Isis Intro To Imf
Diunggah oleh
api-266827271Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Isis Intro To Imf
Diunggah oleh
api-266827271Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Presentation by Lauren Johnson
Who?
Names
ISIS: Islamic State in Iraq and Syria (more common
name)
ISIL: Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant
Levant: region spanning from southern Turkey to Egypt
and including Syria, Lebanon, Israel, the Palestinian
territories and Jordan
What?
Terrorist and insurgent organization
Insurgent: Rebel or revolutionary
Group that broke away from al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda: a radical Islamic group organized by Osama
bin Laden in the 1990s to engage in terrorist activities.
Carried out 9/11 attack on the US.
Sunni militants seeking to form a pure Islamic
state. Thus, concentrated on territorial gains in
the Middle East.
Hostile to America, Americas allies, and Shia
Muslims
Sunni vs Shia
The divide between Sunni and Shia Muslims
originates in dispute after death of Prophet
Muhammad over who should lead Muslim
community.
Sunni Muslims regard themselves as the
traditionalist branch of Islam.
The great majority of Muslims are Sunnis -
estimates suggest the figure is somewhere
between 85% and 90%.
Where?
The Middle East
ISIS
Country Profiles
Government Parliamentary democracy
Mix of civil and Islamic law
History of political corruption (i.e.
Saddam Hussein)
Authoritarian regime
Mix of civil and Islamic law
Economy State-run economy dominated by oil
sector, which provides more than
90% of government revenue
Economy continues to deteriorate
due to ongoing conflict that began in
2011
Social Official religion = Islam (99%)
60%-65% Shia
32%-37% Sunni
Official religion = Islam 87%
74% Sunni
History Gained independence in 1932 Gained independence in 1946
Geography Mostly desert with northern
mountainous regions
Mostly desert
Timeline
ISIS has existed under various names and in various forms since early
1990s
By 2004: Merged with al-Qaeda and named itself al-Qaeda in Iraq, or AQI.
Since the withdrawal of U.S. forces from Iraq in late 2011, the group has
increased attacks on mainly Shiite targets
2013: Increasing violence 2013 leaves early eight thousand civilians dead,
making it Iraqs bloodiest year since 2008
February 2014: al-Qaeda disavows ISIS due to ferocity of its tactics
Disavow: deny any responsibility or support for an individual or group
Why the Concern about ISIS?
Made news in the past few months for:
Dramatic military conquest of Iraqi territory
Ruthless treatment of Iraqi minorities
Multiple videotaped beheadings of Western hostages
Noted for their sophisticated, calculated attacks in the past year. Attacks
include:
Prison breaks (ex. Abu Ghraib _
Police stations
Military checkpoints
Assassinations of local officials and reporters (crippling local agents of
government, allowing ISIS to seize control)
ISISs operational potential comes from its unprecedented wealth
Why the Concern about ISIS?
Presents a continuing humanitarian crisis,
with millions of people fleeing for their lives (i.e.
Iraqi and Syrian refugee crises)
Hundreds of thousands being killed.
Presents a threat to Middle East stability, as ISIS
seeks to erase modern borders between
countries and impose its own version of
fundamentalist law
Fundamentalism a form of a religion that upholds
belief in the strict, literal interpretation of scripture.
Current Action Against ISIS
US lead airstrikes
http://www.theguardian.com
/world/2014/sep/10/obama-
speech-authorise-air-strikes-
against-isis-syria
Airstriker supporters: Saudi
Arabia, Jordan, United Arab
Emirates, Bahrain, Qatar
UN Sanctions
Security Council blacklisted
members of ISIS)
Blacklist means these
individuals will be subject to
international travel ban, asset
freeze and arms embargo
Sources
http://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-27994277
http://www.hscentre.org/middle-east-and-north-
africa/isis-background-ideology-capabilities/
http://www.theatlantic.com/international/archive/2014/08
/isis-a-short-history/376030/
http://www.pbs.org/newshour/rundown/what-is-islamic-
state-iraq-and-syria/
https://www.cia.gov/
http://edition.cnn.com/2014/09/23/world/meast/syria-
airstrikes-countries-involved/
http://english.alarabiya.net/en/News/middle-
east/2014/08/15/U-S-jets-strike-ISIS-armored-vehicles-in-
Iraq-.html
The International
Monetary Fund: An
Introduction
Presentation by Lauren Johnson
International Monetary Fund
In 1944, towards the end of World War II, various countries met in
in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire
Sought to plan post-war international monetary and financial system
A major outcome of the conference was the establishment of the IMF
and the World Bank.
Founded in 1945 with 29 initial member countries
Primary goal of IMF was to rebuild worlds international payment
and trade systems in the wake of World War II.
IMF worked to facilitate trade and loan systems that jump-started
the post-war global economy
IMF Today
Global economic development institution
Headquarters in Washington, DC. Its
Membership comprises 188 of the worlds economies
Works to
Ensure financial stability
promote international trade
promote sustainable economic growth
reduce poverty around the world.
Though a UN specialized agency, the IMF is largely independent, with its
own charter, Board of Directors, governing structure and finances.
Terminology
Quota: How much money countries are obligated to provide to the
IMF. This also determines their voting power in the IMF.
Loan: a sum of money borrowed, that is expected to be paid back
with interest.
Interest: An extra amount of money paid in return for borrowing an
amount of cash
Balance of Payments: The difference between how much a country
spends (for example, on military programs and social programs) and
how much a country earns (through taxes) and borrows (through
loans).
Loan Forgiveness or Debt Relief: When the IMF no longer requires a
government to pay back part or all of its debt.
Least Developed Countries (LDC): Countries with very low incomes
levels and high poverty rates (including high levels of hunger and
child mortality, and low levels of literacy and school enrollment).
The Basics
When a country contributes to IMF, it has
ability to take out loans should it have a
balance of payment problem (when it has
problems paying its bills).
Developed countries make loans to
developing countries
Developing countries can use the money to
stabilize their economies, build roads and
schools, and invest in their people.
Issue
Balance of Payments problems come when a government
Has a loss in tax revenue
Has social spending obligations to keep up
Has another expenditure that it is required for country upkeep
Example: Egypt
losing money because of continued uprisings and regime changes, which
decrease revenue from tourism
Losing money because of increased costs in defense and civil services.
As a result, becomes difficult for borrower nation to maintain basic
services and pay back loans
When a debtor country cannot pay on its loans, it is obligated to either
default or borrow more to finance its expenditures.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Rajkot Chapter 2017 Study Guide Committee: UNSC Agenda: Situation in SyriaDokumen18 halamanRajkot Chapter 2017 Study Guide Committee: UNSC Agenda: Situation in SyriaHitesh ParmarBelum ada peringkat
- Globalization 30 PresentationDokumen24 halamanGlobalization 30 PresentationRowly Pearl Iradiel NedicBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation On SyriaDokumen20 halamanPresentation On SyriaLakshay Arora50% (2)
- Unit-14 (14.7 - 14.10)Dokumen21 halamanUnit-14 (14.7 - 14.10)Tiko BiboBelum ada peringkat
- Global MigrationDokumen24 halamanGlobal MigrationJezamay STaponBelum ada peringkat
- International MigrationDokumen20 halamanInternational MigrationTraveller BoyBelum ada peringkat
- A Lot Depends Upon Perception: CRIME (AnDokumen26 halamanA Lot Depends Upon Perception: CRIME (AnVenkat ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Final Report of the Task Force on Combating Terrorist and Foreign Fighter TravelDari EverandFinal Report of the Task Force on Combating Terrorist and Foreign Fighter TravelBelum ada peringkat
- Governments and Citizens in A Globally Interconnected WorldDokumen29 halamanGovernments and Citizens in A Globally Interconnected WorldAubrey Illurimo100% (2)
- Internal SecurityDokumen114 halamanInternal SecurityKartikey singhBelum ada peringkat
- SyriaDokumen13 halamanSyriaapi-336584764Belum ada peringkat
- World Political EnvironmentDokumen27 halamanWorld Political EnvironmentChayan MehtaBelum ada peringkat
- Neo Liberalism ExternalizedDokumen29 halamanNeo Liberalism ExternalizedTristan LaingBelum ada peringkat
- Sunni-Shia ConflictDokumen11 halamanSunni-Shia Conflictapi-253187784Belum ada peringkat
- CH 10Dokumen27 halamanCH 10Jenny YoonBelum ada peringkat
- Economics 21Dokumen19 halamanEconomics 21tamil verisionBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 3 Globalisation and DevelopmentDokumen29 halamanChap 3 Globalisation and DevelopmentAhmad Albayan MuhammadBelum ada peringkat
- GHS SC Topic Synopsis 2015Dokumen4 halamanGHS SC Topic Synopsis 2015pguclaBelum ada peringkat
- Globalization, Inequality, and DevelopmentDokumen29 halamanGlobalization, Inequality, and DevelopmentFerlynBelum ada peringkat
- Ending Libya's Civil War: Reconciling Politics, Rebuilding SecurityDokumen50 halamanEnding Libya's Civil War: Reconciling Politics, Rebuilding SecurityCarnegie Endowment for International PeaceBelum ada peringkat
- United StatesDokumen13 halamanUnited StatesYassine Afilal Elalami IdrissiBelum ada peringkat
- Hells to Hate: Escaping Man Made HellsDari EverandHells to Hate: Escaping Man Made HellsBelum ada peringkat
- AmawDokumen25 halamanAmawvincentperales2025Belum ada peringkat
- Network Analysis Module 4Dokumen8 halamanNetwork Analysis Module 4Ranjan GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Globalization - Concept and TheoryDokumen22 halamanGlobalization - Concept and TheoryLuu Ngoc Phuong (FGW HCM)Belum ada peringkat
- Foreign Aid: Professor Carolino A. Gamlanga JR., MbaDokumen28 halamanForeign Aid: Professor Carolino A. Gamlanga JR., MbaJose PanganibanBelum ada peringkat
- International Politics: Negotiating Relations Between Nation-StatesDokumen36 halamanInternational Politics: Negotiating Relations Between Nation-StatesAjin LalBelum ada peringkat
- Islamic State of Iraq and The Levant & Al-Qaeda: B. Travis FernanderDokumen14 halamanIslamic State of Iraq and The Levant & Al-Qaeda: B. Travis FernanderTravy FernanderBelum ada peringkat
- RIR 210 WEEK 1 IntroductionDokumen23 halamanRIR 210 WEEK 1 Introductione8815220Belum ada peringkat
- Migs Training Program June 2013 Policy Options For Genocide & Mass Atrocity PreventionDokumen55 halamanMigs Training Program June 2013 Policy Options For Genocide & Mass Atrocity PreventionMigs MontrealBelum ada peringkat
- Global MigrationDokumen29 halamanGlobal MigrationSecretChester MCBelum ada peringkat
- Tafelberg Short: South Africa in BRICS: Salvation or ruination?Dari EverandTafelberg Short: South Africa in BRICS: Salvation or ruination?Belum ada peringkat
- Syrian Civil WarDokumen17 halamanSyrian Civil WardollyBelum ada peringkat
- The World of Globalisation: Countries and Levels of Development Developed CountriesDokumen5 halamanThe World of Globalisation: Countries and Levels of Development Developed CountriesLeireBelum ada peringkat
- Economic Aspects of IR - Notes: National Resource ManagementDokumen3 halamanEconomic Aspects of IR - Notes: National Resource ManagementHareem Zoya WarsiBelum ada peringkat
- Lebanon: A Brief Political HistoryDokumen31 halamanLebanon: A Brief Political HistoryRashad BitarBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding TerrorismDokumen4 halamanUnderstanding TerrorismUsman TirmiziBelum ada peringkat
- GlobalizationDokumen14 halamanGlobalizationPadmesh PuthiyadomBelum ada peringkat
- Challenges To CBMs in 21st CenturyDokumen17 halamanChallenges To CBMs in 21st CenturyUmamah Shaheen KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Intro To IR - Power Point 1Dokumen22 halamanIntro To IR - Power Point 1Nelia OrtegaBelum ada peringkat
- CONTWORLDDokumen12 halamanCONTWORLDMaryrose SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Concerns of the Twenty-First CenturyDari EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Concerns of the Twenty-First CenturyBelum ada peringkat
- A History of International Development Policy: by Robert SauderDokumen43 halamanA History of International Development Policy: by Robert SauderJaugan MarkyBelum ada peringkat
- The Global Role of Theus:Theusasa Security Maximiser'Dokumen19 halamanThe Global Role of Theus:Theusasa Security Maximiser'yuval sharmaBelum ada peringkat
- TerrorismDokumen13 halamanTerrorismotwombeelphasBelum ada peringkat
- IR (Nationalism)Dokumen27 halamanIR (Nationalism)barbie38Belum ada peringkat
- Ccge 105Dokumen19 halamanCcge 105Mary Rose NaboaBelum ada peringkat
- Global MigrationDokumen32 halamanGlobal MigrationgarrytrollanoBelum ada peringkat
- Contemporary WorldDokumen15 halamanContemporary WorldKnight QueenBelum ada peringkat
- Global DividesDokumen15 halamanGlobal DividesiggyBelum ada peringkat
- UNHCR Study Guide 1 NewDokumen13 halamanUNHCR Study Guide 1 NewVELUSAMY MBelum ada peringkat
- The Superpower Myth: The Use and Misuse of American MightDari EverandThe Superpower Myth: The Use and Misuse of American MightBelum ada peringkat
- Module 6 International Factor MovementsDokumen13 halamanModule 6 International Factor MovementsjinalBelum ada peringkat
- ContemporaryDokumen49 halamanContemporaryBARRIENTOS, BERNADETTE H.Belum ada peringkat
- Global Interstate SystemDokumen34 halamanGlobal Interstate SystemAmy PinedaBelum ada peringkat
- Contempo Act. 1Dokumen13 halamanContempo Act. 1Renz EscobarteBelum ada peringkat
- Calalang Vs Williams Digested CaseDokumen2 halamanCalalang Vs Williams Digested CaseKristanne Louise Yu100% (1)
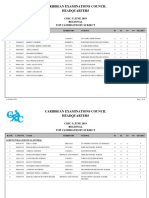
- Regionalmeritlistbysubject2019 Csec 191031164645 PDFDokumen39 halamanRegionalmeritlistbysubject2019 Csec 191031164645 PDFBradlee Singh100% (1)
- Marx:Engels Collected Works - WikipediaDokumen10 halamanMarx:Engels Collected Works - Wikipediagroaci100% (1)
- Class XII History 2010 DelhiDokumen29 halamanClass XII History 2010 DelhiRamita UdayashankarBelum ada peringkat
- Slavoj Zizek - A Permanent State of EmergencyDokumen5 halamanSlavoj Zizek - A Permanent State of EmergencyknalltueteBelum ada peringkat
- Watershed Management PlanDokumen9 halamanWatershed Management Planapi-316015228100% (1)
- 柯 仪南; pinyin: Ke Yinan), a Chinese immigrant entrepreneur who sailed toDokumen13 halaman柯 仪南; pinyin: Ke Yinan), a Chinese immigrant entrepreneur who sailed toNothingBelum ada peringkat
- 2010 Jan11 Subject Jan-DecDokumen132 halaman2010 Jan11 Subject Jan-DecSumit BansalBelum ada peringkat
- Jim Crow PassiveDokumen5 halamanJim Crow PassiveAngel Angeleri-priftis.Belum ada peringkat
- Con Admin NotesDokumen43 halamanCon Admin NotesAnnar e SistanumBelum ada peringkat
- Vidyanali Not Reg SchoolsDokumen62 halamanVidyanali Not Reg SchoolssomunathayyaBelum ada peringkat
- MRP Passport Form (Bangladesh Form)Dokumen4 halamanMRP Passport Form (Bangladesh Form)Muhibbul Muktadir Tanim67% (3)
- Master Soal Penilaian Tengah Semester Gasal 2018-2019Dokumen18 halamanMaster Soal Penilaian Tengah Semester Gasal 2018-2019KSM MTsN4Belum ada peringkat
- Global Governance: Rhea Mae Amit & Pamela PenaredondaDokumen28 halamanGlobal Governance: Rhea Mae Amit & Pamela PenaredondaRhea Mae AmitBelum ada peringkat
- Flores Vs San PedroDokumen3 halamanFlores Vs San PedroLexter CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Backyard Gardening Using Recycled MaterialsDokumen4 halamanBackyard Gardening Using Recycled MaterialsPamela Joyce RiambonBelum ada peringkat
- Decl HelsinkiDokumen195 halamanDecl HelsinkiFernando GomesBelum ada peringkat
- Hoover City Schools Status Report November 2021Dokumen294 halamanHoover City Schools Status Report November 2021Trisha Powell CrainBelum ada peringkat
- PAK UK RelationsDokumen9 halamanPAK UK RelationsHussnain AsgharBelum ada peringkat
- Treasury FOIA Response 6-8-11Dokumen60 halamanTreasury FOIA Response 6-8-11CREWBelum ada peringkat
- G2C Model:passport Sewa: Assignment III E-CommerceDokumen9 halamanG2C Model:passport Sewa: Assignment III E-CommercesagarBelum ada peringkat
- Public Discourse Joseph P. OvertonDokumen7 halamanPublic Discourse Joseph P. Overtoncristian andres gutierrez diazBelum ada peringkat
- Labo, Jr. Vs ComelecDokumen2 halamanLabo, Jr. Vs ComelecAnonymous MmbSn3Belum ada peringkat
- Wellesley News 3.11 PDFDokumen12 halamanWellesley News 3.11 PDFRajesh VermaBelum ada peringkat
- DD Form 4Dokumen4 halamanDD Form 4Arthur BarieBelum ada peringkat
- International Trade TheoryDokumen35 halamanInternational Trade TheorySachin MalhotraBelum ada peringkat
- The Publics RecordsDokumen10 halamanThe Publics RecordsemojiBelum ada peringkat
- National Congress of Unions in The Sugar Industry Vs FerrerDokumen1 halamanNational Congress of Unions in The Sugar Industry Vs FerrerMariz GalangBelum ada peringkat
- Ute Tribe Jurisdiction LetterDokumen3 halamanUte Tribe Jurisdiction LetterGeoff LiesikBelum ada peringkat
- DatuinMA (Activity #5 - NSTP 10)Dokumen2 halamanDatuinMA (Activity #5 - NSTP 10)Marc Alen Porlaje DatuinBelum ada peringkat