512 - Conceptmap
Diunggah oleh
api-282325269Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
512 - Conceptmap
Diunggah oleh
api-282325269Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
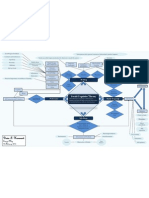
Legend
Red = Differences
Green = Similarities
Italics = Key concepts
Learning Theories
central to
Cognition focus
Behaviour focus
influenced by
central to
similar to
rejects
central to
central to
Behaviourism
Social Learning
Theory
lead to
used for
Self-regulated
learning
Environment
ignores
focuses on
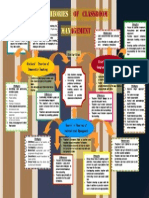
Classroom management
strategies
Personal factors
Organizational
strategies
influenced
by
Organizational
strategies
focuses on
Reading
comprehension
similar to
Cognitive
learning
through
uses
Motivation
through
Learned or unlearned
influenced by
Active participation
Cognition
Advanced
Organizers
Interest
Modeling
through
similar to
Environment
similar to
Stimulus-response
through
with
with
Behaviour
claims
seek
Self-regulation
determines
allow
because
Vicarious learning
such as
Latent learning
New information
Teacher feedback
Forethought
reinforcement
increases
uses
Teacher
encouragement
link to
similar to
changed by
Extinction
depends on
similar to
Consequences
Goal setting
consider
influenced
by
Self-efficacy
aquire
Punishments
increase
similar to
Performing previously
learned behaviours
Short-term memory
relearn
New knowledge
similar to
Self-regulation
Negative
reinforcements
increase frequency
increase frequency
Observed behaviours
relate
later use
Perceived consequences
choose
Response
Learner's choice
similar to
prolongs
decay
Incentives
Social pressures
actively learn
New information
stored as
anchor
can be
Preiously learned
knowledge
decreases
Interest
Positive
reinforcements
Long-term memory
Information forgotten
Motivation
attention to
influenced by
Interest
similar to
depends on
through
decrease frequency
decrease frequency
increase frequency
Attitude
create
search
stores
lost
allows for
Rewards
help aquire
involves
Meaningfulness
enters
Practice
Modeling
precede
relies on
develops
interest
Enactive learning
Model prestige
Previously learned
knowledge
Meaningful Learning
Theory
disinterest
influences
Prior conditioning
affected by
Unobservable mental
processes
influences
Stimuli affects behaviour
based on
based on
Person
with
Schema Theory
stimulates
focussing on
learned through
Previously learned
behaviours
focuses on
Environment
Internal processes
Age
Behavioural
reinforcements
igornes
used for
Environment
Learning in a
social context
can be
Cueing
Shaping
Behavioural
reinforcements
igornes
Curriculum
development
Complex internal
processes
Assimilation Learning
Theory
similar to
used in
focuses on
Classroom management
strategies
Observable and measurable behaviours
Cognitive Information
Processing
central to
igornes
used for
ease intake
Previously learned
knowledge
review
retain
Task requiring new
information
Lessons
create
similar to
Need
retain
& avoid
retain
& repeat
Partial loss of
information
Reinforcement
alters
Information
stored
Task requiring previously
learned information
Meaningfulness
later usage
immediately
used
Desirable
Undesirable
through
encourage
Knowledge
retention
Applied
knowledge
encourage
retains
Mental respresentations
(Schema)
use
Logical
relationships
achieve
organized by
Units
achieve
similar to
Avoid producing
Groups
partial
Meaningful Learning
Produce
Types of
Learning
sucessfully
such as
Rote learning
Discovery Learning
produce or
avoid
Reception Learning
Learning
achieved
Behaviour
capable of
implies
sucessfully
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Concept Map #1 Social Cognitive TheoryDokumen1 halamanConcept Map #1 Social Cognitive TheoryDarin L. HammondBelum ada peringkat
- Adult Learning and Learning StylesDokumen8 halamanAdult Learning and Learning StylesperestainBelum ada peringkat
- 0 - Prof Ed. 4 Home Reading and AssignmentDokumen15 halaman0 - Prof Ed. 4 Home Reading and AssignmentKG AgramonBelum ada peringkat
- Investigating the Emotional and Physical Aspects of the Language ClassroomDari EverandInvestigating the Emotional and Physical Aspects of the Language ClassroomBelum ada peringkat
- Learner-Centered Theories of LearningDokumen57 halamanLearner-Centered Theories of LearningAnonymous E8yT3R4iBelum ada peringkat
- Motivation in Learning and TeachingDokumen18 halamanMotivation in Learning and TeachingWan MaisarahBelum ada peringkat
- Classroom Management: Prepared By: Mrs. Evelyn A. SangalangDokumen30 halamanClassroom Management: Prepared By: Mrs. Evelyn A. Sangalangrdr_apmdBelum ada peringkat
- Social Cognitive TheoryDokumen19 halamanSocial Cognitive TheoryJeevitha RamanBelum ada peringkat
- Characteristics and NeedsDokumen3 halamanCharacteristics and Needsapi-403252407Belum ada peringkat
- Key Topical Takeaways From CourseDokumen3 halamanKey Topical Takeaways From Courseapi-313154885Belum ada peringkat
- Classroom Management Mind MapDokumen1 halamanClassroom Management Mind MapKhairunnisa Sharom100% (4)
- Considerations in Designing A Curriculum Part 2Dokumen3 halamanConsiderations in Designing A Curriculum Part 2liliyayanonoBelum ada peringkat
- Classroom Management For Teachers: Developed by Mitchie NeelDokumen55 halamanClassroom Management For Teachers: Developed by Mitchie NeelJuliet DianneBelum ada peringkat
- Learning TheoriesDokumen76 halamanLearning TheoriesKishoree Chavan100% (1)
- Educ 5312-Research Paper-M Keles 2Dokumen4 halamanEduc 5312-Research Paper-M Keles 2api-316855144Belum ada peringkat
- Learning: General Psychology NotesDokumen12 halamanLearning: General Psychology NotesKizhakkedom Krishnankutty ShijuBelum ada peringkat
- Group 4 - PMTA - BSA1 EDokumen26 halamanGroup 4 - PMTA - BSA1 EAvegail MagtuboBelum ada peringkat
- Hattie Chapter 8Dokumen25 halamanHattie Chapter 8jmstetekluh100% (1)
- DISCIPLINEDokumen10 halamanDISCIPLINEBoaz MokayaBelum ada peringkat
- Mind Map Classroom Management TheoriesDokumen1 halamanMind Map Classroom Management Theoriesleahblack100% (1)
- Adult EducationDokumen16 halamanAdult EducationNing Erestain100% (2)
- Behaviorism TheoryDokumen3 halamanBehaviorism Theorysalma ristantiBelum ada peringkat
- Ed Interventions For Children With Tbi - VelenoDokumen22 halamanEd Interventions For Children With Tbi - Velenoapi-163017967Belum ada peringkat
- Written Report Principles of Teaching 1Dokumen5 halamanWritten Report Principles of Teaching 1Therese Angelie CamacheBelum ada peringkat
- Traditional MethodsDokumen29 halamanTraditional MethodsPao ParelBelum ada peringkat
- Teach Them WellDokumen1 halamanTeach Them WellKINGOFBRANDINGBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 6 Cls ManagementDokumen18 halamanLec 6 Cls Managementsanjida mimmoBelum ada peringkat
- Strategies For Effective Class Room Management and TeachingDokumen10 halamanStrategies For Effective Class Room Management and TeachingSharmila AshrafBelum ada peringkat
- H.E Midterm ReviewerDokumen29 halamanH.E Midterm ReviewerJoshua LadagaBelum ada peringkat
- Written Asgn Unit 2 5240Dokumen4 halamanWritten Asgn Unit 2 5240Zonia NillBelum ada peringkat
- Reflection On Behaviorism and EducationDokumen2 halamanReflection On Behaviorism and EducationDiana Llera Marcelo100% (1)
- Defining Classroom ManagementDokumen10 halamanDefining Classroom Managementklswary4974Belum ada peringkat
- Activity 6Dokumen2 halamanActivity 6Rose Ann N. CrisostomoBelum ada peringkat
- Apunte Importante para El CbestDokumen4 halamanApunte Importante para El CbestCenobioBelum ada peringkat
- Philosophy of Classroom Management by Matthew Cooke 17299158Dokumen17 halamanPhilosophy of Classroom Management by Matthew Cooke 17299158api-355488205Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment Class ManagmentDokumen4 halamanAssignment Class Managmentmadiha raoBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Employee Learning and DevelopmentDokumen40 halamanIntroduction To Employee Learning and DevelopmentramyabuntyBelum ada peringkat
- Phycho - Changes in Attitude of StudentsDokumen5 halamanPhycho - Changes in Attitude of Studentsnarayanansahaana545Belum ada peringkat
- PRINCIPLES OF TEACHING HandoutDokumen8 halamanPRINCIPLES OF TEACHING Handoutjohnmer BaldoBelum ada peringkat
- Classroom Management TechniquesDokumen80 halamanClassroom Management TechniquesReden UloBelum ada peringkat
- EBD ReportDokumen6 halamanEBD ReportAyen YenBelum ada peringkat
- 14learner Centeredprinciples 141125171111 Conversion Gate01Dokumen32 halaman14learner Centeredprinciples 141125171111 Conversion Gate01nemaki lim100% (1)
- Behaviorism This Module abo-WPS OfficeDokumen2 halamanBehaviorism This Module abo-WPS OfficeTeam TheaLleaBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Management KPSDokumen8 halamanLearning Management KPSMegala DeviBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson7 BehaviorismDokumen2 halamanLesson7 BehaviorismCheaze Micah Marie ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Classroom Management in Perspective: Shailini G. Gestosani, M.Ed. College of Teacher Education St. Paul University IloiloDokumen51 halamanClassroom Management in Perspective: Shailini G. Gestosani, M.Ed. College of Teacher Education St. Paul University IloiloshaigestBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 (Research Activity)Dokumen6 halamanChapter 1 (Research Activity)aria oceanaBelum ada peringkat
- Manager Exam 1Dokumen25 halamanManager Exam 1Manny60% (5)
- Classroom Motivation and ManagementDokumen2 halamanClassroom Motivation and ManagementBeejay TaguinodBelum ada peringkat
- How Students LearnDokumen4 halamanHow Students Learnmarichu apiladoBelum ada peringkat
- Classroom Management TheoryDokumen5 halamanClassroom Management TheoryhartbetoskyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Educational Psychology/Reflective Practice: Themes of The ChapterDokumen28 halamanChapter 1 Educational Psychology/Reflective Practice: Themes of The ChapterKhairol NizamBelum ada peringkat
- 2.types & Designs of Ed RSRCHDokumen17 halaman2.types & Designs of Ed RSRCHShe KazumiBelum ada peringkat
- G.O of Ele 3102 Study of PhonologyDokumen4 halamanG.O of Ele 3102 Study of PhonologyOrewa Appiku DesBelum ada peringkat
- Behavior Management ModelsDokumen31 halamanBehavior Management ModelsGowry Sellan GreshBelum ada peringkat
- Nelson & Quick: Managing ChangeDokumen31 halamanNelson & Quick: Managing ChangeSana ZargarBelum ada peringkat
- Profed110 Attitudes and BehaviorsDokumen2 halamanProfed110 Attitudes and BehaviorsMeraki M. AuthworriaBelum ada peringkat
- pr1 ReflectionDokumen2 halamanpr1 Reflectionapi-282325269Belum ada peringkat
- Etec 565m A3 - FinalDokumen9 halamanEtec 565m A3 - Finalapi-282325269Belum ada peringkat
- Etec 531 Media Study Guide AssignmentDokumen5 halamanEtec 531 Media Study Guide Assignmentapi-282325269Belum ada peringkat
- Etec 510 Design Project ProposalDokumen29 halamanEtec 510 Design Project Proposalapi-282325269Belum ada peringkat
- 2014F MAS102 Final ExamDokumen11 halaman2014F MAS102 Final ExamInstantRamenBelum ada peringkat
- Central Bicol State University of Agriculture: - EDUCATIONDokumen13 halamanCentral Bicol State University of Agriculture: - EDUCATIONMarlene A. RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Year at A Glance 2015-2016Dokumen2 halamanYear at A Glance 2015-2016api-295573149Belum ada peringkat
- Barriers To The Uptake of Ict by Teachers ArticleDokumen12 halamanBarriers To The Uptake of Ict by Teachers ArticlepubalanBelum ada peringkat
- Phase 4 CBA AssignmentDokumen3 halamanPhase 4 CBA AssignmentAnna DemlowBelum ada peringkat
- Disadvantages of An Elite EducationDokumen4 halamanDisadvantages of An Elite EducationcolayaBelum ada peringkat
- Pedagogy and Classroom Management 2 PDFDokumen82 halamanPedagogy and Classroom Management 2 PDFSiraj Baloch100% (6)
- Informe Marland 1971Dokumen127 halamanInforme Marland 1971rd1481Belum ada peringkat
- Sample Cover LettersDokumen8 halamanSample Cover Letterskop86328288Belum ada peringkat
- American Campus Vocabulary 50 Words Every College Student Must Know FINALDokumen30 halamanAmerican Campus Vocabulary 50 Words Every College Student Must Know FINALRicardo Lopes de Andrade100% (2)
- Ilp Jordan VieiraDokumen10 halamanIlp Jordan Vieiraapi-312733983Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan in Principles of Teaching 1Dokumen2 halamanLesson Plan in Principles of Teaching 1Ro Se LynBelum ada peringkat
- The NSW Premier's Student Volunteering Awards ProgramDokumen2 halamanThe NSW Premier's Student Volunteering Awards ProgrammitchBelum ada peringkat
- Choose and Write The Letter of Your Answer On The Blank Before Each NumberDokumen3 halamanChoose and Write The Letter of Your Answer On The Blank Before Each NumberMernie Grace Dionesio100% (1)
- Lesson Plan For Teaching WritingDokumen7 halamanLesson Plan For Teaching WritingSaharudin YamatoBelum ada peringkat
- Key Understan Ding To Be Developed Learning ObjectivesDokumen118 halamanKey Understan Ding To Be Developed Learning ObjectivesJaymar Tuatis100% (1)
- Lavdeep Singh Gill PipingDokumen3 halamanLavdeep Singh Gill PipingER NavdeepBelum ada peringkat
- Philippines EFA MDADokumen54 halamanPhilippines EFA MDARebecca Monzon100% (2)
- Stuart Pritchard Microteach ReflectionDokumen1 halamanStuart Pritchard Microteach Reflectionapi-321674909Belum ada peringkat
- RF PWR Word Families - Letter CombinationsDokumen3 halamanRF PWR Word Families - Letter Combinationsapi-278024645Belum ada peringkat
- Compilations of Grammar QuestionsDokumen13 halamanCompilations of Grammar Questionszaini5298Belum ada peringkat
- Edexcel GCE: Core Mathematics C2 Advanced SubsidiaryDokumen58 halamanEdexcel GCE: Core Mathematics C2 Advanced SubsidiarySyed Waqas Arif ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Reviewer QuestionaireDokumen11 halamanReviewer QuestionaireMalou Lucero SolatorioBelum ada peringkat
- Music 19A Syll Autumn 2018Dokumen4 halamanMusic 19A Syll Autumn 2018Ronak Anuj MaldeBelum ada peringkat
- Thinking Farms and Midwest AG AcademyDokumen6 halamanThinking Farms and Midwest AG AcademyrvanderhooningBelum ada peringkat
- Danielson Teacher RubricDokumen115 halamanDanielson Teacher RubricRogelio RomeroBelum ada peringkat
- DLP RW 2018 OrientationDokumen2 halamanDLP RW 2018 Orientationjulieann21bagamaspad100% (1)
- Great Gatsby Final Project Rubric NameDokumen1 halamanGreat Gatsby Final Project Rubric Nameapi-249078658Belum ada peringkat
- Observation Lesson KindergartenDokumen2 halamanObservation Lesson Kindergartenapi-284103669Belum ada peringkat
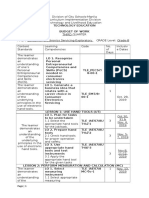
- Budget of Work Electronics Group Sy2019 2020Dokumen4 halamanBudget of Work Electronics Group Sy2019 2020MN Feruelo100% (1)
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: The Infographics EditionDari EverandThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: The Infographics EditionPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2475)
- The Power of Now: A Guide to Spiritual EnlightenmentDari EverandThe Power of Now: A Guide to Spiritual EnlightenmentPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (4125)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDari EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (404)
- The Stoic Mindset: Living the Ten Principles of StoicismDari EverandThe Stoic Mindset: Living the Ten Principles of StoicismPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (12)
- Master Your Emotions: Develop Emotional Intelligence and Discover the Essential Rules of When and How to Control Your FeelingsDari EverandMaster Your Emotions: Develop Emotional Intelligence and Discover the Essential Rules of When and How to Control Your FeelingsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (322)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDari EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BePenilaian: 2 dari 5 bintang2/5 (1)
- Control Your Mind and Master Your Feelings: This Book Includes - Break Overthinking & Master Your EmotionsDari EverandControl Your Mind and Master Your Feelings: This Book Includes - Break Overthinking & Master Your EmotionsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (74)
- Summary: The Laws of Human Nature: by Robert Greene: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDari EverandSummary: The Laws of Human Nature: by Robert Greene: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (30)
- Summary of The Art of Seduction by Robert GreeneDari EverandSummary of The Art of Seduction by Robert GreenePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (46)
- Summary: Atomic Habits by James Clear: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad OnesDari EverandSummary: Atomic Habits by James Clear: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad OnesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1636)
- Becoming Supernatural: How Common People Are Doing The UncommonDari EverandBecoming Supernatural: How Common People Are Doing The UncommonPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1484)
- The Science of Self Discipline: How Daily Self-Discipline, Everyday Habits and an Optimised Belief System will Help You Beat Procrastination + Why Discipline Equals True FreedomDari EverandThe Science of Self Discipline: How Daily Self-Discipline, Everyday Habits and an Optimised Belief System will Help You Beat Procrastination + Why Discipline Equals True FreedomPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (867)
- Indistractable: How to Control Your Attention and Choose Your LifeDari EverandIndistractable: How to Control Your Attention and Choose Your LifePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (6)
- How To Win Friends and Influence People by Dale Carnegie - Book SummaryDari EverandHow To Win Friends and Influence People by Dale Carnegie - Book SummaryPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (557)
- The 5 Second Rule: Transform your Life, Work, and Confidence with Everyday CourageDari EverandThe 5 Second Rule: Transform your Life, Work, and Confidence with Everyday CouragePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (12)
- The One Thing: The Surprisingly Simple Truth Behind Extraordinary ResultsDari EverandThe One Thing: The Surprisingly Simple Truth Behind Extraordinary ResultsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (709)
- The War of Art by Steven Pressfield - Book Summary: Break Through The Blocks And Win Your Inner Creative BattlesDari EverandThe War of Art by Steven Pressfield - Book Summary: Break Through The Blocks And Win Your Inner Creative BattlesPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (274)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeDari EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (254)
- Mastering Productivity: Everything You Need to Know About Habit FormationDari EverandMastering Productivity: Everything You Need to Know About Habit FormationPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (24)
- The 16 Undeniable Laws of Communication: Apply Them and Make the Most of Your MessageDari EverandThe 16 Undeniable Laws of Communication: Apply Them and Make the Most of Your MessagePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (73)
- Quantum Success: 7 Essential Laws for a Thriving, Joyful, and Prosperous Relationship with Work and MoneyDari EverandQuantum Success: 7 Essential Laws for a Thriving, Joyful, and Prosperous Relationship with Work and MoneyPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (38)
- Empath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainDari EverandEmpath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (95)
- Own Your Past Change Your Future: A Not-So-Complicated Approach to Relationships, Mental Health & WellnessDari EverandOwn Your Past Change Your Future: A Not-So-Complicated Approach to Relationships, Mental Health & WellnessPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (85)
- The Slight Edge: Turning Simple Disciplines into Massive Success and HappinessDari EverandThe Slight Edge: Turning Simple Disciplines into Massive Success and HappinessPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (118)
- Summary: $100M Offers: How to Make Offers So Good People Feel Stupid Saying No: by Alex Hormozi: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDari EverandSummary: $100M Offers: How to Make Offers So Good People Feel Stupid Saying No: by Alex Hormozi: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (17)