Chemical Bonding
Diunggah oleh
api-3043505010 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
20 tayangan2 halamanCovalent bonds are formed when electrons are shared equally between metals and nonmetals. Nonpolar covalent bonds between nonmetals and metals are called ionic covalent bonds. Polar bonds are called polar covalent nonmetals. Ionic bonds are formed between oppositely charged ions. The energy required to separate one mole of a solid ionic compound into its gaseous ions increases as the charges on the ions increase and the distance between them decreases
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
chemical bonding
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniCovalent bonds are formed when electrons are shared equally between metals and nonmetals. Nonpolar covalent bonds between nonmetals and metals are called ionic covalent bonds. Polar bonds are called polar covalent nonmetals. Ionic bonds are formed between oppositely charged ions. The energy required to separate one mole of a solid ionic compound into its gaseous ions increases as the charges on the ions increase and the distance between them decreases
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
20 tayangan2 halamanChemical Bonding
Diunggah oleh
api-304350501Covalent bonds are formed when electrons are shared equally between metals and nonmetals. Nonpolar covalent bonds between nonmetals and metals are called ionic covalent bonds. Polar bonds are called polar covalent nonmetals. Ionic bonds are formed between oppositely charged ions. The energy required to separate one mole of a solid ionic compound into its gaseous ions increases as the charges on the ions increase and the distance between them decreases
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
Chapter 8: Chemical Bonding
Chemical Bond
Ionic Bond
Covalent Bond
Metallic Bond
Valence Electrons
Lattice Energy
Bond Polarity
Nonpolar Covalent
Bonds
Polar Covalent
Bonds
Electronegativity
Dipole
Dipole Moment
Octet
Bond Enthalpy
Lewis Symbols
Octet Rule
Strong attractive force between atoms or ions
Attraction between oppositely charged ions, formed through
transfer of electrons between metals and nonmetals
Sharing of electrons between nonmetals
Bonds between metals where electrons are free to move
throughout
Electrons involved in bonding
The energy required to separate one mole of a solid ionic
compound into its gaseous ions
Describes the distribution of shared electrons in a covalent
bond
Covalent bonds where electrons are shared equally
Covalent bonds where electrons are shared unequally
The ability of an atom to attract electrons
The separation of a charge
In a polar molecule, one side will have a partial positive and
the other will have a partial negative
A full valence shell ( 8 electrons)
The energy required to break a bond
Valence electrons are represented as dots around the
chemical symbol
Atoms gain, lose or share electron to obtain a full outer shell
(octet)
Ionic Bonding
Metals lose electrons, nonmetals gain electrons
Lattice Energy
Lattice energy increases as the charges on the ions increase and as the distance
between them decreases.
Electronegativity
Electronegativity increases to the right and decreases down a group on the periodic
table.
Determining the Type of Bond
The difference in Electronegativity determines whether a bond will be polar or
nonpolar:
0 0.4
0.5 1.9
> 2..0
nonpolar covalent {nonmetals}
polar covalent {nonmetals}
ionic {metal & nonmetals}
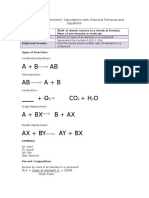
Drawing Lewis Structures
1. Count the total # of valence electrons
2. Arrange the atoms and connect with single bonds (usually least EN atom is
the central atom)
3. Complete the octets ( H only has 2 e-)
4. Check:
- Number of valence electrons (if too many, use multiple bonds)
- Each atom has an octet
Exceptions to the Octet Rule:
1. Less than an Octet
2. Odd number of electrons
3. More than an Octet ( central atom is bonded to more than 4 atoms or has
additional lone pairs)
Strength of Covalent Bonds:
- Bond strength increase from single to double to triple
- The greater the bond strength, the greater the enthalpy
Hrxn = Hbonds broken - Hbonds formed
Enthalpy Diagram
Bond Broken
Reactants
Bond formed
Products
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular GeometryDokumen211 halamanChapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometryonline purchaseBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDokumen13 halamanChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureVishal MalikBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding Ionic Bonding Characteristics of Ionic CompoundsDokumen2 halamanChemical Bonding Ionic Bonding Characteristics of Ionic CompoundsBittu100% (1)
- Chemical bonding: The essential concepts of electron sharing and transferDokumen54 halamanChemical bonding: The essential concepts of electron sharing and transferSam LoveBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bond TypesDokumen5 halamanChemical Bond Typesapi-287081563Belum ada peringkat
- Catenary Sag-Tension Calculator (Even and Uneven)Dokumen2 halamanCatenary Sag-Tension Calculator (Even and Uneven)mohsin160Belum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding Test ReviewDokumen5 halamanChemical Bonding Test ReviewAlakh Jagtap100% (1)
- Bonding Ionic CovalentDokumen30 halamanBonding Ionic CovalentRaul MejiaBelum ada peringkat
- L3 Polar and Nonpolar Covalent MoleculesDokumen33 halamanL3 Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Molecules1256- FRONDA, RHOVIC D.Belum ada peringkat
- Say Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDokumen13 halamanSay Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structuresivaranjini S.VBelum ada peringkat
- CHEMICAL BONDING KEY CONCEPTSDokumen73 halamanCHEMICAL BONDING KEY CONCEPTSHANNAH JULIA CAPUNGCOBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Info About Glaze FormulationsDokumen3 halamanBasic Info About Glaze FormulationsThongMaVanBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Types of Chemical BondsDokumen12 halaman3 Types of Chemical BondsSaediRisquéBriskeyBelum ada peringkat
- Three Main Types of Chemical BondingDokumen49 halamanThree Main Types of Chemical Bondingjasumin91Belum ada peringkat
- Lewis Theory Valence Electrons Are The Electrons Involved in BondingDokumen15 halamanLewis Theory Valence Electrons Are The Electrons Involved in BondingmaryBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 7 Slides - General Chemistry - Open StaxDokumen96 halamanChapter - 7 Slides - General Chemistry - Open Staxonline purchaseBelum ada peringkat
- CH 6 Chemical BondingDokumen14 halamanCH 6 Chemical Bondingapi-240972605Belum ada peringkat
- SCIENCE To ReviewDokumen4 halamanSCIENCE To ReviewMichaela Gwyneth SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding 1Dokumen7 halamanChemical Bonding 1rhiannemitchbBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry: The Central Science: 8.S: Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding (Summary)Dokumen6 halamanChemistry: The Central Science: 8.S: Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding (Summary)Harshal BandkarBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding ScriptDokumen4 halamanChemical Bonding ScriptAkhil MathewBelum ada peringkat
- 2023 Grade 11 Learner Support DocumentDokumen131 halaman2023 Grade 11 Learner Support DocumentanathinothandoBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingDokumen46 halamanBasic Concepts of Chemical BondingHendri KurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- Pptx5 Chemical BondingDokumen39 halamanPptx5 Chemical BondingLumbay, Jolly MaeBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding and Bonding TheoriesDokumen55 halamanChemical Bonding and Bonding Theoriesnxumalopat2Belum ada peringkat
- Warm Up 11/8/2010: in Your Own Words, Answer The FollowingDokumen11 halamanWarm Up 11/8/2010: in Your Own Words, Answer The Followingdwolfe25Belum ada peringkat
- Chem 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingDokumen2 halamanChem 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingKuo SarongBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical BondingDokumen22 halamanChemical BondingJr CarpelaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding/s2 Kimia UnpDokumen36 halamanChemical Bonding/s2 Kimia UnpIda HidayatiBelum ada peringkat
- Mariano Marcos State University: PCHM 121: Pharmaceutical Inorganic Chemistry With Qualitative AnalysisDokumen14 halamanMariano Marcos State University: PCHM 121: Pharmaceutical Inorganic Chemistry With Qualitative AnalysisKaizenBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding (Ionic and Covalent)Dokumen15 halamanChemical Bonding (Ionic and Covalent)MB LoterteBelum ada peringkat
- Gen Chem 2 Chemical BondingDokumen53 halamanGen Chem 2 Chemical BondingNoella may de MesaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding Class 11Dokumen18 halamanChemical Bonding Class 11bansarigadhvi23Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture-3-Chemical Bonds and Functional GroupsDokumen64 halamanLecture-3-Chemical Bonds and Functional GroupsWiza MulengaBelum ada peringkat
- 2020 2.4 Chemistry GZDokumen187 halaman2020 2.4 Chemistry GZgeetub1Belum ada peringkat
- Chemistry 3 Bonding and Chemical ReactionDokumen10 halamanChemistry 3 Bonding and Chemical ReactionRosely PaquiteBelum ada peringkat
- CH 04. Bonding: AP Chemistry Basic Lecture Course Light VersionDokumen33 halamanCH 04. Bonding: AP Chemistry Basic Lecture Course Light VersionHARPACABelum ada peringkat
- CHEM 10a Unit 4Dokumen3 halamanCHEM 10a Unit 4McHaley HalBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical BondingDokumen27 halamanChemical BondingLovejoy TiñaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Chemical BondingDokumen20 halamanIntroduction To Chemical BondingDe AktivedBelum ada peringkat
- Science: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesDokumen9 halamanScience: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesAriel Lomugdang PatricioBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 5: Trends and BondingDokumen42 halamanUnit 5: Trends and BondingConnor MarshmanBelum ada peringkat
- CHEMICAL BONDING Ionic BondDokumen22 halamanCHEMICAL BONDING Ionic BondnwdpggbhktBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical BondingDokumen69 halamanChemical Bondingirenerielo19Belum ada peringkat
- 16: Drawing Molecules - Lewis Structures: High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat SheetDokumen1 halaman16: Drawing Molecules - Lewis Structures: High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat Sheetbooty holeBelum ada peringkat
- # Week 3 NotesDokumen13 halaman# Week 3 Notestimx123yBelum ada peringkat
- Polar and Nonpolar MoleculesDokumen32 halamanPolar and Nonpolar MoleculeshensoncarlosjrBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2Dokumen22 halamanChapter 2mehrunnisaqaisar111Belum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding Types and Forces ExplainedDokumen6 halamanChemical Bonding Types and Forces ExplaineddanielmahsaBelum ada peringkat
- Module 3: Chemical Bonding and NomenclatureDokumen11 halamanModule 3: Chemical Bonding and NomenclatureJay Mark CapanangBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 - Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingDokumen2 halamanChapter 8 - Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingIngratsusi MarvianiBelum ada peringkat
- Co2 - Chemical BondingDokumen49 halamanCo2 - Chemical BondingKel SarmientoBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding Types Explained in 40 CharactersDokumen14 halamanChemical Bonding Types Explained in 40 CharacterselisaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding Notes ExamDokumen4 halamanChemical Bonding Notes ExamMermz96Belum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding NotesDokumen2 halamanChemical Bonding Notesseema sahniBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 1-4 2 NotesDokumen22 halamanChapter 4 1-4 2 NotesKarelene SotoBelum ada peringkat
- Compiled Lecture in General Chemistry (Organic Chemistry) (Midterm) CcjeDokumen21 halamanCompiled Lecture in General Chemistry (Organic Chemistry) (Midterm) CcjeEmil Vince T. CumilangBelum ada peringkat
- Chem 101 Lec: Pt.1 Chemical BondingDokumen36 halamanChem 101 Lec: Pt.1 Chemical BondingSarip RymahBelum ada peringkat
- Chem Notes - Chapter 8Dokumen2 halamanChem Notes - Chapter 8Ray OakBelum ada peringkat
- Lewis SymbolDokumen20 halamanLewis SymbolVivian May J. GuibalaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.Dari EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.Belum ada peringkat
- Electron StructureDokumen4 halamanElectron Structureapi-304350501Belum ada peringkat
- StoichiometryDokumen2 halamanStoichiometryapi-304350501Belum ada peringkat
- ThermochemistryDokumen3 halamanThermochemistryapi-304350501Belum ada peringkat
- Molecular Geometry and Bonding TheoriesDokumen2 halamanMolecular Geometry and Bonding Theoriesapi-304350501Belum ada peringkat
- Periodic TrendsDokumen2 halamanPeriodic Trendsapi-304350501Belum ada peringkat
- Matter and MeasurementDokumen2 halamanMatter and Measurementapi-304350501Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 10: Gases: T A B A BDokumen2 halamanChapter 10: Gases: T A B A Bapi-304350501Belum ada peringkat
- Atoms Molecules and IonsDokumen3 halamanAtoms Molecules and Ionsapi-304350501Belum ada peringkat
- Aqueous Reactions and StoichiometryDokumen2 halamanAqueous Reactions and Stoichiometryapi-304350501Belum ada peringkat
- Deha Halfen Kkt-EDokumen52 halamanDeha Halfen Kkt-ENandeesha RameshBelum ada peringkat
- Conductor and SuperconductorDokumen12 halamanConductor and Superconductorankesh_ghoghariBelum ada peringkat
- Basic USIT InterpretationDokumen10 halamanBasic USIT InterpretationMehdi NorouziBelum ada peringkat
- Mandi Gobindgarh Hazardous Waste Report NGT April2021Dokumen7 halamanMandi Gobindgarh Hazardous Waste Report NGT April2021arbaz khanBelum ada peringkat
- Dektite Diverter and Retrofit Dektite Diverter: Pipe FlashingsDokumen2 halamanDektite Diverter and Retrofit Dektite Diverter: Pipe FlashingscherandinhoBelum ada peringkat
- To Measure The Head Loss (HL) in A Pipe of Uniform Diameter (D)Dokumen6 halamanTo Measure The Head Loss (HL) in A Pipe of Uniform Diameter (D)Syed Ali Hasnain NaqviBelum ada peringkat
- Fibre Rope - Terminology and Good PracticesDokumen19 halamanFibre Rope - Terminology and Good PracticesLe Quyen NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Asignment - Chapter 1 PDFDokumen3 halamanAsignment - Chapter 1 PDFDo Cong Minh100% (1)
- Important To Write The Correct Structure FromDokumen16 halamanImportant To Write The Correct Structure FromR A V IBelum ada peringkat
- Organic compound solubility behavior factorsDokumen19 halamanOrganic compound solubility behavior factorsAJBelum ada peringkat
- Xyron™ Grades and Properties XYRON™Dokumen5 halamanXyron™ Grades and Properties XYRON™Radhakrishnan RajanBelum ada peringkat
- RM Pattern UK 208printDokumen36 halamanRM Pattern UK 208printMarcelo Alberto AiresBelum ada peringkat
- Gambian Petroleum Products StandardsDokumen33 halamanGambian Petroleum Products StandardsSerge KohemunBelum ada peringkat
- PF2579EN00EMDokumen2 halamanPF2579EN00EMVinoth KumarBelum ada peringkat
- ZINCALUME Steel Technical Bulletins V14.0Dokumen31 halamanZINCALUME Steel Technical Bulletins V14.0beck.26Belum ada peringkat
- VCI Film PaperDokumen2 halamanVCI Film Paperpackaging meBelum ada peringkat
- Curtain Wall Design and TestingDokumen9 halamanCurtain Wall Design and TestingUzair SiddiqueBelum ada peringkat
- Cryogenic Transfer Line ChilldownDokumen10 halamanCryogenic Transfer Line ChilldownIgnacio ChaparroBelum ada peringkat
- M&MSDokumen2 halamanM&MSASIST MechBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Mind Map PDFDokumen16 halamanBiology Mind Map PDFAditya PrakashBelum ada peringkat
- R.C.C Beam Design GuideDokumen20 halamanR.C.C Beam Design Guidebishal dasBelum ada peringkat
- National Senior Certificate: Physical Sciences: Chemistry (P2) JUNE 2023Dokumen14 halamanNational Senior Certificate: Physical Sciences: Chemistry (P2) JUNE 2023Aneess ChouaneBelum ada peringkat
- Air-Liquid Heat ExchangersDokumen6 halamanAir-Liquid Heat ExchangersUnilab100% (17)
- Philippines mining industry statistics reportDokumen1 halamanPhilippines mining industry statistics reportACBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Shilajit ResinDokumen2 halamanNatural Shilajit ResinMadhav RaghavanBelum ada peringkat
- Pozzolith 575: Chloride Accelerating AdmixtureDokumen2 halamanPozzolith 575: Chloride Accelerating AdmixtureFrancois-Belum ada peringkat
- SoapsDokumen7 halamanSoapsLucita P. CatarajaBelum ada peringkat