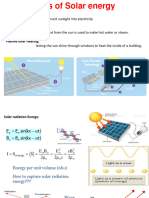
Photovoltaic Cell Close Read
Diunggah oleh
api-291560513Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Photovoltaic Cell Close Read
Diunggah oleh
api-291560513Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Photovoltaic Cell Close Read
Name__________________________________ Period________ Date___________
Vocabulary:
Sensitized: To make a photographic film, plate, or other medium sensitive to light by
coating it with a chemical
Semiconductor: A solid substance that allows some electricity to pass through it.
Photo-sensitized: Made sensitive to light
Anode: The positive electrode in an electrolytic cell
Cathode: The negative electrode of an electrolytic cell
Electrolyte: A chemical compound that separates into ions in a solution and is able to
conduct electricity.
Stability: The condition of being stable
Doped: to add a substance such as arsenic or antimony to a semiconductor material like
silicon or germanium during the manufacturing process in order to increase its
conductivity
Fermi levels: The term used to describe the top of the collection of electron energy levels
Interface: To touch or meet at a surface, place, or point, or make things join in this way
Depleted: Less of something that existed before
Accumulated: To get more and more of something over a period of time
Photon: A unit of energy in the form of light
Oxide: A compound that contains oxygen, usually combined with a metal
Bio-mimetic: A machine that acts like (mimics) an organism
Bionic: A machine that replaces an organisms function
Porosity: The ratio of space taken up by pores in a material.
Nanoparticles: particles between 1 and 100 nanometers in size.
Catalyst: A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself
undergoing any change
Matrix: A substance in which something is embedded or enclosed
Ruthenium-polypyridine dye: A type of photosensitive dye
h: Shorthand for light (Planks constant times nu)
Diffusion: The spread of one substance into another
Ion redox mediator: A substance attached to an electrode that assists in transferring
electrons.
Regeneration: The process of restoring a substance to a usable state after exhaustion.
Gradient: A measure of change in a physical quantity such as temperature or pressure over
a particular distance
First Read (Scan):
1) What is being discussed?
2) What are the two types of Photoelectric cells in the article?
3) What are the three subparagraphs included in the discussion for Dye-sensitized Solar
Cells?
Second Read (General Information):
1) Who Invented the DSSC?
2) What are two attractive features for the DSSC?
3) What are the 3 main parts of a DSSC?
Third Read (Details):
1) In a traditional photocell, what happens to the UV energy? Why?
2) What is the biggest problem with the current technology?
3) What is the source of electrons in a DSSC?
4) What are the main processes that occur in a DSSC?
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Optical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsDari EverandOptical Sources, Detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and ApplicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Notes For Year 10 Science Mid-Course Exam 2004Dokumen5 halamanNotes For Year 10 Science Mid-Course Exam 2004Dog DogBelum ada peringkat
- 1 DSSCDokumen5 halaman1 DSSCHarish Saikiran BhavirisettyBelum ada peringkat
- Wiki Dye Sensitized Solar Cell-2Dokumen12 halamanWiki Dye Sensitized Solar Cell-2singhadityaramBelum ada peringkat
- Preboard GEASDokumen2 halamanPreboard GEASJerry LubiBelum ada peringkat
- Unit V Emerging Solar Cell TechnologiesDokumen16 halamanUnit V Emerging Solar Cell TechnologiesArchana Diwakar RanjishBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 5 - Photodetectors and Noise: 1.1 Thermoelectric DetectorsDokumen23 halamanLecture 5 - Photodetectors and Noise: 1.1 Thermoelectric DetectorsArindam SenBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 10Dokumen17 halamanLecture 10Average GuyBelum ada peringkat
- UE Geas1Dokumen4 halamanUE Geas1markbogsBelum ada peringkat
- 5summary of Thesis or ResearchDokumen9 halaman5summary of Thesis or Researchtrần văn hùngBelum ada peringkat
- Definitions & FormulaeDokumen7 halamanDefinitions & FormulaeAlex AntiaBelum ada peringkat
- Phy 802 Physics of Sensors HW 04Dokumen3 halamanPhy 802 Physics of Sensors HW 04jitenderthakur490Belum ada peringkat
- Edexcel IAL Chemistry A-Level: Unit 5: Transition Metals and Organic Nitrogen ChemistryDokumen12 halamanEdexcel IAL Chemistry A-Level: Unit 5: Transition Metals and Organic Nitrogen ChemistryMer CyBelum ada peringkat
- MaterialsDokumen2 halamanMaterialsCHARLES KENT DOLOTINABelum ada peringkat
- Solar Cells Resemble PhotosynthesisDokumen10 halamanSolar Cells Resemble PhotosynthesisELLEN KOH YEAN YEBelum ada peringkat
- Greg Herman Environmental Health and Safety Radiation Protection 814-865-6391 Gsh12@psu - EduDokumen132 halamanGreg Herman Environmental Health and Safety Radiation Protection 814-865-6391 Gsh12@psu - EduSpoiled BratBelum ada peringkat
- Week 16Dokumen14 halamanWeek 16Harry Jhonley LabisteBelum ada peringkat
- Intoduction: First, The Reactions Take Place in The Excited State of TheDokumen7 halamanIntoduction: First, The Reactions Take Place in The Excited State of TheYousef EssamBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar Report Organic Light Emitting DiodeDokumen23 halamanSeminar Report Organic Light Emitting DiodesaRAth asgaRdian100% (3)
- Dye Sensitized Solar CellDokumen21 halamanDye Sensitized Solar CellMichel G. RahalBelum ada peringkat
- Ib Chemistry DefinitionsDokumen5 halamanIb Chemistry DefinitionsChe Jen Wang100% (1)
- Week 7 Optical Communication SystemDokumen56 halamanWeek 7 Optical Communication SystemNaEem KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Important Points To Remember For NsoDokumen4 halamanImportant Points To Remember For NsoAgriyae JainBelum ada peringkat
- HSC Chemistry Research Task - Grätzell CellDokumen3 halamanHSC Chemistry Research Task - Grätzell CellMina TadrosBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Conversion MaterialsDokumen24 halamanEnergy Conversion MaterialsHosheel ChauhanBelum ada peringkat
- Ib Chemistry - Definitions (V.1) Topic 1 - StoichiometryDokumen9 halamanIb Chemistry - Definitions (V.1) Topic 1 - StoichiometryNikole GualdrónBelum ada peringkat
- Alfa, Beta y Gamma RelaxationDokumen24 halamanAlfa, Beta y Gamma RelaxationCesar Saldias0% (1)
- Organic Electronics: Yiyang Gong EE183Dokumen23 halamanOrganic Electronics: Yiyang Gong EE183Shre ChatterjeeBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Levels of Semiconductor, Conductors and InsulatorsDokumen53 halamanEnergy Levels of Semiconductor, Conductors and InsulatorsTawki BakiBelum ada peringkat
- Dye Sensitized Solar CellDokumen13 halamanDye Sensitized Solar CellEr Vbhor ShrmaBelum ada peringkat
- EBB 424E Semiconductor Devices and Optoelectronics: Part II - Optoelectronics DR Zainovia LockmanDokumen50 halamanEBB 424E Semiconductor Devices and Optoelectronics: Part II - Optoelectronics DR Zainovia LockmanSudhanshu VermaBelum ada peringkat
- To Study Variation of Current Using A LDR - Physics Astronomy Project TopicsDokumen7 halamanTo Study Variation of Current Using A LDR - Physics Astronomy Project Topicsashamishra01981Belum ada peringkat
- Glossary For BatteryDokumen4 halamanGlossary For BatteryMicah TaguinodBelum ada peringkat
- Ece 422 ReviewerDokumen5 halamanEce 422 ReviewerVince MarananBelum ada peringkat
- Dye Sensitised Solar CellsDokumen6 halamanDye Sensitised Solar CellsSonaa RajagopalBelum ada peringkat
- Tarea 1 - Ledis Oliva Buelvas CalderonDokumen4 halamanTarea 1 - Ledis Oliva Buelvas Calderonledys oliva buelvas calderonBelum ada peringkat
- There Are Two Main Types of Semiconductor MaterialsDokumen4 halamanThere Are Two Main Types of Semiconductor MaterialsGaurav TheHeartbreakerBelum ada peringkat
- Stress Strain CurveDokumen5 halamanStress Strain CurveRukhsar RasheedBelum ada peringkat
- Nano Technology of Solar EnergyDokumen5 halamanNano Technology of Solar EnergySMITARANISAHOOBelum ada peringkat
- Semiconductors (Lecture Notes)Dokumen5 halamanSemiconductors (Lecture Notes)Pauline Luna0% (1)
- Applied Physics Important Questions-II MidDokumen7 halamanApplied Physics Important Questions-II Midlaxminarayana yadavaliBelum ada peringkat
- Artigo Inorganica Chimica ActaDokumen65 halamanArtigo Inorganica Chimica ActaNoemi MarxBelum ada peringkat
- PhotosynthesisDokumen56 halamanPhotosynthesisvuminhtut66Belum ada peringkat
- Prepare Unit, Tools, and Workplace For Installation and ServiceDokumen8 halamanPrepare Unit, Tools, and Workplace For Installation and ServiceG-ONE PAISONESBelum ada peringkat
- Semiconductor: How Conductivity Increases With Increase in Temperature?Dokumen14 halamanSemiconductor: How Conductivity Increases With Increase in Temperature?Kamal Deo PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- Edenglen Physical Science DefinitionsDokumen17 halamanEdenglen Physical Science DefinitionsTanaka ChirawuBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 3-5Dokumen49 halamanLecture 3-5SAMBHAV GOEL 21104033Belum ada peringkat
- MEE 220-Part.2Dokumen22 halamanMEE 220-Part.2Mahmoud RashwanBelum ada peringkat
- Instrumental AnalysisDokumen7 halamanInstrumental AnalysisGabriel EngongaBelum ada peringkat
- 621 Unit 3Dokumen60 halaman621 Unit 3Aarav MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Jayavel Chem FinalDokumen16 halamanJayavel Chem FinalAvi ABelum ada peringkat
- Dye Sensitized Solar CellsDokumen21 halamanDye Sensitized Solar CellsTin BaynosaBelum ada peringkat
- كيمياء تحليلية A+2024Dokumen29 halamanكيمياء تحليلية A+2024zloa616Belum ada peringkat
- Light Dependent ResistorDokumen4 halamanLight Dependent ResistorShailesh RanawareBelum ada peringkat
- Development Team: Energy and EnvironmentDokumen19 halamanDevelopment Team: Energy and Environmentmjrobust05Belum ada peringkat
- Sanket09 2021 123Dokumen19 halamanSanket09 2021 123Chetan KannakeBelum ada peringkat
- PhotochemistryDokumen22 halamanPhotochemistryJegadeeswaran SBelum ada peringkat
- Electrochemistry DMDNDokumen4 halamanElectrochemistry DMDNYdyfr FsytBelum ada peringkat
- Rohini 73227582967Dokumen3 halamanRohini 73227582967MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Electronic Circuits: Syed Muhammad Rehan Ali Phone No. 03335577508 Whatsapp. 03175115649Dokumen39 halamanElectronic Circuits: Syed Muhammad Rehan Ali Phone No. 03335577508 Whatsapp. 03175115649Syed Mohammad Rehan AliBelum ada peringkat
- Academic Vocabulary-MolesDokumen1 halamanAcademic Vocabulary-Molesapi-291560513Belum ada peringkat
- What Is A Mole SummativeDokumen8 halamanWhat Is A Mole Summativeapi-291560513Belum ada peringkat
- Conversion GoDokumen1 halamanConversion Goapi-291560513Belum ada peringkat
- University of BahrainDokumen35 halamanUniversity of Bahrainapi-291560513Belum ada peringkat
- Lab Report Rubric: Score Points 100% 85% 80% 70% 0%Dokumen4 halamanLab Report Rubric: Score Points 100% 85% 80% 70% 0%api-291560513Belum ada peringkat
- 1 Making ConversionsDokumen23 halaman1 Making Conversionsapi-291560513Belum ada peringkat
- Inquiry Worksheet: Name - Period: - Date: - What Do You Know? 1Dokumen5 halamanInquiry Worksheet: Name - Period: - Date: - What Do You Know? 1api-291560513Belum ada peringkat
- Scientific ArgumentationDokumen11 halamanScientific Argumentationapi-291560513Belum ada peringkat
- DSSC Lesson PlanDokumen3 halamanDSSC Lesson Planapi-291560513Belum ada peringkat
- Informal Argumentation FormatDokumen2 halamanInformal Argumentation Formatapi-291560513Belum ada peringkat
- M M Lab Lesson PlanDokumen4 halamanM M Lab Lesson Planapi-291560513Belum ada peringkat
- ArgumentationDokumen2 halamanArgumentationapi-291560513Belum ada peringkat
- Mass-Moles GoDokumen1 halamanMass-Moles Goapi-291560513Belum ada peringkat
- Academic Vocabulary-MolesDokumen1 halamanAcademic Vocabulary-Molesapi-291560513Belum ada peringkat
- Summative PadletDokumen3 halamanSummative Padletapi-291560513Belum ada peringkat
- Transistors F11Dokumen56 halamanTransistors F11chuck87268426100% (1)
- Uitm-Fkestudent - Handbook. - Final Edited Version - 13 Dis. 2011-EditDokumen99 halamanUitm-Fkestudent - Handbook. - Final Edited Version - 13 Dis. 2011-EditsilentsioBelum ada peringkat
- ECE1002 Reference Material I Drift DiffusionDokumen94 halamanECE1002 Reference Material I Drift DiffusionNITHISH KANNABelum ada peringkat
- ECE Technicalquestion Question1Dokumen5 halamanECE Technicalquestion Question1Brent BaldovinoBelum ada peringkat
- PH3256 DHDokumen19 halamanPH3256 DHdigitalepcsBelum ada peringkat
- N2 Industrial ElectronicsDokumen46 halamanN2 Industrial ElectronicsbokangtsogangBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Concepts of Crystal StructureDokumen4 halamanBasic Concepts of Crystal StructureThe Hamster VoyageBelum ada peringkat
- Electro Engineering MaterialDokumen0 halamanElectro Engineering Materialwww.bhawesh.com.npBelum ada peringkat
- Semiconductor Fundamentals-2ed R. F. Pierret Prentice Hall 1988 PDFDokumen154 halamanSemiconductor Fundamentals-2ed R. F. Pierret Prentice Hall 1988 PDFMina SamehBelum ada peringkat
- Avionics SystemsDokumen647 halamanAvionics SystemsAhmed Abdoul Zaher100% (10)
- Felipe Barría Cáceres: Modelling The Interaction of Fullerene Derivatives With Hybrid Perovskite SurfaceDokumen1 halamanFelipe Barría Cáceres: Modelling The Interaction of Fullerene Derivatives With Hybrid Perovskite SurfaceFelipe Hernán Barría CáceresBelum ada peringkat
- Said DissertationDokumen129 halamanSaid DissertationSaeed AzarBelum ada peringkat
- Dgca M-4 Mcqs Part-1Dokumen20 halamanDgca M-4 Mcqs Part-1Abhishek SoniBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture NoteDokumen12 halamanLecture Notedjun033Belum ada peringkat
- Accelerated Life Test of High BrightnessDokumen9 halamanAccelerated Life Test of High BrightnessDiepMiuDiepMiuBelum ada peringkat
- Electronic Circuits For The Evil Genius - Full Inventory PDFDokumen5 halamanElectronic Circuits For The Evil Genius - Full Inventory PDFJos100% (1)
- Electrical and Electronic Properties of SolidsDokumen47 halamanElectrical and Electronic Properties of SolidsSoumyadeep PradhanBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 3.1 Physics of SemiconductorsDokumen14 halamanChap 3.1 Physics of SemiconductorsAhmed AlsharifBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technologies Devices, Circuits and SystemsDokumen652 halamanAdvanced Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technologies Devices, Circuits and SystemsSatadal Gupta0% (1)
- VersaopublicadaonlineDokumen10 halamanVersaopublicadaonlineHector HarrisBelum ada peringkat
- Modified WKB Approximation For Fowler-Nordheim Tunneling Phenomenon in Nano-Structure Based SemiconductorsDokumen18 halamanModified WKB Approximation For Fowler-Nordheim Tunneling Phenomenon in Nano-Structure Based Semiconductorsmaheshwarivikas1982Belum ada peringkat
- EC2151 Lecture NotesDokumen62 halamanEC2151 Lecture NotesJahith HussainBelum ada peringkat
- B.Tech B 2013Dokumen87 halamanB.Tech B 2013d00brightBelum ada peringkat
- Ferroelectric Polarization Effect On SurfaceDokumen31 halamanFerroelectric Polarization Effect On SurfaceAna Maria TrandafirBelum ada peringkat
- Solution Manual For Modern Semiconductor Devices For Integrated Circuits by Hu PDFDokumen18 halamanSolution Manual For Modern Semiconductor Devices For Integrated Circuits by Hu PDFa44070629950% (18)
- CMPDokumen15 halamanCMPJayadeva DasaBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 1 - Introduction To IcDokumen40 halamanTopic 1 - Introduction To IcPojee Tasek100% (1)
- Digital Coin TosserDokumen15 halamanDigital Coin TosserDayo BalogunBelum ada peringkat
- Other 22122021211053993Dokumen6 halamanOther 22122021211053993Dhrubajit Acharya Bishal 222-15-6242Belum ada peringkat
- Material Science and Engineering: Basics ofDokumen12 halamanMaterial Science and Engineering: Basics ofChelvoju Rohith KumarBelum ada peringkat