Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase
Diunggah oleh
Falaq2Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase
Diunggah oleh
Falaq2Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase
Inhibitors
Nevirapine, Delavirdine, Efavirenz,
and Etravirine
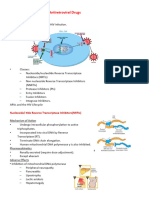
Mechanism of action
These drugs are direct noncompetitive inhibitors of HIV-1
reverse transcriptase. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase
inhibitors block RNA-dependent and DNA-dependent polymerase
activities by inducing a conformational change that
disrupts the enzymes catalytic site. Unlike the nucleoside
reverse transcriptase inhibitors, these drugs do not require intracellular
phosphorylation for their actions. These drugs potentiate
the actions of other antiretroviral drugs.
Clinical use
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors are used in
combination with other antiretroviral agents to treat HIV
infections.
Pharmacokinetics
These drugs are metabolized by the P450 enzymes and are
susceptible to numerous drug interactions by drugs that
induce or inhibit the hepatic P450 microsomal enzymes.
Adverse effects
This drug class has been associated with potentially fatal
hepatotoxicity, although etravirine appears to be the safest
in this regard. Efavirenz has been associated with adverse psychiatric
effects. Severe, life-threatening skin rashes, including
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrosis, may
also occur.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Antiviral Drugs Classification and MechanismsDokumen56 halamanAntiviral Drugs Classification and MechanismsciccianoBelum ada peringkat
- Antiviral DRUGSDokumen20 halamanAntiviral DRUGSyasin shifa100% (1)
- An Introduction to Mechanisms in Pharmacology and TherapeuticsDari EverandAn Introduction to Mechanisms in Pharmacology and TherapeuticsBelum ada peringkat
- Antiviral Drugs Medical StudentsDokumen59 halamanAntiviral Drugs Medical Studentstummalapalli venkateswara rao67% (3)
- 29 Anti-Viral Drugs PDFDokumen43 halaman29 Anti-Viral Drugs PDFabhishek talokarBelum ada peringkat
- Handbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionDari EverandHandbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionPenilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- Etravirine drug information and interactionsDokumen3 halamanEtravirine drug information and interactionsRosher Deliman JanoyanBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Anti Retroviral Drugs 2012Dokumen29 halaman3 Anti Retroviral Drugs 2012Youths With PurposesBelum ada peringkat
- SUBMITTED BY Nahima Anhum SUBMITTED TO DR - Maimoona MSC - Microbiology 2 Semester University of HaripurDokumen17 halamanSUBMITTED BY Nahima Anhum SUBMITTED TO DR - Maimoona MSC - Microbiology 2 Semester University of Haripursandeepv08Belum ada peringkat
- Six classes of antiretroviral agentsDokumen14 halamanSix classes of antiretroviral agentsSeffia riandiniBelum ada peringkat
- Antiviral Agents for HIV TreatmentDokumen18 halamanAntiviral Agents for HIV TreatmentNutan Desai RaoBelum ada peringkat
- Antiviral Drugs for Influenza, Hepatitis & MoreDokumen57 halamanAntiviral Drugs for Influenza, Hepatitis & MoreInes Atas TupasBelum ada peringkat
- Antiviral Agents: Jillian H. Davis Dept. of Pharmacology March 31, 2004Dokumen63 halamanAntiviral Agents: Jillian H. Davis Dept. of Pharmacology March 31, 2004mishra_nidhiBelum ada peringkat
- Drug InteractionsDokumen36 halamanDrug Interactionsbaker371100% (2)
- CCC GRP 6Dokumen61 halamanCCC GRP 6Stacy JumaBelum ada peringkat
- Nnrtis: Nonnucleoside Reverse Trancriptase InhibitorsDokumen12 halamanNnrtis: Nonnucleoside Reverse Trancriptase InhibitorsMalueth AnguiBelum ada peringkat
- Antiretroviral TherapyDokumen41 halamanAntiretroviral TherapySami YGBelum ada peringkat
- AntiviralDokumen17 halamanAntiviralDRx Raju ChandranBelum ada peringkat
- PALMK-IV - 6 - Obat Antivirus Ganjil 2122Dokumen34 halamanPALMK-IV - 6 - Obat Antivirus Ganjil 2122Oktavia Marintan ManullangBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation: Anti Viral DrugsDokumen29 halamanPresentation: Anti Viral DrugsUmama WarrichBelum ada peringkat
- Efavirenz Chem OlympicsDokumen1 halamanEfavirenz Chem OlympicsdreamingsnowBelum ada peringkat
- Antiviral AgentsDokumen14 halamanAntiviral AgentsKate MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Adverse Effects of ArvsDokumen10 halamanAdverse Effects of ArvsAllan Takudzwa MpeperekiBelum ada peringkat
- Importance of Adherence to Antiretroviral Drugs (ARVsDokumen20 halamanImportance of Adherence to Antiretroviral Drugs (ARVsSalihu MustaphaBelum ada peringkat
- All Document Reader 1706850489833Dokumen21 halamanAll Document Reader 1706850489833motivationtogrindBelum ada peringkat
- Extrapyramid Synd 3Dokumen4 halamanExtrapyramid Synd 3Zahra Namika AiharaBelum ada peringkat
- PrepDokumen36 halamanPrepsameralhameerBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Ons: AdverseDokumen5 halamanDrug Ons: AdverseMisty CheifBelum ada peringkat
- S 000 LBLDokumen27 halamanS 000 LBLDan Angelo Lawagan FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Antiviral Drugs Limit Viral Growth Through Multiple MechanismsDokumen90 halamanAntiviral Drugs Limit Viral Growth Through Multiple MechanismsshBelum ada peringkat
- Adverse Drug Reactions and PharmacologyDokumen49 halamanAdverse Drug Reactions and PharmacologySupreet Singh Malhi0% (1)
- Slide - K-27 - Farmakologi AntivirusDokumen36 halamanSlide - K-27 - Farmakologi AntivirusFaisal AlhasBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Interactions With Tuberculosis TherapyDokumen5 halamanDrug Interactions With Tuberculosis TherapypriyankaBelum ada peringkat
- Anti Viral DrugsDokumen3 halamanAnti Viral Drugsbilal ahmadBelum ada peringkat
- Antiviral Drugs: Mechanisms and ExamplesDokumen47 halamanAntiviral Drugs: Mechanisms and ExamplesKunal JaatBelum ada peringkat
- Antiviral ChemotherapyDokumen59 halamanAntiviral ChemotherapyDiriba feyisaBelum ada peringkat
- 9) AntiretroviralDokumen79 halaman9) AntiretroviralOkot ChristopherBelum ada peringkat
- Burchum & Rosenthal: Lehne's Pharmacology For Nursing Care, 9th EditionDokumen9 halamanBurchum & Rosenthal: Lehne's Pharmacology For Nursing Care, 9th Editionhockeyman1584Belum ada peringkat
- Systemic ComplicationsDokumen51 halamanSystemic ComplicationsKhushi DesaiBelum ada peringkat
- PHAT-4106 Assignment on N-Oxidation and Drug ToxicityDokumen13 halamanPHAT-4106 Assignment on N-Oxidation and Drug ToxicitySayema KhanumBelum ada peringkat
- Antiviral DrugsDokumen4 halamanAntiviral DrugsD'poetrii Dewi SuryaniBelum ada peringkat
- Dooley PDFDokumen18 halamanDooley PDFMualliful UmmaBelum ada peringkat
- 21-Antiviral Agents IIDokumen40 halaman21-Antiviral Agents IIShashidharan Menon100% (1)
- Drugs For The Treatment of AidsDokumen17 halamanDrugs For The Treatment of AidsEdgar David SigarlakiBelum ada peringkat
- Study of History and Progress Made in Anti Viral Drugs Used in Hiv/Aids TreatmentDokumen18 halamanStudy of History and Progress Made in Anti Viral Drugs Used in Hiv/Aids TreatmentAYUSH RANJANBelum ada peringkat
- NevirapineDokumen2 halamanNevirapineمحمد عريف حكيمBelum ada peringkat
- Pharma Lesson 3Dokumen3 halamanPharma Lesson 3BabyJane GRomeroBelum ada peringkat
- Anti-Herpes Drugs for HSV TreatmentDokumen44 halamanAnti-Herpes Drugs for HSV TreatmentMohammed WasimBelum ada peringkat
- HIV Drugs-2019Dokumen23 halamanHIV Drugs-2019salva sambaaBelum ada peringkat
- Antiviral DrugsDokumen44 halamanAntiviral DrugsMohammed WasimBelum ada peringkat
- Adverse Drug Reactions 23 24 1Dokumen37 halamanAdverse Drug Reactions 23 24 1Hasan kahhalehBelum ada peringkat
- EfavirenzDokumen3 halamanEfavirenzRosher Deliman JanoyanBelum ada peringkat
- Roger Case Study and Nursing Process 2Dokumen9 halamanRoger Case Study and Nursing Process 2E.R.OBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Resistance and Synergism MechanismsDokumen40 halamanDrug Resistance and Synergism MechanismsShaun李好Belum ada peringkat
- Summary of Product Characteristics: Edronax 4 MGDokumen9 halamanSummary of Product Characteristics: Edronax 4 MGddandan_2Belum ada peringkat
- 38.ANTIRETROVIRALS PDFDokumen5 halaman38.ANTIRETROVIRALS PDFireneBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Drug Interactions 2Dokumen133 halamanDrug Drug Interactions 2joo saadBelum ada peringkat
- Dress Agep SSJ Net Scars Med Clin N Am 2021Dokumen21 halamanDress Agep SSJ Net Scars Med Clin N Am 2021Sebastian PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Compilation of Antiviral Drug Leaflets: Project in PharmacologyDokumen32 halamanCompilation of Antiviral Drug Leaflets: Project in PharmacologydaleascabanoBelum ada peringkat
- Drug & Therapeutic InteractionsDokumen28 halamanDrug & Therapeutic Interactionsفاطمة الجش.Belum ada peringkat
- Inhibition of Intracellular Synthesis byDokumen1 halamanInhibition of Intracellular Synthesis byFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Inhibitors of Viral NeuraminidaseDokumen1 halamanInhibitors of Viral NeuraminidaseFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Imiquimod, Podofilox, and SinecatechinsDokumen1 halamanImiquimod, Podofilox, and SinecatechinsFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Inhibitors of Viral UncoatingDokumen1 halamanInhibitors of Viral UncoatingFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Benzyl AlcoholDokumen1 halamanBenzyl AlcoholFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Treatment of TachyaarrhythmiaDokumen1 halamanTreatment of TachyaarrhythmiaFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- AmrinoneDokumen1 halamanAmrinoneFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- A. Mechanism. (1) (2) B. Therapeutic Uses.: Arbs: Prototype Drug-ValsartanDokumen1 halamanA. Mechanism. (1) (2) B. Therapeutic Uses.: Arbs: Prototype Drug-ValsartanFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Ralteg RavirDokumen1 halamanRalteg RavirFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Synthetic Catecholamine: Dobutamine DobutamineDokumen1 halamanSynthetic Catecholamine: Dobutamine DobutamineFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Treatment of Tachyarrhythmias1Dokumen1 halamanTreatment of Tachyarrhythmias1Falaq2Belum ada peringkat
- ACE InhibitorsDokumen1 halamanACE InhibitorsFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Protease InhibitorsDokumen1 halamanProtease InhibitorsFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Class II DrugsDokumen1 halamanClass II DrugsFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Fusion InhibitorsDokumen1 halamanFusion InhibitorsFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Class IC DrugDokumen1 halamanClass IC DrugFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Direct Thrombin InhibitorsDokumen1 halamanDirect Thrombin InhibitorsFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- MaravirocDokumen1 halamanMaravirocFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Vitamin K AntagonistsDokumen1 halamanVitamin K AntagonistsFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Class I DrugsDokumen1 halamanClass I DrugsFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Class IB DrugDokumen1 halamanClass IB DrugFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- First Generation ThrombolyticsDokumen1 halamanFirst Generation ThrombolyticsFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Adenosine Diphosphate InhibitorsDokumen1 halamanAdenosine Diphosphate InhibitorsFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: Causes of ArrhythmiasDokumen1 halamanAntiarrhythmic Drugs: Causes of ArrhythmiasFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- SalicylatesDokumen1 halamanSalicylatesFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Glycoprotein IIbDokumen1 halamanGlycoprotein IIbFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Phosphodiesterase InhibitorsDokumen1 halamanPhosphodiesterase InhibitorsFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- Heparins: Unfractionated HeparinDokumen2 halamanHeparins: Unfractionated HeparinFalaq2Belum ada peringkat
- TerbinafineDokumen1 halamanTerbinafineFalaq2Belum ada peringkat