Form 2: The World Through Our Senses
Diunggah oleh
Hamidah HamidJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Form 2: The World Through Our Senses
Diunggah oleh
Hamidah HamidHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Form 2
Chapter 1
The world through
our senses
yschow@smkbpj(a) 1
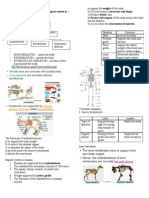
1.1 Sensory Organs and Their Functions
A sensory organ is an organ that enables the body to respond to
stimuli.
A stimulus is a change in the surroundings that can be detected by
the sensory organs.
The five sensory organs are eye, ear, nose, tongue and skin.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 2
The ability of the sensory organs to detect stimuli is
called senses.
Sensory organ Sense Stimuli
Eye Sight Light
Ear Hearing Sound
Nose Smell Chemical in air
yschow@smkbpj(a) 3
Nose Smell Chemical in air
Tongue Taste Chemical in foods
Skin Touch Pressure, heat, cold,
touch
Pathway from stimulus to response.
Stimulus
Receptor in
sensory organ Effectors
(muscle)
Response
yschow@smkbpj(a) 4
Sensory
nerves
Brain
Motor
nerves
(muscle)
1.2 Sense of Touch
yschow@smkbpj(a) 5
1.2 Sense of Touch
The skin is a sensory organ which responds to the
sense of touch.
There are five types of receptors in the skin.
Receptor Stimuli (sensitive to)
Cold receptors Cold substances
yschow@smkbpj(a) 6
Cold receptors Cold substances
Heat receptors Heat
Pain receptors Pain
Pressure receptors Large pressure
Touch receptors Small pressure (touch )
The sensitivity of the skin depends on
(a) the thickness of epidermis
(b) the number of receptors present
Fingertip and neck are more sensitive .
Elbow , knee and back side are not so Elbow , knee and back side are not so
sensitive to touch.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 7
Braille letters are specifically designed symbols for
stimulating the fingertips, which allows blind people to
read
1.3 Sense of Smell
yschow@smkbpj(a) 8
1.3 Sense of Smell
Mucus is produced to help keep the
receptors moist.
When you inhale, the chemicals
from the food enter the nasal cavity
and dissolve in the mucus.
The smell receptors are stimulated.
The impulses from the smell
receptors are sent to the brain by
the olfactory nerves for
interpretation.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 9
When we catch a cold, too much mucus is
produced and this makes the receptors less
sensitive.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 10
Cold = flu (selsema )
1.4 1.4
Sense of
Taste
yschow@smkbpj(a) 11
1.4 Sense of Taste
The tongue contains many taste
buds. The taste buds are the taste
receptors.
There are four types of taste There are four types of taste
receptors.
These receptors are sensitive to
sweet sweet, salty salty, sour sour and bitter bitter tastes.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 12
How do you taste?
The taste buds are able to detect
the taste of the food when the
food is dissolved in saliva.
The taste receptors will be
stimulated and impulses are stimulated and impulses are
produced.
The impulses are sent to the brain
for interpretation.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 13
1.5 Sense of Hearing
yschow@smkbpj(a) 14
1.5 Sense of Hearing
The ear is a sensory organ for hearing and
balancing.
The car can be
divided into divided into
three sections:
i) outer ear,
ii) middle ear and
iii) inner ear.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 15
How do we hear ?
1. The pinna collects sound
waves and directs them
into the auditory canal
and to the eardrum.
2. The eardrumbegins to
vibrate and the
vibrations are
transferred to the
ossicles
yschow@smkbpj(a) 16
3. The ossicles magnify the vibrations and pass them
to the oval window.
4. The oval window transmits the vibrations to the
cochlea.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 17
5. The cochlea converts the vibrations into impulses.
6. The impulses are sent by the auditory nerves to the
brain for interpretation.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 18
1.6 Sense of Sight
yschow@smkbpj(a) 19
How do we see ?
When you look at an object, the light rays from the object enter the
eye.
The light rays are refracted by cornea, aqueous humour, lens and
vitreous humour.
An image is formed on the retina. Impulses are produced and are
sent to the brain by the optic nerves.. sent to the brain by the optic nerves..
yschow@smkbpj(a) 20
1.7 Light and Sight
Light is a form of energy and light
travels in straight lines. This causes
the formation of eclipses.
Light cannot travel through opaque
objects. Thus, shadows are formed.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 21
Light can be reflected
When light hits a surface, some of it bounces off or is
reflected.
Mirrors are very shiny surfaces designed to reflect nearly
all the light that hits them.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 22
When you look in a flat
mirror, you see a reflection
of yourself which is the
same size as you but back
to front.
Light can be refracted
When light travels from one medium to another of
different density, its speed changes.
This causes the light ray to bend.
This is known as refraction.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 23
Effect of light refraction
a) The swimming pool appears to be shallower
than its actual depth.
b) A straw in a glass of water appears to be b) A straw in a glass of water appears to be
bent.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 24
Vision defects
There are three defects of vision:
(a) Short-sightedness ( Rabun jauh )
can see near objects clearly but not distant objects.
(b) Long-sightedness ( Rabun dekat ) (b) Long-sightedness ( Rabun dekat )
can see far objects clearly but not near objects.
(c) Astigmatism (Rabun silau )
both far and near objects are blur.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 25
Short-sightedness Long-sightedness Astigmatism
can see near objects
clearly
can see far objects clearly both far and near objects
are blur
The images of distant
objects are formed
in front of the retina.
The images of nearby
objects are formed
at the back of retina.
Caused by irregular
surface of the cornea.
Using diverging
(concave) lens.
using converging (convex)
lens.
Using cylindrical lenses.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 26
Testing astigmatism ( text pg 23)
Normal eye
yschow@smkbpj(a) 27
Close your right eye and hold this page about one arms length
from your left eye.
Look at the figure .
Have an astigmatism
Optical illusion
yschow@smkbpj(a) 28
Optical illusion
yschow@smkbpj(a) 29
Sometimes our brains do not accurately
interpret what we see.
This phenomenon is known as optical illusion. This phenomenon is known as optical illusion.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 30
It's amazing how our brain works.
This should be proof enough, we don't always see what we think we see.
Blind spot
Text book pg 24
This boy is chasing a butterfly - time to end this madness.
Close your left eye and look at the boy with your right eye. Then move your
head closer to or further from the screen until ... the butterfly disappears !
You can't see the butterfly because it's exactly in front of your blind spot, the
place where the optical nerves enter the eye.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 31
When images fall on the blind spot, they cannot be seen.
Stereoscopic (binocular) vision
Stereoscopic vision is a vision
involving both eyes both eyes.
Humans Humans and most predators predators have
stereoscopic vision. stereoscopic vision.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 32
Advantages of stereoscopic vision
(a) Able to see objects in three
dimensions.
(b) Able to estimate the (b) Able to estimate the
distance accurately.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 33
Monocular vision
Monocular vision is a vision
involving only one eye one eye. .
Animals of prey Animals of prey normally have
monocular vision.
Monocular vision has a wider wider
scope of vision scope of vision.
This enables the prey to detect to detect
the presence of predators easily predators easily
yschow@smkbpj(a) 34
The various devices used to overcome the
limitations of sight include
microscope,
magnifying glass,
telescope,
binoculars,
ultrasound scanning device,
X-ray and
periscope.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 35
1.8 Sound and Hearing
Sound is produced when objects vibrate. vibrate.
A medium mediumis needed for the sound to travel.
Hence, sound cannot travel through vacuum vacuum. Hence, sound cannot travel through vacuum vacuum.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 36
Sound can be reflected
Sound can be reflected by smooth and hard surfaces reflected by smooth and hard surfaces
and it is absorbed by soft and rough surfaces.
Echo Echo is the reflected sound. Echo can be used to: Echo Echo is the reflected sound. Echo can be used to:
(a) estimate the depth of sea
(b) identify a school of fish
(c) detect the presence of submarines
yschow@smkbpj(a) 37
Hearing defects
There are two major types of
(a) The first type involves the outer and middle ear.
For example, the earwax can block sound waves and cause
temporary loss of hearing.
(b) The second type involves damage to the inner ear.
For example, toxins are produced as a result of diphtheria or
scarlet fever. These toxins damage the cochlea and cause
permanent loss of hearing.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 38
Protect our ears
Dont do this !! Dont do this !!
yschow@smkbpj(a) 39
Use earplug or earmuffs
Loud music
cause hearing loss
How to overcome hearing loss ?
yschow@smkbpj(a) 40
Hearing aid
Artificial cochlea
Surgery
Human hearing limit
Our ears can only detect sound of frequencies
between 20 Hz and 20000 Hz 20 Hz and 20000 Hz.
Sounds with frequencies 20 000 Hz and
above are ultrasonic sounds. These sounds can above are ultrasonic sounds. These sounds can
be detected by animals such as bats, cats and
dolphins.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 41
Stereophonic hearing
Stereophonic hearing is hearing with both ears. hearing with both ears.
Stereophonic hearing helps us to determine the determine the
direction of sound. direction of sound.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 42
1.9 Stimuli and Responses in Plants
Plants respond to
stimuli like light,
water , touch and
gravity.
Different parts of the
plant respond to
different stimuli.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 43
There are two types of responses:
(a) Tropism
Tropism is the directional growth of the part of a plant directional growth of the part of a plant in
response to an external stimulus.
(b) Nastic movements
The direction of the response is not dependent on the not dependent on the The direction of the response is not dependent on the not dependent on the
direction of the stimulus direction of the stimulus
yschow@smkbpj(a) 44
Venus fly trap Pitcher Plants
Mimosa pudica
Types of tropisms
yschow@smkbpj(a) 45
(a) Phototropism :
Response
to light
(c) Hydrotropism :
Response
to water
(b) Geotropism :
Response
to gravity
(d) Thigmotropism:
Response
to touch
When the part of the
plant grows towards
the stimulus, it is
called positive
tropism.
Shoot is Shoot is
negative negative
geotropism geotropism
When the part of the
plant grows away
from the stimulus, it is
called negative negative
tropism. tropism.
yschow@smkbpj(a) 46
Roots are Roots are
positive positive
geotropism . geotropism .
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The World of Visual Illusions: Optical Tricks That Defy Belief!Dari EverandThe World of Visual Illusions: Optical Tricks That Defy Belief!Penilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- Science Form 2 Chapter 1 - 10Dokumen14 halamanScience Form 2 Chapter 1 - 10Nur Atiah Daud88% (8)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 3Dokumen23 halamanForm 2 Science Chapter 3qq23592% (25)
- Form 2 Science NoteDokumen16 halamanForm 2 Science NoteMyName Tiff94% (16)
- SC F2 CH1Dokumen59 halamanSC F2 CH1amalina rohaizan50% (2)
- Form 2 Science Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 1Dokumen6 halamanForm 2 Science Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 1Kelvin0% (1)
- Biodiversity Form 2 Science Chapter 3Dokumen18 halamanBiodiversity Form 2 Science Chapter 3Angie Kong Su MeiBelum ada peringkat
- Science Form 1 - Chapter 1.1 by KelvinDokumen33 halamanScience Form 1 - Chapter 1.1 by KelvinKelvin100% (2)
- Science Form 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionDokumen18 halamanScience Form 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionAutumn JJ100% (3)
- Science Form 2 Chapter 1 NotesDokumen19 halamanScience Form 2 Chapter 1 NotesAngie Kong Su Mei100% (2)
- Year 5 Science:HeatDokumen7 halamanYear 5 Science:HeatRaj King50% (2)
- Math Chapter 1.1 Form 1 by KelvinDokumen15 halamanMath Chapter 1.1 Form 1 by KelvinKelvin100% (1)
- F2 Chap 3 MCQDokumen5 halamanF2 Chap 3 MCQSuriya GunalanBelum ada peringkat
- Pt3 Science Seminar ModuleDokumen28 halamanPt3 Science Seminar ModuleSuntharan Muniandy100% (5)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ScienceDokumen10 halamanChapter 1 Introduction To Sciencenaza977583% (18)
- Nutrition Notes Science Form 2Dokumen9 halamanNutrition Notes Science Form 2Veloo Gunasagaran100% (3)
- Science Form 1 Chapter 3Dokumen7 halamanScience Form 1 Chapter 3huisinBelum ada peringkat
- Form 1 Chapter 7 HeatDokumen4 halamanForm 1 Chapter 7 HeatJin TangBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet Science Form 2 Chapter 1Dokumen5 halamanWorksheet Science Form 2 Chapter 1KhadijahMadhadzirBelum ada peringkat
- Science Form 3 Chapter 2Dokumen31 halamanScience Form 3 Chapter 2rosya100% (5)
- Science Form 2 Notes (Chapter 1 - Chapter 4)Dokumen20 halamanScience Form 2 Notes (Chapter 1 - Chapter 4)AmirulNazheefBinZakaria73% (11)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 5Dokumen62 halamanForm 2 Science Chapter 5qq23585% (41)
- Science Form 2Dokumen4 halamanScience Form 2lembu_sihat77100% (1)
- Respiration Form 3Dokumen21 halamanRespiration Form 3P.m. KaruBelum ada peringkat
- Form 1 Science Chapter 4Dokumen33 halamanForm 1 Science Chapter 4qq23595% (21)
- Form 3 Module Chapter 4 Reativity of MetalsDokumen11 halamanForm 3 Module Chapter 4 Reativity of Metalsgrace_lo_1100% (1)
- F2 CHP 2 Ecosystem (Chinese)Dokumen12 halamanF2 CHP 2 Ecosystem (Chinese)ChuahSiewHoonBelum ada peringkat
- Form 2 Chapter 3Dokumen7 halamanForm 2 Chapter 3naza977588% (8)
- Exercise Chapter 5 Form 1 2016Dokumen2 halamanExercise Chapter 5 Form 1 2016Nor Adila100% (1)
- Form 1 Science NotesDokumen20 halamanForm 1 Science NotesMyName Tiff68% (25)
- Module Science Pt3Dokumen11 halamanModule Science Pt3lccjane8504Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Biodiversity Form 2 KSSMDokumen34 halamanChapter 1 Biodiversity Form 2 KSSMAthirah SulaimanBelum ada peringkat
- Science Form 1-Chapter 3Dokumen37 halamanScience Form 1-Chapter 3Mohamad Tarmizi100% (2)
- F3 Chapter 2 RespirationDokumen13 halamanF3 Chapter 2 RespirationJue Hazea GoldshopBelum ada peringkat
- Science Form 2 Concept MapDokumen10 halamanScience Form 2 Concept MapNuar100% (1)
- Form 3 Chapter 6Dokumen7 halamanForm 3 Chapter 6naza9775100% (6)
- STF Mid Year Science Form 1 2009 Paper2Dokumen12 halamanSTF Mid Year Science Form 1 2009 Paper2Syahrul67% (3)
- Biology Topical Exercise Form 4 Chapter 2Dokumen13 halamanBiology Topical Exercise Form 4 Chapter 2SanjeefKumrIIBelum ada peringkat
- Science Form 1 Chapter 1Dokumen13 halamanScience Form 1 Chapter 1huisin100% (1)
- Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 8Dokumen28 halamanBiology Form 4 Notes Chapter 8debbyhooi100% (2)
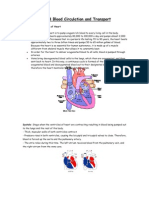
- Science Form 3 Blood Circulation and TransportDokumen8 halamanScience Form 3 Blood Circulation and Transportkc_hani0% (1)
- STF Science Module 1 (PMR) Chapter 1: Introduction To Science Section ADokumen8 halamanSTF Science Module 1 (PMR) Chapter 1: Introduction To Science Section AzuaihaBelum ada peringkat
- FORM 2, Chap 03-BiodiversityDokumen15 halamanFORM 2, Chap 03-BiodiversitySyahrul100% (11)
- Science Form 1 Chapter 2Dokumen29 halamanScience Form 1 Chapter 2qq23588% (68)
- Modul Science Form 2Dokumen36 halamanModul Science Form 2Nur Atiah Daud94% (18)
- What Is This ? How Can You Detect The Presence?Dokumen79 halamanWhat Is This ? How Can You Detect The Presence?Nurul Ain Mat HussinBelum ada peringkat
- F2 Science Chpt1Dokumen24 halamanF2 Science Chpt1Yong SiewkuanBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 9Dokumen95 halamanLecture 9Madeha AshrafBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1: The World Through Our SencesDokumen60 halamanChapter 1: The World Through Our SencesummahputeriBelum ada peringkat
- Identifikasi Jurnal - Facebook Profiles Reflect Actual Personality, Not Self-IdealizationDokumen6 halamanIdentifikasi Jurnal - Facebook Profiles Reflect Actual Personality, Not Self-IdealizationFika_nBelum ada peringkat
- BioPsy Lecture5 UpdatedDokumen43 halamanBioPsy Lecture5 UpdatedMuhammad Amir sohailBelum ada peringkat
- Science Form 2 Chapter 1Dokumen9 halamanScience Form 2 Chapter 1Lim Cj100% (2)
- Sense of VisionDokumen34 halamanSense of VisionqqqqqBelum ada peringkat
- Sensation and PerceptionDokumen95 halamanSensation and PerceptionSalvari VitasBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System Reflexes and Senses: Physiology Lab-4 October, 2018Dokumen21 halamanNervous System Reflexes and Senses: Physiology Lab-4 October, 2018Madhu LodhiBelum ada peringkat
- SP304 Lecture 2: Sensation: Week 7Dokumen68 halamanSP304 Lecture 2: Sensation: Week 7Shawn JohnsonBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 7 SensationDokumen32 halamanLec 7 SensationSyed Ifran EjazBelum ada peringkat
- CH # 4 Perception and SensationDokumen18 halamanCH # 4 Perception and SensationHafiz Mudasir MustafviBelum ada peringkat
- B05 L8 VisionDokumen21 halamanB05 L8 Visionspotifymailhamza12Belum ada peringkat
- Sensation & Perception: Basic TerminologyDokumen47 halamanSensation & Perception: Basic TerminologyVikas SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Yearly Lesson Plan (Physics F5) 2016Dokumen28 halamanYearly Lesson Plan (Physics F5) 2016qq235100% (1)
- 2013 Yearly Plan For Science f2Dokumen25 halaman2013 Yearly Plan For Science f2qq235100% (1)
- Jawapan Modul SN T4 B5 PDFDokumen16 halamanJawapan Modul SN T4 B5 PDFqq235Belum ada peringkat
- Form 2 SN Chapter 4Dokumen55 halamanForm 2 SN Chapter 4qq23597% (30)
- Yearly Plan Physics Form 5 2013Dokumen17 halamanYearly Plan Physics Form 5 2013qq2350% (1)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 5Dokumen62 halamanForm 2 Science Chapter 5qq23585% (41)
- March Test 2011 Answers Scheme: Show Correct UnitDokumen5 halamanMarch Test 2011 Answers Scheme: Show Correct Unitqq235100% (1)
- Physics Form 4 Yearly Lesson Plan 2010Dokumen26 halamanPhysics Form 4 Yearly Lesson Plan 2010Mohd Khairul AnuarBelum ada peringkat
- Support and MovementDokumen24 halamanSupport and Movementqq235100% (9)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 7Dokumen32 halamanForm 2 Science Chapter 7qq23582% (11)
- Form 1 Science Chapter 5 Part 1Dokumen21 halamanForm 1 Science Chapter 5 Part 1qq235100% (1)
- Introduction To ScienceDokumen68 halamanIntroduction To Scienceqq235100% (3)
- TransformerDokumen30 halamanTransformerqq235Belum ada peringkat
- Form 2 Science Chapter 2 (Part 1)Dokumen29 halamanForm 2 Science Chapter 2 (Part 1)qq23595% (37)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 2 (Part 2)Dokumen28 halamanForm 2 Science Chapter 2 (Part 2)qq23592% (38)
- Sel SKEMA PHYS 3Dokumen5 halamanSel SKEMA PHYS 3qq235Belum ada peringkat
- Form 5 Chapter 3Dokumen46 halamanForm 5 Chapter 3qq23571% (7)
- PressureDokumen60 halamanPressureqq235Belum ada peringkat
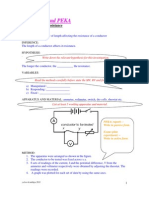
- Peka F5 Length Vs ResistanceDokumen3 halamanPeka F5 Length Vs Resistanceqq23580% (5)
- Form 5 - Peka 1Dokumen15 halamanForm 5 - Peka 1qq23583% (6)
- Form 3 Science, Chapter 1Dokumen47 halamanForm 3 Science, Chapter 1qq23586% (56)
- Soalan Fokus SPM 2009 Set 2 (ANS)Dokumen26 halamanSoalan Fokus SPM 2009 Set 2 (ANS)qq235Belum ada peringkat
- Trial Perak 2009 Fizik 3 SPMDokumen15 halamanTrial Perak 2009 Fizik 3 SPMfizmieBelum ada peringkat
- D Desktop g3Dokumen3 halamanD Desktop g3qq235100% (1)
- P 2Dokumen7 halamanP 2qq235100% (3)
- Skema Fizik SPM Trial Perak 2009Dokumen16 halamanSkema Fizik SPM Trial Perak 2009fizmie100% (2)
- MastelDokumen13 halamanMastelCharles TitoneBelum ada peringkat
- Myopia APDF PDFDokumen14 halamanMyopia APDF PDFRao Sab100% (1)
- Alcon Data For FDA SubmissionDokumen27 halamanAlcon Data For FDA SubmissionVinod RathoreBelum ada peringkat
- Microincision Cataract SurgeryDokumen20 halamanMicroincision Cataract SurgeryviticodocBelum ada peringkat
- Wave LightDokumen7 halamanWave LightRyan RockBelum ada peringkat
- L11 Astigmatism Fan & BlockDokumen14 halamanL11 Astigmatism Fan & BlockDjbr MohBelum ada peringkat
- 4 OPT422 ARes 004Dokumen14 halaman4 OPT422 ARes 004Marco MelikianBelum ada peringkat
- Progress in The Spectacle Correction of Presbyopia PDFDokumen27 halamanProgress in The Spectacle Correction of Presbyopia PDFjuliogarridoBelum ada peringkat
- Corneal Collagen CrosslinkDokumen308 halamanCorneal Collagen CrosslinkFabio Cavalcante100% (1)
- Progressive Lens DispensingDokumen29 halamanProgressive Lens DispensingJackson AraujoBelum ada peringkat
- Reflexes and Special SensesDokumen66 halamanReflexes and Special SensesPamela Agatha PunoBelum ada peringkat
- Optical Power Measurment Using Image Processing TechniquesDokumen5 halamanOptical Power Measurment Using Image Processing TechniquesAbdelsalam HamdiBelum ada peringkat
- Aberrometry NotesDokumen3 halamanAberrometry NotesVero VillamorBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1 Refraction - v1Dokumen21 halamanLecture 1 Refraction - v1Soumya Ranjan PandaBelum ada peringkat
- Trabeculectomy-Related Corneal ComplicationsDokumen7 halamanTrabeculectomy-Related Corneal ComplicationsDian Putri NingsihBelum ada peringkat
- JJ TECNIS Toric Spec SheetDokumen2 halamanJJ TECNIS Toric Spec Sheetaldo paezBelum ada peringkat
- Astigmatic Change in Manual Small Incision Cataract Surgery (MSICS) With Chevron Type of IncisionDokumen6 halamanAstigmatic Change in Manual Small Incision Cataract Surgery (MSICS) With Chevron Type of IncisionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyBelum ada peringkat
- Refraction Error: Alvina Elsa BidariDokumen25 halamanRefraction Error: Alvina Elsa BidariBayu AdityaBelum ada peringkat
- Case Pres )Dokumen18 halamanCase Pres )Justin Faye VibarBelum ada peringkat
- Myopia, Hyperopia and Astigmatism: A Complete Review With View of DifferentiationDokumen5 halamanMyopia, Hyperopia and Astigmatism: A Complete Review With View of DifferentiationAnasthasia hutagalungBelum ada peringkat
- Refraction 2Dokumen47 halamanRefraction 2RuDy RaviBelum ada peringkat
- Case 3:myopiaDokumen24 halamanCase 3:myopiaarifamri92Belum ada peringkat
- Refractive Errors Mexico-27-Feb-2016REV3Dokumen12 halamanRefractive Errors Mexico-27-Feb-2016REV3solo ConsinceridadBelum ada peringkat
- Lasik: Eyeglasses Contact LensesDokumen3 halamanLasik: Eyeglasses Contact Lensesvandana singhBelum ada peringkat
- Astigmatism Definition, Etiology, Classification, Diagnosis and Non-Surgical TreatmentDokumen17 halamanAstigmatism Definition, Etiology, Classification, Diagnosis and Non-Surgical TreatmentRisky AmaliaBelum ada peringkat
- Reffractive ErrorsDokumen13 halamanReffractive ErrorsSagiraju SrinuBelum ada peringkat
- MR Shyam OD 21.5 T3Dokumen2 halamanMR Shyam OD 21.5 T3SaidasBelum ada peringkat
- Trial Sets and Trial FramesDokumen16 halamanTrial Sets and Trial FramesJúnior AlvesBelum ada peringkat
- Ophthalmology Lectures PDFDokumen88 halamanOphthalmology Lectures PDFsharenBelum ada peringkat