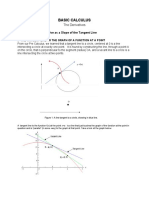
Chapter 8 Study Guide
Diunggah oleh
api-313891381Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 8 Study Guide
Diunggah oleh
api-313891381Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 8 Study Guide
Inverse Variation
Direct variation
Inverse variation
k=
y
x
k = xy
K is the constant of variation
K must be the same for all (x,y) points if there is inverse variation
Example: Assume x and y vary inversely. If x = 4 when y = 12, write the function tat model the
inverse variation
y=
k
x
y=
48
x
Reciprocal Functions
Form f(x) =
1
x
where x 0
A family of functions that includes those functions that models inverse variation
a
( xh)
General form: y =
Parent function: y =
+k h
1
x
Asymptote
An imaginary line that a graph approaches but never touches
To transform y =
1
x
to y =
a
( xh)
+k
|a| is bigger than 1 stretch
|a| is between 0 and 1 shrink/compress
a < 0 (negative) reflect about x-axis
h is the vertical asymptote (moves vertically)
k is the horizontal asymptote (moves horizontally)
Rational Functions
Can be written as f(x) =
P (x )
Q(x)
P(x) is a function
Q(x) is a function
Q(x) 0
Continuous Graph
Has no jumps, breaks, or holes
Can trace it with your pencil without lifting your pencil
Discontinuous Graph
Not continuous
f(x) =
P (x )
Q(x)
if Q(x) = 0 at x-a, then x=a is a point of discontinuity
Steps:
1) Factor the numerator and the denominator
2) What will make the denominator zero?
Removable simplifies with the numerator
Nonremovable does not reduce
Finding Intercepts
Find out intercepts after reducing
X-Intercept
1) Set numerator equal to zero
2) Solve for x (x,0)
Y-Intercept
1) Set all xs equal to zero
2) Solve for y (0,y)
Domain
All x-values except when there is a discontinuity
Holes
Occurs at a removable discontinuity
Ordered pair
X=# plug in x and solve for y
Vertical Asymptotes
Nonremovable discontinuities
X=#
Line
Steps:
1)
2)
3)
4)
Factor numerator and denominator
Find zeros of the denominator
Cross out zeros that are also zeros of the numerator
Remaining zeros are vertical asymptotes in the form x=zero
Horizontal Asymptote
Compare degree of numerator (dN) and degree of denominator (dD)
If dN < dD . The horizontal asymptote is y=0
If dN > dD . There is no horizontal asymptote
If dN = dD . The horizontal asymptote is y=
leading coefficient of numerator
leaing coefficient of denominator
Simplest Form Rational Equations
Numerator AND denominator have no common factors
Factor both, reduce
Division
Steps:
1)
2)
3)
4)
Multiply by reciprocal
Factor
Restrictions
Reduce
Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions
Steps:
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
Factor
Common Denominator
Write as ONE fraction
Multiple/combine like terms (numerator)
Re-Factor
Simplify if possible
Solving Rational Equations
Steps:
1)
2)
3)
4)
Factor to find LCD
Multiple each side by LCD
Simplify and solve
Check for extraneous in original equation
*** LCD Least Common Denominator
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Frederick Douglass Final EssayDokumen3 halamanFrederick Douglass Final Essayapi-313891381100% (1)
- Determinet The Domain of Rational Functions Identify Vertical or Horizontal Asymptotes Graphs Rational FunctionsDokumen13 halamanDeterminet The Domain of Rational Functions Identify Vertical or Horizontal Asymptotes Graphs Rational Functionsm29402102Belum ada peringkat
- Rational Functions: A Function F Represented by Where P (X) and Q (X) Are Polynomials andDokumen48 halamanRational Functions: A Function F Represented by Where P (X) and Q (X) Are Polynomials andJulius Ivan SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Rational Functions: A Function F Represented by Where P (X) and Q (X) Are Polynomials andDokumen48 halamanRational Functions: A Function F Represented by Where P (X) and Q (X) Are Polynomials andJulius Ivan SantosBelum ada peringkat
- EC270 CH2 Math Lecture Slides WEBDokumen37 halamanEC270 CH2 Math Lecture Slides WEBDavidBelum ada peringkat
- IV) Graphing Rational Functions PDFDokumen21 halamanIV) Graphing Rational Functions PDFKhaye Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Asymptotes, Holes, and Graphing Rational FunctionsDokumen4 halamanAsymptotes, Holes, and Graphing Rational Functions1DerfulHarrehBelum ada peringkat
- 03 Rational FunctionsDokumen37 halaman03 Rational FunctionsJudy Ann ShengBelum ada peringkat
- Math 150 Exam 1 Review SheetDokumen3 halamanMath 150 Exam 1 Review SheetTuongVNguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Rational FunctionsDokumen14 halamanIntroduction To Rational FunctionsdennisBelum ada peringkat
- Rational Functions Domain and AsymptotesDokumen18 halamanRational Functions Domain and AsymptotesDarrel SusayaBelum ada peringkat
- Intercepts, Zeroes, and Asymptotes of Rational FunctionsDokumen33 halamanIntercepts, Zeroes, and Asymptotes of Rational Functionsaiza100% (2)
- Lecture 2.1: Vector Calculus CSC 84020 - Machine Learning: Andrew RosenbergDokumen46 halamanLecture 2.1: Vector Calculus CSC 84020 - Machine Learning: Andrew RosenbergAli BhuttaBelum ada peringkat
- Vertical and Horizontal AsymptotesDokumen23 halamanVertical and Horizontal AsymptotesAmirul Mohamad KhuldiBelum ada peringkat
- Section 3.2 NotesDokumen4 halamanSection 3.2 NotesJean GBelum ada peringkat
- Graphs of Functions ExplainedDokumen10 halamanGraphs of Functions ExplainedHaoyu WangBelum ada peringkat
- Genmath Module 6Dokumen9 halamanGenmath Module 6Jenray DacerBelum ada peringkat
- Defining Linear TransformationsDokumen9 halamanDefining Linear TransformationsAshvin GraceBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 15 DifferenciationDokumen37 halamanChapter 15 DifferenciationminhazBelum ada peringkat
- Asymptote SDokumen4 halamanAsymptote Sbkjr2008Belum ada peringkat
- Rational Function NoteDokumen63 halamanRational Function NoteMark Francis HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Review Math FoundationDokumen8 halamanReview Math FoundationPrince Arc MiguelBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 Study Guide: Equations (Memorize)Dokumen4 halamanChapter 8 Study Guide: Equations (Memorize)jjwtayBelum ada peringkat
- Vertical and Horizontal Asymptotes of Rational FunctionsDokumen2 halamanVertical and Horizontal Asymptotes of Rational Functionsscarlet100% (2)
- MTH101 Lec#1Dokumen28 halamanMTH101 Lec#1Omar HaroonBelum ada peringkat
- Derivatives: A Physics 100 TutorialDokumen18 halamanDerivatives: A Physics 100 TutorialPervela BruhaspathiBelum ada peringkat
- MHF4U Unit 1Dokumen9 halamanMHF4U Unit 1Daniswara HafidzBelum ada peringkat
- Rational Functions: A Rational Function Is A Function of The FormDokumen18 halamanRational Functions: A Rational Function Is A Function of The FormRaquel disomimbaBelum ada peringkat
- HSCMaths Ext 231341Dokumen30 halamanHSCMaths Ext 231341Robert HigginsBelum ada peringkat
- 14 - Rational Function - MC - Guide and LabDokumen13 halaman14 - Rational Function - MC - Guide and LabElsa BrounsBelum ada peringkat
- Section1 2-FilledDokumen9 halamanSection1 2-FilledSononameBelum ada peringkat
- Final RevisionDokumen21 halamanFinal Revisionsprinklesdb16Belum ada peringkat
- Calculus FULLDokumen107 halamanCalculus FULLkanishkaBelum ada peringkat
- Properties & Formulae Sheet (CSTM 0120)Dokumen10 halamanProperties & Formulae Sheet (CSTM 0120)CTLBelum ada peringkat
- Calculus To First ExamDokumen9 halamanCalculus To First ExamSteven WalkerBelum ada peringkat
- Graph Rational FunctionsDokumen8 halamanGraph Rational Functionsalayca cabatanaBelum ada peringkat
- GauntletDokumen6 halamanGauntletsuvo baidyaBelum ada peringkat
- PC Functions RationalDokumen11 halamanPC Functions RationalHector R.Belum ada peringkat
- Pre CalcDokumen2 halamanPre Calcapi-213604106Belum ada peringkat
- Mathematical Techniques For Economic Analysis: Australian National University DR Reza HajargashtDokumen60 halamanMathematical Techniques For Economic Analysis: Australian National University DR Reza HajargashtWu YichaoBelum ada peringkat
- Find x and y intercepts of polynomial functionsDokumen21 halamanFind x and y intercepts of polynomial functionsjudeBelum ada peringkat
- 3.1 Graphs of Polynomial FunctionsDokumen17 halaman3.1 Graphs of Polynomial FunctionsJonalyn Bautista-CanlasBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Calculus: Derivatives ExplainedDokumen25 halamanBasic Calculus: Derivatives ExplainedKrrje IBelum ada peringkat
- Algebraic Curves: Analytic Geometry by Fuller and Tarwater Pages 161-170Dokumen15 halamanAlgebraic Curves: Analytic Geometry by Fuller and Tarwater Pages 161-170leepatrickbanezBelum ada peringkat
- Asymptote Horizontal Asymptote: Horizontal Asymptotes Are Horizontal Lines To Which The Function IsDokumen19 halamanAsymptote Horizontal Asymptote: Horizontal Asymptotes Are Horizontal Lines To Which The Function IsMohd Hazwan ZulkifliBelum ada peringkat
- EC2104 Lecture 2Dokumen40 halamanEC2104 Lecture 2GeekgodBelum ada peringkat
- Algebra1section3 3Dokumen11 halamanAlgebra1section3 3api-358505269Belum ada peringkat
- KEY CONCEPTS OF RATIONAL FUNCTIONSDokumen10 halamanKEY CONCEPTS OF RATIONAL FUNCTIONSRobert John Basia BernalBelum ada peringkat
- Finite Element Analysis of Structural SystemsDokumen255 halamanFinite Element Analysis of Structural SystemsANANTHAN HASSANBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics For Management Concept Summary: AlgebraDokumen10 halamanMathematics For Management Concept Summary: AlgebraJAY BHAVIN SHETH (B14EE014)Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 M 1Dokumen22 halamanChapter 3 M 1Isra WaheedBelum ada peringkat
- Math Report - 041207Dokumen13 halamanMath Report - 041207Gian AnireBelum ada peringkat
- Graph of Polynomial FunctionDokumen27 halamanGraph of Polynomial FunctionJulie IsmaelBelum ada peringkat
- CBR KalkulusDokumen20 halamanCBR KalkulusYon setiawanBelum ada peringkat
- Rational Function IntroductionDokumen23 halamanRational Function IntroductionUddin NimatBelum ada peringkat
- DiagnosticTests From Stewart (Nby T1 1617)Dokumen13 halamanDiagnosticTests From Stewart (Nby T1 1617)kirutiggaBelum ada peringkat
- L 06Dokumen27 halamanL 06Geek FdhifubBelum ada peringkat
- Transformation Parent FunctionsDokumen15 halamanTransformation Parent Functionsqqvhc2x2prBelum ada peringkat
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDari EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (8)
- Jazz Age Short AnswerDokumen1 halamanJazz Age Short Answerapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- Puerto RicoDokumen12 halamanPuerto Ricoapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- Carnaval de PonceDokumen3 halamanCarnaval de Ponceapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- BiomarkersDokumen1 halamanBiomarkersapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- Cleidocranial DysplasiaDokumen4 halamanCleidocranial Dysplasiaapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- Annotated BibliographyDokumen7 halamanAnnotated Bibliographyapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- Research Paper Rough DraftDokumen5 halamanResearch Paper Rough Draftapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- Care For CreationDokumen7 halamanCare For Creationapi-314065532Belum ada peringkat
- Forensic Science-O J Simpson CaseDokumen4 halamanForensic Science-O J Simpson Caseapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- History Midterm AnswerDokumen2 halamanHistory Midterm Answerapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- Saint Agatha PresentationDokumen5 halamanSaint Agatha Presentationapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- Finding Unknown Substances LabDokumen4 halamanFinding Unknown Substances Labapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- Light Project 1Dokumen16 halamanLight Project 1api-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- Resume GrubbsDokumen2 halamanResume Grubbsapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- Cap GrubbsDokumen2 halamanCap Grubbsapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- Cell Project - Organelle DescriptionsDokumen1 halamanCell Project - Organelle Descriptionsapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- Comparative EssayDokumen3 halamanComparative Essayapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- The Holocaust and Beyond QuestionsDokumen6 halamanThe Holocaust and Beyond Questionsapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- Gel Electrophoresis Lab ReportDokumen8 halamanGel Electrophoresis Lab Reportapi-313891381100% (2)
- Pi Day Project With Marissa and Ella Marissa BeckDokumen6 halamanPi Day Project With Marissa and Ella Marissa Beckapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- Final Exam Study GuideDokumen6 halamanFinal Exam Study Guideapi-313891381100% (1)
- Spanish Project With GillianDokumen21 halamanSpanish Project With Gillianapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- The Evolution of Working ConditionsDokumen4 halamanThe Evolution of Working Conditionsapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- College EssayDokumen5 halamanCollege Essayapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- Developmental Theory in Real LifeDokumen21 halamanDevelopmental Theory in Real Lifeapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- Wwi Modern WarfareDokumen2 halamanWwi Modern Warfareapi-313891381Belum ada peringkat
- Physics Homework Solutions - 100 100Dokumen1 halamanPhysics Homework Solutions - 100 100rahulBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set 1Dokumen32 halamanProblem Set 1bobBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE Class 11 Maths Sample Paper 01 SolutionsDokumen22 halamanCBSE Class 11 Maths Sample Paper 01 SolutionsabcBelum ada peringkat
- Taylor SeriesDokumen13 halamanTaylor SeriesSandip Desai100% (1)
- Planning and Scheduling - CPMDokumen30 halamanPlanning and Scheduling - CPMTeguh Setyo PurwantoBelum ada peringkat
- Calculate Keq for Equilibrium ReactionsDokumen4 halamanCalculate Keq for Equilibrium ReactionsJana AldourBelum ada peringkat
- MAT122 Scheme 2022-2023 Sem 2Dokumen5 halamanMAT122 Scheme 2022-2023 Sem 2Lesley SimonBelum ada peringkat
- 6-Titrimetric Methods of AnalysisDokumen15 halaman6-Titrimetric Methods of Analysisnids75% (4)
- Rubrics in Assessing Student's LearningDokumen4 halamanRubrics in Assessing Student's LearningJOHNBBelum ada peringkat
- Aplicatie 4Dokumen35 halamanAplicatie 4AndreeaPopescuBelum ada peringkat
- Mathopolis Questions Q9Dokumen2 halamanMathopolis Questions Q9ski3013Belum ada peringkat
- VariationDokumen6 halamanVariationPSYCHO / FLOWBelum ada peringkat
- DBA MathsDokumen98 halamanDBA Mathsvictor chisengaBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of Analytical Methods Not MineDokumen20 halamanClassification of Analytical Methods Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonBelum ada peringkat
- Column and Thin Layer ChromatographyDokumen5 halamanColumn and Thin Layer Chromatographymarilujane80% (5)
- Questions On Conformal Mapping and Differential EquationsDokumen4 halamanQuestions On Conformal Mapping and Differential EquationsnithinBelum ada peringkat
- MSM 112 - Limits Differentiation - T2Dokumen2 halamanMSM 112 - Limits Differentiation - T2Francis ShiliwaBelum ada peringkat
- Minggu 2 Dan 3 - Stability PDFDokumen43 halamanMinggu 2 Dan 3 - Stability PDFFahmi RizalBelum ada peringkat
- Abou-Faycal Trott ShamaiDokumen12 halamanAbou-Faycal Trott ShamaiNguyễn Minh DinhBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 3 - Operations On SignalsDokumen8 halamanLab 3 - Operations On Signalsziafat shehzadBelum ada peringkat
- CLA Week3Dokumen13 halamanCLA Week3susheendhar vijayBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 9 Infinite Series 2018Dokumen150 halamanChapter 9 Infinite Series 2018hayaBelum ada peringkat
- Differential EquationsDokumen8 halamanDifferential EquationsRodziah Nasir80% (5)
- Integral Transforms in Applied MathematicsDokumen109 halamanIntegral Transforms in Applied Mathematicschoni singh0% (1)
- Chapter 5 Thesis Sample QualitativeDokumen8 halamanChapter 5 Thesis Sample Qualitativeqpftgehig100% (2)
- Chapter 1 Measure of Central TendecyDokumen22 halamanChapter 1 Measure of Central Tendecysyahrilazuan8Belum ada peringkat
- Jawapan: 1.1 Fungsi 1Dokumen7 halamanJawapan: 1.1 Fungsi 1Yun XingBelum ada peringkat
- Numerical ComputionsDokumen103 halamanNumerical ComputionsHassan AlsafiBelum ada peringkat
- QCC BasicDokumen7 halamanQCC BasicRina RomanoBelum ada peringkat
- MATH SylDokumen79 halamanMATH SylReby RoyBelum ada peringkat