-MitosisAVINASH VARMABelum ada peringkat
- The Cell CycleDokumen3 halamanThe Cell CycleAngelooBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 4Dokumen8 halamanLesson 4Marie Antonette BaligodBelum ada peringkat
- Cell CycleDokumen111 halamanCell Cyclepreyaaa pascuaBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Division: Dr. P. Pokorski University of Michigan - Dearborn Department of BiologyDokumen52 halamanCell Division: Dr. P. Pokorski University of Michigan - Dearborn Department of BiologyZuha HarithBelum ada peringkat
- Final Examination-BiologyDokumen15 halamanFinal Examination-BiologyAlliah MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Week 2Dokumen8 halamanWeek 2lilyrosemary.masilangBelum ada peringkat
- Cell DivisionDokumen8 halamanCell DivisionNusrat ShoshiBelum ada peringkat
- Cell DivisionDokumen8 halamanCell DivisionAlbert Delos SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDokumen7 halamanMitosis Vs MeiosisJD DX100% (1)
- Module 2 Meiosis and MitosisDokumen88 halamanModule 2 Meiosis and MitosisSevdred CadelinaBelum ada peringkat
- Eukaryotic CellsDokumen6 halamanEukaryotic CellsbaneBelum ada peringkat
- BIO T4 KSSM Chapter 6 - DLPDokumen62 halamanBIO T4 KSSM Chapter 6 - DLPcikguana79Belum ada peringkat
- MitosisDokumen15 halamanMitosisJorge MurieteBelum ada peringkat
- MitosisDokumen3 halamanMitosisLea Mari JavierBelum ada peringkat
- The Cell CycleDokumen9 halamanThe Cell Cyclesalahuddin_md5935Belum ada peringkat
- Mitosis and Meiosis: Emmel, Keisya, Florencia, Joci, Joseph 9BDokumen23 halamanMitosis and Meiosis: Emmel, Keisya, Florencia, Joci, Joseph 9BJoshlyn AnnabelleBelum ada peringkat
- Mitosis Is A Process Where A Single Cell Divides Into Two Identical Daughter Cells (Cell Division)Dokumen10 halamanMitosis Is A Process Where A Single Cell Divides Into Two Identical Daughter Cells (Cell Division)Holly Mc Kenzie Layson DalmanBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment in Science: Jeamnard Balitaan II-ShakespeareDokumen7 halamanAssignment in Science: Jeamnard Balitaan II-ShakespeareCatherine PagdonsolanBelum ada peringkat
- 4.2 Cell As A Unit of LifeDokumen7 halaman4.2 Cell As A Unit of Lifehola adiosBelum ada peringkat
- Cell CycleDokumen12 halamanCell CycleRusselBelum ada peringkat
- HeredityDokumen2 halamanHeredityAngelika TibayanBelum ada peringkat
- BiologyDokumen17 halamanBiologyMuskan ShreeBelum ada peringkat
- GenbioDokumen3 halamanGenbioMhariane MabborangBelum ada peringkat
- M3 Writing AnalysisDokumen4 halamanM3 Writing AnalysisGood ChannelBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5Dokumen14 halamanChapter 5ingridvirginia2006Belum ada peringkat
- Mitosis and MeiosisDokumen13 halamanMitosis and MeiosisS3 Oxibillo, Gabriel Dominic C.Belum ada peringkat
- Bio SciDokumen3 halamanBio ScilowdicakesBelum ada peringkat
- Cell DivisionDokumen27 halamanCell DivisionLavinia DonaldBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Cell DivisionDokumen1 halamanWhat Is Cell Divisiongenemari gonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Cytogenetics Mitosis & Meiosis and Their DiferrencesDokumen11 halamanCytogenetics Mitosis & Meiosis and Their DiferrencesGeemilReyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5: Cellular ReproductionDokumen3 halamanChapter 5: Cellular ReproductionDarwin Competente LagranBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure and Cell DivisionDokumen70 halamanCell Structure and Cell DivisionAMALIA INDAH ALLIZA ALLIZABelum ada peringkat
- Vic Sample Notes BiologyDokumen20 halamanVic Sample Notes BiologyEvangelene Esquillo SanaBelum ada peringkat
- Civil EngineeringDokumen7 halamanCivil Engineeringapi-260947636Belum ada peringkat
- 3 0 KT KeytermsDokumen2 halaman3 0 KT Keytermsapi-291998889Belum ada peringkat
- 1 1 KT KeytermsDokumen2 halaman1 1 KT Keytermsapi-291531815Belum ada peringkat
- Design ProposalDokumen1 halamanDesign Proposalapi-260947636Belum ada peringkat
- PosterDokumen1 halamanPosterapi-260947636Belum ada peringkat
- Research and Reference Photos 32Dokumen2 halamanResearch and Reference Photos 32api-260947636Belum ada peringkat
- Sound Card Fnished PDFDokumen1 halamanSound Card Fnished PDFapi-260947636Belum ada peringkat
- Layout TechniquesDokumen8 halamanLayout Techniquesapi-260947636Belum ada peringkat
- Color Booklet 2Dokumen6 halamanColor Booklet 2api-260947636Belum ada peringkat
- Design MixDokumen1 halamanDesign Mixapi-260947636Belum ada peringkat
- Analyzing Graph DataDokumen2 halamanAnalyzing Graph Dataapi-260947636Belum ada peringkat
- PlagiarismDokumen1 halamanPlagiarismapi-260947636Belum ada peringkat
- Hot TopicsDokumen12 halamanHot Topicsapi-260947636Belum ada peringkat
- Copyright PosterDokumen1 halamanCopyright Posterapi-260947636Belum ada peringkat
- Renaldo Waldron 7.31.14: Southeast RaleighDokumen6 halamanRenaldo Waldron 7.31.14: Southeast Raleighapi-260947636Belum ada peringkat
- 2013 Fall Buying A Laptop RevisedDokumen2 halaman2013 Fall Buying A Laptop Revisedapi-260947636Belum ada peringkat
- Design of Corn ThresherDokumen11 halamanDesign of Corn ThresherFrancisco ToroBelum ada peringkat
- Grammar For TOEFLDokumen23 halamanGrammar For TOEFLClaudia Alejandra B0% (1)
- Wetlands Denote Perennial Water Bodies That Originate From Underground Sources of Water or RainsDokumen3 halamanWetlands Denote Perennial Water Bodies That Originate From Underground Sources of Water or RainsManish thapaBelum ada peringkat
- Espn NFL 2k5Dokumen41 halamanEspn NFL 2k5jojojojo231Belum ada peringkat
- Water and Wastewater For Fruit JuiceDokumen18 halamanWater and Wastewater For Fruit JuiceJoyce Marian BelonguelBelum ada peringkat
- DMSCO Log Book Vol.25 1947Dokumen49 halamanDMSCO Log Book Vol.25 1947Des Moines University Archives and Rare Book RoomBelum ada peringkat
- Organizational Behavior (Perception & Individual Decision Making)Dokumen23 halamanOrganizational Behavior (Perception & Individual Decision Making)Irfan ur RehmanBelum ada peringkat
- Hypnosis ScriptDokumen3 halamanHypnosis ScriptLuca BaroniBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Control SystemDokumen9 halamanIntroduction To Control SystemAbdulhakam Abubakar YusufBelum ada peringkat
- MC Donald'sDokumen30 halamanMC Donald'sAbdullahWaliBelum ada peringkat
- Purposeful Activity in Psychiatric Rehabilitation: Is Neurogenesis A Key Player?Dokumen6 halamanPurposeful Activity in Psychiatric Rehabilitation: Is Neurogenesis A Key Player?Utiru UtiruBelum ada peringkat
- Entrepreneurial Skills and Intention of Grade 12 Senior High School Students in Public Schools in Candelaria Quezon A Comprehensive Guide in Entrepreneurial ReadinessDokumen140 halamanEntrepreneurial Skills and Intention of Grade 12 Senior High School Students in Public Schools in Candelaria Quezon A Comprehensive Guide in Entrepreneurial ReadinessAngelica Plata100% (1)
- Logic of English - Spelling Rules PDFDokumen3 halamanLogic of English - Spelling Rules PDFRavinder Kumar80% (15)
- CAPE Env. Science 2012 U1 P2Dokumen9 halamanCAPE Env. Science 2012 U1 P2Christina FrancisBelum ada peringkat
- People Vs Felipe Santiago - FCDokumen2 halamanPeople Vs Felipe Santiago - FCBryle DrioBelum ada peringkat
- SQ1 Mogas95Dokumen1 halamanSQ1 Mogas95Basant Kumar SaxenaBelum ada peringkat
- CURRENT DEVELOPMENT OF SLAG VALORISATION IN ChinaDokumen13 halamanCURRENT DEVELOPMENT OF SLAG VALORISATION IN ChinaHung LeBelum ada peringkat
- HTTP Parameter PollutionDokumen45 halamanHTTP Parameter PollutionSpyDr ByTeBelum ada peringkat
- Equivalence ProblemsDokumen2 halamanEquivalence ProblemsRomalyn GalinganBelum ada peringkat
- Tour Guiding and Escort Services - 301Dokumen95 halamanTour Guiding and Escort Services - 301Zane 19531Belum ada peringkat
- Field Assignment On Feacal Sludge ManagementDokumen10 halamanField Assignment On Feacal Sludge ManagementSarah NamyaloBelum ada peringkat
- ISIS Wood Product Solutions Selects Cloud-Hosting Partner Real Cloud Solutions LLCDokumen2 halamanISIS Wood Product Solutions Selects Cloud-Hosting Partner Real Cloud Solutions LLCdevaprBelum ada peringkat
- Charles P. Jones, Investments: Analysis and Management, Eleventh Edition, John Wiley & SonsDokumen20 halamanCharles P. Jones, Investments: Analysis and Management, Eleventh Edition, John Wiley & SonsRizki AuliaBelum ada peringkat
- Grafton Business Services 2023Dokumen61 halamanGrafton Business Services 2023Vigh ZsoltBelum ada peringkat
- Ignorance Is The Curse of God. Knowledge Is The Wing Wherewith We Fly To Heaven."Dokumen3 halamanIgnorance Is The Curse of God. Knowledge Is The Wing Wherewith We Fly To Heaven."Flori025Belum ada peringkat
- FPSCDokumen15 halamanFPSCBABER SULTANBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Financial PlanDokumen38 halamanSample Financial PlanPatrick IlaoBelum ada peringkat
- Narrative ReportDokumen6 halamanNarrative ReportAlyssa Marie AsuncionBelum ada peringkat
- Chain of CommandDokumen6 halamanChain of CommandDale NaughtonBelum ada peringkat
- Marriage Families Separation Information PackDokumen6 halamanMarriage Families Separation Information PackFatima JabeenBelum ada peringkat