Patient Information Brain Cancer (The Basics)
Diunggah oleh
Juliana Prizzka0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
3 tayangan2 halamanBrain
Judul Asli
Patient information Brain cancer (The Basics)
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniBrain
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
3 tayangan2 halamanPatient Information Brain Cancer (The Basics)
Diunggah oleh
Juliana PrizzkaBrain
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
Patient information: Brain cancer (The Basics)
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/brain-cancer-the-basics?so...
Official reprint from UpToDate
www.uptodate.com 2015 UpToDate
Patient information: Brain cancer (The Basics)
Written by the doctors and editors at UpToDate
What is brain cancer? Brain cancer happens when normal cells in the brain change into abnormal
cells, and grow out of control. There are different types of brain cancer. Some types grow very slowly.
Others grow much faster.
As brain cancer grows, it can spread into normal parts of the brain. It can also cause swelling in the
brain. These can cause symptoms.
What are the symptoms of brain cancer? Often, one of the first symptoms of brain cancer is a
seizure. Seizures are caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain. A seizure can cause a person
to:
Pass out
Stiffen and then have jerking movements of the arms or legs
Lose muscle control throughout the body
Other symptoms of brain cancer can include:
Headache, often with nausea or vomiting
Vision changes, such as double vision or a loss of vision
Memory problems or having trouble thinking clearly
Weakness or numbness in the arms or legs
Personality changes
These symptoms can also be caused by conditions that are not brain cancer. But you should let your
doctor or nurse know if you have any of these symptoms.
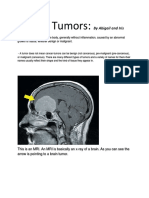
Is there a test for brain cancer? Yes. Doctors use imaging tests such as CT or MRI scans to
diagnose brain cancer. These tests create images of your brain, and can show tumors or abnormal
growths.
After an imaging test, your doctor might follow up with another test called a biopsy. During a biopsy, a
doctor takes a very small sample of the brain tissue. He or she will look at the sample under a
microscope to see if cancer is present.
The right treatment for you will depend a lot on the type of brain cancer you have, and how fast the
cancer is growing. Your treatment will also depend on your symptoms, age, and other health problems.
How is brain cancer treated? Different treatments can include:
Surgery During surgery, doctors try to remove as much of the cancer as possible. Often, brain
cancer cannot be cured with surgery, but surgery might reduce symptoms and help people live
longer. On the other hand, surgery can also lead to more symptoms or problems. This is because
healthy parts of the brain can be damaged during surgery.
Radiation therapy Radiation kills cancer cells. People might receive radiation therapy after
surgery, or when surgery is not possible.
Chemotherapy Chemotherapy is the term doctors use to describe a group of medicines that kill
cancer cells. People might receive these medicines during or after radiation therapy to keep the
1 of 2
11/19/15 7:22 PM
Patient information: Brain cancer (The Basics)
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/brain-cancer-the-basics?so...
cancer from growing, spreading, or coming back.
People with brain cancer also receive treatment for any symptoms they have. For example, people might
take medicines to control seizures.
What happens after treatment? After treatment, you will be checked every so often to see if the
cancer comes back. Follow up tests usually include imaging tests. You should watch for the symptoms
listed above, because having those symptoms could mean the cancer has come back. Tell your doctor
or nurse if you have any symptoms.
What happens if the cancer comes back or spreads? If the cancer comes back or spreads, you
might have more surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation.
What else should I do? It is important to follow all your doctors instructions about visits and tests.
Its also important to talk to your doctor about any side effects or problems you have during treatment.
Getting treated for brain cancer involves making many choices, such as what treatment to have and
when.
Always let your doctors and nurses know how you feel about a treatment. Any time you are offered a
treatment, ask:
What are the benefits of this treatment? Is it likely to help me live longer? Will it reduce or prevent
symptoms?
What are the downsides to this treatment?
Are there other options besides this treatment?
What happens if I do not have this treatment?
Patient information: What are clinical trials? (The Basics)
Patient information: Seizures in adults (Beyond the Basics)
Patient information: Primary low-grade glioma in adults (Beyond the Basics)
Patient information: High-grade glioma in adults (Beyond the Basics)
Patient information: Meningioma (Beyond the Basics)
All topics are updated as new evidence becomes available and our peer review process is complete.
This topic retrieved from UpToDate on: Nov 19, 2015.
The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical
advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your own physician or other qualified health
care professional regarding any medical questions or conditions. The use of UpToDate content is
governed by the UpToDate Terms of Use. 2015 UpToDate, Inc. All rights reserved.
Topic 15364 Version 4.0
2 of 2
11/19/15 7:22 PM
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Cancer AwarenessDokumen20 halamanCancer AwarenessArul Nambi Ramanujam100% (3)
- Key Lab Tests For A Wellness Tune - DR Wes YoungbergDokumen4 halamanKey Lab Tests For A Wellness Tune - DR Wes YoungbergblancorBelum ada peringkat
- NCCS Understanding Radiation Therapy (Eng)Dokumen20 halamanNCCS Understanding Radiation Therapy (Eng)Benjamin NgBelum ada peringkat
- Zero To Finals MedicineDokumen352 halamanZero To Finals MedicinePlay100% (23)
- A Simple Guide to Adrenal Cancer, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDari EverandA Simple Guide to Adrenal Cancer, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- CancerDokumen4 halamanCancerTeeVee ThailandBelum ada peringkat
- Cancer: What they don't tell you and what you need to knowDari EverandCancer: What they don't tell you and what you need to knowBelum ada peringkat
- Braiin CancerDokumen6 halamanBraiin CancerTia RamadhanyBelum ada peringkat
- Brain Tumor: Types of TreatmentDokumen13 halamanBrain Tumor: Types of Treatmentyash vardhanBelum ada peringkat
- Treating Cervical Cancer: General Treatment InformationDokumen23 halamanTreating Cervical Cancer: General Treatment InformationPrincess Kae TabonesBelum ada peringkat
- When To See A DoctorDokumen11 halamanWhen To See A DoctorMellisa Faith Yebes GoBelum ada peringkat
- Side Effects of ChemotherapyDokumen6 halamanSide Effects of ChemotherapyDolores LopesBelum ada peringkat
- Cancer ProjectDokumen9 halamanCancer ProjectBilal KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Treating Nasopharyngeal Cancer: General Treatment InformationDokumen14 halamanTreating Nasopharyngeal Cancer: General Treatment InformationAmemonsajaah AmemonBelum ada peringkat
- Brain tumor signs, symptoms and diagnosisDokumen18 halamanBrain tumor signs, symptoms and diagnosisJulia BerryBelum ada peringkat
- Article About Brain CancerDokumen3 halamanArticle About Brain CancerJessica RobertBelum ada peringkat
- Brain Tumor SymtomsDokumen3 halamanBrain Tumor SymtomsvsalaiselvamBelum ada peringkat
- Treating Gallbladder Cancer - A Quick GuideDokumen9 halamanTreating Gallbladder Cancer - A Quick GuideSpongebob57Belum ada peringkat
- Thyroid Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and StagingDokumen24 halamanThyroid Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and StagingDao Trung HaiBelum ada peringkat
- 8776 00Dokumen30 halaman8776 00Elma MufidhaBelum ada peringkat
- Sunitinib Sarcoma (ImmunoSarc2) - Cancer Research UDokumen8 halamanSunitinib Sarcoma (ImmunoSarc2) - Cancer Research UKen HoBelum ada peringkat
- Coping With The Physical Impact ofDokumen52 halamanCoping With The Physical Impact oftanugirotraBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid Cancer TreatmentDokumen3 halamanThyroid Cancer TreatmentevanBelum ada peringkat
- How Is Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Treated?Dokumen43 halamanHow Is Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Treated?Nadhila ByantBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Brain CancerDokumen3 halamanWhat Is Brain Canceryash vardhanBelum ada peringkat
- Treating Colorectal Cancer: Local TreatmentsDokumen54 halamanTreating Colorectal Cancer: Local TreatmentsMariya DavisBelum ada peringkat
- Medulloblastoma - Childhood - Treatment OptionsDokumen4 halamanMedulloblastoma - Childhood - Treatment OptionsrayndijrBelum ada peringkat
- Immune System DisordersDokumen6 halamanImmune System DisordersMiss OriginalBelum ada peringkat
- Resection Chemotherapy: - and - Prognosis Treatment and PrognosisDokumen4 halamanResection Chemotherapy: - and - Prognosis Treatment and PrognosisTristan LicayanBelum ada peringkat
- Oral CancerDokumen12 halamanOral CancerAnthony HartonoBelum ada peringkat
- Quick Facts About Gallbladder CancerDokumen8 halamanQuick Facts About Gallbladder CancerDebkanti ChakrabortyBelum ada peringkat
- Treating Laryngeal and Hypopharyngeal CancerDokumen32 halamanTreating Laryngeal and Hypopharyngeal Cancerandre halimBelum ada peringkat
- Treating Bladder CancerDokumen33 halamanTreating Bladder CancerVlad CiobanuBelum ada peringkat
- Living With and After Prostate CancerDokumen68 halamanLiving With and After Prostate Cancerdebass3Belum ada peringkat
- Ca Breast5Dokumen87 halamanCa Breast5kiranjeet35Belum ada peringkat
- What Is Hepatocellular Carcinoma?Dokumen5 halamanWhat Is Hepatocellular Carcinoma?Sarah ItsninaBelum ada peringkat
- What Is CancerDokumen7 halamanWhat Is CancerAlejandra Olmos 603Belum ada peringkat
- Tumors Annabelle IrisDokumen5 halamanTumors Annabelle Irisapi-370876509Belum ada peringkat
- Charlie Guidarini ABC-8-7-1 Brain Tumors (Adult)Dokumen7 halamanCharlie Guidarini ABC-8-7-1 Brain Tumors (Adult)Michael SheenBelum ada peringkat
- Brain Tumor - Adults: Contents of This PageDokumen5 halamanBrain Tumor - Adults: Contents of This PageSam StancerBelum ada peringkat
- Treating Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)Dokumen38 halamanTreating Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)Nisak HumairokBelum ada peringkat
- What Is The Brain?Dokumen34 halamanWhat Is The Brain?Sasikumar ChakkarapaniBelum ada peringkat
- Chemotherapy Side EffectsDokumen6 halamanChemotherapy Side EffectslintangBelum ada peringkat
- Symptoms of A Brain TumourDokumen5 halamanSymptoms of A Brain TumournandaBelum ada peringkat
- Frequent urination causes and treatmentsDokumen6 halamanFrequent urination causes and treatmentscl14kmiBelum ada peringkat
- Long-Term Side Effects of Cancer TreatmentDokumen7 halamanLong-Term Side Effects of Cancer TreatmentMarwa HayonBelum ada peringkat
- Treating Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: How Is CML Treated?Dokumen28 halamanTreating Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: How Is CML Treated?Diya BestunBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnosis and Treatment Hot NoduleDokumen4 halamanDiagnosis and Treatment Hot NoduleGame overBelum ada peringkat
- When Cancer Comes Back: Cancer RecurrenceDokumen17 halamanWhen Cancer Comes Back: Cancer RecurrenceAnoop JayaramBelum ada peringkat
- The Edited VersionsDokumen11 halamanThe Edited VersionsThusitha NuwanthiBelum ada peringkat
- WP Contentuploads201803newly Diagnosed PDFDokumen32 halamanWP Contentuploads201803newly Diagnosed PDFArkan TaifoorBelum ada peringkat
- Prostate Cancer: Living With and AfterDokumen60 halamanProstate Cancer: Living With and Afterroberts_kobeBelum ada peringkat
- Pituitary Tumor ManagementDokumen9 halamanPituitary Tumor ManagementNicole Anne TungolBelum ada peringkat
- A Simple Guide to Pheochromocytoma (Updated), Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDari EverandA Simple Guide to Pheochromocytoma (Updated), Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Cancer Types of TreatmentDokumen1 halamanBreast Cancer Types of TreatmentNoor Rateb AlmajaliBelum ada peringkat
- Tumorile CerebraleDokumen2 halamanTumorile CerebralePaladi IasminaBelum ada peringkat
- Ca ColonDokumen49 halamanCa ColonBarryBelum ada peringkat
- Chemotherapy: Department of Clinical HaematologyDokumen12 halamanChemotherapy: Department of Clinical HaematologyJulio Andro ArtamulandikaBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment PsychologyDokumen7 halamanAssignment Psychologyanamashraf837Belum ada peringkat
- WileycancerDokumen11 halamanWileycancerapi-310375757Belum ada peringkat
- Clarisonic Mia 2Dokumen1 halamanClarisonic Mia 2Juliana PrizzkaBelum ada peringkat
- Neo Stig MineDokumen6 halamanNeo Stig MineJuliana PrizzkaBelum ada peringkat
- Angio FibromaDokumen10 halamanAngio FibromaJuliana PrizzkaBelum ada peringkat
- Try Out Final Semester 1 TestDokumen6 halamanTry Out Final Semester 1 TestJuliana PrizzkaBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Things You Can DoDokumen2 halaman5 Things You Can DoJuliana PrizzkaBelum ada peringkat
- Efficacy of Spinal Cord Stimulators in TreatingDokumen4 halamanEfficacy of Spinal Cord Stimulators in TreatinggonzaloBelum ada peringkat
- Efficacy of Spinal Cord Stimulators in TreatingDokumen4 halamanEfficacy of Spinal Cord Stimulators in TreatinggonzaloBelum ada peringkat
- Tramadol InfiltrationDokumen5 halamanTramadol InfiltrationJuliana PrizzkaBelum ada peringkat
- Proposed Mechanisms For Association Between Opioid Usage and Cancer Recurrence After SurgeryDokumen5 halamanProposed Mechanisms For Association Between Opioid Usage and Cancer Recurrence After SurgeryJuliana PrizzkaBelum ada peringkat
- Proposed Mechanisms For Association Between Opioid Usage and Cancer Recurrence After SurgeryDokumen5 halamanProposed Mechanisms For Association Between Opioid Usage and Cancer Recurrence After SurgeryJuliana PrizzkaBelum ada peringkat
- Tramadol InfiltrationDokumen5 halamanTramadol InfiltrationJuliana PrizzkaBelum ada peringkat
- WHO Nervous System Tumors (Sudah)Dokumen3 halamanWHO Nervous System Tumors (Sudah)Juliana PrizzkaBelum ada peringkat
- Serotonin Syndrome Manifesting As Patient IV AnestesiaDokumen3 halamanSerotonin Syndrome Manifesting As Patient IV AnestesiaJuliana PrizzkaBelum ada peringkat
- Incidence of Primary Brain Tumors (Sudah)Dokumen4 halamanIncidence of Primary Brain Tumors (Sudah)Juliana PrizzkaBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis of Brain Tumors (Sudah)Dokumen12 halamanClinical Presentation and Diagnosis of Brain Tumors (Sudah)Juliana PrizzkaBelum ada peringkat
- MR Spectroscopy Brain Tumors (Sudah)Dokumen1 halamanMR Spectroscopy Brain Tumors (Sudah)Juliana PrizzkaBelum ada peringkat
- Dinda SDokumen16 halamanDinda SLulu SupergirlBelum ada peringkat
- WHO Brain Tumor Classification by Histology and Grade (Sudah)Dokumen2 halamanWHO Brain Tumor Classification by Histology and Grade (Sudah)Juliana PrizzkaBelum ada peringkat
- Avinoam B. Safran, M.DDokumen1 halamanAvinoam B. Safran, M.DJuliana PrizzkaBelum ada peringkat
- Avinoam B. Safran, M.DDokumen1 halamanAvinoam B. Safran, M.DJuliana PrizzkaBelum ada peringkat
- Hirlan&ISADokumen6 halamanHirlan&ISAJuliana PrizzkaBelum ada peringkat