Section 5.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities: Name
Diunggah oleh
sarasmile20090 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
129 tayangan2 halamanIn this lesson you learned how to verify trigonometric identities. An identity is.. An equation that is true for all real values. Look for opportunities to factor an expression, add fractions, square a binomial.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
5-2
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniIn this lesson you learned how to verify trigonometric identities. An identity is.. An equation that is true for all real values. Look for opportunities to factor an expression, add fractions, square a binomial.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
129 tayangan2 halamanSection 5.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities: Name
Diunggah oleh
sarasmile2009In this lesson you learned how to verify trigonometric identities. An identity is.. An equation that is true for all real values. Look for opportunities to factor an expression, add fractions, square a binomial.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
Section 5.
2 • Verifying Trigonometric Identities 101
Name______________________________________________
Section 5.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities
Objective: In this lesson you learned how to verify trigonometric
identities.
I. Introduction (Page 382) What you should learn
How to plan a strategy
The key to verifying identities is . . . the ability to use the for verifying
fundamental identities and the rules of algebra to rewrite trigonometric identities
trigonometric expressions.
An identity is . . . an equation that is true for all real values
in the domain of the variable.
II. Verifying Trigonometric Identities (Pages 382−386)
What you should learn
Complete the following list of guidelines for verifying How to verify
trigonometric identities: trigonometric identities
1) Work with one side of the equation at a time. It is often better
to work with the more complicated side first.
2) Look for opportunities to factor an expression, add fractions,
square a binomial, or create a monomial denominator.
3) Look for opportunities to use the fundamental identities. Note
which functions are in the final expression you want. Sines and
cosines pair up well, as do secants and tangents, and cosecants
and cotangents.
4) If the preceding guidelines do not help, try converting all
terms to sines and cosines.
5) Always try something. Even paths that lead to dead ends
provide insights.
Example 1: Describe a strategy for verifying the identity
sin θ tan θ + cos θ = sec θ . Then verify the
identity.
Begin by converting all terms to sines and cosines.
Larson/Hostetler Precalculus/Precalculus with Limits Notetaking Guide IAE
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
102 Chapter 5 • Analytic Trigonometry
Example 2: Describe a strategy for verifying the identity
sin 2 x(csc x − 1)(csc x + 1) = 1 − sin 2 x . Then
verify the identity.
Because the left side is more complicated, start
with it. Begin by multiplying (csc x − 1) by
(csc x + 1), and then search for a fundamental
identity that can be used to replace the result.
Example 3: Verify the identity
cot 5 α = cot 3 α csc 2 α − cot 3 α .
Additional notes
Homework Assignment
Page(s)
Exercises
Larson/Hostetler Precalculus/Precalculus with Limits Notetaking Guide IAE
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Sec 1E - Chapter 1 - Factors and MultiplesDokumen15 halamanSec 1E - Chapter 1 - Factors and Multiplesyusdi afandiBelum ada peringkat
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2023: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Further Pure Mathematics (4PM1) Paper 2Dokumen28 halamanMark Scheme (Results) January 2023: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Further Pure Mathematics (4PM1) Paper 2Rishona D' Souza100% (2)
- Introduction To Mathematical Analysis-Igor KrizDokumen517 halamanIntroduction To Mathematical Analysis-Igor KrizAnonymous wIY2EFacG100% (6)
- Data Management 12 Mcgraw Hill Ryerson Education 2014Dokumen3 halamanData Management 12 Mcgraw Hill Ryerson Education 2014dsu9068014% (7)
- Trig Identities HandoutDokumen6 halamanTrig Identities HandoutBekki VanderlendeBelum ada peringkat
- CH 2Dokumen11 halamanCH 2Hugocgrg22Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 Technique of IntegrationDokumen40 halamanChapter 8 Technique of IntegrationNURUL YAHSIFAH SYQELLA BINTI YAHYA BK21110100Belum ada peringkat
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDokumen18 halamanTrigonometric IdentitiesJhunard Christian O. AsayasBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 05Dokumen54 halamanChapter 0510026722Belum ada peringkat
- Exponential Expressions and the Order of OperationsDokumen8 halamanExponential Expressions and the Order of OperationsalexBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 8 MathematicsDokumen11 halamanGrade 8 Mathematicsmoona imranBelum ada peringkat
- DAA QbankDokumen10 halamanDAA QbankANSHU PATELBelum ada peringkat
- Trig Identities GuideDokumen31 halamanTrig Identities GuideJomar DiegoBelum ada peringkat
- Exam in ET2421 Simulation (4.5 HP) : Answers On Separate Paper and Torn-Apart Papers Will Be DisregardedDokumen6 halamanExam in ET2421 Simulation (4.5 HP) : Answers On Separate Paper and Torn-Apart Papers Will Be DisregardedSaddam HossenBelum ada peringkat
- Creative Thinking in Mathematics To Improve The Proof of Graph Labeling TheoremsDokumen19 halamanCreative Thinking in Mathematics To Improve The Proof of Graph Labeling TheoremsFaiBelum ada peringkat
- IB Mathematics AI SL Notes For Number and AlgebraDokumen14 halamanIB Mathematics AI SL Notes For Number and Algebrated exBelum ada peringkat
- Algorithms: A Brief Introduction Notes: Section 2.1 of RosenDokumen6 halamanAlgorithms: A Brief Introduction Notes: Section 2.1 of RosenHorizon 99Belum ada peringkat
- Algorithms: A Brief Introduction Notes: Section 2.1 of RosenDokumen6 halamanAlgorithms: A Brief Introduction Notes: Section 2.1 of RosenHorizon 99Belum ada peringkat
- MTH603 FINAL TERM SOLVED MCQsDokumen7 halamanMTH603 FINAL TERM SOLVED MCQsmc200400896 MUHAMAMDA AWAISBelum ada peringkat
- MYP III Math Summative Aassessment IB Criteria BDokumen4 halamanMYP III Math Summative Aassessment IB Criteria BMich CastillejaBelum ada peringkat
- Section 9.5 The Binomial Theorem: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 9.5 The Binomial Theorem: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- Time: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100: MBA (Sem I) Theory Examination 2018-19 Business StatisticsDokumen2 halamanTime: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100: MBA (Sem I) Theory Examination 2018-19 Business StatisticsEshu GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- Cot Pre Cal January 18,2023-1Dokumen4 halamanCot Pre Cal January 18,2023-1jocelyn pataBelum ada peringkat
- PCCH 5Dokumen56 halamanPCCH 5gaBelum ada peringkat
- Some Things Every Math Major Should KnowDokumen2 halamanSome Things Every Math Major Should KnowDon OneBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 05Dokumen56 halamanChapter 05itsmohanecomBelum ada peringkat
- Real Numbers PDFDokumen6 halamanReal Numbers PDFJugal JaiswalBelum ada peringkat
- Real Numbers PDFDokumen6 halamanReal Numbers PDFJugal JaiswalBelum ada peringkat
- Real Numbers PDFDokumen6 halamanReal Numbers PDFJugal JaiswalBelum ada peringkat
- FandI CT4 200709 ReportDokumen19 halamanFandI CT4 200709 ReportTuff BubaBelum ada peringkat
- ADA Que Bank 2022-2023Dokumen14 halamanADA Que Bank 2022-2023Chavda ShaktisinhBelum ada peringkat
- CH 3 NotesDokumen20 halamanCH 3 NotesMarina XuBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 5 Basic Trig IdentitiesDokumen16 halamanUnit 5 Basic Trig Identitiesapi-276566085Belum ada peringkat
- 1.1 Algorithm ParadigmsDokumen32 halaman1.1 Algorithm ParadigmsStanley WangBelum ada peringkat
- 3 - Design and Analysis of AlgorithmsDokumen188 halaman3 - Design and Analysis of AlgorithmsUdupiSri groupBelum ada peringkat
- HW 1Dokumen4 halamanHW 1Anonymous gUySMcpSqBelum ada peringkat
- Polynomial Functions Unit 3 ReviewDokumen17 halamanPolynomial Functions Unit 3 ReviewCarolyn LawBelum ada peringkat
- Machine Learning Model Predicts House PricesDokumen9 halamanMachine Learning Model Predicts House PricesEducation VietCoBelum ada peringkat
- Data Mining Practice Final SolDokumen5 halamanData Mining Practice Final SolMussie TekleBelum ada peringkat
- Section 5.4 Sum and Difference Formulas: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 5.4 Sum and Difference Formulas: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- NBA Accreditation Blooms Questions and Rubrics For Indirect AssessmentDokumen15 halamanNBA Accreditation Blooms Questions and Rubrics For Indirect AssessmentDr Narayana Swamy Ramaiah100% (1)
- Lecture 7&8 (Brute Force)Dokumen35 halamanLecture 7&8 (Brute Force)DeependraBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 6: Permutations and Combinations: PrerequisitesDokumen5 halamanChapter 6: Permutations and Combinations: PrerequisitesGhulam HassanBelum ada peringkat
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDokumen37 halamanTrigonometric IdentitieskateBelum ada peringkat
- Trig Derivative FormulasDokumen9 halamanTrig Derivative FormulasDaniel BrownBelum ada peringkat
- Trig DerivativesDokumen9 halamanTrig DerivativesMarcos Bumagat Gardoce Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- Final ExamDokumen18 halamanFinal ExamNeda'a HamedBelum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen2 halamanUntitledFrance MaligasoBelum ada peringkat
- (N) (N) Log N: CompulsoryDokumen7 halaman(N) (N) Log N: CompulsoryHambarde AtharvaBelum ada peringkat
- 9ph0 03 Ms Nov 2021 Edexcel A Level PhysicsDokumen20 halaman9ph0 03 Ms Nov 2021 Edexcel A Level PhysicssenseiBelum ada peringkat
- Proof Involving Trigonometric FunctionsDokumen7 halamanProof Involving Trigonometric FunctionsIm rich lolBelum ada peringkat
- Tips For Proving Trig IdentitiesDokumen1 halamanTips For Proving Trig IdentitiesSalvadora1Belum ada peringkat
- Module-III (Math 002)Dokumen32 halamanModule-III (Math 002)kd2spytjzgBelum ada peringkat
- Level 3 Statistics Statistically Based Reports: NCEA - Walkthrough GuideDokumen48 halamanLevel 3 Statistics Statistically Based Reports: NCEA - Walkthrough GuideTharanga Devinda JayathungaBelum ada peringkat
- Csci 360 Exam 1 Review.pdfDokumen1 halamanCsci 360 Exam 1 Review.pdf2fz4np5b5xBelum ada peringkat
- Applied Mathematical Economics - Assignment 1 - 0Dokumen10 halamanApplied Mathematical Economics - Assignment 1 - 0patra eddieBelum ada peringkat
- Different Methods of Proof Flow ChartsDokumen57 halamanDifferent Methods of Proof Flow ChartsLeomill Mendiola II0% (1)
- Mathematics: Complete Question BankDokumen6 halamanMathematics: Complete Question BankJugal JaiswalBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Approximation of Error 1 PDFDokumen55 halamanChapter 2 Approximation of Error 1 PDFJomari Tobes SatorreBelum ada peringkat
- Ial P2 MSDokumen22 halamanIal P2 MSnonBelum ada peringkat
- Section 12.4 Limits at Infinity and Limits of Sequences: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 12.4 Limits at Infinity and Limits of Sequences: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- Section 12.3 The Tangent Line Problem: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 12.3 The Tangent Line Problem: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- 12 2Dokumen2 halaman12 2sarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- Section 12.5 The Area Problem: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 12.5 The Area Problem: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- 12 1Dokumen4 halaman12 1sarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- Section 10.9 Polar Equations of Conics: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 10.9 Polar Equations of Conics: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- Section 11.3 The Cross Product of Two Vectors: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 11.3 The Cross Product of Two Vectors: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- Section 11.2 Vectors in Space: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 11.2 Vectors in Space: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- Section 10.7 Polar Coordinates: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 10.7 Polar Coordinates: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- 11 4Dokumen2 halaman11 4sarasmile2009100% (1)
- Section 10.8 Graphs of Polar Equations: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 10.8 Graphs of Polar Equations: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- Analytic Geometry in Three Dimensions: Section 11.1 The Three-Dimensional Coordinate SystemDokumen2 halamanAnalytic Geometry in Three Dimensions: Section 11.1 The Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systemsarasmile2009100% (1)
- Section 10.6 Parametric Equations: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 10.6 Parametric Equations: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- Section 10.2 Introduction To Conics: Parabolas: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 10.2 Introduction To Conics: Parabolas: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- 10 4Dokumen2 halaman10 4sarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- Section 10.3 Ellipses: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 10.3 Ellipses: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- Section 8.4 The Determinant of A Square Matrix: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 8.4 The Determinant of A Square Matrix: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- Section 10.5 Rotation of Conics: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 10.5 Rotation of Conics: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- Section 9.5 The Binomial Theorem: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 9.5 The Binomial Theorem: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- Topics in Analytic Geometry: Section 10.1 LinesDokumen2 halamanTopics in Analytic Geometry: Section 10.1 Linessarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- 9 7Dokumen2 halaman9 7sarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- 8 5Dokumen2 halaman8 5sarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- Section 8.3 The Inverse of A Square Matrix: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 8.3 The Inverse of A Square Matrix: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- Section 9.6 Counting Principles: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 9.6 Counting Principles: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- 9 3Dokumen2 halaman9 3sarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- 9 1Dokumen2 halaman9 1sarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- 9 2Dokumen2 halaman9 2sarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- 8 1Dokumen4 halaman8 1sarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- Section 7.6 Linear Programming: NameDokumen2 halamanSection 7.6 Linear Programming: Namesarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- 8 2Dokumen4 halaman8 2sarasmile2009Belum ada peringkat
- 2 Po1 PDFDokumen13 halaman2 Po1 PDFakileshwardinaBelum ada peringkat
- Mobile Robots & Kinematics: Session 2: Nicol As Ilich Samus February 27, 2014Dokumen5 halamanMobile Robots & Kinematics: Session 2: Nicol As Ilich Samus February 27, 2014Nicolás Ilich SamusBelum ada peringkat
- Math 2 PDFDokumen2 halamanMath 2 PDFJOBS & SUCCESS STORIES & ISLAM100% (1)
- 5 Complex Numbers and Functions: 5.1 Arithmetic in CDokumen27 halaman5 Complex Numbers and Functions: 5.1 Arithmetic in CVincent ZhangBelum ada peringkat
- Math101Course Pack2Dokumen191 halamanMath101Course Pack2ChiOfGreeBelum ada peringkat
- 2016 Complex Analysis Problems SolutionsDokumen102 halaman2016 Complex Analysis Problems Solutionsas_5kBelum ada peringkat
- Exponential TrendDokumen4 halamanExponential TrendYasemin UğurBelum ada peringkat
- Associated Legendre functions: solutions to Legendre differential equationDokumen8 halamanAssociated Legendre functions: solutions to Legendre differential equationHaris IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Calicut University Engineering Syllabus 2014 SchemeDokumen186 halamanCalicut University Engineering Syllabus 2014 SchemebbjahbsBelum ada peringkat
- ITF Errorless-1Dokumen9 halamanITF Errorless-1ashmitaramoliya123Belum ada peringkat
- Y X C y X CDokumen12 halamanY X C y X CK.Prasanth KumarBelum ada peringkat
- (Iii) Mod-Amplitude Form of Complex Number: Operations On Complex NumbersDokumen5 halaman(Iii) Mod-Amplitude Form of Complex Number: Operations On Complex NumbersAlex AukrinBelum ada peringkat
- Anna University (Reg 2013) : Multiple Choice QuestionDokumen38 halamanAnna University (Reg 2013) : Multiple Choice QuestionRàghûl FasBelum ada peringkat
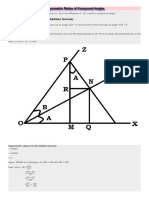
- Trigonometric Ratios of Compound AnglesDokumen6 halamanTrigonometric Ratios of Compound AnglesJaishree RamBelum ada peringkat
- Section 1.3 - Evaluating Limits AnalyticallyDokumen20 halamanSection 1.3 - Evaluating Limits Analyticallyseetha_thundena301Belum ada peringkat
- ProbSet #3 COE0013Dokumen6 halamanProbSet #3 COE0013Jego CreenciaBelum ada peringkat
- Trignometry TableDokumen2 halamanTrignometry TableSantosh BadhaniBelum ada peringkat
- B.Tech 1st Year Revised StructureDokumen48 halamanB.Tech 1st Year Revised StructureAkhilesh PrajapatiBelum ada peringkat
- Short Table of Integrals by PierceDokumen162 halamanShort Table of Integrals by PiercemmcyoungBelum ada peringkat
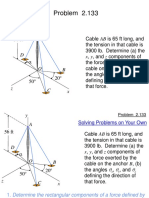
- Cable Tension Force Components and Direction AnglesDokumen5 halamanCable Tension Force Components and Direction AnglesluifrodriguezbBelum ada peringkat
- Quarter 2 Lesson 1-2 (Week 7)Dokumen28 halamanQuarter 2 Lesson 1-2 (Week 7)Angelo ResuelloBelum ada peringkat
- Laplace Table PDFDokumen2 halamanLaplace Table PDFMaxi EurekaBelum ada peringkat
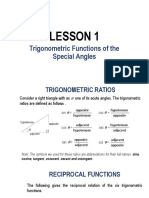
- Trig 1 NotesDokumen7 halamanTrig 1 NotesMrs. HedrickBelum ada peringkat
- Calculus by BeamerDokumen84 halamanCalculus by BeamerPat AgbadaBelum ada peringkat
- Analytic Functions and the Cauchy-Riemann EquationsDokumen3 halamanAnalytic Functions and the Cauchy-Riemann EquationsPuneeth SaiBelum ada peringkat
- Pre-Calculus Chapter 5 Trigonometric Identities: Reciprocal Identities Even/Odd IdentitiesDokumen2 halamanPre-Calculus Chapter 5 Trigonometric Identities: Reciprocal Identities Even/Odd IdentitiesDrew ClaryBelum ada peringkat
- Inverse Trigonometric Function (Theory) Module-2Dokumen8 halamanInverse Trigonometric Function (Theory) Module-2Raju SinghBelum ada peringkat
- SMathStudio.0 85.NumericFunctions - Article.Eng PDFDokumen8 halamanSMathStudio.0 85.NumericFunctions - Article.Eng PDFpiramidonBelum ada peringkat