Pedigree Analysis
Diunggah oleh
api-240662720Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Pedigree Analysis
Diunggah oleh
api-240662720Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Pedigree Analysis
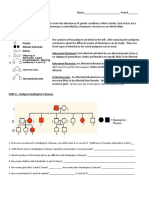
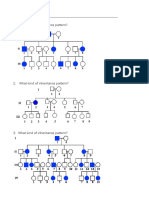
A pedigree is a diagram that shows the occurrence and appearance, or phenotype, of a particular
genetic trait from one generation to the next in a family.
Genotypes can be determined with an understanding of inheritance and probability.
Generations are represented by Roman numerals
Each person in a generation is numbered
Males are _____________________
Females are ___________________
Affected individuals are
_____________________________
Line connecting I-1 and I-2 is called the
_______________________________
Line extending down from marriage line is called the __________________________________
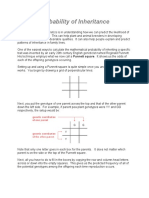
Determining Genotypes
All shaded symbols represent individuals who are homozygous recessive.
Rule 1: Assign two recessive genes to any person on a pedigree whose symbol is shaded. These
people express the recessive trait being studied. If the trait is sex-linked, shaded males
will carry one copy of the recessive allele on their X chromosome
Rule 2: Assign one dominant gene to any person on a pedigree whose symbol is unshaded. These
people express the dominant trait being studied
This allows us to predict some of the genes for the remaining people in the pedigree. A Punnett square
can be used to help determine the remaining genotype possibilities.
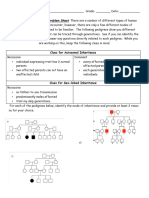
Autosomal Inheritance
Sex-linked Inheritance
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance
Trait should not skip generations.
An affected person married to a "normal" person should have approximately 50% of the
offspring being affected. (Also indicates that the affected individual is heterozygous).
Distribution of the trait should be close to equal distribution among the sexes.
Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
Trait often skips generations.
Distribution of the trait should be close to equal distribution among the sexes.
If both of the parents are affected, all of the children should be affected.
Most affected individuals have "normal" parents.
When a "normal" person is married to an affected individual, all of the children are normal
(indicating the normal parent is homozygous dominant).
If a "normal" person is married to an affected individual and one or more of the children are
affected, then approximately half of the children should be affected. (Showing that the "normal"
parent is heterozygous).
Sex-linked Dominant Inheritance
Trait should not skip generations.
Affected males must come from affected mothers.
Approximately half of the children of an affected female are affected. (Figuring the mother is
heterozygous)
All the daughters, but none of the sons, of an affected father are affected.
For a female child to be affected, the father or the mother must be affected
Sex-linked Recessive Inheritance
Most of the affected individuals are males.
For a female child to be affected, the father must be affected and the mother must be affected
or a carrier.
All of the sons of an affected mother must be affected.
For a male child to be affected, the mother must be affected or a carrier. (Many times this can be
determined by studying males in the mothers family line)
Approximately half of the sons of carrier females should be affected.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Non-Mendelian Genetics PracticeDokumen13 halamanNon-Mendelian Genetics PracticeMariquit M. Lopez67% (3)
- Lab 02 Extra - Extentions To Mendelian GeneticsDokumen6 halamanLab 02 Extra - Extentions To Mendelian Genetics13ucciBelum ada peringkat
- HorticultureDokumen168 halamanHorticultureagni sahanaBelum ada peringkat
- 520l0553 PDFDokumen52 halaman520l0553 PDFVasil TsvetanovBelum ada peringkat
- Non-Mendelian Patterns of Inheritance IntroductionDokumen39 halamanNon-Mendelian Patterns of Inheritance IntroductionErica NatividadBelum ada peringkat
- Pedigree AnalysisDokumen18 halamanPedigree AnalysisSanjeet YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Modules For General Biology 2Dokumen24 halamanLearning Modules For General Biology 2Albert Rosete0% (1)
- Human Genetics and PedigreeDokumen37 halamanHuman Genetics and Pedigreekholoud220100% (1)
- Exercise 6 Pedigree Analysis 1Dokumen10 halamanExercise 6 Pedigree Analysis 1neil gutierrezBelum ada peringkat
- Service Manual: RP-6000 MK6 LTD RP-6000 MK6 BDokumen44 halamanService Manual: RP-6000 MK6 LTD RP-6000 MK6 BFivor EdwardsBelum ada peringkat
- DuctBank For Electrical SystemDokumen4 halamanDuctBank For Electrical SystemAnonymous XYAPaxjbYBelum ada peringkat
- Sex LinkageDokumen32 halamanSex LinkageRichmon AlamanBelum ada peringkat
- Roots Prefixes and Suffixes in BiologyDokumen9 halamanRoots Prefixes and Suffixes in Biologyapi-240662720Belum ada peringkat
- Roots Prefixes and Suffixes in BiologyDokumen9 halamanRoots Prefixes and Suffixes in Biologyapi-240662720Belum ada peringkat
- Genetics 2Dokumen50 halamanGenetics 2Clara Mae100% (1)
- AP Human Geography Review Unit 2Dokumen18 halamanAP Human Geography Review Unit 2BaselOsman50% (2)
- Concrete ON MALDIVESDokumen55 halamanConcrete ON MALDIVESKãrthìçk JkrBelum ada peringkat
- Investigating Inherited TraitsDokumen12 halamanInvestigating Inherited TraitsNoora AtariBelum ada peringkat
- Sr. IBS DAS Consultant EngineerDokumen4 halamanSr. IBS DAS Consultant EngineerMohamed KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Reference:: PedigreeDokumen10 halamanReference:: PedigreeJems SumayaBelum ada peringkat
- Pedigree Worksheet: (Both Parents Could Be Heterozygous)Dokumen3 halamanPedigree Worksheet: (Both Parents Could Be Heterozygous)DaddyBraccBelum ada peringkat
- Unlock SGCh23Dokumen8 halamanUnlock SGCh23Silax100% (1)
- Bio Pedigree AnalysisDokumen3 halamanBio Pedigree AnalysisKarthika UmashankarBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics AssignmentDokumen20 halamanGenetics AssignmentPérvéz NázírBelum ada peringkat
- Pedigree Analysis Chart Identification TipsDokumen2 halamanPedigree Analysis Chart Identification TipssriBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A Pedigree.Dokumen7 halamanWhat Is A Pedigree.Sheryl Lou AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- LG 3.1 Pedigree AnalysisDokumen27 halamanLG 3.1 Pedigree AnalysisAeon BeluanBelum ada peringkat
- Pedigree Analysis From Biology For NEET 2019Dokumen3 halamanPedigree Analysis From Biology For NEET 2019misostudy100% (1)
- Genetics and Genetic CounsellingDokumen26 halamanGenetics and Genetic Counsellingmaria theresa SalvillaBelum ada peringkat
- Sex Linked InheritanceDokumen5 halamanSex Linked InheritanceSheryl Lou AngelesBelum ada peringkat
- Cytological and Mathematical Basis of InheritanceDokumen6 halamanCytological and Mathematical Basis of InheritanceJobelle CajipoBelum ada peringkat
- Patterns of Genetic InheritanceDokumen9 halamanPatterns of Genetic InheritanceSaidBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics and HeredityDokumen6 halamanGenetics and HeredityRenjyl Gay DeguinionBelum ada peringkat
- Pedigary AnalysisDokumen4 halamanPedigary Analysissneh lataBelum ada peringkat
- GeneticsDokumen27 halamanGeneticsKatherine CampillosBelum ada peringkat
- GeneticsDokumen32 halamanGeneticsyuuki konnoBelum ada peringkat
- Supnet - Laboratory Report 3Dokumen3 halamanSupnet - Laboratory Report 3Ako Si Vern ÖBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics: Mode of InheritanceDokumen46 halamanGenetics: Mode of InheritanceHandrex MadrigalBelum ada peringkat
- Sex Linkage: Characters Which Are Associate More With One GenderDokumen28 halamanSex Linkage: Characters Which Are Associate More With One GenderFakhri NasharulBelum ada peringkat
- Pedigree Chart Notes: Genetic Family TreeDokumen7 halamanPedigree Chart Notes: Genetic Family Treest72136Belum ada peringkat
- PEDIGREEDokumen8 halamanPEDIGREEAgim CallajBelum ada peringkat
- Human Genetics in Nursing Practice NUR 473: by Dr. Khaloud Alzahrani Assistant Professor in Molecular GeneticsDokumen45 halamanHuman Genetics in Nursing Practice NUR 473: by Dr. Khaloud Alzahrani Assistant Professor in Molecular GeneticsBarrak AldosaryBelum ada peringkat
- Pedigree WorksheetDokumen4 halamanPedigree Worksheetleister.hidalgoBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Genetics: Mode of InheritanceDokumen35 halamanMedical Genetics: Mode of InheritanceSadiBelum ada peringkat
- HeredityDokumen72 halamanHereditySein Hla KyawBelum ada peringkat
- Biology 3Dokumen34 halamanBiology 3Amilhasan KnaikBelum ada peringkat
- BIOLOGY 3.ppsxDokumen34 halamanBIOLOGY 3.ppsxFranc VenturaBelum ada peringkat
- Patterns of InheritanceDokumen22 halamanPatterns of InheritanceKetch Tim InfanteBelum ada peringkat
- PEDGREEDokumen2 halamanPEDGREEStelio GuimarãesBelum ada peringkat
- Incomplete Multiple AllelesDokumen8 halamanIncomplete Multiple AllelesMarc RusselBelum ada peringkat
- Inheritance and PedigreeDokumen6 halamanInheritance and PedigreeNiranjan S ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Chapter 7Dokumen3 halamanBiology Chapter 7JUDY100% (1)
- General Biology 2Dokumen6 halamanGeneral Biology 2Christianne Joseph MonzonBelum ada peringkat
- Non Mendelian PrinciplesDokumen38 halamanNon Mendelian PrinciplesEzra Denise Lubong RamelBelum ada peringkat
- PedigreesDokumen3 halamanPedigreesapi-358494331100% (1)
- Learning Modules For General Biology 2Dokumen12 halamanLearning Modules For General Biology 2Albert Rosete0% (1)
- Pedigrees Lesson PDFDokumen7 halamanPedigrees Lesson PDFaimifarzana98Belum ada peringkat
- Topic 6-Pedigree ChartsDokumen4 halamanTopic 6-Pedigree ChartsWinndell DupresBelum ada peringkat
- PedigreeDokumen5 halamanPedigreeEnter tainmentBelum ada peringkat
- Phenotypes and Genotypes 7Dokumen4 halamanPhenotypes and Genotypes 7Rashed Aiman Sameer Alsayyed AlalqamawiBelum ada peringkat
- Life Sciences GR 12 Theory Booklet GeneticsDokumen9 halamanLife Sciences GR 12 Theory Booklet GeneticschiomsonzahBelum ada peringkat
- 4th Week Cross Cytology Lecture October 32020 1Dokumen58 halaman4th Week Cross Cytology Lecture October 32020 1terryortiz825Belum ada peringkat
- PDF - Pedigree WorksheetDokumen2 halamanPDF - Pedigree Worksheetapi-280769158100% (3)
- Inheritance Activity (Has Bonus Assignment Along With The Lab)Dokumen7 halamanInheritance Activity (Has Bonus Assignment Along With The Lab)Leah HerbertBelum ada peringkat
- General Biology 2 Second SemesterDokumen49 halamanGeneral Biology 2 Second SemesterRuthie TabanguilBelum ada peringkat
- Pedigrees ReviewDokumen4 halamanPedigrees ReviewMichael SopranoBelum ada peringkat
- Patterns of Inheritance and PedigreeDokumen58 halamanPatterns of Inheritance and Pedigreemus zaharaBelum ada peringkat
- 3 AdDokumen40 halaman3 AdSree Harini SBelum ada peringkat
- Test ReviewDokumen1 halamanTest Reviewapi-240662720Belum ada peringkat
- Non-Mendelian ReviewDokumen2 halamanNon-Mendelian Reviewapi-240662720Belum ada peringkat
- Mitosis, Meiosis, Genetic Variability, Sex Determination 3Dokumen15 halamanMitosis, Meiosis, Genetic Variability, Sex Determination 3api-240662720Belum ada peringkat
- Punnett SquaresDokumen14 halamanPunnett Squaresapi-240662720Belum ada peringkat
- Punnett SquaresDokumen14 halamanPunnett Squaresapi-240662720Belum ada peringkat
- Dna ReviewDokumen1 halamanDna Reviewapi-240662720Belum ada peringkat
- CarbonfootprintDokumen1 halamanCarbonfootprintapi-240662720Belum ada peringkat
- Excretory ReviewDokumen2 halamanExcretory Reviewapi-240662720Belum ada peringkat
- Rockwell Allen BradleyDokumen73 halamanRockwell Allen BradleymaygomezBelum ada peringkat
- B2 - Effects of UV-C Treatment and Cold Storage On Ergosterol and Vitamin D2 Contents in Different Parts of White and Brown Mushroom (Agaricus Bisporus)Dokumen6 halamanB2 - Effects of UV-C Treatment and Cold Storage On Ergosterol and Vitamin D2 Contents in Different Parts of White and Brown Mushroom (Agaricus Bisporus)Nadya Mei LindaBelum ada peringkat
- Orchestral Recording, January 2006Dokumen10 halamanOrchestral Recording, January 2006Rhys WilliamsBelum ada peringkat
- Vanilla Farming: The Way Forward: July 2019Dokumen6 halamanVanilla Farming: The Way Forward: July 2019mituBelum ada peringkat
- The 50 Most Inspiring Travel Quotes of All TimeDokumen4 halamanThe 50 Most Inspiring Travel Quotes of All Timeungku1Belum ada peringkat
- Safety Data Sheet: Section 1. Identification Jotun Essence Easy CleanDokumen11 halamanSafety Data Sheet: Section 1. Identification Jotun Essence Easy CleanHồng PhongBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation On Anther Culture: Submitted To Submitted byDokumen22 halamanPresentation On Anther Culture: Submitted To Submitted byvishnu0751Belum ada peringkat
- Paper 2 Phy 2019-2023Dokumen466 halamanPaper 2 Phy 2019-2023Rocco IbhBelum ada peringkat
- Classic Plan: Dog/Cat BedDokumen3 halamanClassic Plan: Dog/Cat BedRobson DiasBelum ada peringkat
- Indian Standard: Methods of Chemical Testing of LeatherDokumen75 halamanIndian Standard: Methods of Chemical Testing of LeatherAshish DixitBelum ada peringkat
- Tabla QuimicaDokumen12 halamanTabla QuimicaPablo PasqualiniBelum ada peringkat
- 2019 BMS1021 Practice Questions Answers PDFDokumen12 halaman2019 BMS1021 Practice Questions Answers PDFaskldhfdasjkBelum ada peringkat
- UNDP NP Dhangadhi SWM TOR FinalDokumen4 halamanUNDP NP Dhangadhi SWM TOR FinalNirmal K.c.Belum ada peringkat
- Surface & Subsurface Geotechnical InvestigationDokumen5 halamanSurface & Subsurface Geotechnical InvestigationAshok Kumar SahaBelum ada peringkat
- Management Science - Lecture 2Dokumen9 halamanManagement Science - Lecture 2Nicole SallanBelum ada peringkat
- Union Fork & Hoe No. 19Dokumen68 halamanUnion Fork & Hoe No. 19Jay SBelum ada peringkat
- Appetizer Summative TestDokumen36 halamanAppetizer Summative TestArgelynPadolinaPedernalBelum ada peringkat
- Carriages and Mounts SeriesDokumen92 halamanCarriages and Mounts Seriessudhirm16Belum ada peringkat
- Sensors & Transducers: (Code: EI 401)Dokumen4 halamanSensors & Transducers: (Code: EI 401)Mayukh BiswasBelum ada peringkat
- EOCR 종합 EN 2015 PDFDokumen228 halamanEOCR 종합 EN 2015 PDFShubhankar KunduBelum ada peringkat
- Titanvene ll0209sr Product Data SheetpdfDokumen1 halamanTitanvene ll0209sr Product Data SheetpdfHanry WRBelum ada peringkat
- Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering Faculty of Chemical and Materials Engineering University of The Punjab LahoreDokumen10 halamanInstitute of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering Faculty of Chemical and Materials Engineering University of The Punjab LahoreMUmairQrBelum ada peringkat
- Volume 2 Part 1 - Civil & Arch SpecificationsDokumen173 halamanVolume 2 Part 1 - Civil & Arch Specificationsanish100% (1)