Pneumo Coccus
Diunggah oleh
introvoyz041Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Pneumo Coccus
Diunggah oleh
introvoyz041Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
BAS 10/9/02
The Pneumococcus
Key Points:
Strep pneumococcus is the most common cause of community-acquired pneumonia
Classically presents with abrupt onset of fever, chills, cough, and pleuritic chest pain but
presentation can vary
HIV patients are at increased risk of bacterial pneumonia with CD4 counts < 500 cells/cm3
Microbiology
The organism was first identified in 1881
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a Gram-positive, alpha-hemolytic bacterium
Pathogenesis
The pneumococcus is present in the nasopharynx of 50% of asymptomatic people at any time
Pneumonia is likely from aerosolization into the alveoli where they enter alveolar type II cells
Pneumocci multiply in alveoli and pass through the pores of Cohn thus, lobar consolidation
Meningitis is likely from transient bacteremia with invasion at the choroids plexus
Epidemiology
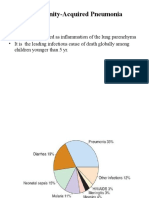
The pneumococcus is the most common cause of community-acquired pneumonia
Isolated in 5-18% of cases but likely the most common cause of culture-negative
S. pneumo accounts for 2/3 of all bacteremic pneumonias
Risk factors for invasive pneumococcal infection include:
Tobacco, EtOH, splenectomy
S. pneumococcus is likely the second most common cause of meningitis
Clinical Features of pneumococcal pneumonia
Classically: abrupt onset of fever, chills, cough, pleuritic chest pain
Can cause bronchopneumonia (not lobar) which depends on serotype
Can present similar to atypical or walking pneumonia
Diagnosis of pneumococcal pneumonia
Chest Xray classically shows lobar consolidation, but can show nearly anything
Sputum gram stain can be helpful but sputum culture was negative in 50% of bactermia pts.
Always obtain blood cultures BEFORE antibiotics
Complications of pneumococcal pneumonia
Typically uncomplicated with complete recovery
Bacteremia with subsequent seeding of other foci is seen in 25% of cases
Other complications include parapneumonic effusion, empyema, lung abscess
Treatment
The current rate of penicillin resistance is 21%
Isolates here show 0% ceftriaxone resistance and 6% levofloxacin resistance
Pneumococcus in HIV/AIDS
Increased risk of bacterial pneumonia with CD4 count < 500 cells/cm3
Clinical presentation typically doesnt differ from immunocompetent hosts
Radiographs can have lobar consolidation, reticulonodular infiltrates, or patchy infiltrates
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Pneumonia 2Dokumen43 halamanPneumonia 2Chol ArouBelum ada peringkat
- Pneumonia in Adults: 25 Years HIV-related ProblemsDokumen35 halamanPneumonia in Adults: 25 Years HIV-related ProblemsgibreilBelum ada peringkat
- PNEUMONIADokumen25 halamanPNEUMONIAcabdinuux32Belum ada peringkat
- Pneumonia TB Student Version RevisedDokumen145 halamanPneumonia TB Student Version RevisedShania robertsBelum ada peringkat
- PnumoniaDokumen33 halamanPnumoniamex GbrekorkosBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Aspects of Medical Chest Diseases:: by Dr. Sana Bashir DPT, MS-CPPTDokumen18 halamanClinical Aspects of Medical Chest Diseases:: by Dr. Sana Bashir DPT, MS-CPPTbkdfiesefllBelum ada peringkat
- 6 - PneumoniaDokumen22 halaman6 - Pneumoniazubairshahid1061Belum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Manifestations of HIVDokumen11 halamanPulmonary Manifestations of HIVashuBelum ada peringkat
- PneumoniaDokumen33 halamanPneumoniarabeccabeckybonbonBelum ada peringkat
- Pneumonia 150514133315 Lva1 App6892Dokumen34 halamanPneumonia 150514133315 Lva1 App6892SadiaBelum ada peringkat
- PneumoniaDokumen86 halamanPneumoniakhushisinghal.cse22Belum ada peringkat
- Jayalakshmi Preetha M CRIDokumen64 halamanJayalakshmi Preetha M CRIJayalakshmi PreethaBelum ada peringkat
- Surgical Aspects of Pulmonary Infections: Kibrom Gebreselassie, MD, FCS-ECSA Cardiovascular and Thoracic SurgeonDokumen60 halamanSurgical Aspects of Pulmonary Infections: Kibrom Gebreselassie, MD, FCS-ECSA Cardiovascular and Thoracic SurgeonVincent SerBelum ada peringkat
- Lect 8 Pneumonia PDFDokumen68 halamanLect 8 Pneumonia PDFRaghad AbdullaBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatric Community-Acquired PneumoniaDokumen60 halamanPediatric Community-Acquired PneumoniaIkea Balhon100% (1)
- PneumoniaDokumen48 halamanPneumoniaDammaqsaa W BiyyanaaBelum ada peringkat
- Pneumonia in Plab PDFDokumen6 halamanPneumonia in Plab PDFBeaulahBelum ada peringkat
- CSMC TB ReportingDokumen31 halamanCSMC TB ReportingDebbie LanceroBelum ada peringkat
- Hemothorax AND PneumoniaDokumen43 halamanHemothorax AND Pneumoniaashoaib0313Belum ada peringkat
- PneumoniaDokumen120 halamanPneumoniaSaklenali LoniBelum ada peringkat
- File 18587Dokumen10 halamanFile 18587Mohammed MuthanaBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of PneumoniaDokumen13 halamanClassification of PneumoniaRaisa DilaBelum ada peringkat
- Bronchitis PneumoniaDokumen27 halamanBronchitis PneumoniaCininta Anisa Savitri100% (1)
- Deep Mycosis-Pneumocystis PneumoniaDokumen11 halamanDeep Mycosis-Pneumocystis Pneumoniamadfoxx1999Belum ada peringkat
- Lower Airway DiseasesDokumen70 halamanLower Airway DiseasesAavash PradhanBelum ada peringkat
- Community Acquired Pneumonia Nelson 400Dokumen37 halamanCommunity Acquired Pneumonia Nelson 400fatima chrystelle nuñalBelum ada peringkat
- L 5 - Lungs PathologyDokumen128 halamanL 5 - Lungs PathologyDiana Popovici100% (1)
- Pathology Slide #6+7Dokumen73 halamanPathology Slide #6+7Ibrahim MigdadyBelum ada peringkat
- Pneumonia 1Dokumen53 halamanPneumonia 1Sardor AnorboevBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Tuberculosis: Group 5 Latosa, Selene Lee, Guk Lim, Johanna Magalona, Stephen Mendoza, ColeenDokumen22 halamanPathophysiology of Tuberculosis: Group 5 Latosa, Selene Lee, Guk Lim, Johanna Magalona, Stephen Mendoza, ColeenAlexander Santiago ParelBelum ada peringkat
- PatomekanismeDokumen18 halamanPatomekanismeEdwin Pasha Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- File 18588Dokumen4 halamanFile 18588Mohammed MuthanaBelum ada peringkat
- 17 PneumoniaDokumen30 halaman17 PneumoniaCabdiBelum ada peringkat
- Central Academy: Biology ProjectDokumen12 halamanCentral Academy: Biology ProjectMastbleBelum ada peringkat
- Suppurative Lung DiseasesDokumen39 halamanSuppurative Lung Diseasesmatchees-gone rogueBelum ada peringkat
- Pneumonia WW ReportDokumen29 halamanPneumonia WW ReportAradhanaRamchandaniBelum ada peringkat
- Radiology - Chest InfectionsDokumen183 halamanRadiology - Chest InfectionsRold Brio SosBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical PresentationDokumen54 halamanClinical PresentationSêrâphîm HâdíBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatric NotesDokumen61 halamanPediatric NotesMatusala BafaBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory Viruses: Organisms Causing PneumoniaDokumen17 halamanRespiratory Viruses: Organisms Causing PneumoniaSherree HayesBelum ada peringkat
- Resp - Infection 2023Dokumen48 halamanResp - Infection 2023Hashim AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- By: Anghel Ștefan (6A) Prisacariu Arina (6A) Robu Amalia (6A) Ștefan Valentina (6A)Dokumen21 halamanBy: Anghel Ștefan (6A) Prisacariu Arina (6A) Robu Amalia (6A) Ștefan Valentina (6A)Mihnea PriBelum ada peringkat
- M Pneumoniae,: Community-Acquired PneumoniaDokumen3 halamanM Pneumoniae,: Community-Acquired PneumoniaOlaru CatalinaBelum ada peringkat
- Opportunistic Infections in HivDokumen10 halamanOpportunistic Infections in HivAdinarayana KashyapBelum ada peringkat
- Childhood TuberculosisDokumen60 halamanChildhood TuberculosisyosephBelum ada peringkat
- Opportunistic Lung Infections 1Dokumen40 halamanOpportunistic Lung Infections 1XavierBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 27 - Lower Respiratory ProblemsDokumen10 halamanChapter 27 - Lower Respiratory Problemsjosie teehBelum ada peringkat
- Tuberculosis in Infancy and ChildhoodDokumen55 halamanTuberculosis in Infancy and ChildhoodIna AguilarBelum ada peringkat
- Tuberculosis in ChildrenDokumen50 halamanTuberculosis in Childrenmy Lord JesusBelum ada peringkat
- PneumoniaDokumen27 halamanPneumoniamohammedghassan53Belum ada peringkat
- Pathology of Pulmonary InfectionDokumen32 halamanPathology of Pulmonary InfectionAda JoraimiBelum ada peringkat
- Tropical DiseasesDokumen44 halamanTropical DiseasesOsmanBelum ada peringkat
- BronchopneumoniDokumen23 halamanBronchopneumonisyarifah naziraBelum ada peringkat
- PneumoniaDokumen24 halamanPneumoniaWidhi AstutiBelum ada peringkat
- Lung AbscessDokumen27 halamanLung AbscessMalueth Angui100% (1)
- CommunityDokumen2 halamanCommunityMarlowe Adlei Novedo PabloBelum ada peringkat
- MeningococcemiaDokumen1 halamanMeningococcemiaintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- Group 2 Community Acquired PneumoniaDokumen24 halamanGroup 2 Community Acquired PneumoniaalyanadayritBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesDari EverandMedical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesBelum ada peringkat
- MeningococcemiaDokumen1 halamanMeningococcemiaintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- Meningitis PLUS: Goetz: Textbook of Clinical Neurology, 1st EdDokumen1 halamanMeningitis PLUS: Goetz: Textbook of Clinical Neurology, 1st Edintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- Malaria: Ovale, and P. MalariaeDokumen1 halamanMalaria: Ovale, and P. Malariaeintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- NomaDokumen2 halamanNomaintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- NephRotic SyndromeDokumen2 halamanNephRotic Syndromeintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- Lymph Angio Leio Myomato SisDokumen2 halamanLymph Angio Leio Myomato Sisintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- Neurology 102Dokumen2 halamanNeurology 102introvoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- PancreatitisDokumen2 halamanPancreatitisintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- Polio & PostPolioDokumen2 halamanPolio & PostPoliointrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- Mucomyst and Contrast NephropathyDokumen1 halamanMucomyst and Contrast Nephropathyintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- Neurosyphilis: Mandell: Principles and Practice of Infectious Disease, 5 Ed, PP 2476-2489. Uptodate 2002Dokumen1 halamanNeurosyphilis: Mandell: Principles and Practice of Infectious Disease, 5 Ed, PP 2476-2489. Uptodate 2002Drashua AshuaBelum ada peringkat
- MyocarditisDokumen1 halamanMyocarditisintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- ParotitisDokumen2 halamanParotitisYusuf KarimBelum ada peringkat
- PericarditisDokumen1 halamanPericarditisintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- PheochromocytomaDokumen2 halamanPheochromocytomaintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- Neurologic Complications of SLEDokumen2 halamanNeurologic Complications of SLEintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- PE The BasicsDokumen2 halamanPE The Basicsintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- Polymyositis, DermatomyositisDokumen2 halamanPolymyositis, Dermatomyositisintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- Prostate Cancer: Pearls and Myths From The UrologistsDokumen2 halamanProstate Cancer: Pearls and Myths From The Urologistsintrovoyz041100% (1)
- RhabdomyolysisDokumen2 halamanRhabdomyolysisintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- Pneumo CoccusDokumen1 halamanPneumo Coccusintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- Pneumothorax 1Dokumen2 halamanPneumothorax 1dunia_suslinaBelum ada peringkat
- Pyle PhlebitisDokumen1 halamanPyle Phlebitisintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary EdemaDokumen2 halamanPulmonary EdemaMuhammad Bayu Zohari HutagalungBelum ada peringkat
- Renal Tubular AcidosisDokumen2 halamanRenal Tubular AcidosisHeather WatersBelum ada peringkat
- Reversible Posterior LeukoencephalopathyDokumen2 halamanReversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathyintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- Rhabdomyolysis PLUSDokumen2 halamanRhabdomyolysis PLUSintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- Red Cell AplasiaDokumen2 halamanRed Cell Aplasiaintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat
- RV InfarctDokumen2 halamanRV Infarctintrovoyz041Belum ada peringkat