Nursing Care Plan For Functional Urinary Incontinence NCP
Diunggah oleh
dericJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Nursing Care Plan For Functional Urinary Incontinence NCP
Diunggah oleh
dericHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Student Nurses Community
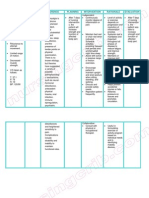
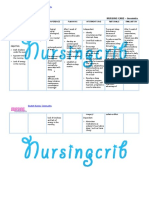
NURSING CARE PLAN Functional Urinary Incontinence
ASSESSMENT
SUBJECTIVE:
I feel the urge to
void, but I cant
reach the toilet on
time, as verbalized
by the patient
DIAGNOSIS
INFERENCE
PLANNING
Functional
urinary
incontinence
related to
neuromuscul
ar limitation
(left sided
weakness)
Muscle weakness
After 48 hours of
nursing interventions,
the patient will be
able to:
Impairment of
mobility and
dexterity
Inability to reach
the toilet in time
OBJECTIVES:
Weakened
muscle tone (left
side is weak)
Urine leakage
Urine leakage/
passing of urine in
inappropriate
places
experience fewer
episodes (or no
episodes) of
incontinence
Use adaptive
equipment to
reduce or
eliminate
incontinence
related to
impaired mobility
or dexterity
Use portable
urinary collection
devices or urine
containment
devices when
access to the
toilet is not
feasible
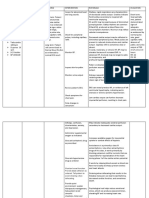
INTERVENTIONS
Independent:
Perform a focused
history of the
incontinence
including duration,
frequency and
severity of leakage
episodes, and
alleviating and
aggravating factors.
Complete a bladder
log of diurnal and
nocturnal urine
elimination patterns
and patterns of
urinary leakage.
Assess patient's
recognition of need to
urinate
Assess client for
established/chronic
incontinence: stress
urinary incontinence,
RATIONALE
The history
provides clues to
the causes, the
severity of the
condition, and its
management.
The bladder log
provides a more
objective
verification of urine
elimination
patterns as
compared with the
history and a
baseline against
which the results of
management can
be evaluated.
Patients with
functional
incontinence are
incontinent
because they
cannot get to an
EVALUATION
After 48 hours
of nursing
interventions,
goal met. Fewer
episodes of
incontinence
were noted;
patient was able
to use adaptive
equipment and
portable urinary
collection
devices.
Student Nurses Community
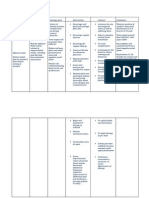
urge urinary
incontinence, reflex,
or extraurethral
("total") urinary
incontinence. If
present, begin
treatment for these
forms of urine loss.
Assess client for
mobility, including
ability to rise from
chair and bed; ability
to transfer to toilet
and ambulate; and
need for physical
assistive devices
such as a cane,
walker, or wheel
chair.
Assess client for
dexterity, including
the ability to
manipulate buttons,
hooks, snaps, Velcro,
and zippers needed
to remove clothing.
Consult physical or
occupational
therapist to promote
optimal toilet access
as indicated.
appropriate place
to void.
Institutionalized
patients are often
labeled
"incontinent"
because their
requests for
toileting are
unmet. Elderly
patients with
cognitive
impairment may
recognize need to
void, but may be
unable to express
the need.
Functional
incontinence often
coexists with
another form of
urinary leakage,
particularly among
the elderly
Functional
continence requires
the ability to gain
access to a toilet
facility, either
independently or
with the assistance
Student Nurses Community
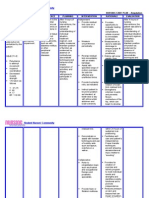
Provide an
appropriate, safe
urinary receptacle
such as a 3-in-1
commode, female or
male hand-held
urinal, no-spill urinal,
or containment
device when toileting
access is limited by
immobility or
environmental
barriers.
Assist the person to
alter their wardrobe
(Select loose-fitting
clothing with stretch
waist bands rather
than buttoned or
zippered waist;
minimize buttons,
snaps, and multilayered clothing; and
substitute Velcro or
other easily loosened
systems for buttons,
hooks, and zippers in
existing clothing.)
Assist the client with
limited mobility.
assist the client to
of devices to
increase mobility
Functional
continence requires
the ability to
remove clothing to
urinate
These receptacles
provide access to a
substitute toilet
and enhance the
potential for
functional
continence
To maximize
toileting access.
To obtain
evaluation for a
physical therapist
and to obtain
assistive devices as
indicated. Shoes
with a nonskid sole
maximize traction
when arising from
a chair and
transferring to the
toilet.
A toileting schedule
Student Nurses Community
select shoes with a
nonskid sole
Establish a toileting
schedule.
Perform perineal skin
care, including
routine cleansing
following incontinent
episodes, daily
cleaning and drying
of perineal skin, and
use of moisture
barriers as indicated.
Dependent:
Encourage prescribed
use of
sympathomimetics
and estrogens as
ordered
assures the patient
of a specified time
for voiding, and
reduces episodes
of functional
incontinence.
Routine cleansing
and daily cleaning
with appropriate
products help
maintain integrity
of perineal skin and
prevent secondary
cutaneous
infections
To increase
sphincter tone and
improve muscle
tone.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Nursing Care Plan for Urinary Retention and Memory ImpairmentDokumen5 halamanNursing Care Plan for Urinary Retention and Memory ImpairmentColeen Comelle Huerto60% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPderic71% (7)
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen1 halamanNursing Care PlanSHeenah Qo100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Planmjoie_baby6568470100% (6)
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDokumen2 halamanImpaired Urinary EliminationHaon Anasu67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan - Impaired Physical MobilityDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan - Impaired Physical MobilitySusan Croce57% (7)
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisDokumen4 halamanNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisLighto RyusakiBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Retention, RevisedDokumen2 halamanUrinary Retention, RevisedKim Beverly100% (5)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDokumen1 halamanNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlansDokumen4 halamanNursing Care PlansanreilegardeBelum ada peringkat
- Self Care Deficit NCP Alzheimer's DiseaseDokumen4 halamanSelf Care Deficit NCP Alzheimer's DiseaseHanna Se75% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For Urinary RetentionDokumen4 halamanNursing Care Plan Risk For Urinary RetentionReginald Julia100% (2)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Scientific Rationale EvaluationDokumen5 halamanAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Scientific Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losanta100% (2)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPDokumen2 halamanBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPCyrus De Asis100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan for Urinary Tract Infection (UTIDokumen19 halamanNursing Care Plan for Urinary Tract Infection (UTIYudistiro Adi Nugroho100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen10 halamanNursing Care PlanMalou SanBelum ada peringkat
- Student Nurses’ Community NURSING CARE PLAN – Renal FailureDokumen2 halamanStudent Nurses’ Community NURSING CARE PLAN – Renal FailureAldrein GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationDokumen1 halamanAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationJulie Ann100% (2)
- NCP Nursing Care Plan For Urinary Tract InfectionsDokumen4 halamanNCP Nursing Care Plan For Urinary Tract InfectionsRaveen mayi89% (9)
- Managing Urinary Tract Obstruction Nursing InterventionsDokumen8 halamanManaging Urinary Tract Obstruction Nursing Interventionsjyaba0% (1)
- NCP MS DbiDokumen2 halamanNCP MS DbiSj EclipseBelum ada peringkat
- FHN - Nursing Care Plan Constipation)Dokumen3 halamanFHN - Nursing Care Plan Constipation)blahniksBelum ada peringkat
- NCP LocDokumen2 halamanNCP LocMel RodolfoBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues and Data Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan: Cues and Data Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationPaul Cubacub100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPderic83% (6)
- Amputation Rehab: Exercises & Stump CareDokumen5 halamanAmputation Rehab: Exercises & Stump CareRazelAnneValinoBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract Infection, (UTI) Is An Infection of One orDokumen4 halamanUrinary Tract Infection, (UTI) Is An Infection of One orLorebellBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Chronic ConfusionDokumen4 halamanNCP Chronic ConfusionLyka DianaBelum ada peringkat
- Pt Pain Relief Prostate EnlargementDokumen2 halamanPt Pain Relief Prostate EnlargementBobby Valencerina100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen13 halamanNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- NCP Hip FractureDokumen1 halamanNCP Hip FractureStephanie Lorraine Zuniga100% (5)
- Student Nurses' Guide to Managing ConstipationDokumen2 halamanStudent Nurses' Guide to Managing ConstipationGio Baduria100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan FibromyalgiaDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan Fibromyalgiaderic90% (10)
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Dokumen3 halamanNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Caroline ChaBelum ada peringkat
- Afib NCPDokumen3 halamanAfib NCPGen RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertonic SolutionsDokumen4 halamanHypertonic SolutionsVanessa PaguiriganBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Sexual DysfunctionDokumen2 halamanNCP Sexual DysfunctionFull Eros100% (5)
- NCP Urinary Tract InfectionDokumen4 halamanNCP Urinary Tract InfectiondollythesheepBelum ada peringkat
- Improving Comfort with Endotracheal TubeDokumen1 halamanImproving Comfort with Endotracheal TubeSelwynVillamorPatenteBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plans For Renal CalculiDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plans For Renal CalculiRaveen mayi77% (22)
- NCP-impaired Urinary Elimination-TAHBSODokumen3 halamanNCP-impaired Urinary Elimination-TAHBSOtinatin9890% (1)
- NCPDokumen4 halamanNCPMichelleBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen5 halamanNursing Care PlanAnju Luchmun100% (2)
- Clinical Instructor: Mrs. Ramon A. Galicia, RN: Krystlle Lyre G. Cordero 4Bcn San Beda College Nursing Care PlanDokumen4 halamanClinical Instructor: Mrs. Ramon A. Galicia, RN: Krystlle Lyre G. Cordero 4Bcn San Beda College Nursing Care Planstarcordero100% (2)
- NCPDokumen2 halamanNCPJhel NabosBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Acute Pain RT CancerDokumen3 halamanNCP Acute Pain RT CancerCharissa Magistrado De LeonBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Incontinence Guide for Care and ManagementDokumen5 halamanUrinary Incontinence Guide for Care and ManagementfakrulnersmudaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing InterventionDokumen3 halamanNursing InterventionElaine Marie SeraficaBelum ada peringkat
- Union Test Prep Nclex Study GuideDokumen115 halamanUnion Test Prep Nclex Study GuideBradburn Nursing100% (2)
- AmputationDokumen2 halamanAmputationFabian Ugalino Pino Jr.100% (3)
- Catheterization and Perineal Care-PPT-1Dokumen49 halamanCatheterization and Perineal Care-PPT-1AinaB Manalo100% (1)
- Urinary EliminationDokumen26 halamanUrinary EliminationyeshumasihBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Incontinence Nursing ManagementDokumen3 halamanUrinary Incontinence Nursing ManagementRnspeakcomBelum ada peringkat
- Case PresentationDokumen4 halamanCase PresentationAlhaisa BejemilBelum ada peringkat
- Female Urinary Catheter Insertion GuideDokumen9 halamanFemale Urinary Catheter Insertion GuideIsabel AranconBelum ada peringkat
- Female Urinary Catheter Insertion GuideDokumen9 halamanFemale Urinary Catheter Insertion GuideVinz Khyl G. CastillonBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Review: Managing Urinary Incontinence in Older PeopleDokumen15 halamanClinical Review: Managing Urinary Incontinence in Older PeopleMatthias WollfBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary CatheterizationDokumen41 halamanUrinary CatheterizationSteffiBelum ada peringkat
- Bladder TrainingDokumen6 halamanBladder TrainingDhea DohongBelum ada peringkat
- Bladder TrainingDokumen6 halamanBladder TrainingDhea DohongBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan For HemodialysisDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan For Hemodialysisderic80% (20)
- Nursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide PoisoningDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide Poisoningderic73% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPderic88% (40)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPDokumen4 halamanNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For GlaucomaDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan For Glaucomaderic79% (28)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPDokumen4 halamanNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPderic100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPderic79% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For AmputationDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan For Amputationderic80% (25)
- Nursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVderic81% (16)
- Nursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPderic100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPDokumen5 halamanNursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPderic100% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPDokumen5 halamanNursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPderic100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPDokumen4 halamanNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPderic79% (133)
- Nursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPDokumen5 halamanNursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPderic82% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPderic100% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPderic85% (46)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPderic100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPderic88% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPderic88% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPderic67% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPderic67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPDokumen3 halamanNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPderic71% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPDokumen8 halamanNursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPderic87% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPDokumen14 halamanNursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPderic92% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPderic100% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPderic83% (23)
- Classification of Endometriosis: Birmingham, AlabamaDokumen2 halamanClassification of Endometriosis: Birmingham, AlabamaAsela SubhasingheBelum ada peringkat
- 01 NGT Procedure With RationaleDokumen4 halaman01 NGT Procedure With RationaleAryaj SulitBelum ada peringkat
- Aeromonas InfectionDokumen27 halamanAeromonas Infection周治剛Belum ada peringkat
- Marginal Zone Lymphomas: Subtypes: MALT (Extranodal), Nodal, SplenicDokumen2 halamanMarginal Zone Lymphomas: Subtypes: MALT (Extranodal), Nodal, SplenicwwxxmmBelum ada peringkat
- A Laser Peripheral Iridotomy Would Most Likely Relieve AngleDokumen2 halamanA Laser Peripheral Iridotomy Would Most Likely Relieve AngleGlaucoma UnhasBelum ada peringkat
- Dengue Virus Infection - Prevention and Treatment - UpToDateDokumen32 halamanDengue Virus Infection - Prevention and Treatment - UpToDateAnderson SilvaBelum ada peringkat
- Tatalaksana Tekanan Tinggi Intrakranial Pada Anak-DikonversiDokumen48 halamanTatalaksana Tekanan Tinggi Intrakranial Pada Anak-DikonversiAbdurrahman Arsyad As SiddiqiBelum ada peringkat
- Akapulko or Acapulco in English Is A Shrub Found Throughout The PhilippinesDokumen6 halamanAkapulko or Acapulco in English Is A Shrub Found Throughout The PhilippinesJon Adam Bermudez SamatraBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan for Postpartum PainDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan for Postpartum PainJoseph Nawen Sindiong100% (1)
- Substance-Related Disorders: Ms. Jocelyn Alcera Nazario, RN MANDokumen149 halamanSubstance-Related Disorders: Ms. Jocelyn Alcera Nazario, RN MAN102680Belum ada peringkat
- Basinger Abraham - ConsultationDokumen80 halamanBasinger Abraham - ConsultationVikas NairBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Respiratory Failure For StudentDokumen41 halamanAcute Respiratory Failure For Studentapi-379952350% (4)
- ZakriyaDokumen6 halamanZakriyaapi-512107573Belum ada peringkat
- About This Leaflet: FibroadenomaDokumen2 halamanAbout This Leaflet: FibroadenomaEnvhy WinaBelum ada peringkat
- Bipolar Affective Disorder: Captain DR Yujal Man Singh Neuropsychiatrist, Shree Birendra HospitalDokumen15 halamanBipolar Affective Disorder: Captain DR Yujal Man Singh Neuropsychiatrist, Shree Birendra HospitalYujal Man SinghBelum ada peringkat
- ECMO For COVID 19 Updated 2021 Guidelines From.98326Dokumen42 halamanECMO For COVID 19 Updated 2021 Guidelines From.98326risanataliasiburianBelum ada peringkat
- The Complete Hematopathology GuideDokumen113 halamanThe Complete Hematopathology GuideJenny SBelum ada peringkat
- VAERS Report Details Deaths and Adverse Events Following COVID VaccinesDokumen234 halamanVAERS Report Details Deaths and Adverse Events Following COVID VaccinesbeneBelum ada peringkat
- Perioperative Fluid Management in ChildrenDokumen31 halamanPerioperative Fluid Management in ChildrenRashmi SahaBelum ada peringkat
- AphasiaDokumen71 halamanAphasiaVarun B RenukappaBelum ada peringkat
- BAD Cryotherapy Update March 2018 - Lay Review March 2018Dokumen4 halamanBAD Cryotherapy Update March 2018 - Lay Review March 2018Mehret TechaneBelum ada peringkat
- PAVSDMAPCAsDokumen3 halamanPAVSDMAPCAsRajesh SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Bacterial Patterns and Antibiotic Resistance in Grade Two Diabetic UlcersDokumen15 halamanBacterial Patterns and Antibiotic Resistance in Grade Two Diabetic UlcersNadya AbigailBelum ada peringkat
- Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVHDokumen5 halamanCauses, Symptoms and Treatment of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVHJàson Vòrhees100% (1)
- Crohn's Disease Case Study: Matt SimsDokumen14 halamanCrohn's Disease Case Study: Matt SimsKipchirchir AbednegoBelum ada peringkat
- Diabetes Mellitus in Children 1Dokumen89 halamanDiabetes Mellitus in Children 1Vinay PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Intranasal Steroids in PediatricsDokumen39 halamanIntranasal Steroids in PediatricsKishore ChandkiBelum ada peringkat
- IDSA Molnupiravir GuidelineDokumen10 halamanIDSA Molnupiravir GuidelineJaz ButuyanBelum ada peringkat
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Gerd) : By: Therese Jane TimbalopezDokumen14 halamanGastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Gerd) : By: Therese Jane Timbalopezjoyrena ochondraBelum ada peringkat
- Gastroenterology - Lower GI Bleeding - SOAP Note - Maitreyi RamanDokumen4 halamanGastroenterology - Lower GI Bleeding - SOAP Note - Maitreyi RamanFrancieudo Sampaio100% (1)