ECSE-4730: Computer Communication Networks (CCN) Chapter 5
Diunggah oleh
uflilla0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
21 tayangan12 halamanIEEE 802. Wireless LAN - 2 Basic Service Set (bss) contains: wireless hosts access point (AP): base station BSS's combined to form distribution system (DS) IEEE 802. MAC Protocol: CSMA / CA 802. CSMA sender: - if sense channel idle for DISF sec. Then transmit entire frame (no collision detection) receiver: if received OK return ACK after SIFS IEEE 802. Frame has transmission time field others (hearing sat
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
ECSE-4730: Computer Communication Networks (CCN) Chapter 5:
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniIEEE 802. Wireless LAN - 2 Basic Service Set (bss) contains: wireless hosts access point (AP): base station BSS's combined to form distribution system (DS) IEEE 802. MAC Protocol: CSMA / CA 802. CSMA sender: - if sense channel idle for DISF sec. Then transmit entire frame (no collision detection) receiver: if received OK return ACK after SIFS IEEE 802. Frame has transmission time field others (hearing sat
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
21 tayangan12 halamanECSE-4730: Computer Communication Networks (CCN) Chapter 5
Diunggah oleh
uflillaIEEE 802. Wireless LAN - 2 Basic Service Set (bss) contains: wireless hosts access point (AP): base station BSS's combined to form distribution system (DS) IEEE 802. MAC Protocol: CSMA / CA 802. CSMA sender: - if sense channel idle for DISF sec. Then transmit entire frame (no collision detection) receiver: if received OK return ACK after SIFS IEEE 802. Frame has transmission time field others (hearing sat
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PPT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 12
ECSE-4730: Computer
Communication Networks (CCN)
Chapter 5: The Data Link Layer - 3
Shivkumar Kalyanaraman: shivkuma@ecse.rpi.edu
Biplab Sikdar: sikdab@rpi.edu
http://www.ecse.rpi.edu/Homepages/shivkuma
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute © Shivkumar Kalvanaraman & © Biplab Sikdar 1
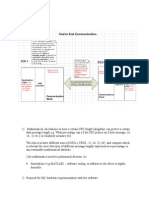
Ethernet Switches - 1
• layer 2 (frame) forwarding,
filtering using LAN
addresses
• Switching: A-to-B and A’-
to-B’ simultaneously, no
collisions
• large number of interfaces
• often: individual hosts,
star-connected into switch
• Ethernet, but no
collisions!
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute © Shivkumar Kalvanaraman & © Biplab Sikdar 2
Ethernet Switches - 2
• cut-through switching: frame forwarded
from input to output port without awaiting
for assembly of entire frame
• slight reduction in latency
• combinations of shared/dedicated,
10/100/1000 Mbps interfaces
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute © Shivkumar Kalvanaraman & © Biplab Sikdar 3
Ethernet Switches - 3
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute © Shivkumar Kalvanaraman & © Biplab Sikdar 4
IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN - 1
• Wireless LANs: untethered (often mobile)
networking
• IEEE 802.11 standard:
• MAC protocol
• unlicensed frequency spectrum: 900Mhz,
2.4Ghz
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute © Shivkumar Kalvanaraman & © Biplab Sikdar 5
IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN - 2
• Basic Service Set (BSS) (a.k.a. “cell”)
contains:
• wireless hosts
• access point (AP): base station
• BSS’s combined to form distribution system
(DS)
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute © Shivkumar Kalvanaraman & © Biplab Sikdar 6
Ad Hoc Networks
• Ad hoc network: IEEE 802.11 stations can
dynamically form network without AP
• Applications:
• “laptop” meeting in conference room,
car
• interconnection of “personal” devices
• battlefield
• IETF MANET
(Mobile Ad hoc Networks)
working group
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute © Shivkumar Kalvanaraman & © Biplab Sikdar 7
IEEE 802.11 MAC Protocol:
CSMA/CA
802.11 CSMA sender:
- if sense channel idle for
DISF sec.
then transmit entire frame
(no collision detection)
-if sense channel busy
then binary backoff
802.11 CSMA receiver:
if received OK
return ACK after SIFS
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute © Shivkumar Kalvanaraman & © Biplab Sikdar 8
IEEE 802.11 MAC Protocol
802.11 CSMA Protocol:
others
• NAV: Network
Allocation
Vector
• 802.11 frame has
transmission time field
• others (hearing sata)
defer access for NAV
time units
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute © Shivkumar Kalvanaraman & © Biplab Sikdar 9
Hidden Terminal effect
• hidden terminals: A, C cannot hear each
other
• obstacles, signal attenuation
• collisions at B
• goal: avoid collisions at B
• CSMA/CA: CSMA with Collision Avoidance
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute © Shivkumar Kalvanaraman & © Biplab Sikdar 10
Collision Avoidance: RTS-CTS
exchange - 1
• CSMA/CA: explicit channel
reservation
• sender: send short RTS:
request to send
• receiver: reply with
short CTS: clear to send
• CTS reserves channel for
sender, notifying (possibly
hidden) stations
• Avoid hidden station
collisions
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute © Shivkumar Kalvanaraman & © Biplab Sikdar 11
Collision Avoidance: RTS-CTS
exchange - 2
• RTS and CTS short:
• collisions less likely, of
shorter duration
• end result similar to
collision detection
• IEEE 802.11 allows:
• CSMA
• CSMA/CA: reservations
• polling from AP
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute © Shivkumar Kalvanaraman & © Biplab Sikdar 12
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- NTS Book For GAT GeneralDokumen142 halamanNTS Book For GAT GeneralMuzaffar AhsanBelum ada peringkat
- Inflation Adjustment CalcDokumen2 halamanInflation Adjustment CalcuflillaBelum ada peringkat
- P5.2. The Temperature Distribution of A Thick Flat Plate, Initially at A Uniform TemperatureDokumen3 halamanP5.2. The Temperature Distribution of A Thick Flat Plate, Initially at A Uniform TemperatureuflillaBelum ada peringkat
- Applied Control CW2Dokumen2 halamanApplied Control CW2uflillaBelum ada peringkat
- Block DiagDokumen11 halamanBlock DiaguflillaBelum ada peringkat
- Resistance vs. Temperature CharacteristicDokumen1 halamanResistance vs. Temperature CharacteristicuflillaBelum ada peringkat
- NTS Book For GAT GeneralDokumen142 halamanNTS Book For GAT GeneralMuzaffar AhsanBelum ada peringkat
- Di SteigenDokumen1 halamanDi SteigenuflillaBelum ada peringkat
- Ri and Ro of The Inverting AmplifierDokumen8 halamanRi and Ro of The Inverting Amplifierlizhi0007Belum ada peringkat
- Forces LabDokumen4 halamanForces LabuflillaBelum ada peringkat
- New Moon (Feb-14)Dokumen5 halamanNew Moon (Feb-14)uflillaBelum ada peringkat
- Moving Man Phet Lab ActivityDokumen5 halamanMoving Man Phet Lab Activityuflilla50% (4)
- LiveCRC LastestDokumen1 halamanLiveCRC LastestuflillaBelum ada peringkat
- P5.2. The Temperature Distribution of A Thick Flat Plate, Initially at A Uniform TemperatureDokumen3 halamanP5.2. The Temperature Distribution of A Thick Flat Plate, Initially at A Uniform TemperatureuflillaBelum ada peringkat
- Philippine StoryDokumen1 halamanPhilippine StoryuflillaBelum ada peringkat
- Fictitious Gravitation ActivityDokumen3 halamanFictitious Gravitation ActivityuflillaBelum ada peringkat
- Math 251 - Multivariable Calculus - Exam 1: American Football and Vector FunctionsDokumen2 halamanMath 251 - Multivariable Calculus - Exam 1: American Football and Vector FunctionsuflillaBelum ada peringkat
- 332:506 Control Theory I I - Fall 2007: Vericag@ece - Rutgers.eduDokumen1 halaman332:506 Control Theory I I - Fall 2007: Vericag@ece - Rutgers.eduuflillaBelum ada peringkat
- Moving Man Phet Lab ActivityDokumen5 halamanMoving Man Phet Lab Activityuflilla50% (4)
- hw2 SolDokumen5 halamanhw2 SoluflillaBelum ada peringkat
- Hooke's Law: Version: 28 Feb 06Dokumen5 halamanHooke's Law: Version: 28 Feb 06uflillaBelum ada peringkat
- Indianfilmindustry 091006102009 Phpapp02Dokumen10 halamanIndianfilmindustry 091006102009 Phpapp02uflillaBelum ada peringkat
- Philippine StoryDokumen1 halamanPhilippine StoryuflillaBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines For Synopsis Thesis PHD Degree Punjab UniversityDokumen5 halamanGuidelines For Synopsis Thesis PHD Degree Punjab Universityfarooqsami4uBelum ada peringkat
- Matlab Code Specs For Optimization LoopDokumen7 halamanMatlab Code Specs For Optimization LoopuflillaBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Paper: Counter Terrorism Department (Government of The Punjab) (Psychological Test For The Post of Corporals)Dokumen2 halamanSample Paper: Counter Terrorism Department (Government of The Punjab) (Psychological Test For The Post of Corporals)uflillaBelum ada peringkat
- Forces LabDokumen4 halamanForces LabuflillaBelum ada peringkat
- Projectile+Motion+Lab+ +3Dokumen2 halamanProjectile+Motion+Lab+ +3uflillaBelum ada peringkat
- Play With The Sims Motion The Ramp: - Equal - 980N - 294 NDokumen3 halamanPlay With The Sims Motion The Ramp: - Equal - 980N - 294 NuflillaBelum ada peringkat
- Wind EnergyDokumen29 halamanWind EnergyuflillaBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Introduction To Wifi StandardDokumen33 halamanIntroduction To Wifi StandardnithinalwaysBelum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen16 halamanUntitledMuhamed zameelBelum ada peringkat
- Mobile Computing Lecture NotesDokumen312 halamanMobile Computing Lecture Notessen19841Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 - CN - 20CSPW401Dokumen68 halamanUnit 2 - CN - 20CSPW401MAGESH K SEC 2020Belum ada peringkat
- CS 602 Computer Network Unit 3Dokumen22 halamanCS 602 Computer Network Unit 3NeEmMaBelum ada peringkat
- Cascading Attacks On Wi-Fi Networks: Theory and ExperimentsDokumen12 halamanCascading Attacks On Wi-Fi Networks: Theory and ExperimentsSnake ChickenBelum ada peringkat
- MaxThru802112003 1Dokumen8 halamanMaxThru802112003 1shaik shariffBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 3Dokumen101 halamanUnit 3ashwani tyagiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-2 (WMC) (1) Wireless CommunicationDokumen59 halamanChapter-2 (WMC) (1) Wireless Communicationdine62611Belum ada peringkat
- MAC Protocols For Ad-Hoc Wireless NetworksDokumen55 halamanMAC Protocols For Ad-Hoc Wireless NetworksIqra HanifBelum ada peringkat
- Throughput Enhancement of IEEE 802.11 WLAN For Next Generation CommunicationsDokumen68 halamanThroughput Enhancement of IEEE 802.11 WLAN For Next Generation Communicationsnurcoe1902100% (1)
- Class:-BE Sub:-Wsns: MCQ Question BankDokumen13 halamanClass:-BE Sub:-Wsns: MCQ Question BankShashaBelum ada peringkat
- Wi-Fi in Healthcare White PaperDokumen36 halamanWi-Fi in Healthcare White Paperstar227Belum ada peringkat
- Mac Lecture 2Dokumen20 halamanMac Lecture 2ปิยะ ธโรBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Evaluation of Underwater Medium Access Control Protocols At-Sea ExperimentsDokumen10 halamanPerformance Evaluation of Underwater Medium Access Control Protocols At-Sea Experimentsal shayokhBelum ada peringkat
- Ravi ThesisDokumen87 halamanRavi ThesisDeepak SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-3-The Data Link Layer (Edited)Dokumen24 halamanUnit-3-The Data Link Layer (Edited)Neeraj KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Wireless and Mobile NetworksDokumen70 halamanWireless and Mobile NetworksDurga KBelum ada peringkat
- IoT WSN Module 5 2018 by Prof SV 1 PDFDokumen43 halamanIoT WSN Module 5 2018 by Prof SV 1 PDFmanju0071Belum ada peringkat
- Determine Best Fit TopologyDokumen41 halamanDetermine Best Fit Topologynuri mohammed100% (1)
- Multiple Access ProtocolDokumen9 halamanMultiple Access ProtocolYashaswi BhaskarlaBelum ada peringkat
- Site SurveyDokumen65 halamanSite SurveyJoan ViloriaBelum ada peringkat
- Cs8591 - CN Unit 2Dokumen53 halamanCs8591 - CN Unit 2Vidhya RajBelum ada peringkat
- A Survey of LoRaWAN Simulation Tools in Ns 3Dokumen10 halamanA Survey of LoRaWAN Simulation Tools in Ns 3Abdurahim AbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- Electronics: Cooperative, Connected and Automated Mobility (CCAM) : Technologies and ApplicationsDokumen4 halamanElectronics: Cooperative, Connected and Automated Mobility (CCAM) : Technologies and ApplicationsmraabsBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 v8.0Dokumen29 halamanChapter 7 v8.0Ganesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 9Dokumen64 halamanChapter 9Parag Kumbhar07Belum ada peringkat
- CCN Unit 2Dokumen129 halamanCCN Unit 2Shreya PadukoneBelum ada peringkat
- CS 4441 - Networks II: Wi-FiDokumen22 halamanCS 4441 - Networks II: Wi-FiGemma Ubuhle TsotetsiBelum ada peringkat
- RTN510 V100 Product DescriptionDokumen81 halamanRTN510 V100 Product DescriptionRandy DookheranBelum ada peringkat