05 Protokol
Diunggah oleh
otsunDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
05 Protokol
Diunggah oleh
otsunHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Konsep Jaringan Komputer
Protokol Jaringan
Protokol Jaringan
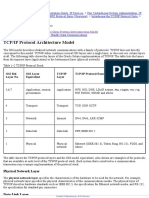
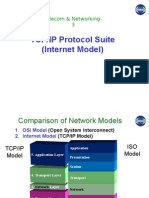
Dalam OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) layer,
jaringan dibagi menjadi 7 lapisan yaitu
Application
Presentation
Session
Transport
Network
Data Link
Physical
Protokol Jaringan
Dalam arsitektur TCP/IP terbagi menjadi
Application
Transport
Network
Network Acces Layer
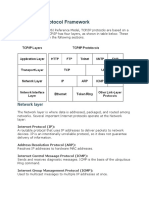
Protokol TCP/IP walaupun bisa dikaitkan dengan
model OSI, tetapi dia tidaklah sepenuhnya sama.
Dalam kaitannya dengan protokol stack, kadang2
dalam protokol stack TCP/IP tidak membutuhkan
layer presentation dan session
Protokol Stack TCP/IP dikaitkan
dalam model OSI
Dalam Aplication Layer
BOOTP: Bootstrap Protocol
DCAP: Data Link Switching Client Access Protocol
DHCP: Dynamic Host Conguration Protocol
DNS: Domain Name Systems
FTP: File Transfer Protocol
Finger: User Information Protocol
HTTP: Hypertext Transfer Protocol
S-HTTP: Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol (S-HTTP)
IMAP & IMAP4: Internet Message Access Protocol
Application Layer
IPDC: IP Device Control
IRCP (IRC): Internet Relay Chat Protocol
LDAP: Lightweighted Directory Access Protocol
MIME (S-MIME): Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (Secure MIME)
NAT: Network Address Translation
NNTP: Network News Transfer Protocol
NTP: Network Time Protocol
POP & POP3: Post Ofce Protocol (version 3)
RLOGIN: Remote Login in Unix
RMON: Remote Monitoring MIBs in SNMP
Application Layer
SLP: Service Location Protocol
SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
SNMP: Simple Network Management Protocol
SNTP: Simple Network Time Protocol
TELNET: TCP/IP Terminal Emulation Protocol
TFTP: Trivial File Transfer Protocol
URL: Uniform Resource Locator
X-Window: X Window or X Protocol or X System
Presentation Layer
Session Layer
LPP: Lightweight Presentation Protocol
RPC: Remote Procedure Call protocol
Transport Layer
ITOT: ISO Transport Over TCP/IP
RDP: Reliable Data Protocol
RUDP: Reliable UDP
TALI: Transport Adapter Layer Interface
TCP: Transmission Control Protocol
UDP: User Datagram Protocol
Network Layer
Routing
Multicast
MPLS Protocols
Network Layer
Routing
BGP/BGP4: Border Gateway Protocol
EGP: Exterior Gateway Protocol
IP: Internet Protocol
IPv6: Internet Protocol version 6
ICMP/ICMPv6: Internet Control Message Protocol
IRDP: ICMP Router Discovery Protocol
Mobile IP: IP Mobility Support Protocol for IPv4 & IPv6
NARP: NBMA Address Resolution Protocol
NHRP: Next Hop Resolution Protocol
Network Layer
Routing
OSPF: Open Shortest Path First
RIP (RIP2): Routing Information Protocol
RIPng: RIP for IPv6
RSVP: Resource ReSerVation Protocol
VRRP: Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
Network Layer
Multicast
BGMP: Border Gateway Multicast Protocol
DVMRP: Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol
IGMP: Internet Group Management Protocol
MARS: Multicast Address Resolution Server
MBGP: Multiprotocol BGP
MOSPF: Multicast OSPF
MSDP: Multicast Source Discovery Protocol
MZAP: Multicast-Scope Zone Announcement Protocol
PGM: Pragmatic General Multicast Protocol
PIM-DM: Protocol Independent Multicast - Dense Mode
PIM-SM: Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode
Network Layer
MPLS protocol
MPLS: Multi-Protocol Label Switching
CR-LDP: Constraint-Based Label Distribution
Protocol
LDP: Label Distribution Protocol
RSVP-TE: Resource ReSerVation Protocol-Trafc
Engineering
Data Link Layer
ARP and InARP: Address Resolution Protocol
and Inverse ARP
IPCP and IPv6CP: IP Control Protocol and IPv6
Control Protocol
RARP: Reverse Address Resolution Protocol
SLIP: Serial Line IP
Protokol yang lain
LAN, MAN, WAN, SAN, Security VPN
Sumber
IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force)
Darpa (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency)
ISO (International Organization for Standardization)
Application Layer
BOOTP
Berbasiskan protokol UDP/IP yang mengijinkan host yang
booting untuk mengconfigurasikan dirinya secara dinamik dan
tanpa perlu bantuan pengguna.
Port yang digunakan adalah UDP port nomor 67 yang
digunakan oleh server penyedia layanan IP dan
UDP port number 68 yang digunakan oleh klien.
Klien BOOTP melakukan broadcast paket tunggal yang yang
disebut BOOTREQUEST packet yang berisi physical network
address dari klien
Sumber http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc1542.pdf
BOOTP
Application Layer
DHCP Dynamic Host Conguration Protocol
DHCP adalah alternatif lain dari network IP
management protocol, Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP).
DHCP adalah protokol yang lebih advanced, tetapi
keduanya menggunakan konfigurasi protokol
manajemen yang sama.
Sumber http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc2131.pdf
DHCP
Application Layer
DNS: Domain Name System (Service) protocol
Merupakan distributed Internet directory service.
DNS banyak digunakan untuk mentranslasikan antara domain name dengan
IP address dan digunakan untuk mengendalikan pengiriman Internet email.
DNS memiliki dua aspek independent:
Menspesifikasi sintaks nama dan aturan untuk pendelegasian authority
melalui nama.
Sintaksnya adalah :local.group.site
Menspesifikasikan implementasi dari distributed computing system yang
mengefisiensikan pemetaan antara nama dan alamat.
Sumber http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc1034.pdf
DNS
Application Layer
FTP: File Transfer Protocol
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) memungkinkan sharing
file antar host.
FTP menggunakan TCP untuk membuat koneksi
virtual untuk kontrol informasi dan kemudian membuat
koneksi TCP yang terpisah untuk transfer data.
Sumber http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc959.pdf
Application Layer
Fungsi penting dariFTP adalah:
1) untuk mendukung sharing dari file (program
komputer dan atau data);
2) untuk mendorong secara tidak langsung atau secara
lengkap (melalui program) penggunaan computer
remote;
3) untuk melindungi pengguna dari variasi dalam le
storage systems diantara hosts;
4) untuk mentransfer data secara reliable dan efciently.
HTTP: Hypertext Transfer
Protocol
HTTP adalah protokol pada level aplikasi dengan
keringanan dan kecepatan yang diperlukan untuk
distribusi, kolaborasi, sistem informasi hipermedia.
HTTP banyak digunakan oleh World-Wide Web
global information sejak 1990.
Sumber :
http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc1945.pdf
Untuk https
http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc2660.pdf
HTTP Request dan Response
IMAP & IMAP4: Internet Message
Access Protocol (version 4)
IMAP adalah suatu metode untuk mengakses email yang
tersimpan pada server email.
IMAP mengijinkan program email klien untuk mengakses
pesan yang tersimpan secara remote seperti mereka
tersimpan di lokal.
Email yang tersimpan pada server IMAP dapat
dimanipulasi dari komputer desktop secara remote, tanpa
perlu mentransfer pesan atau files bolak-balik antara
komputer.
http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc3501.pdf
POP and POP3: Post Ofce
Protocol (version 3)
Post Ofce Protocol didesain untuk mengijinkan
komputer workstation untuk secara dinamik
mengakses email yang terdapat pada server host.
POP3 adalah versi terakhir saat ini.
Transmisi POP3 terlihat seperti pesan data antar
host. Pesan berupa perintah atau pesan balasan.
http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc1939.pdf
SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer
Protocol
SMTP adalah sebuah protokol yang didesain untuk
transfer email secara reliable dan efisien.
SMTP adalah layanan surat yang dimodelkan pada
layanan transfer file FTP.
SMTP mentransfer pesan email antara sistem dan
menyediakan peringatan berkaitan dengan email
yang masuk.
http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc2821.pdf
URL: Uniform Resource Locator
URL adalah sintak dan sematik untuk string yang
kompak yang merepresentasikan dari sumber daya
yang tersedia di internet.
<scheme>:<scheme-specific-part>
Example : http://d14n-materikuliah.blogspot.com
Sumber :
http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc1738.pdf
Presentation Layer
LPP: Lightweight Presentation Protocol
LPP mendeskripsikan sebuah pendekatan untuk menyediakan
dukungan stream-lined layanan aplikasi OSI diatas jaringan
berbasis TCP/IP
LPP pada asalnya diturunkan dari kebutuhan untuk menjalankan
ISO Common Management Information Protocol (CMIP) pada
jaringan berbasis TCP/IP.
Sumber
http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc1085.pdf
http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc2126.pdf
Session Layer Protocols
RPC: Remote Procedure Call protocol
RPC adalah protokol untuk meminta layanan dari program yang
terletak di remote komputer melalui jaringan, tanpa harus
memahami lapisan di bawah teknologi jaringan.
RPC mengasumsikan keberadaan dari low-level
transport protocol, seperti TCP atau UDP, untuk membawa
pesan data antara program yang berkomunikasi.
RPC menggunakan client/server model.
http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc1831.pdf
http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc1057.pdf
Transport Layer Protocols
TCP: Transmission Control Protocol
TCP adalah protokol pada layer transport dalam TCP/IP
suite, yang mana menyediakan pengiriman stream yang
reliable dan layanan koneksi virtual pada aplikasi dengan
acknowledgement yang berurutan dengan retransmisi
paket ketika dibutuhkan.
Bersamaan denagn Internet Protocol (IP), TCP merupakan
heart of the Internet protocols.
http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc793.pdf
http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc3168.pdf
UDP: User Datagram Protocol
UDP adalah connectionless transport layer yang mana
menyediakan layanan yang sederhana dan unreliable
message untuk layanan transaction-oriented.
UDP secara dasar adalah antarmuka antara IP dan
proses di layer diatasnya.
UDP protocol ports membedakan banyak aplikasi yang
berjalan pada satu device dari yang lain.
http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc768.pdf
Network Layer Protocols
IP: Internet Protocol (Ipv4)
IP adalah protokol yang berisi informasi pengalamatan dan
beberapa kontrol informasi yang membuat paket dapat
diroutekan dalam jaringan.
IP adalah protokol utama pada layer network di TCP/IP
protocol suite.
IP adalah sama untuk komunikasi LAN dan WAN.
IP memiliki dua tugas utama yaitu menyediakan
connectionless, best-effort delivery dari datagrams melalui
sebuah jaringan; dan menyediakan fragmentasi dan
reassembli dari datagram untuk mendukung data link dengan
berbagai ukuran MTU (maximum-transmission unit).
http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc791.pdf
Data Link Layer Protocols
ARP and InARP: Address Resolution Protocol
and Inverse ARP
Digunakan untuk memetakan antara IP dengan alamat
fisik dari peralatan jaringan / MAC address
http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc826.pdf
http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc2390.pdf
http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc2625.pdf
RARP: Reverse Address Resolution Protocol
RARP mengijinkan peralatan dalam jaringan LAN
untuk merequest IP dari tabel di server gateway Address
Resolution Protocol (ARP) table atau cache.
Administrator jaringan membuat suatu tabel pada local
area networks gateway router yang memetakan antara
alamat physical machines (Media Access Control MAC) dengan IP address.
RARP dapat digunakan pada Ethernet, Fiber
Distributed-Data Interface, dan Token Ring LANs.
http://ietfreport.isoc.org/rfc/PDF/rfc903.pdf
Daftar Pustaka
Javvin Technology Inc, Network Protocols
Handbook second edition
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 4 Protokol PengalamatanDokumen44 halaman4 Protokol Pengalamatananon_615742149Belum ada peringkat
- TCP/IP Protocol Architecture Model: Previous: Protocol Layers and The Open Systems Interconnection ModelDokumen5 halamanTCP/IP Protocol Architecture Model: Previous: Protocol Layers and The Open Systems Interconnection ModelGreen ZoneBelum ada peringkat
- The OSI ModelDokumen6 halamanThe OSI ModelAakash ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 TCP IP Reference ModelDokumen43 halamanChapter 4 TCP IP Reference Modelamanuelfitsum589Belum ada peringkat
- TCP/IP Protocol Stack ExplainedDokumen24 halamanTCP/IP Protocol Stack ExplainedToni-ann WillisBelum ada peringkat
- Protocol NotesDokumen11 halamanProtocol NotesThiba SivanaihBelum ada peringkat
- 1-4 TCP-IP ModelDokumen4 halaman1-4 TCP-IP ModelDragan StančevBelum ada peringkat
- TCP IP Protocol Architecture ModelDokumen6 halamanTCP IP Protocol Architecture Modelayesha chBelum ada peringkat
- Internet Protocols: Web TechnologyDokumen37 halamanInternet Protocols: Web TechnologyMobewtime StylesBelum ada peringkat
- List of Network ProtocolsDokumen5 halamanList of Network Protocolsanon_563889070Belum ada peringkat
- Network and Transport Layers: Tcp/Ip and OsiDokumen42 halamanNetwork and Transport Layers: Tcp/Ip and OsiSomnath LahaBelum ada peringkat
- Imp For InterviewDokumen16 halamanImp For InterviewPravin PuriBelum ada peringkat
- What Is The TCP/IP Model? TCP/IP Model Helps You To Determine How A Specific Computer Should BeDokumen18 halamanWhat Is The TCP/IP Model? TCP/IP Model Helps You To Determine How A Specific Computer Should BePhilip EdebuBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 6: Network and Transport Layers: Business Data Communications, 4eDokumen42 halamanTopic 6: Network and Transport Layers: Business Data Communications, 4eBelachew AndualemBelum ada peringkat
- CN Assignment PDFDokumen9 halamanCN Assignment PDFVaishnavi VenkatBelum ada peringkat
- OSI and TCP - IP Lecture SlideDokumen28 halamanOSI and TCP - IP Lecture SlideBobby IgbeBelum ada peringkat
- TCPIP ModelDokumen9 halamanTCPIP Modelroysayanccp05Belum ada peringkat
- NETWORK PROTOCOLS REVIEWDokumen11 halamanNETWORK PROTOCOLS REVIEWRose of sharonBelum ada peringkat
- Network Protocols: Dr. Ahmed MusaDokumen16 halamanNetwork Protocols: Dr. Ahmed MusaAkram TaBelum ada peringkat
- It First ChapterDokumen76 halamanIt First ChapterRohan RathoreBelum ada peringkat
- TCP IP ModelDokumen13 halamanTCP IP ModelDevakumarBelum ada peringkat
- TCP IP ModelDokumen13 halamanTCP IP ModelRanjeet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- ProtocolsDokumen3 halamanProtocolsDavid OwnerBelum ada peringkat
- TCP - IP ProtocolDokumen38 halamanTCP - IP ProtocolShanu SilvaBelum ada peringkat
- List of ProtocolsDokumen5 halamanList of Protocolshbbela34Belum ada peringkat
- Siem VijayaaDokumen35 halamanSiem VijayaanagarjunaBelum ada peringkat
- The TCP/IP Protocol Framework: Network LayerDokumen2 halamanThe TCP/IP Protocol Framework: Network LayerMirza AzizBelum ada peringkat
- Security Information and Event ManagementDokumen35 halamanSecurity Information and Event ManagementGowtham SagarBelum ada peringkat
- D. The Tcp/Ip Reference Model: ProtocolDokumen7 halamanD. The Tcp/Ip Reference Model: ProtocolEcho greenBelum ada peringkat
- WT UNIT 1 Lecture 1.2 Protocols Governing The WebDokumen20 halamanWT UNIT 1 Lecture 1.2 Protocols Governing The WebSACHIDANAND CHATURVEDIBelum ada peringkat
- TCP IP ModelDokumen31 halamanTCP IP ModelJaveed AhamedBelum ada peringkat
- Layer 1 ProtocolsDokumen6 halamanLayer 1 Protocolssubhash321100% (1)
- Application LayerDokumen7 halamanApplication LayerKhushi KhengarBelum ada peringkat
- Protocols Per LayersDokumen5 halamanProtocols Per LayersDipin C PBelum ada peringkat
- TCP/IP Protocol Suite (Internet Model) : Telecom & Networking-3Dokumen20 halamanTCP/IP Protocol Suite (Internet Model) : Telecom & Networking-3Romana ShanBelum ada peringkat
- ProtocolsDokumen1 halamanProtocolsJorge LangleyBelum ada peringkat
- TCP-UDP Ports LIst-2Dokumen14 halamanTCP-UDP Ports LIst-2Giuseppe IndennitateBelum ada peringkat
- 1 StudyDokumen7 halaman1 StudyAman GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture - 5 - 6 OSI - TCPIP SuiteDokumen31 halamanLecture - 5 - 6 OSI - TCPIP SuiteSalar AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Data CommunicationsDokumen4 halamanData CommunicationsAtiqurRahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Network+ Exam Cram Study SheetDokumen3 halamanNetwork+ Exam Cram Study SheetDan Sheets86% (21)
- Osi LayerDokumen5 halamanOsi LayerJoseBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Week 1Dokumen4 halamanTutorial Week 1Lasse IngdahlBelum ada peringkat
- TCP IpDokumen8 halamanTCP IpGauravBelum ada peringkat
- DecaDokumen9 halamanDecaKen Archer SeleraBelum ada peringkat
- Web Design and Devlopment Assignment 1Dokumen16 halamanWeb Design and Devlopment Assignment 1Nurye NigusBelum ada peringkat
- Vulnerabilities TCP IpDokumen117 halamanVulnerabilities TCP IpedgarBelum ada peringkat
- ECE541 Data Networks 1: Application Layer Functionality and ProtocolsDokumen27 halamanECE541 Data Networks 1: Application Layer Functionality and ProtocolsUnicorn54Belum ada peringkat
- TCPIP Lecture16Dokumen115 halamanTCPIP Lecture16Tuan BeoBelum ada peringkat
- Etti - RST IV - Sem.I - Rezolvari - RSDokumen25 halamanEtti - RST IV - Sem.I - Rezolvari - RSbeiculescugeorgeBelum ada peringkat
- SAN & NAS Protocols OverviewDokumen21 halamanSAN & NAS Protocols OverviewSahil SuriBelum ada peringkat
- Application Layer Functionality and ProtocolsDokumen92 halamanApplication Layer Functionality and ProtocolsVossKarrBelum ada peringkat
- Ericsson UCIP Library for XML-RPC CallsDokumen3 halamanEricsson UCIP Library for XML-RPC Callsyannis_benBelum ada peringkat
- Application LayerDokumen5 halamanApplication Layerjohn_wlmns3929Belum ada peringkat
- CMP822 - Assignment SolutionDokumen16 halamanCMP822 - Assignment SolutionOdunuga JuliusBelum ada peringkat
- Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP and Internet ApplicationsDokumen34 halamanProtocol Architecture, TCP/IP and Internet ApplicationscilentBelum ada peringkat
- 3fundamentals of NetworkingDokumen6 halaman3fundamentals of NetworkingGiemer HerreraBelum ada peringkat