Vitamin Mineral Reference Guide
Diunggah oleh
Eleni Kostara0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
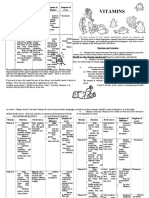
39 tayangan2 halamanVitamin / Mineral Symptoms Anemia Dysphagia Koiloncychia Enteropathy Fatigue Rapid heart rate / palpitations Decreased work performance Impaired learning ability Anorexia Gait ataxia Paresthesia Muscle cramps Irritability. Iron replacement therapy, up to 300 mg / d elemental iron, usually as 3 or 4 tablets given during the course of the day.
Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniVitamin / Mineral Symptoms Anemia Dysphagia Koiloncychia Enteropathy Fatigue Rapid heart rate / palpitations Decreased work performance Impaired learning ability Anorexia Gait ataxia Paresthesia Muscle cramps Irritability. Iron replacement therapy, up to 300 mg / d elemental iron, usually as 3 or 4 tablets given during the course of the day.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
39 tayangan2 halamanVitamin Mineral Reference Guide
Diunggah oleh
Eleni KostaraVitamin / Mineral Symptoms Anemia Dysphagia Koiloncychia Enteropathy Fatigue Rapid heart rate / palpitations Decreased work performance Impaired learning ability Anorexia Gait ataxia Paresthesia Muscle cramps Irritability. Iron replacement therapy, up to 300 mg / d elemental iron, usually as 3 or 4 tablets given during the course of the day.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
Vitamin and Mineral Reference Guide
Vitamin/Mineral Symptoms Diagnosis Treating the Deficiency
Anemia CBC; low Hgb/Hct, low MCV Iron replacement therapy, up to 300 mg/d
Dysphagia Decreased serum iron elemental iron, usually as 3 or 4 tablets given
Koiloncychia Decreased percentage of during the course of the day
Enteropathy saturation Iron preparations should be taken on an
Iron empty stomach because food can inhibit iron
Fatigue Increased TIBC
Rapid heart rate/palpitations Increased transferrin absorption
Decreased work performance Decreased serum ferritin When oral treatment has failed or with severe
Impaired learning ability anemia, IV iron infusion should be considered
Anorexia Decreased urinary thiamin With hyperemesis, parenteral doses of 100
Gait ataxia excretion mg/d for the first 7 days, followed by daily
Paresthesia Decreased RBC transketolase oral doses of 50 mg/d until complete recovery
Muscle cramps Decreased serum thiamin Simultaneous therapeutic doses of other
Thiamin/B1 Irritability Increased lactic acid waste soluble vitamins
Increased pyruvate Magnesium deficiency must be treated
simultaneously
Administration with food reduces rates of
absorption
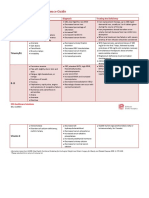
Pernicious anemia CBC; elevated MCV, high RDW, 1000 ug/wk IM for 8 weeks, then 1000 ug/mo
Pale with slightly icteric skin and Howell-Jolly bodies, IM for life or 350-500 ug/d oral crystalline B12
eyes reticulocytopenia Neurologic defects might not reverse with
Fatigue, light-headedness, or Low serum B12 supplementation
vertigo Increased MMA and increased
Shortness of breath homocysteine
Tinnitus Decreased transcobalamin II-B12
B-12
Palpitations, rapid pulse, angina Neurologic disease can occur with
and symptoms of congestive failure normal hematocrit
Numbness and paresthesia in
extremities
Ataxia
Anorexia
Diarrhea
EES Healthcare Solutions
DSL 11-0583
Osteomalacia Decreased 25- 50,000 IU/wk ergocalciferol (D2) orally or
Disorders of calcium deficiency; hydroxycholecalciferol intramuscularly, for 8 weeks
rachitic tetany Decreased serum phosphorus
Increased serum alkaline
Vitamin D phosphatase
Increased parathyroid hormone
Decreased urinary calcium
Decreased or normal serum
calcium
Information taken from ASMBS Allied Health Nutritional Guidelines for the Surgical Weight Loss Patient, Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases 2008. 4; S73-S108.
*Please note that this is not an all inclusive list.
EES Healthcare Solutions
DSL 11-0583
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Vitamin Function Food Sources Symptom of Deficiency Symptom of ExcessDokumen3 halamanVitamin Function Food Sources Symptom of Deficiency Symptom of ExcessBimo OmibBelum ada peringkat
- B Vitamins 1Dokumen1 halamanB Vitamins 1api-245692797Belum ada peringkat
- Vitamin What The Vitamin Does Significant Food Sources B1 (Thiamin)Dokumen4 halamanVitamin What The Vitamin Does Significant Food Sources B1 (Thiamin)Safi BroBelum ada peringkat
- Interpret Your Lab ReportsDokumen30 halamanInterpret Your Lab ReportspeibBelum ada peringkat
- Table Vitamins PDFDokumen3 halamanTable Vitamins PDFthomasqilBelum ada peringkat
- Vitamin Chart1Dokumen2 halamanVitamin Chart1api-281864644Belum ada peringkat
- Vitamins, Herbs, and Nutrition HandoutsDokumen16 halamanVitamins, Herbs, and Nutrition HandoutsK Borbon (K.Borbon)Belum ada peringkat
- PIN2215 Trigger Point InjectionsDokumen3 halamanPIN2215 Trigger Point InjectionsBob AdleBelum ada peringkat
- CSO Olympiad Book For Class 6Dokumen14 halamanCSO Olympiad Book For Class 6harnil trivediBelum ada peringkat
- Betaine HCL Digestive Enzymes: Kefir The Gut Health ProtocolDokumen2 halamanBetaine HCL Digestive Enzymes: Kefir The Gut Health ProtocolNico Pop100% (1)
- VitaminsDokumen1 halamanVitaminsnalandaBelum ada peringkat
- ECG Crib SheetDokumen2 halamanECG Crib Sheetkp180surfingBelum ada peringkat
- Wellen EcgDokumen9 halamanWellen EcgElokBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine DisruptorsDokumen50 halamanEndocrine DisruptorsSnowangeleyes AngelBelum ada peringkat
- DefibrillationDokumen9 halamanDefibrillationJara Maris Moreno BudionganBelum ada peringkat
- Fat Soluble: Vitamins and Minerals Vitamins Vitamin Food Sources Health Benefit DeficiencyDokumen2 halamanFat Soluble: Vitamins and Minerals Vitamins Vitamin Food Sources Health Benefit DeficiencyJthan ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- 13 Antacids and Controllers UpdDokumen63 halaman13 Antacids and Controllers Updone_nd_onlyuBelum ada peringkat
- What Is AphasiaDokumen4 halamanWhat Is AphasiaValentina DubBelum ada peringkat
- RN Pharmacology IV Push ReferanceDokumen12 halamanRN Pharmacology IV Push ReferanceMissK2216Belum ada peringkat
- Weston Price Sobre K2Dokumen104 halamanWeston Price Sobre K2Antonella MarreirosBelum ada peringkat
- Digestive System: Reported By:Era Denise A. Allego & Yleah Kyla D. SoletaDokumen28 halamanDigestive System: Reported By:Era Denise A. Allego & Yleah Kyla D. SoletaEnerita AllegoBelum ada peringkat
- Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDokumen38 halamanSexually Transmitted Diseaserana arslanBelum ada peringkat
- The Nutritional Relationships of ThyroidDokumen5 halamanThe Nutritional Relationships of ThyroidKawooya IsmaelBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar Stress FinalDokumen98 halamanSeminar Stress FinalSakthi DeviBelum ada peringkat
- Vitamin B12 - Essential For Healthy Blood, Brain, and Dna: Homocysteine and Cardiovascular DiseaseDokumen3 halamanVitamin B12 - Essential For Healthy Blood, Brain, and Dna: Homocysteine and Cardiovascular Diseaseizeldien5870Belum ada peringkat
- c22 Microbiology Tortora TestbankDokumen16 halamanc22 Microbiology Tortora Testbankwhitewave25Belum ada peringkat
- MineralsDokumen87 halamanMineralsHaren Aizhel TenderoBelum ada peringkat
- 100 Test Aarogya 2.0:: Mrs - Gunjan MisraDokumen19 halaman100 Test Aarogya 2.0:: Mrs - Gunjan Misramomo misraBelum ada peringkat
- Mineral Metabolism and Abnormalities: Le Duong Hoang Huy M.D Email: Huyldh@pnt - Edu.vnDokumen66 halamanMineral Metabolism and Abnormalities: Le Duong Hoang Huy M.D Email: Huyldh@pnt - Edu.vnLam NgoBelum ada peringkat
- Final Calcium Magnesium Ratio 3 1 12 PDFDokumen2 halamanFinal Calcium Magnesium Ratio 3 1 12 PDFHitesh Verma100% (1)
- Metadichol: Rheumatoid Arthritis A Case StudyDokumen4 halamanMetadichol: Rheumatoid Arthritis A Case StudyDr P.R. RaghavanBelum ada peringkat
- Lipid Absorption and Transport UptakeDokumen218 halamanLipid Absorption and Transport UptakeSimra Zahid100% (1)
- Hematinics BPTDokumen17 halamanHematinics BPTbpt2Belum ada peringkat
- Gettheglow Ebook v2Dokumen23 halamanGettheglow Ebook v2SabrinaHaldemannBelum ada peringkat
- Vitamin B GroupDokumen31 halamanVitamin B GroupDereen NajatBelum ada peringkat
- Supplements UPDATED - OCT 2023Dokumen9 halamanSupplements UPDATED - OCT 2023r_sendhilBelum ada peringkat
- Vitamin A: Vitamin and Mineral InteractionsDokumen17 halamanVitamin A: Vitamin and Mineral InteractionsissaiahnicolleBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine NCLEX PN Pract & ANS Questions IIDokumen13 halamanEndocrine NCLEX PN Pract & ANS Questions IIYA HOBelum ada peringkat
- Trace ElementsDokumen5 halamanTrace ElementsFaithBelum ada peringkat
- How Your Thyroid Reacts To Skin Care IngredientsDokumen8 halamanHow Your Thyroid Reacts To Skin Care Ingredientsma ceciBelum ada peringkat
- AnemiaDokumen42 halamanAnemiameutia wardhanie ganieBelum ada peringkat
- NCP (Diarrhea)Dokumen2 halamanNCP (Diarrhea)Rodj Bilang Jr.83% (30)
- Tony Huge Top 10 ProtocolsDokumen12 halamanTony Huge Top 10 Protocolsryarok1Belum ada peringkat
- Role of Magnesium and CalciumDokumen5 halamanRole of Magnesium and CalciumsemiBelum ada peringkat
- Vitamin B6 Deficiency, A Simple Guide to the Condition, its Treatment and Related DiseasesDari EverandVitamin B6 Deficiency, A Simple Guide to the Condition, its Treatment and Related DiseasesBelum ada peringkat
- RosuvastatinDokumen1 halamanRosuvastatinJoshua KellyBelum ada peringkat
- Nutrition and VitaminDokumen70 halamanNutrition and VitaminTob JurBelum ada peringkat
- 10 1097@01 JAA 0000522145 52305 AaDokumen2 halaman10 1097@01 JAA 0000522145 52305 AaAwal Safar M100% (1)
- IV Push List PedsDokumen5 halamanIV Push List PedskrizzywhizzyBelum ada peringkat
- Nutrition: Vitamin and MineralDokumen15 halamanNutrition: Vitamin and MineralSmkdpb PontianBelum ada peringkat
- Vitamins: Fat-Soluble Vitamins (Vitamin A, D, E, K) Water-Soluble Vitamins (Vitamin B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12, C)Dokumen14 halamanVitamins: Fat-Soluble Vitamins (Vitamin A, D, E, K) Water-Soluble Vitamins (Vitamin B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12, C)Danica Antiquerra PeñaBelum ada peringkat
- Personal Mastery: Concepts and Methods From Peter Senge'sDokumen21 halamanPersonal Mastery: Concepts and Methods From Peter Senge'sMuhammad NajeebBelum ada peringkat
- Intravenous Nutrient SolutionsDokumen28 halamanIntravenous Nutrient SolutionsElsayed AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Food Matters Food Additives To AvoidDokumen1 halamanFood Matters Food Additives To AvoidPopescu Bogdan ConstantinBelum ada peringkat
- Non-Essential Amino Acids Nitrogen MetabolismDokumen21 halamanNon-Essential Amino Acids Nitrogen Metabolismpradeep36Belum ada peringkat
- Benefits of ProbioticsDokumen2 halamanBenefits of ProbioticsGeo IuliaBelum ada peringkat
- 20 03 12 - How-To-Fix-A-Broken-Diet-Infographic-Printer-3Dokumen5 halaman20 03 12 - How-To-Fix-A-Broken-Diet-Infographic-Printer-3sm V15Belum ada peringkat
- Vitamin For Final MCQDokumen14 halamanVitamin For Final MCQSajia Abedin 1821432649Belum ada peringkat
- Vitamins NotesDokumen8 halamanVitamins NotesEllyBelum ada peringkat
- 1MENIEREDokumen6 halaman1MENIEREsunny_jr_Belum ada peringkat
- Nutrients Why - Benefits, Risk & Side Effects Side Effects (Overdose) How-Natural Source/ Supplements DosesDokumen7 halamanNutrients Why - Benefits, Risk & Side Effects Side Effects (Overdose) How-Natural Source/ Supplements Dosesjohnsonkk125Belum ada peringkat
- Liver EnzymesDokumen6 halamanLiver EnzymesWande AyodeleBelum ada peringkat
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome PTH 617 PresentationDokumen14 halamanIrritable Bowel Syndrome PTH 617 Presentationapi-621438645Belum ada peringkat
- Hyper BrochureDokumen2 halamanHyper BrochureVksudhar SanamBelum ada peringkat
- PeroxisomesDokumen2 halamanPeroxisomesIndigoSilverBelum ada peringkat
- Male Hypogonadism: EAU Guidelines OnDokumen34 halamanMale Hypogonadism: EAU Guidelines OnAyu sri WidianiBelum ada peringkat
- Fluids & Electrolytes 5Dokumen14 halamanFluids & Electrolytes 5Justin Angelo SildoraBelum ada peringkat
- AnemiaDokumen3 halamanAnemiaGhadeer AbedBelum ada peringkat
- COMPILATIONSSSSDokumen976 halamanCOMPILATIONSSSSANNooonynmousBelum ada peringkat
- Iso Iec GuidesDokumen2 halamanIso Iec GuidesEleni KostaraBelum ada peringkat
- Vitamin Mineral Reference GuideDokumen2 halamanVitamin Mineral Reference GuideEleni KostaraBelum ada peringkat
- Small Claims - Practical GuideDokumen52 halamanSmall Claims - Practical GuideNarry MarkmvBelum ada peringkat
- 2010 Foreclosure Guide For Homeowners in CaliforniaDokumen74 halaman2010 Foreclosure Guide For Homeowners in California83jjmackBelum ada peringkat
- Real Estate Law and Subdivided Lands LawDokumen197 halamanReal Estate Law and Subdivided Lands LawEleni Kostara100% (1)
- Real Estate Law and Subdivided Lands LawDokumen197 halamanReal Estate Law and Subdivided Lands LawEleni Kostara100% (1)
- Assignment 1 Part 1 A1Dokumen10 halamanAssignment 1 Part 1 A1garrenaBelum ada peringkat
- Klinefelter Syndrome in Clinical Practice. Nat Clin Pract Urol 4:192-204Dokumen14 halamanKlinefelter Syndrome in Clinical Practice. Nat Clin Pract Urol 4:192-204Anonymous LAWfm7Belum ada peringkat
- Drug Study - Ello - Ampicillin - MultivitaminsDokumen3 halamanDrug Study - Ello - Ampicillin - MultivitaminsCHRISTINE GRACE ELLOBelum ada peringkat
- "COVID Is Fake Sick Actually Have Influenza A or B", by Dr. Derek KnaussDokumen2 halaman"COVID Is Fake Sick Actually Have Influenza A or B", by Dr. Derek KnaussSANDRA BAGGBelum ada peringkat
- Make-Up Improves The Quality of Life of Acne Patients Without Aggravating Acne Eruptions During TreatmentsDokumen3 halamanMake-Up Improves The Quality of Life of Acne Patients Without Aggravating Acne Eruptions During TreatmentsfitrizeliaBelum ada peringkat
- Tetanus: Guerrero, Djameica Danielle RDokumen16 halamanTetanus: Guerrero, Djameica Danielle RDjameica GuerreroBelum ada peringkat
- Normal Digestion / Absorption of FatDokumen5 halamanNormal Digestion / Absorption of FatMarc Michael Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- 1 InfectionDokumen41 halaman1 InfectionIMA MSN TNBelum ada peringkat
- Behavior and Mental Status Can Be Early Signs of Impaired Gas ExchangeDokumen2 halamanBehavior and Mental Status Can Be Early Signs of Impaired Gas ExchangeJoanna Marie Lumbre BalbiranBelum ada peringkat
- Corona Virus (Covid19) : The Grim RealityDokumen6 halamanCorona Virus (Covid19) : The Grim RealityGenevieve GayosoBelum ada peringkat
- Broiler Breeder DiseasesDokumen12 halamanBroiler Breeder DiseasesvetbcasBelum ada peringkat
- PediatricsDokumen21 halamanPediatricsManoj KumarBelum ada peringkat
- TN Maulana VL PalpebraeDokumen10 halamanTN Maulana VL Palpebraemonyet65Belum ada peringkat
- Histological Features of Candidiasis: By:Mamdouh Dagsh Alshrifi ID:321103259Dokumen14 halamanHistological Features of Candidiasis: By:Mamdouh Dagsh Alshrifi ID:321103259Mamdouh D AlrwailiBelum ada peringkat
- ICMR GuidelinesType2diabetes2018 0Dokumen82 halamanICMR GuidelinesType2diabetes2018 0VISHWANATH MARSHIVANIKARBelum ada peringkat
- ICD-10 TK Pedsos 2013Dokumen10 halamanICD-10 TK Pedsos 2013Ludi Dhyani RahmartaniBelum ada peringkat
- Andaman Fever A New EntityDokumen6 halamanAndaman Fever A New EntitySheepu SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- V1.0-Emergency Plan For Prevention and Control of New Coronavirus - Disease-CPPESEA PDFDokumen12 halamanV1.0-Emergency Plan For Prevention and Control of New Coronavirus - Disease-CPPESEA PDFNutthakarn WisatsiriBelum ada peringkat
- Midterm Activity ScitechDokumen3 halamanMidterm Activity ScitechKean KaiBelum ada peringkat
- Pathology of Common Glomerular Syndromes: DR Purushotham KrishnappaDokumen34 halamanPathology of Common Glomerular Syndromes: DR Purushotham KrishnappaTarin IslamBelum ada peringkat
- Soal PTS Bahasa Inggris Kelas XiDokumen3 halamanSoal PTS Bahasa Inggris Kelas XiHafiz AriBelum ada peringkat