Unit 6 Methodsgraphicorganizer
Diunggah oleh
api-2657811080 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
19 tayangan6 halamanJudul Asli
unit6methodsgraphicorganizer
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
19 tayangan6 halamanUnit 6 Methodsgraphicorganizer
Diunggah oleh
api-265781108Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 6
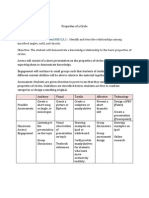
Unit 6: Methods Gathering Grid
MODELING METACOGNITION CATEGORIES LECTURE NOTE TAKING
Modeling is one of the
most powerful ways to
transmit an Academic
Disposition, reasoning
skills, and the Procedural
Information of your domain
to students, because
students learn by observing
and emulating the teacher
and the other students
(Duplass, 203).
thinking about thinking
Teachers model
metacognition by:
1. Articulate Information
Knowledge from the
domain.
2. Use and employ the
executive processes of the
domain.
3. Conduct discussions.
4. Share ideas.
5. Organize the classroom.
6. Structure the learning
experience.
(Duplass, 205).
SUMMARY OF METHOD
Many types of lectures.
Lectures are short with
breakout discussions and
debriefing afterwards. The
purpose is for students to
reconstruct the knowledge.
There are different ways to
organize lectures, which
should be based on the
nature of the content.
He also lists best practices.
Recommends teaching
students to use Cornell
Note-Taking System.
There are six steps in note
taking: Record, Reduce,
Recite, Reflect, Review,
Recapitulate.
Suggests teaching students
how to do this - lecture
about it, model it, have
students compare and
showing students the
teachers version.
The role of the teacher is to
model empathy for the
students, to show personal
integrity, and to set
appropriate expectations.
Teachers who are creative,
diligent, prepared, flexible,
well prepared and
organized model the kinds
of behavior that will help
the student to be successful
(Duplass, 204).
1.Teachers are to model out
loud how to think about
solving a problem.
2. During whole class
reading ask students the
types of questions they
should be thinking about
while reading.
3. The teacher models
verbally how he or she
thought about how to
answer a question (Duplass,
205-206).
ROLE OF THE TEACHER
To plan and strategize
delivery and organization
of the lecture so that
students can reconstruct the
knowledge being presented.
Also, lecturing prepares
students for learning later in
life.
Teach students how to take
notes and how to work with
those notes so they learn
the info. Probably teach the
six steps and walk them
through it.
Students will display
appropriate or inappropriate
models of behavior and
critical thinking skills.
To observe the teacher and
to practice what he or she
sees and hears.
ROLE OF THE STUDENT
To actively engage with the
material to reconstruct
knowledge. To actively
participate in discussions
and ask questions.
To learn the six steps of
note taking and actually do
it and practice it each time
they are given a lecture.
Duplass-page 206. Table 27.1 on page 208 lists Two websites are listed on
EXAMPLES OR RESOURCES
LISTED IN TEXT
and describes the different
kinds of lectures. Table
27.2 on page 210 lists kinds
of organizations and best
practices.
page 211 as well as the six
steps on note taking.
QUESTIONING ANALOGIES CATEGORIES GRAPHIC ORGANIZERS GROUP LEARNING
How do well-planned questions
convert students from passive to
active learners?
How can they help develop
higher-order thinking, as
classified by Blooms
taxonomy?
If students do not answer
questions right away, is it
appropriate for a teacher to wait
longer? If there is still no
answer, should teachers repeat,
rephrase, simplify, and break
down the question, never giving
in and providing the answer?
Analogies work to bridge
knowledge that is already
known by the student, and
knowledge that is yet to
be taught. It takes many
forms, and if used
properly, analogies can
help student to learn,
retain, and relate
information together.
Analogies can be either a
simile or metaphor and
include three parts: topic,
vehicle, and matching
characteristics.
SUMMARY OF METHOD
Paper based formats (not a
worksheet) that assist
students in developing
concepts and placing
information into the correct
schemas.
They are appropriate for all
ages, visually enhance
learning, accommodate all
learning styles, easy to use,
require students to
reconstruct their knowledge
of the topic when writing
them.
There are two categories to
group learning: breakout
groups and cooperative
learning. Breakout groups
are essentially asking your
students to pair up and
discuss something, do an
activity in class, etc. Coop
learning involves more
formally assigned groups to
produce a larger project
such as a short film or a
research project.
The Prepared Questioner
Structurer of effective and
efficient questions
Creator of an environment
conducive to questioning (must
there be sufficient time for
thought before answers are
required?)
Assessor of answers (Should
teachers assess students based on
the thought they put into their
answers?)
To construct analogies to
be better aid the students
connection within content
and other subject areas
To be mindful of what is
being compared and make
sure that the students are
able to understand the
characteristics presented
without bias.
ROLE OF THE TEACHER
Can be used as a
transparency on the
overhead, as boardwork, or
drawn by the student.
Allows the teacher to model
how to organize concepts
and analyze them.
Can be used to gauge
student topic knowledge
Teacher must decide the
parameters of the
assignment, how
participation is to be graded
and who will be in the
groups.
The Thinker and Answerer
Should students be held
accountable both to the material
To make the connections
presented
To create their own
ROLE OF THE STUDENT
This format will allow
students to retain
information longer and
Students must master the
use of appropriate social
skills and cooperation to get
and the questioning
environment?
Will students use and develop
critical thinking skills?
analogies
To find relationships
generate more sophisticated
interpretations of the
content.
makes the student more
involved with the content
and increases accountability
with reading expectations.
the work done and achieve
the result the teacher is
looking for.
Socratic Method -Meno
classics.mit.edu/Plato/meno.html
Page 216 has a quote from Ferris
Buellers Day Off (Is this an
example of how not to do
questioning?)
Table 29.1 on Duplass pg.
220
Ex: The Civil war was
like two brothers fighting
(simile)
Ex: Walk softly and carry
a big stick
(metaphor)
EXAMPLES OR RESOURCES
LISTED IN TEXT
examples-venn diagram,
data retrieval chart,
timeline, cause-and-effect
chart, concept map.
www.eduplace.com/graphic
organizer/ for organizers in
PDF format
http://college.hmco.com/ed
ucation/duplass/1e/students/
graphic.html for more
examples
Duplass, page 227: U of M
website and Kagan and
Assoc. website. See also
page 230 for some
examples and ideas of
activities.
DISCUSSIONS CASE STUDIES CATEGORIES
SELF-DIRECTED
INSTRUCTION
MEDIA-BASED
RESOURCES
A teacher prompted and
guided discussion of the
content to allow
comfortable and casual free
thinking amongst the
students about the topic.
A formalized version of
discussion, a case study is a
discussion based problem
solving approach to critical
thinking.
SUMMARY OF METHOD
A way to customize the
learning experience; a more
independent form of study
than teacher-centered
approach. Differs from
typical task because it takes
a longer time to complete
and the focus is on the
responsibility of the
individual student for their
work and product.
Technology should be used
in a judicious way in the
classroom. The teacher
should select technology
resources that enhance and
add to a lesson but not
make the focus of the
lesson the resource. Best
practices for technology
include: use technology as
attention getters (videos),
use as closing or summary
(clip of documentary), clips
no more than 20 minutes in
length, and to hold students
accountable for the content.
To guide the discussion
towards an intended topic
or conclusion, but willing
to be patient enough to
allow students to find said
conclusion without just
giving out the answer.
Also to maintain neutrality
amongst student discussion.
Presenting the case to be
studied; revealing the true
outcome of the study only
after the students have
found their own
conclusions.
ROLE OF THE TEACHER
Shifts responsibility for
learning to the student.
Teacher defines the
parameters of the tasks by
defining the process,
content and products. Little
intervention by the teacher
are possible. Teacher must
define scope of the
instruction. Teacher must
clearly delineate the limits
of acceptable collaboration
with peers.
The teacher should pre-
select video clips and not
rely on full-length videos-
the maximum length for
any video should not
exceed 20 minutes.
Internet resources should be
carefully considered and
prescreened. The teacher
should rely on free
resources including online
encyclopedias, open source
software, free educational
software, copyright free
image databases, free
educational subscriptions,
etc. to supplement school-
purchased software and
equipment.
To be actively participating
in the critical thinking
process of the desired topic.
To be the main instigator in
the problem solving
precess.
ROLE OF THE STUDENT
The student must rely on
his or her own initiative to
bring his or her learning to
successful outcome. The
students takes charge of
their own learning.
The student is likely
technology savvy and often
knows more than the
instructor. Role of
technology as it relates to
homework is evolving.
Role of technology in
classroom is evolving with
advent of tablets, etc.
pg 233-236 Duplass
best practices for discussion
on page 234
The focus is not on what
you will say, but how you
will respond to the student
pg 236-237 Duplass
organization of cases on pg
237
EXAMPLES OR RESOURCES
LISTED IN TEXT
The student chooses one of
the wars America fought in,
but all the students must
draw a timeline. They are
usually multiday or week
projects. Page 243
Book is out of date, so
free online databases
copyright free online photo
databases
free online encyclopedias
content-specific software
sites from reputable
institutions w/ .gov or .edu
domains, museums, etc.
lesson planning guides for
teachers
PRACTICE HOMEWORK CATEGORIES FIELD TRIPS GUEST SPEAKERS
-- overlearn procedural
knowledge and basic skills
following instruction
-- can take place in
classroom or as homework
-- guided practice takes
place with teacher
-- independent practice
allows no assistance
= a form of independent
practice
-- practice skills learned in
class
-- learn baseline of
information before a lesson
-- apply concepts learned in
class by completing
assignments
-- learn self-discipline
SUMMARY OF METHOD
Field trips could be
anywhere out of the
classroom. Think about
where you could teach this
lesson to better engage
students. It may involve
travel and transportation to
an alternate location. It may
involve pre-approval for
space within your
school/district or from
administration.
Identify experts that can
come to your classroom to
provide relevant/first hand
instruction on a topic at the
cognitive level of the
student. This should be
preplanned so you know
what will be taught and said
by the guest speaker.
-- in guided practice,
teacher observes and gives
feedback
-- give grades with lower
value than a test
-- create engaging,
meaningful, challenging
tasks
-- in independent practice,
teacher provides little or no
assistance but gives grades
with lower value than a test
so student takes work
seriously
-- assign work that is not
mundane or unnecessary
-- assign work that matches
a students level of
participation in the
classroom learning process
that preceded the
homework -- assign only
work the student can do
-- clearly explain the
assignment
ROLE OF THE TEACHER
Make a pretrip visit. Will
you run tour or a guide?
Prepare learners for what
they are going to
experience and what the
expectations of them will
be. Make arrangements
with field trip site, reserve
and plan for transportation,
think about meals, get
permission slip and health
information when leaving
school property. Prepare
students for representing
the school in the
community. Students with
special needs. Additional
chaperones? Attendance
checks?
Having heard the guest
speaker before is
advantageous before
booking them. Is he/she
engaging? Can he/she teach
at the students level? Is
he/she flexible with the
time.
Schedule premeetings to
discuss what you want
taught and time frame
(think of class for
instruction, Q&A). Share
technology availability.
Arrange meeting place for
day of. Have students
prepare questions in
advance of the guest
speaker. Encourage realia,
visual aids, etc.
-- in guided practice, may
consult with group but must
produce his/her own
product
-- in independent practice,
student completes task with
no asssistance
-- do the homework
-- use homework planner,
deliver homework to
teacher
ROLE OF THE STUDENT
Actively participate in the
lesson at the site. Ask
appropriate questions if
given the chance (which
would be prepared for
ahead of time because you
would have alerted them to
this opportunity). Follow all
directions from the teacher
and field trip site staff.
Prepare questions in
advance. Demonstrate
active listening during
presentation. Ask questions
when given the opportunity.
Complete any required
homework/reflection.
-- geography /social studies
student could be given
latitudes and longitudes and
find cities or could be given
cities and calculate latitudes
and longitudes
-- English teacher could
model analyzing plot and
conflict in short story and
have students practice
applying same process to
new story
-- Improving Academic
Achievement Through
Creative Alternatives to
Traditional Homework
Strategies
-- Strategies to Improve
Student Motivation to
Complete Homework
Assignments
-- The Homework Spot
(http://www.homeworkspot
.com/)
EXAMPLES OR RESOURCES
LISTED IN TEXT
Virtual Field Trips
http://curry.edschool.virgini
a.edu/curry/class/Museums/
Teacher_Guide/
See Duplass page 253
Partnerships and Topics decided by this cool online random picker http://classtools.net/
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Calculus Unit Plan OutlineDokumen2 halamanCalculus Unit Plan Outlineapi-265781108Belum ada peringkat
- 2 SidewkshtDokumen2 halaman2 Sidewkshtapi-265781108Belum ada peringkat
- CurrentcontentDokumen2 halamanCurrentcontentapi-265781108Belum ada peringkat
- TechnologyDokumen2 halamanTechnologyapi-265781108Belum ada peringkat
- WongnwongDokumen2 halamanWongnwongapi-265781108Belum ada peringkat
- Indiv Lesson PlanDokumen6 halamanIndiv Lesson Planapi-265781108Belum ada peringkat
- ZH CMPDokumen4 halamanZH CMPapi-265781108Belum ada peringkat
- ReflectionprincetoactDokumen2 halamanReflectionprincetoactapi-265781108Belum ada peringkat
- WTDokumen2 halamanWTapi-265781108Belum ada peringkat
- ZH UdlDokumen1 halamanZH Udlapi-265781108Belum ada peringkat
- ZH Classroom ExpectationsDokumen1 halamanZH Classroom Expectationsapi-265781108Belum ada peringkat
- Integrated Lesson PlanzhDokumen6 halamanIntegrated Lesson Planzhapi-265781108Belum ada peringkat
- Edpsy Mid2Dokumen5 halamanEdpsy Mid2api-265781108Belum ada peringkat
- Rti InclDokumen3 halamanRti Inclapi-265781108Belum ada peringkat
- The Viterbo StandardDokumen2 halamanThe Viterbo Standardapi-265781108Belum ada peringkat
- Zachary Hirschman ResumeDokumen2 halamanZachary Hirschman Resumeapi-265781108Belum ada peringkat
- Attitude and Disposition FormzhDokumen2 halamanAttitude and Disposition Formzhapi-265781108Belum ada peringkat
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- TNTET Reference BookDokumen7 halamanTNTET Reference BookKanthavel ThillaiBelum ada peringkat
- Reaction Paper 1 EvaluationDokumen2 halamanReaction Paper 1 Evaluationanet_brea_10% (1)
- Assure Model Lesson PlanDokumen3 halamanAssure Model Lesson Planapi-362437833Belum ada peringkat
- Ravens SPMDokumen6 halamanRavens SPMpriyaanne0% (1)
- Introduction To Psychology of Learning - Lecture NotesDokumen12 halamanIntroduction To Psychology of Learning - Lecture NotesJulie ClarizaBelum ada peringkat
- Questioning SkillDokumen2 halamanQuestioning SkillAinul Mardhyah100% (1)
- Time Management Self AssessmentDokumen2 halamanTime Management Self AssessmentVaraprasath Sivaram67% (3)
- PPG DLL Q2 Sept 30-Oct 2Dokumen3 halamanPPG DLL Q2 Sept 30-Oct 2Eloisa Micah GuabesBelum ada peringkat
- The Concept of Instructional DesignDokumen27 halamanThe Concept of Instructional DesignAbbhy Mhae Antonio Ceriales100% (1)
- Observation Protocol 4Dokumen2 halamanObservation Protocol 4Tanja IvanovskaBelum ada peringkat
- Student Engagement Look Fors Ask Abouts ChecklistDokumen2 halamanStudent Engagement Look Fors Ask Abouts Checklistapi-367519610100% (1)
- ICT DiaryDokumen8 halamanICT Diarymrtroom2Belum ada peringkat
- Cornell Note PDFDokumen2 halamanCornell Note PDFJojebelle Kate Iyog-cabanletBelum ada peringkat
- DLL Science 7 QTR 1 M1. W1Dokumen3 halamanDLL Science 7 QTR 1 M1. W1joan marie Pelias100% (1)
- Benefits of Lifelong LearningDokumen2 halamanBenefits of Lifelong Learningathina mogro terrazasBelum ada peringkat
- Nazareth Institute of Alfonso Government Recognized CHED / TESDA / BID AccreditedDokumen1 halamanNazareth Institute of Alfonso Government Recognized CHED / TESDA / BID AccreditedMaria Gilane Releen100% (1)
- Trick QuestionDokumen69 halamanTrick Questionphamlinh_cnn7625Belum ada peringkat
- Kinds of QuestionsDokumen6 halamanKinds of QuestionsJune CostalesBelum ada peringkat
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Mil11/121Mil-Iiia-1 Mil11/121Mil-Iiia-2Dokumen2 halamanDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Mil11/121Mil-Iiia-1 Mil11/121Mil-Iiia-2Elsie Alcover Relacion100% (1)
- Mathematical Investigation HandnotesDokumen1 halamanMathematical Investigation HandnotesmichacheBelum ada peringkat
- Module 6 (Prof Ed 16 PT)Dokumen7 halamanModule 6 (Prof Ed 16 PT)natsu dragneel75% (8)
- Oral Communication in Context 11Dokumen4 halamanOral Communication in Context 11Margielane AcalBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment 1 FINALS BDokumen6 halamanAssessment 1 FINALS BKhrisAngelPeñamanteBelum ada peringkat
- Context Clues Self AssessmentDokumen7 halamanContext Clues Self Assessmentapi-273081218Belum ada peringkat
- Ayugan Elementary School: Classroom Observation Tool - Rpms For Teacher I-III Rating SheetDokumen4 halamanAyugan Elementary School: Classroom Observation Tool - Rpms For Teacher I-III Rating SheetFrancia N. MasagcaBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Objectives As My Guiding Star: My Performance (How I Will Be Rated)Dokumen6 halamanLesson Objectives As My Guiding Star: My Performance (How I Will Be Rated)HermisBelum ada peringkat
- Aquino Acei4 FinalDokumen2 halamanAquino Acei4 Finalapi-243059309Belum ada peringkat
- 20th & 21st Century Classroom Management PioneersDokumen16 halaman20th & 21st Century Classroom Management PioneersSamantha TrotterBelum ada peringkat
- Critical ThinkingDokumen4 halamanCritical ThinkingginaBelum ada peringkat
- Light Vehicle Driving NC II: AutomotiveDokumen6 halamanLight Vehicle Driving NC II: AutomotiveRhendel SanchezBelum ada peringkat