6.4.3.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Default Gateway Issues
Diunggah oleh
ParthPatelDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
6.4.3.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Default Gateway Issues
Diunggah oleh
ParthPatelHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Default Gateway Issues
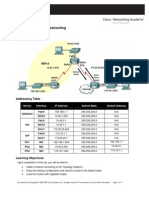
Topology
2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 1 of 7
Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Default Gateway Issues
Addressing Table
Defa
ult
Interfac
Device
IP Address
Subnet
Gate
Mask
255.255.255
way
G0/0
192.168.10.1
.0
255.255.255
N/A
G0/1
192.168.11.1
.0
255.255.255
N/A
S1
VLAN 1
192.168.10.2
.0
255.255.255
S2
VLAN 1
192.168.11.2
.0
255.255.255
PC1
NIC
192.168.10.10
.0
255.255.255
PC2
NIC
192.168.10.11
.0
255.255.255
PC3
NIC
192.168.11.10
.0
255.255.255
PC4
Objectives
NIC
192.168.11.11
.0
R1
Part 1: Verify Network Documentation and Isolate Problems
Part 2: Implement, Verify, and Document Solutions
2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 2 of 7
Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Default Gateway Issues
Background
For a device to communicate across multiple networks, it must be configured
with an IP address, subnet mask, and a default gateway. The default gateway is
used when the host wants to send a packet to a device on another network. The
default gateway address is generally the router interface address attached to
the local network to which the host is connected. In this activity, you will finish
documenting the network. You will then verify the network documentation by
testing end-to-end connectivity and troubleshooting issues. The troubleshooting
method you will use consists of the following steps:
1 Verify the network documentation and use tests to isolate problems.
2 Determine an appropriate solution for a given problem.
3 Implement the solution.
4 Test to verify the problem is resolved.
5 Document the solution.
Throughout your CCNA studies, you will encounter different descriptions of the
troubleshooting method, as well as different ways to test and document issues
and solutions. This is intentional. There is no set standard or template for
troubleshooting. Each organization develops unique processes and
documentation standards (even if that process is we dont have one).
However, all effective troubleshooting methodologies generally include the
above steps.
Note: If you are proficient with default gateway configurations, this activity
might seem more involved than it should be. You can, most likely, quickly
discover and solve all the connectivity issues faster than following these
procedures. However, as you proceed in your studies, the networks and
problems you encounter will become increasingly more complex. In such
situations, the only effective way to isolate and solve issues is to use a
methodical approach such as the one used in this activity.
2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 3 of 7
Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Default Gateway Issues
Verify Network Documentation and Isolate Problems
In Part 1 of this activity, complete the documentation and perform connectivity
tests to discover issues. In addition, you will determine an appropriate solution
for implementation in Part 2.
Step 1:
Verify the network documentation and isolate any problems.
a. Before you can effectively test a network, you must have complete
documentation. Notice in the Addressing Table that some information is
missing. Complete the Addressing Table by filling in the missing default
gateway information for the switches and the PCs.
b. Test connectivity to devices on the same network. By isolating and correcting
any local access issues, you can better test remote connectivity with the
confidence that local connectivity is operational.
A verification plan can be as simple as a list of connectivity tests. Use the
following tests to verify local connectivity and isolate any access issues. The
first issue is already documented, but you must implement and verify the
solution during Part 2.
2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 4 of 7
Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Default Gateway Issues
Testing and Verification Documentation
Successf
Verifie
Test
PC1 to
ul?
Issues
IP address
Solution
Change PC1 IP
PC2
PC1 to
No
on PC1
address
S1
PC1 to
No
No
No
S1
R1
S1
No
No
S1
Note: The table is an example; you must create your own document. You can
use paper and pencil to draw a table, or you can use a text editor or
spreadsheet. Consult your instructor if you need further guidance.
c. Test connectivity to remote devices (such as from PC1 to PC4) and document
any problems. This is frequently referred to as end-to-end connectivity. This
means that all devices in a network have the full connectivity allowed by the
network policy.
Note: Remote connectivity testing may not be possible yet, because you
must first resolve local connectivity issues. After you have solved those
issues, return to this step and test connectivity between networks.
Step 2:
Determine an appropriate solution for the problem.
a. Using your knowledge of the way networks operate and your device
configuration skills, search for the cause of the problem. For example, S1 is
not the cause of the connectivity issue between PC1 and PC2. The link lights
are green and no configuration on S1 would cause traffic to not pass
between PC1 and PC2. So the problem must be with PC1, PC2, or both.
b. Verify the device addressing to ensure it matches the network
documentation. For example, the IP address for PC1 is incorrect as verified
with the ipconfig command.
c. Suggest a solution that you think will resolve the problem and document it.
For example, change the IP address for PC1 to match the documentation.
2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 5 of 7
Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Default Gateway Issues
Note: Often there is more than one solution. However, it is a troubleshooting
best practice to implement one solution at a time. Implementing more than
one solution could introduce additional issues in a more complex scenario.
Part 2: Implement, Verify, and Document Solutions
In Part 2 of this activity, you will implement the solutions you identified in Part 1.
You will then verify the solution worked. You may need to return to Part 1 to
finish isolating all the problems.
Step 1:
Implement solutions to connectivity problems.
Refer to your documentation in Part 1. Choose the first issue and implement
your suggested solution. For example, correct the IP address on PC1.
2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 6 of 7
Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Default Gateway Issues
Step 2:
Verify that the problem is now resolved.
a. Verify your solution has solved the problem by performing the test you used
to identify the problem. For example, can PC1 now ping PC2?
b. If the problem is resolved, indicate so in your documentation. For example, in
the table above, a simple checkmark would suffice in the Verified column.
Step 3:
Verify that all issues are resolved.
a. If you still have an outstanding issue with a solution that has not yet been
implemented, return to Part 2, Step 1.
b. If all your current issues are resolved, have you also resolved any remote
connectivity issues (such as can PC1 ping PC4)? If the answer is no, return to
Part 1, Step 1c to test remote connectivity.
PC1 cannot ping PC2 because has an ip address that does no belong to
the network PC1 is attached to.
Device cannot ping S2 and S2 cannot ping any device because S2 is
missing an IP address.
Remote devices cannot ping PC4 because PC4 has the wrong default
gateway configured.
Remote devices cannot ping S1 because S1 is missing a default
gateway configuration.
Suggested Scoring Rubric
Task
Complete Network
Documentation
Document Issues and
Solutions
Packet Tracer Score (Issues
Resolved)
Total Score
2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Possib
Earne
le
Points
Points
20
45
35
100
Page 7 of 7
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionDari EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- The Complete Guide to Getting Certified Cisco CCNA 200-301: Complete Your CCNA Exam Training and Preparation with 400 Exam Level Practice QuestionDari EverandThe Complete Guide to Getting Certified Cisco CCNA 200-301: Complete Your CCNA Exam Training and Preparation with 400 Exam Level Practice QuestionBelum ada peringkat
- 6.4.3.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Default Gateway Issues Instructions IGDokumen4 halaman6.4.3.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Default Gateway Issues Instructions IGBen White100% (1)
- CCNA A Spring 2016 6.4.3.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Default Gateway Issues Instructions IGDokumen4 halamanCCNA A Spring 2016 6.4.3.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Default Gateway Issues Instructions IGJame Chan50% (4)
- 6.4.3.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Default Gateway Issues InstructionsDokumen4 halaman6.4.3.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Default Gateway Issues Instructionsslider11880% (1)
- 6 4 3 4Dokumen4 halaman6 4 3 4johnBelum ada peringkat
- 7.2.4.9 Packet Tracer - Configuring IPv6 Addressing - ILMDokumen4 halaman7.2.4.9 Packet Tracer - Configuring IPv6 Addressing - ILMkds20850Belum ada peringkat
- 10.3.5-Packet-Tracer - Troubleshoot-Default-Gateway-IssuesDokumen4 halaman10.3.5-Packet-Tracer - Troubleshoot-Default-Gateway-IssuescesarBelum ada peringkat
- 10.3.5 Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Default Gateway Issues - ILMDokumen3 halaman10.3.5 Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Default Gateway Issues - ILMAnastasia KalliBelum ada peringkat
- 6.4.3.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Default Gateway Issues InstructionsDokumen4 halaman6.4.3.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Default Gateway Issues InstructionsAlexander HallBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Two Lab-5 - Troubleshoot Default Gateway IssuesDokumen3 halamanChapter Two Lab-5 - Troubleshoot Default Gateway IssuesFedasa BoteBelum ada peringkat
- 9.2.3.15 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Using Documentation To Solve IssuesDokumen5 halaman9.2.3.15 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Using Documentation To Solve IssuesPujiHstBelum ada peringkat
- 3.2.4.7 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting A VLAN Implementation - Scenario 1 Instructions PDFDokumen3 halaman3.2.4.7 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting A VLAN Implementation - Scenario 1 Instructions PDFShaunBelum ada peringkat
- 3.2.4.7 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting A VLAN Implementation - Scenario 1 InstructionsDokumen3 halaman3.2.4.7 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting A VLAN Implementation - Scenario 1 InstructionsnskpotulaBelum ada peringkat
- 7 3 2 9Dokumen5 halaman7 3 2 9johnBelum ada peringkat
- 8.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Pinging and Tracing To Test The Path InstructionsDokumen5 halaman8.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Pinging and Tracing To Test The Path InstructionsSameh Ahmed HassanBelum ada peringkat
- Troubleshooting Computer Network System: By: Alyssa Joi Viloria Tracy Mae Quizon Jerico RayoDokumen30 halamanTroubleshooting Computer Network System: By: Alyssa Joi Viloria Tracy Mae Quizon Jerico RayoDanilo AggabaoBelum ada peringkat
- RESPOSTAS - 7.3.2.9 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting IPv4 and IPv6 Addressing - ILMDokumen4 halamanRESPOSTAS - 7.3.2.9 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting IPv4 and IPv6 Addressing - ILMGabriel AlvesBelum ada peringkat
- CCNPv7 TSHOOT Lab4-1 Layer-2-Issues StudentDokumen10 halamanCCNPv7 TSHOOT Lab4-1 Layer-2-Issues StudentThomas Schougaard TherkildsenBelum ada peringkat
- CSS10-W8 Quarter 2 GR 10Dokumen4 halamanCSS10-W8 Quarter 2 GR 10Elaine CharisseBelum ada peringkat
- Frontline Network TroubleshootingDokumen6 halamanFrontline Network Troubleshootingw_dhallBelum ada peringkat
- Troubleshooting Network ProblemsDokumen73 halamanTroubleshooting Network Problemsaa wantsBelum ada peringkat
- CSS 12 Combined Modules Q2 Week 2Dokumen17 halamanCSS 12 Combined Modules Q2 Week 2Rhynz BanastonBelum ada peringkat
- Identifying and ResolvingDokumen48 halamanIdentifying and Resolvingyami adiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapters Study Materials Packet Tracer Labs Online AssignmentsDokumen20 halamanChapters Study Materials Packet Tracer Labs Online AssignmentsMărian IoanBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Network TroubleshootingDokumen9 halamanBasic Network TroubleshootingNeeraj Mishra50% (2)
- 9.1.1.8 Packet Tracer Troubleshooting ChallengeDokumen5 halaman9.1.1.8 Packet Tracer Troubleshooting ChallengeOrlyn Valencia100% (5)
- 6.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshoot Network ProblemsDokumen2 halaman6.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshoot Network ProblemsMaria JiminianBelum ada peringkat
- q4 Module1 2 g9 Css San Jacinto NhsDokumen8 halamanq4 Module1 2 g9 Css San Jacinto NhsAimee Joy L HermosoraBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 9 Lab 9-1, Network Mirror: Ccnpv7 TshootDokumen8 halamanChapter 9 Lab 9-1, Network Mirror: Ccnpv7 TshootJean-Pierre Roux0% (3)
- Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Layer 2 Issues: Physical TopologyDokumen10 halamanChapter 4 Lab 4-1, Layer 2 Issues: Physical Topologypan0% (5)
- Q3-CSS11 - Las 3Dokumen10 halamanQ3-CSS11 - Las 3jazel aquinoBelum ada peringkat
- 8.1.1.8 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Documenting The Network InstructionsDokumen5 halaman8.1.1.8 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Documenting The Network InstructionsEdwin BenitezBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 9.2.1Dokumen11 halamanLesson 9.2.1Rye Rye LasorBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Infrastruktur Sistem InformasiDokumen25 halamanLaporan Infrastruktur Sistem InformasisaktirolBelum ada peringkat
- SysAdmin CH 2Dokumen8 halamanSysAdmin CH 2Mirko MekonenBelum ada peringkat
- Handouts4-Final: Tcp/Ip Ipx/Spx Netbeui Subnet MaskDokumen3 halamanHandouts4-Final: Tcp/Ip Ipx/Spx Netbeui Subnet MaskLeonard FernandoBelum ada peringkat
- Network troubleshooting strategiesDokumen33 halamanNetwork troubleshooting strategiesEndale GirumeBelum ada peringkat
- How to troubleshoot home network and internet connection problemsDokumen22 halamanHow to troubleshoot home network and internet connection problemsGoodsonBelum ada peringkat
- 8.1.2.14 Lab - Test The Wireless NIC in WindowsDokumen6 halaman8.1.2.14 Lab - Test The Wireless NIC in WindowsMohammed AwelBelum ada peringkat
- ESwitching Lab 7 5 1 Brent v1.4Dokumen20 halamanESwitching Lab 7 5 1 Brent v1.4Surapich ChairgulprasertBelum ada peringkat
- Fredirick Jay Persigas Bsit 3 A Packet Tracer - Implementing Basic Connectivity TopologyDokumen5 halamanFredirick Jay Persigas Bsit 3 A Packet Tracer - Implementing Basic Connectivity TopologyMarc Jae PersigasBelum ada peringkat
- (IJCST-V5I4P2) :B Bindu Sahitya Devi, G Nageswara RaoDokumen4 halaman(IJCST-V5I4P2) :B Bindu Sahitya Devi, G Nageswara RaoEighthSenseGroupBelum ada peringkat
- EW 7209APg ManualDokumen44 halamanEW 7209APg ManualGabriel H. MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- 3.2.4.7 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting A VLAN Implementation - Scenario 1 InstructionsDokumen3 halaman3.2.4.7 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting A VLAN Implementation - Scenario 1 Instructionsrugun silitongaBelum ada peringkat
- 9.1.1.8 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Documenting The Network Instructions PDFDokumen5 halaman9.1.1.8 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Documenting The Network Instructions PDFJemuelVillonBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines For Testing Computer Systems and Network: Quarter 2-Week 5 ModuleDokumen6 halamanGuidelines For Testing Computer Systems and Network: Quarter 2-Week 5 ModuleReicy Mae TrinidadBelum ada peringkat
- 8.1.1.8 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Documenting The Network InstructionsDokumen5 halaman8.1.1.8 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Documenting The Network Instructionsiqbal pandu0% (1)
- Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Common Network Problems: Addressing TableDokumen15 halamanPacket Tracer - Troubleshoot Common Network Problems: Addressing TableCheese BurgerBelum ada peringkat
- IPv6 Implementation Acceptance Test Plan 1.0-SignedDokumen10 halamanIPv6 Implementation Acceptance Test Plan 1.0-SignedClaude OyekaBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnosing Computer FaultsDokumen8 halamanDiagnosing Computer FaultsSACATA NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL100% (1)
- Ali CCNab8 ReportDokumen7 halamanAli CCNab8 ReportMuhammad Ali RajarBelum ada peringkat
- Cot410 Work Sheet 1-1Dokumen11 halamanCot410 Work Sheet 1-1Mike McAlesterBelum ada peringkat
- CCNA Training - New CCNAv3 Questions Covering STP, Routing Tables, Multicast & MoreDokumen25 halamanCCNA Training - New CCNAv3 Questions Covering STP, Routing Tables, Multicast & MoreRemi PaternackBelum ada peringkat
- D Chs LM Module3 q1 q2 DecDokumen151 halamanD Chs LM Module3 q1 q2 DecHari Ng Sablay89% (9)
- EtherNet/IP and Logix troubleshooting guideDokumen13 halamanEtherNet/IP and Logix troubleshooting guideimmanjBelum ada peringkat
- CCN LAB ASSIGNMENT 1 - (VLANS AND TRUNKING LAB) - 26feb2020Dokumen4 halamanCCN LAB ASSIGNMENT 1 - (VLANS AND TRUNKING LAB) - 26feb2020luhoni jonaBelum ada peringkat
- ITN v6 Instructor Packet Tracer Manual PDFDokumen160 halamanITN v6 Instructor Packet Tracer Manual PDFRahmat SuhatmanBelum ada peringkat
- 17.4.6 Lab - Test Network Latency With Ping and TracerouteDokumen4 halaman17.4.6 Lab - Test Network Latency With Ping and TracerouteFernando AlburquerqueBelum ada peringkat
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Dari EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Appendix Packet Tracer - Configuring An Integrated RouterDokumen3 halamanAppendix Packet Tracer - Configuring An Integrated RouterParthPatelBelum ada peringkat
- 11.2.4.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring Secure Passwords and SSHDokumen2 halaman11.2.4.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring Secure Passwords and SSHParthPatelBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 7 - Viewing Wireless and Wired NIC InformationDokumen11 halamanLab 7 - Viewing Wireless and Wired NIC InformationParthPatelBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 5 - Configuring A Switch Managment AddressDokumen10 halamanLab 5 - Configuring A Switch Managment AddressParthPatelBelum ada peringkat
- 3.3.3.3 Packet Tracer - Explore A Network InstructionsDokumen5 halaman3.3.3.3 Packet Tracer - Explore A Network InstructionsWendhz ÜüBelum ada peringkat
- 11.2.4.8 Lab - Securing Network DevicesDokumen8 halaman11.2.4.8 Lab - Securing Network DevicesParthPatel60% (5)
- 11.3.3.3 Packet Tracer - Using Show CommandsDokumen2 halaman11.3.3.3 Packet Tracer - Using Show CommandsParthPatel0% (1)
- Appendix Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2Dokumen4 halamanAppendix Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2ParthPatelBelum ada peringkat
- 11.4.1.3 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting ChallengeDokumen3 halaman11.4.1.3 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting ChallengeParthPatel0% (1)
- 11.2.4.7 Lab - Examining Telnet and SSH in WiresharkDokumen9 halaman11.2.4.7 Lab - Examining Telnet and SSH in WiresharkParthPatel100% (2)
- 11.3.2.2 Packet Tracer - Test Connectivity With TracerouteDokumen3 halaman11.3.2.2 Packet Tracer - Test Connectivity With TracerouteParthPatelBelum ada peringkat
- 10.2.2.9 Lab - Observing DNS ResolutionDokumen5 halaman10.2.2.9 Lab - Observing DNS ResolutionasdfjklBelum ada peringkat
- 11.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeDokumen4 halaman11.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeParthPatel0% (1)
- 11.2.5.7 Packet Tracer - Backing Up Configuration FilesDokumen2 halaman11.2.5.7 Packet Tracer - Backing Up Configuration FilesParthPatel33% (3)
- 11.2.4.6 Lab - Accessing Network Devices With SSHDokumen6 halaman11.2.4.6 Lab - Accessing Network Devices With SSHParthPatel0% (3)
- 10.3.1.4 Packet Tracer Multiuser - Implement ServicesDokumen4 halaman10.3.1.4 Packet Tracer Multiuser - Implement ServicesParthPatel0% (1)
- 9.3.1.2 Packet Tracer Simulation - Exploration of TCP and UDP CommunicationDokumen6 halaman9.3.1.2 Packet Tracer Simulation - Exploration of TCP and UDP CommunicationParthPatel0% (1)
- 10.4.1.2 Packet Tracer Multiuser - Tutorial InstructionsDokumen3 halaman10.4.1.2 Packet Tracer Multiuser - Tutorial InstructionsKamijou SekaiBelum ada peringkat
- 8.3.1.4 Packet Tracer - Implementing A Subnetted IPv6 Addressing SchemeDokumen3 halaman8.3.1.4 Packet Tracer - Implementing A Subnetted IPv6 Addressing SchemeParthPatel0% (1)
- 8.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeDokumen2 halaman8.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeParthPatel0% (1)
- 10.2.2.7 Packet Tracer - DNS and DHCPDokumen4 halaman10.2.2.7 Packet Tracer - DNS and DHCPParthPatelBelum ada peringkat
- Configure and Use FTP ServersDokumen4 halamanConfigure and Use FTP ServersParthPatelBelum ada peringkat
- 10.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Web and EmailDokumen5 halaman10.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Web and EmailParthPatelBelum ada peringkat
- 9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme InstructDokumen4 halaman9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme InstructGanti nama100% (1)
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1Dokumen5 halaman8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1ParthPatel33% (6)
- 8.1.4.8 Lab - Designing and Implementing A Subnetted IPv4 Addressing SchemeDokumen12 halaman8.1.4.8 Lab - Designing and Implementing A Subnetted IPv4 Addressing SchemeParthPatel90% (31)
- 8.1.4.6 Lab - Calculating IPv4 SubnetsDokumen7 halaman8.1.4.6 Lab - Calculating IPv4 SubnetscgruBelum ada peringkat
- 7.3.2.9 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting IPv4 and IPv6 AddressingDokumen5 halaman7.3.2.9 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting IPv4 and IPv6 AddressingParthPatel0% (3)
- 7.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeDokumen2 halaman7.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeParthPatel100% (1)
- 7.3.2.8 Lab - Mapping The InternetDokumen8 halaman7.3.2.8 Lab - Mapping The InternetParthPatel0% (5)
- 8.1.3.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2 InstructionsDokumen5 halaman8.1.3.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2 Instructionsbass amadouBelum ada peringkat
- Ccna Packet Tracer TutorialDokumen10 halamanCcna Packet Tracer TutorialRiq Rogers SemaBelum ada peringkat
- Configure Network and DHCP ServersDokumen9 halamanConfigure Network and DHCP ServersPartha Sarathi NandiBelum ada peringkat
- WIFI Interface Printer Setting InstructionDokumen3 halamanWIFI Interface Printer Setting InstructionJeffersonTolottiBelum ada peringkat
- 8.2.8 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine Ethernet FramesDokumen10 halaman8.2.8 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine Ethernet FramesNguyễn Bảo HưngBelum ada peringkat
- SmoothWall Server & GreenBow IPsec VPN ConfigurationDokumen13 halamanSmoothWall Server & GreenBow IPsec VPN ConfigurationgreenbowBelum ada peringkat
- Instruction Manual: Airbox Cellular RouterDokumen17 halamanInstruction Manual: Airbox Cellular RouteracharlessBelum ada peringkat
- CCNA Training Hot Standby Router Protocol HSRP TutorialDokumen4 halamanCCNA Training Hot Standby Router Protocol HSRP Tutorialokotete evidenceBelum ada peringkat
- SAJOL - 4.5.1-Lab-Inter-Vlan-Routing-ChallengeDokumen3 halamanSAJOL - 4.5.1-Lab-Inter-Vlan-Routing-ChallengeJenie SajolBelum ada peringkat
- Shorewall Setup GuideDokumen32 halamanShorewall Setup GuidetithleangBelum ada peringkat
- 11.7.5-Packet-Tracer - Subnetting-ScenarioDokumen5 halaman11.7.5-Packet-Tracer - Subnetting-Scenariostudy timeBelum ada peringkat
- PROLINK H5004N ADSL - PsDokumen68 halamanPROLINK H5004N ADSL - PsRuel BalabisBelum ada peringkat
- Module 16: Troubleshoot Static and Default Routes: Instructor MaterialsDokumen18 halamanModule 16: Troubleshoot Static and Default Routes: Instructor MaterialsSalma BesbesBelum ada peringkat
- Build Router NetworkDokumen6 halamanBuild Router NetworkMuhammad MudassirBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 Case StudyDokumen3 halamanChapter 5 Case StudynescarvillaBelum ada peringkat
- BETTOR TITO DELUXE S2000 INSTALLATION v10Dokumen9 halamanBETTOR TITO DELUXE S2000 INSTALLATION v10ROGER EBYBelum ada peringkat
- Configure Static Routing Between NetworksDokumen29 halamanConfigure Static Routing Between NetworksUmer SharifBelum ada peringkat
- Mtcna PDFDokumen271 halamanMtcna PDFErfin SugionoBelum ada peringkat
- Package Contents: Quickstart GuideDokumen2 halamanPackage Contents: Quickstart GuideJudyrey P. MediavilloBelum ada peringkat
- CCNA 1 - Final Exam (Fersi 1)Dokumen4 halamanCCNA 1 - Final Exam (Fersi 1)FahrurroziBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4: Routing ConceptsDokumen66 halamanChapter 4: Routing ConceptsDiane GutierrezBelum ada peringkat
- CCNA 3 Final Exam Answers (2012)Dokumen27 halamanCCNA 3 Final Exam Answers (2012)Juan Diego Arellano VitelaBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco TAC Entry Training - 5 - Routing Concepts PDFDokumen62 halamanCisco TAC Entry Training - 5 - Routing Concepts PDFFerasHamdanBelum ada peringkat
- Secure Workloads VM Series OracleDokumen9 halamanSecure Workloads VM Series Oracleneaman_ahmedBelum ada peringkat
- Cisco Packet TracerDokumen8 halamanCisco Packet TracerViranshi SanghaviBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5Dokumen4 halamanChapter 5Luci IonicaBelum ada peringkat
- 9.2.3.5 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine A UDP DNS CaptureDokumen6 halaman9.2.3.5 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine A UDP DNS Capture雪山飛狐0% (3)
- Enraf Cookbook Wireless Interface 4417783Dokumen30 halamanEnraf Cookbook Wireless Interface 4417783Anonymous zdCUbW8HfBelum ada peringkat
- LP-5420G User GuideDokumen81 halamanLP-5420G User Guidenelsongil211Belum ada peringkat
- 5 6 3Dokumen11 halaman5 6 3Tárcio AlmeidaBelum ada peringkat