Control Engine - 1kd-Ftv and 2kd-Ftd
Diunggah oleh
Eulicer ArmengolJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Control Engine - 1kd-Ftv and 2kd-Ftd
Diunggah oleh
Eulicer ArmengolHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-147
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM
1. General
The engine control system of the 1KD-FTV and 2KD-FTV engines has the following system.
2KD-FTV
1KD-FTV 2KD-FTV
High
Version
System
Outline
Fuel Injection
Volume Control
(See page EG-156)
Based on the signals received from the sensors, the engine ECU
determines the fuel injection volume in accordance with the engine
condition.
Fuel Injection
Timing Control
(See page EG-157)
Based on the signals received from the sensors, the engine ECU
determines the fuel injection timing in accordance with the engine
condition.
During Starting
Control
(See page EG-158)
To facilitate startability, the engine ECU optimally controls the injection
volume and injection timing during starting.
Idle Speed
Control
(See page EG-159)
The engine ECU determines the idle speed in accordance with the engine
condition, and controls the fuel injection volume in order to maintain the
target idle speed.
Fuel Pressure
Control
(See page EG-160)
Pilot Injection
Control
(See page EG-163)
Glow Plug
Control
Based on the signals received from the sensors, the engine ECU
determines the fuel pressure via SCV (Suction Control Valve) in
accordance with the engine condition.
Based on the signals received from the sensors, the engine ECU
determines pilot injection volume/timing, and interval (between pilot
injection and main injection) in accordance with the engine condition.
Controls the length of time when the current is applied to the glow plugs,
in accordance with the coolant temperature.
Intake Shutter
Control
(See page EG-164)
Controls the intake shutter valve (throttle valve) opening angle in
accordance with the engine condition.
Fully close the intake shutter valve (throttle valve) in order to reduce the
vibration when the engine is stopped.
Swirl Control
(See page EG-164)
Based on the signals received from the sensors, the engine ECU controls
the vacuum that is directed to the actuator via the VSV, in order to open
and close the valve.
Turbocharger
Control
(See page EG-165)
Based on the signals received from the sensors, the engine ECU controls
the actuator in accordance with the engine condition.
EGR Control
(See page EG-169)
Controls the EGR volume via EGR valve in accordance with the engine
condition.
Air Conditioner
Cut-Off Control*1
By controlling the air conditioner compressor ON or OFF in accordance
with the engine condition, drivability is maintained.
Engine
Immobilizer*2
Prohibits fuel injection if an attempt is made to start the engine with an
invalid ignition key.
Diagnosis
(See page EG-171)
When the engine ECU detects a malfunction, the engine ECU diagnoses
and memorizes the failed section.
Fail-Safe
(See page EG-171)
When the engine ECU detects a malfunction, the engine ECU stops or
controls the engine according to the data already stored in the memory.
*1: Models with Air Conditioner
*2: Models with Engine Immobilizer System
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-148
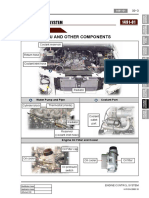
2. Construction
The configuration of the engine control system in the 1KD-FTV and 2KD-FTV engines is as shown in
the following chart.
INTAKE SHUTTER VALVE
POSITION SENSOR
#1
VLU
#2
#3
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR
#4
INJF
No.1 INJECTOR
E
D
U
No.2 INJECTOR
No.3 INJECTOR
No.4 INJECTOR
NE
PCV
SUCTION CONTROL VALVE
PCR1
INTAKE SHUTTER CONTROL
LUSL
PIM
Torque Motor (Rotary Solenoid type)
TURBO PRESSURE SENSOR
EGR CONTROL
THA
INTAKE AIR TEMP. SENSOR
WATER TEMP. SENSOR
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
POSITION SENSOR
EGR
THW
Engine
ECU
EGRC
GLOW PLUG CONTROL
VPA2
THF
SCV
INTAKE AIR TEMP. SENSOR*2
Glow Plug Relay
VG
IREL
FUEL TEMP. SENSOR
VSV (for EGR Valve Close)*1
VPA
GREL
AIR FLOW METER*1
Vacuum Regulating Valve
(for EGR Valve Control)
THIA
EDU RELAY
VSV (for Swirl Control Valve)*1
Close)
TURBOCHARGER CONTROL*1
EGR VALVE
POSITION SENSOR*3
EGLS
VNTO
Turbo Motor Driver
VNTI
STOP LIGHT SWITCH
ALTERNATOR
STP
ST1ALT
Nozzle Vane
Position Sensor
DC Motor
271EG132
(Continued)
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-149
A/C AMPLIFIER*7
IGNITION SWITCH
STA
Starting Signal (ST Terminal)
Ignition Signal (IG Terminal)
ACT
IGSW
Magnetic Clutch Actuation Signal
AC1
Engine Idle-Up Signal
4
CRUISE CONTROL MAIN SWITCH*
CCS
BATT
BATTERY
COMBINATION METER
MREL Engine ECU
MAIN RELAY
+B
TRANSPONDER KEY ECU*5
IMO
IMI
TC
SIL
DLC3
WFSE
W
GIND
PI
SPD
DM
TACH
TRANSMISSION CONTROL ECU*
CAN+
ECT CONTROL
CAN-
THWO
*1: Only for 1KD-FTV Engine
*2: Only for Models with Intercooler
*3: Only for 2KD-FTV Engine
*4: Only for Models with Cruise Control System
*5: Only for Models with Engine Immobilizer System
*6: Only for Models with Automatic Transmission
*7: Only for Models with Air Conditioner System
*8: Only for Models with Multi Information Display
Check Engine
Warning Light
Glow Indicator Light
Cruise MAIN
Indicator Light*4
Vehicle Speed Signal
Injection Volume Signal*8
Tachometer
Water Temp. Signal
271EG133
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-150
3. Engine Control System Diagram
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
Ignition Switch Signal
Stop Light Switch Signal
Air conditioner Signal*1
Glow Relay
Vehicle Speed Signal
Suction Control
Valve
Engine
ECU
Fuel Temp.
Sensor
Supply Pump
Atmospheric
Pressure Sensor
VSV*2
(EGR Valve Close)
Common-Rail
Fuel Pressure
Sensor
Intake Air
Temp. Sensor*2
Intake Air
Temp.
Sensor*3
Intercooler*3
E-VRV
EDU
Relay
EDU
Intake
Shutter
Assy.
EGR Valve
Position Sensor*4
Turbo Pressure
Sensor
Air Flow Meter*2
Intake Air
Temp. Sensor*4
DC Motor*2
Nozzle Vane
Position Sensor*2
Glow Plug
VSV*2
(Swirl
Control
Valve)
Injector
Turbo Motor
Driver*2
Water
Temp.
Sensor
Camshaft
Position Sensor
Crankshaft
Position Sensor
*1: Only for Models with Air Conditioner
*2: Only for 1KD-FTV Engine
*3: Only for Models with Intercooler
*4: Only for 2KD-FTV Engine
271EG134
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-151
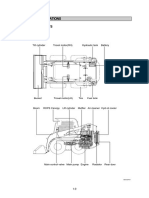
4. Layout of Main Components
EDU
E-VRV
Turbo Pressure Sensor
Air Flow Meter*1
Intake Air
Temp. Sensor*2
Glow Plug
Injector
Intake Air
Temp. Sensor*3
Intake Shutter Valve
Position Sensor
Fuel
Pressure
Sensor
Torque Motor
(Rotary Solenoid type)
VSV*1
(EGR Valve Close)
EGR Valve
Position Sensor*2
Water
Temp.
Sensor
Check Engine
Warning Light
Glow
Indicator Light
VSV*1
(Swirl Control
Valve)
Engine ECU
Transmission
Control ECU*4
Common-Rail
Crankshaft
Position Sensor
Camshaft Position
Sensor
Fuel Temp.
Sensor
Stop Light
Switch
SCV
Supply Pump
DLC3
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
LHD Model
*1: Only for 1KD-FTV Engine
*2: Only for 2KD-FTV Engine
*3: Only for Models with Intercooler
*4: Only for Models with Automatic Transmission
271EG135
Turbo Motor
Driver*1
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-152
5. Main Components of Engine Control System
General
The main components of the 1KD-FTV and 2KD-FTV engine control system are as follows:
Components
Engine ECU
Outline
32-bit CPU
Quantity
Function
The engine ECU effects overall control of the engine
control system to suit the operating conditions of the
engine in accordance with the signals provided by
the sensors.
EDU
DC/DC Converter
The EDU is used to drive the injector at high speeds.
The EDU has realized high-speed driving under high
fuel pressure conditions through the use of a DC/DC
converter that provides a high voltage, quickcharging system.
Turbo Pressure
Sensor
Semiconductor
Silicon Chip Type
This sensor uses built-in semiconductors to detect
the intake manifold pressure.
Atmospheric Pressure
Sensor
Semiconductor
Silicon Chip Type
This sensor, which is built into the engine ECU, uses
semiconductors to detect the atmospheric pressure.
Fuel Pressure Sensor
Semiconductor
Strain Gauge Type
This sensor uses built-in semiconductors to detect
the internal pressure of the common-rail.
Crankshaft
Position Sensor
Pick-up Coil Type
(Rotor Teeth /36-2)
This sensor detects the engine speed and performs
the cylinder identification.
Camshaft
Position Sensor
Air Flow Meter
(1KD-FTV Engine)
Water Temperature
Sensor
Pick-up Coil Type
(Rotor Teeth /5)
This sensor performs the cylinder identification.
Hot-wire Type
Thermistor Type
Thermistor Type
Thermistor Type
Thermistor Type
Intake Shutter Valve
Position Sensor
No-contact Type
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
No-contact Type
Contact Type
Intake Air
Temperature Sensor
Intake Air
Temperature Sensor
(for Intercooler)
Fuel Temperature
Sensor
EGR Valve
Position Sensor
(2KD-FTV Engine)
SCV
Suction Control
Valve
Injector
Linear Solenoid
Valve
8-hole Type
(1KD-FTV Engine)
6-hole Type
(2KD-FTV Engine)
This sensor uses a built-in hot-wire to directly detect
the intake air volume.
This sensor detects the engine coolant temperature
by means of an internal thermistor.
This sensor, which is provided at the air cleaner
outlet, detects the intake air temperature by means
of an internal thermistor.
On the 1KD-FTV engine, this sensor is built into
the airflow meter.
This sensor, which is provided only on the models
with an intercooler, detects the intake air
temperature past the intercooler.
This sensor detects the fuel temperature in the
supply pump by means of an internal thermistor.
This sensor detects the intake shutter valve (throttle
valve) opening angle.
This sensor detects the amount of pedal effort
applied to the accelerator pedal.
The basic construction and operation of this sensor
are the same as in the 1TR-FE and 2TR-FE
engines. For details, see page EG-46.
This sensor detects the actual amount of the EGR
valve opening.
The SCV position is controlled by the signals from
the ECU, and a fuel volume that suits the SCV
position is drawn into the pumping portion (plunger
portion).
The injector contains a solenoid valve that opens and
closes to increase or decrease the pressure in the
control chamber. This causes the nozzle needle to
open and close the valve, which results in fuel
injection.
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-153
Engine ECU
The 32-bit CPU of the engine ECU is used to increase the speed for processing the signals.
Each of the 2KD-FTV engine and the 2KD-FTV High Version engine is equipped with an engine
ECU that contains an engine control program that differs from each other. However, both engine
models share the same mechanical components.
On the models equipped with the A340E and A340F automatic transmissions, the engine ECU
maintains communication with a separate, independent ECT ECU through CAN (Controller Area
Network). Thus, engine control is effected in coordination with ECT control.
Turbo Pressure Sensor
The turbo pressure sensor consists of a semiconductor which utilizes the characteristic of a silicon chip
that changes its electrical resistance when pressure is applied to it. The sensor converts the intake air
pressure into an electrical signal, and sends it to the engine ECU in an amplified form.
Sensor Unit
(V)
5
Output
Voltage
(kPa)
100
250
Intake Manifold Pressure
271EG136
Fuel Pressure Sensor
The fuel pressure sensor consists of a semiconductor which utilizes the characteristic of a silicon chip
that changes its electrical resistance when pressure is applied to it. This sensor is mounted on the
common-rail, outputs a signal that represents the fuel pressure in the common-rail to the engine ECU, in
order to constantly regulate the fuel at an optimal pressure.
Detection Portion
(V)
Output
Voltage
(MPa)
Fuel Pressure
271EG137
EG-154
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
Crankshaft Position Sensor and Camshaft Position Sensor
The timing rotor of the crankshaft consists of 34 teeth, with 2 teeth missing. The crankshaft position
sensor outputs the crankshaft rotation signals every 10, and the missing teeth are used to determine
the top-dead-center.
To detect the camshaft position, a protrusion that is provided on the timing pulley is used to generate 5
pulse for every 2 revolution of the crankshaft.
Camshaft
Position Sensor
Camshaft Position Sensor
34 Pulse/360 CA
5 Pulse/720 CA
224EG41
Sensor Output Waveforms
5 Pulse/720 CA
180 CA
180 CA
34 Pulse/360 CA
180 CA
34 Pulse/360 CA
271EG138
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-155
Intake Shutter Valve Position Sensor
The intake shutter valve position sensor is mounted on the intake shutter assembly, to detect the opening
angle of the intake shutter valve (throttle valve), the intake shutter valve position sensor converts the
magnetic flux density that changes when the magnetic yoke (located on the same axis as the intake
shutter valve shaft) rotates around the hall IC into electric signals to operate the intake shutter valve
control motor.
Hall IC
Output
Voltage
(V)
Magnet
271EG82
Intake Shutter Valve
(Throttle Valve)
100
Intake Shutter Valve Position Ratio ()
271EG83
258AE62
EG-156
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
6. Fuel Injection Volume Control
The engine ECU calculates two types of values: the basic injection volume and the maximum injection
volume. Then, the engine ECU compares the basic and maximum injection volumes, and determines the
smaller calculated value to be the final injection volume.
Basic Injection Volume
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
Crankshaft
Position Sensor
Engine Speed
Engine ECU
Calculation of
Basic Injection
Volume
ISC* Correction
Water Temp. Sensor
*: Idle Speed Control
224EG44
Maximum Injection Volume
Engine ECU
Basic/Maximum
Injection Volume
(Map data inside of ECU)
Crankshaft
Position Sensor
Engine Speed
Water Temp. Sensor
Maximum Injection
Volume Correction
Fuel Temp. Sensor
Intake Air
Temp Sensor
Turbo Pressure
Sensor
Air Flow Meter*
Intake Air Volume*
224EG46
*: Only for 1KD-FTV Engine
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-157
Final Injection Volume Decision
Engine ECU
Basic Injection Volume
Fuel Pressure
Comparison
Final
EDU
Maximum Injection
Volume
Injector
224EG48
7. Fuel Injection Timing Control
Fuel injection timing is controlled as shown below.
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
Crankshaft
Position Sensor
Engine Speed
Engine ECU
Basic Injection Timing
Water Temp. Sensor
Intake Air Temp.
Sensor
Correction
Turbo Pressure Sensor
Injection Timing
EDU
Injection
201EG45
EG-158
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
8. During Starting Control
Injection Volume Control
The starting injection volume is determined by adjusting the basic injection volume in accordance with
the starter ON signals (ON time) and coolant temperature sensor signals and engine speed signal. When
the engine is cold, the coolant temperature will be lower and the injection volume will be greater.
Engine ECU
Basic Injection
Volume
+
Starter Signal
Correction
Water Temp.
Sensor
Crankshaft
Position Sensor
224EG50
Injection Timing Control
To determine the starting injection timing, the target injection timing is corrected in accordance with the
starter signals, water temperature, and engine speed.
When the water temperature is low, if the engine speed is high, the injection timing is advanced.
Engine ECU
Starter Signal
Target Injection
Timing Correction
Water Temp.
Sensor
Crankshaft
Position Sensor
224EG51
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-159
9. Idle Speed Control
Fuel injection timing is controlled as shown below.
Engine ECU
Accelerator
Pedal Position
Sensor
Water Temp. Sensor
Target Speed
Calculation
Vehicle Speed Sensor
Starter Signal
A/C Signal*
Idle-up Signal
Comparison
Actual Engine Speed
Injection Volume
Correction
Crankshaft
Position Sensor
*: with Air Conditioner
233EG14
EG-160
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
10. Fuel Pressure Control
General
Engine ECU calculates the target injection pressure (32~160MPa/1KD-FTV, 30~160MPa/2KD-FTV)
base on the engine conditions, that are the signals from the acceleration pedal position sensor and the
crankshaft position sensor.
To control fuel pressure, signals sent to SCV (Suction Control valve) of the supply pump regulate the
pumping volume, so that the pressure detected by the pressure sensor matches the target injection
pressure.
Fuel Pressure Sensor
Pressure Limiter
Common-rail
Injector
Supply Pump
SCV
Fuel Temp. Sensor
EDU
Calculation of
target injection
pressure
Engine ECU
Crankshaft
Position
Sensor
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
271EG139
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-161
System Operation
1) General
The engine ECU controls the opening of the SCV in order to regulate the volume of fuel that is
pumped by the supply pump to the common-rail. Consequently, the fuel pressure in the common-rail is
controlled to the target injection pressure.
2) SCV Opening Small
(a) When the opening of the SCV is small, the fuel suction area is kept small, which decrease the
transferable fuel quantity.
(b) The plunger strokes fully, however, the suction volume becomes small due to the small suction area.
Therefore, the difference of the volume between the geometry volume and the suction volume is in
vacuum condition.
(c) Pumping will start at the time when the fuel pressure has become higher than the common-rail
pressure.
Fuel Pumping Mass
Plunger TDC
Plunger BDC
Pumping
Starting Point
Cam
Stroke
SCV
Small Suction
Area
(a)
(b)
(c)
245EG13
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-162
3) SCV Opening Large
(a) When the opening of the SCV is large, the fuel suction area is kept large, which increase the
transferable fuel quantity.
(b) If the plunger strokes fully, the suction volume will increase because the suction area is large.
(c) Pumping will start at the time when the fuel pressure has become higher than the common-rail
pressure.
Fuel Pumping Mass
Pumping
Starting Point
Cam
Stroke
Large Suction
Area
(a)
(b)
(c)
245EG14
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-163
11. Pilot Injection Control
Pilot injection is a method that provides an auxiliary fuel injection before the main fuel injection takes
place. The purpose of pilot injection is to gently start the combustion of the fuel of the main injection in
order to reduce combustion noise.
State
Pilot Injection
Pilot Injection
Ordinarily Injection
Main Injection
Fuel Injection
Combustion
Pressure
168EG23
During pilot injection, the pilot injection volume, timing, and interval (Between pilot injection and
main injection) are controlled as shown below.
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
Crankshaft
Position Sensor
Engine Speed
Engine ECU
Basic Pilot Injection
(Volume, Timing, Interval)
Intake Air Temp.
Sensor
Correction
Water Temp. Sensor
Turbo Pressure Sensor
Pilot Injection
(Volume, Timing, Interval)
EDU
Injection
201EG45
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-164
12. Intake Shutter Control
The opening of the intake shutter valve (throttle valve) that is installed on the intake manifold is
controlled by the engine ECU in accordance with engine condition.
As a result, the noise that is generated during idling and deceleration, as well as the noise and vibration
that are generated when the engine is stopped, have been reduced and this control makes it possible to
re-circulate the exhaust gas in accordance with the driving condition.
Intake Shutter
Valve Position
Sensor
Intake Shutter Valve
Control Motor
Engine Speed
Vehicle Speed
Water Temp.
Intake Shutter
Valve
Engine
ECU
Intake Air Temp.
Accelerator Pedal
Position
Intake Air Pressure
Ignition Switch
271EG140
13. Swirl Control (Only for 1KD-FTV Engine)
The engine ECU determines the swirl control valve position (open or closed) based on the engine
conditions (engine speed and accelerator pedal effort). Then, it switches the vacuum that is applied to the
actuator diaphragm via the VSV, in order to open and close the swirl control valve.
In the low engine speed range, the engine ECU closes the swirl control valve to strengthen the swirl in
the combustion chamber, thus promoting the mixture of fuel and air and stabilizing combustion. When
the engine speed increases to the medium or high-speed range, the engine ECU fully opens the swirl
control valve. On a cold engine, the engine ECU fully closes the swirl control valve to reduce the amount
of white smoke emissions.
Intake Port
Vacuum
Swirl Control Pump
Valve
Accelerator Pedal Position
Combustion Chamber
Engine Speed
Actuator
Engine ECU
VSV
271EG90
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-165
14. Turbo Charger Control (Only for 1KD-FTV Engine)
General
The engine ECU controls the nozzle vane position using the turbo motor driver, in order to obtain the
calculated target turbo pressure appropriate to the engine operating condition.
The engine ECU calculates the optimal nozzle vane position in accordance with the driving conditions
(engine speed, injection volume, atmospheric pressure, and water temperature etc), and sends a target
nozzle vane position signal to the turbo motor driver. The turbo motor driver controls the nozzle vane
position in accordance with this signal and the actual nozzle vane position signal provided by the
nozzle vane position sensor.
DC Motor
Turbo Pressure
Sensor
Nozzle Vane
Position
Sensor
Actual Nozzle
Vane Position
Atmospheric
Pressure
Sensor
Nozzle Vane
Position Control
Crankshaft
Position Sensor
Injector
Engine ECU
Water Temp.
Sensor
Target Nozzle Vane Position Signal
Turbo Motor
Driver
Intake Air Temp.
Sensor
Turbocharger Control Status
271EG141
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-166
Construction
1) General
Variable nozzle vane device is established on the turbine (exhaust) side, and consisted of a DC motor,
nozzle vane position sensor, linkage, drive arm, unison ring, driven arms and nozzle vanes.
DC Motor
Nozzle Vane
Position Sensor
Turbine
Wheel
Linkage
Nozzle Vane
Full-Close Stopper
Driven Arm
Unison Ring
Drive Arm
271EG142
Service Tip
To control the nozzle vane position, the turbo motor driver renders the contact position of the
linkage with the full-close stopper (thus fully closing the nozzle vane) as the zero point for the
nozzle vane position sensor.
If the turbocharger has been reinstalled or replaced, turn the ignition switch from ON to OFF
once, and make sure that the linkage comes in contact with the full-close stopper.
The full-close stopper position, which is adjusted at the factory at the time of shipment, is not
serviceable in the field. For this reason, if the linkage does not come in contact with the full-close
stopper during an inspection, the turbocharger assembly must be replaced.
Never attempt to loosen or tighten the locknut of the full-close stopper because it will adversely
affect the performance of the engine.
For details, see the Hilux Repair Manual.
Linkage
Open
Full-Close
Stopper
Close
Lock Nut
271EG143
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-167
2) Nozzle Vane Position Sensor
The nozzle vane position sensor consists of a Hall IC and a magnetic yoke that rotates in unison with
the movement of the linkage that actuates the nozzle vane. The nozzle vane position sensor converts
the changes in the magnetic flux that are caused by the rotation of the DC motor (hence, the rotation of
the magnetic yoke) into electric signals, and outputs them to the turbo motor driver. The turbo motor
driver determines the actual nozzle vane position from the electric signals in order to calculate the
target nozzle vane position.
Hall IC
4.5
Magnetic Yoke
Full Close
Output
Voltage
(V.)
Sensor Vane
0.5
Full Open
Nozzle Vane Position
Full Close
Full Open
271EG148
Sensor Vane
271EG147
System Diagram
Nozzle Vane Position Sensor
Magnetic
Yoke
Magnet
VCX1
VSX1
Hall IC
Sensor Vane
E2X1
Turbo Motor
Driver
Magnet
271EG149
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-168
Operation
1) At Engine Low Speed Range
When the engine is running in a low speed range, the DC motor presses down the linkage by a signal
from the turbo motor driver. The tip of the linkage rotates the unison ring counterclockwise through a
drive arm.
The unison ring contains a driven arm, which is placed through the cutout portion of the unison ring.
This driven arm also moves in the direction of the rotation of the unison ring. The fulcrum of the
driven arm is an axis that is integrated with the nozzle vane behind the plate. When the driven arm
moves counterclockwise, the nozzle vane moves toward the closing direction. This results in
increasing the velocity of the exhaust gas flowing to the turbine, as well as the speed of the turbine. As
a result, torque is improved when the engine is running at low speeds.
DC Motor
Nozzle Vane
Linkage
Linkage
Gas Flow
Fulcrum
Unison Ring
Plate
Drive Arm
Driven Arm
Cutout Portion
Driven Arm
271EG144
2) At Engine Medium-to-High Speed Range
When the engine is running in a medium-to-high speed range, the DC motor pulls up the linkage by a
signal from the turbo motor driver. With this, the driven arm moves clockwise and this opens the
nozzle vane and holds the specified supercharging pressure. Thus, lowering the back pressure and
improving the output and fuel consumption.
271EG145
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-169
15. EGR Control System
General
The table below lists the differences between the EGR system on the 1KD-FTV and 2KD-FTV engines,
as well as the differences in their control contents.
Engine
Differences
1KD-FTV
A VSV (Vacuum Switching Valve) is provided for EGR valve close
control.
2KD-FTV
2KD-FTV High Version
An EGR valve position sensor is provided for detecting the EGR valve
position.
EGR Control for 1KD-FTV Engine
By sensing the engine driving conditions, the engine ECU electrically operates both the E-VRV (for
EGR valve control) and VSV (for EGR valve close), which controls the magnitude of vacuum
introduced into diaphragm of EGR valve and intake shutter valve (throttle valve) opening position
with intake shutter valve control motor and the amount of recirculating exhaust gas is regulated. EGR
valve opening lift is controlled by modulated negative pressure.
On the 1KD-FTV engine, the VSV (for EGR valve close) is activated when the EGR control is
stopped, in order to introduce the atmospheric pressure to the EGR valve diaphragm and improve
EGR valve closure response.
Intake Shutter
Valve Position
Sensor
Intake
Shutter
Valve
Intake Shutter
Valve Control Motor
EGR
Valve
Vacuum
Pump
Vacuum
Damper
Engine
ECU
Atmospheric
Pressure
Sensor
Intake
Manifold
Crankshaft
Position Sensor
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
Water Temp. Sensor
Turbo Pressure
Sensor
Intake Air
Temp Sensor
Air Flow Meter
E-VRV
(for EGR Valve Control)
Engine
VSV
(for EGR Valve Close)
Exhaust Manifold
271EG150
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-170
EGR Control for 2KD-FTV Engine
By sensing the engine driving conditions and actual amount of EGR valve opening, the engine ECU
electrically operates the E-VRV (for EGR valve control), which controls the magnitude of vacuum
introduced into diaphragm of EGR valve and intake shutter valve (throttle valve) opening position with
intake shutter valve control motor and the amount of recirculating exhaust gas is regulated. EGR valve
opening lift is controlled by modulated negative pressure.
Intake Shutter
Valve Position
Sensor
Intake
Shutter
Valve
Intake Shutter
Valve Control Motor
EGR Valve
Position Sensor
Vacuum
Damper
Vacuum
Pump
Crankshaft
Position Sensor
Engine
ECU
Intake
Manifold
EGR
Valve
Atmospheric
Pressure
Sensor
Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor
Water Temp.
Sensor
Turbo Pressure
Sensor
Intake Air
Temp Sensor
E-VRV
(for EGR Valve Control)
Engine
Exhaust Manifold
271EG131
ENGINE 1KD-FTV AND 2KD-FTV ENGINES
EG-171
16. Diagnosis
The diagnosis system of the 1KD-FTV and 2KD-FTV engines uses the M-OBD (Multiplex On-Board
Diagnosis).
When the Engine ECU detects a malfunction, the engine ECU makes a diagnosis and memorizes the
failed section. Furthermore, the check engine warning light in the combination meter illuminates or
blinks to inform the driver.
The 2-digit DTCs (Diagnostic Trouble Codes) can be accessed by connecting the SST (09843-18040)
to the DLC3 terminals TC and CG, and reading the blinking of the check engine warning light.
By using the intelligent tester II, the 5-digit DTCs and ECU data can be read out. Moreover, the
ACTIVE TEST can be used to drive the actuator by means of the intelligent tester II.
The Engine ECU can output freeze-frame data to the intelligent tester II. This data is stored in the
engine ECU at the very moment when the engine ECU has detected its last data of malfunction.
All the DTCs have been made to correspond to the SAE controlled codes. Some of the DTCs have been
further divided into smaller detection areas than in the past, and new DTCs have been assigned to them.
For details, see the Hilux Repair Manual.
Service Tip
To clear the DTC that is stored in the engine ECU, use a intelligent tester II or disconnect the battery
terminal or remove the EFI fuse for 1 minute or longer.
17. Fail-Safe
When a malfunction is detected by any of the sensors, there is a possibility of an engine or other
malfunction occurring if the ECU were to continue to control the engine control system in the normal
way. To prevent such a problem, the fail-safe function of the ECU either relies on the data stored in
memory to allow the engine control system to continue operating, or stops the engine if a hazard is
anticipated. For details, see the Hilux Repair Manual.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Control Engine 1kd FTV and 2kd FTDDokumen41 halamanControl Engine 1kd FTV and 2kd FTDMuxumad Cabdulahi0% (1)
- Toyota 2kd Engine ContrlDokumen25 halamanToyota 2kd Engine ContrlKamal Semboy67% (3)
- 1kd-Ftv and 2kd-Ftv FipsDokumen8 halaman1kd-Ftv and 2kd-Ftv FipsSultan Ahmed Khan100% (23)
- Hilux 1kd 2kdDokumen5 halamanHilux 1kd 2kdmiguelcastillo91% (35)
- 1KD FTVDokumen10 halaman1KD FTVnicamarcos100% (7)
- 1kd FTVDokumen2 halaman1kd FTVGregory Ashley87% (15)
- Engine 1KD, 2KDDokumen72 halamanEngine 1KD, 2KDjimmy_huamancayo97% (60)
- Common Rail System (CRS) : Toyota 1Kd/2Kd EngineDokumen31 halamanCommon Rail System (CRS) : Toyota 1Kd/2Kd EngineJuan Alberto Bucaro100% (30)
- Toyota 1kd 2kdDokumen31 halamanToyota 1kd 2kdMispa Serv100% (2)
- F7 A2 F8 B1 E1 F6 F5 G1 E4: Position of Parts in Engine CompartmentDokumen3 halamanF7 A2 F8 B1 E1 F6 F5 G1 E4: Position of Parts in Engine CompartmentEtienne van Tonder100% (3)
- 1kd FTV OverhaulDokumen37 halaman1kd FTV OverhaulJehuty8897% (34)
- Denso Toyota Hilux Common RailDokumen68 halamanDenso Toyota Hilux Common RailRonald Yanes93% (71)
- HiluxDokumen11 halamanHiluxCarlos Eduardo Zelidon100% (2)
- TOYOTA Hi Lux FaultCodes 0692Dokumen1 halamanTOYOTA Hi Lux FaultCodes 0692yargen100% (1)
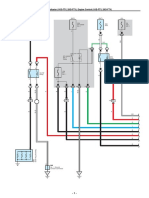
- ECT and A/T Indicator (1KD-FTV, 2KD-FTV), Engine Control (1KD-FTV, 2KD-FTV)Dokumen33 halamanECT and A/T Indicator (1KD-FTV, 2KD-FTV), Engine Control (1KD-FTV, 2KD-FTV)Erick Lizana Neyra100% (4)
- Wiring Diagram ECU 2KD-FTVDokumen13 halamanWiring Diagram ECU 2KD-FTVDam Nguyen87% (95)
- Hilux GD SeriesDokumen17 halamanHilux GD SeriesNging Yu100% (6)
- 2004-2015 Toyota Hilux Fuse Box Diagram Fuse DiagramDokumen12 halaman2004-2015 Toyota Hilux Fuse Box Diagram Fuse DiagramJunior Salazar100% (2)
- 1KD-FTV and 2KD-FTV EnginesDokumen25 halaman1KD-FTV and 2KD-FTV EnginesSergio Olivares Cortes100% (6)
- 04 Engine ProperDokumen5 halaman04 Engine Properwilliam_senati20057051Belum ada peringkat
- Spill Control Valve InspectionDokumen1 halamanSpill Control Valve InspectionArdi AgusmanBelum ada peringkat
- 1K 2KD Fuel Injection Volume ValueDokumen12 halaman1K 2KD Fuel Injection Volume ValueJimmy100% (2)
- 1ktze Pinin-PinoutDokumen11 halaman1ktze Pinin-PinoutKooked100% (9)
- 1zzVS2zz 6Dokumen16 halaman1zzVS2zz 6Ofi de Mo100% (1)
- 9913 Ap 34Dokumen108 halaman9913 Ap 34احمدميدوBelum ada peringkat
- 06imvpu Eg ControlDokumen44 halaman06imvpu Eg Controlvuongspkt12007Belum ada peringkat
- Engine Control System DiagramDokumen8 halamanEngine Control System DiagramGowher QadriBelum ada peringkat
- 1MZ-FE Engine Control SystemRX300 99Dokumen11 halaman1MZ-FE Engine Control SystemRX300 99Jose Calle100% (1)
- Sfi SystemDokumen96 halamanSfi SystemWawan SatiawanBelum ada peringkat
- 3grfse 1Dokumen42 halaman3grfse 1Zoli Borbely100% (3)
- Sistema de Control de EmisionesDokumen45 halamanSistema de Control de EmisionesDavid ParariBelum ada peringkat
- Engine - 1VD-FTV EngineDokumen33 halamanEngine - 1VD-FTV EnginePablo Pérez100% (3)
- GR00001100 13B PDFDokumen342 halamanGR00001100 13B PDFNicu PascalutaBelum ada peringkat
- ASE 2010 L2 Composite VehicleDokumen20 halamanASE 2010 L2 Composite VehicleSeven See67% (3)
- GDIDokumen7 halamanGDIlinhda561Belum ada peringkat
- E - Theory/Operation - Efi: 1991 Mitsubishi MonteroDokumen7 halamanE - Theory/Operation - Efi: 1991 Mitsubishi MonteroAnimemanuel MuñozBelum ada peringkat
- Exhaust Gas RecirculationDokumen15 halamanExhaust Gas RecirculationJesus FloresBelum ada peringkat
- 13a Mfi 1.5LDokumen164 halaman13a Mfi 1.5LDian Zahari Zainal AbidinBelum ada peringkat
- Engine PADokumen49 halamanEngine PAlartsim115Belum ada peringkat
- Toyota Avensis DPFDokumen22 halamanToyota Avensis DPFCarl Anthony Chamberlain100% (3)
- Multiport Fuel System (Mfi) : Group 13ADokumen64 halamanMultiport Fuel System (Mfi) : Group 13Ajagjitemir6014Belum ada peringkat
- V 3 Aac02v3d PDFDokumen48 halamanV 3 Aac02v3d PDFFred Fredy100% (1)
- General General Information: 13A MPIDokumen91 halamanGeneral General Information: 13A MPIDiego SantanaBelum ada peringkat
- ДатчикиDokumen4 halamanДатчикиАндрей ДубовецBelum ada peringkat
- Detroit 60 Datos BásicosDokumen16 halamanDetroit 60 Datos Básicosvictorhernandezrega100% (1)
- E Theory OperationDokumen7 halamanE Theory Operationdguruge8Belum ada peringkat
- Egine Control System: GeneralDokumen18 halamanEgine Control System: GeneralAdrianoTHEBelum ada peringkat
- ASE L2 Composite Vehicle 2007Dokumen0 halamanASE L2 Composite Vehicle 2007Anil YarlagaddaBelum ada peringkat
- G32D DTCDokumen59 halamanG32D DTCPower NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- GR00000900 13a PDFDokumen402 halamanGR00000900 13a PDFNicu PascalutaBelum ada peringkat
- Mono Jetronic (Haynes)Dokumen3 halamanMono Jetronic (Haynes)pieroBelum ada peringkat
- D6CC - Fuel System PDFDokumen45 halamanD6CC - Fuel System PDFduongpn100% (12)
- SsangYong Korando / New Actyon - Engine Control SystemDokumen172 halamanSsangYong Korando / New Actyon - Engine Control Systemtroublezaur80% (5)
- Egine Control System: GeneralDokumen18 halamanEgine Control System: GeneralAnh Tu NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Engine Control System Engine Control System System Diagram: To EsmDokumen40 halamanEngine Control System Engine Control System System Diagram: To EsmAlex RonBelum ada peringkat
- 1KR-FE Engine Control SystemDokumen346 halaman1KR-FE Engine Control SystemMortada Alsonni79% (19)
- Isuzu EngineDokumen53 halamanIsuzu EngineSmaileRun78% (18)
- 4.1 Engine Management System-R1-1 MINYI EFFADokumen24 halaman4.1 Engine Management System-R1-1 MINYI EFFARusonegroBelum ada peringkat
- Ecm Draft-6-10Dokumen5 halamanEcm Draft-6-10api-327987286Belum ada peringkat
- Case IH MX Tractor SRT ManualDokumen81 halamanCase IH MX Tractor SRT Manualhuskerchamps60% (5)
- Group 2 Specifications: 1. Major ComponentsDokumen6 halamanGroup 2 Specifications: 1. Major ComponentsYamilaBelum ada peringkat
- Q4 Science 9 Week 7 1Dokumen4 halamanQ4 Science 9 Week 7 1May LanieBelum ada peringkat
- Electronic Unit Injector - Remove: C6.6 Industrial EngineDokumen12 halamanElectronic Unit Injector - Remove: C6.6 Industrial EngineBassieBelum ada peringkat
- Future 125 1Dokumen100 halamanFuture 125 1TamPhamBelum ada peringkat
- Engine Crec Generic Scan Tool EngDokumen997 halamanEngine Crec Generic Scan Tool EngAlexandru Dumitru ZahariaBelum ada peringkat
- Peec II - Peec III Brake Engine 10 P OkDokumen10 halamanPeec II - Peec III Brake Engine 10 P OkEduardo AlvarezBelum ada peringkat
- Catalogo de Códigos Do Compressor 3CDCDokumen20 halamanCatalogo de Códigos Do Compressor 3CDCEvandro MatosoBelum ada peringkat
- Maintenance Schedules / Maintenance PartsDokumen29 halamanMaintenance Schedules / Maintenance PartsRiki Akbar100% (1)
- Mini Cooper Cooper S Clubman r55 r56 r57 Service Manual 2007 2013 Excerpt Vanos Units Removing and Installing n12 n16 n18 EngineDokumen7 halamanMini Cooper Cooper S Clubman r55 r56 r57 Service Manual 2007 2013 Excerpt Vanos Units Removing and Installing n12 n16 n18 EngineRemo OsamaBelum ada peringkat
- Kle650cbfcdf Parts List PDFDokumen115 halamanKle650cbfcdf Parts List PDFOliverBelum ada peringkat
- Psi Engines Product Sheet PDFDokumen2 halamanPsi Engines Product Sheet PDFDaniel DelgadoBelum ada peringkat
- Power Distribution Box, Rear Integrated Supply Module: Z11 F014 F011 F018 F08 F010 Z2a A361Dokumen9 halamanPower Distribution Box, Rear Integrated Supply Module: Z11 F014 F011 F018 F08 F010 Z2a A361Ninh LỗBelum ada peringkat
- Cooling System (Compatibility Mode)Dokumen28 halamanCooling System (Compatibility Mode)agvassBelum ada peringkat
- 2006 Honda CRF250R Owner'S Manual & Competition HandbookDokumen168 halaman2006 Honda CRF250R Owner'S Manual & Competition Handbookrafael grondinBelum ada peringkat
- Bwts Library 530 623Dokumen27 halamanBwts Library 530 623Tri Minh100% (1)
- Código P0171Dokumen4 halamanCódigo P0171Transmisiones Automáticas ChepeBelum ada peringkat
- Supreme Motors - FusoDokumen61 halamanSupreme Motors - Fusocaidenbourke100% (1)
- Daytona 150cc T-REX Installing Instructions - Chain RollerDokumen5 halamanDaytona 150cc T-REX Installing Instructions - Chain RollerMinibikeTechBelum ada peringkat
- Title: Boom Cylinder Model Number: E42 Serial Number: AG3411001 & AboveDokumen3 halamanTitle: Boom Cylinder Model Number: E42 Serial Number: AG3411001 & AboveJhon EcheverryBelum ada peringkat
- 03 Combustion ChamberDokumen13 halaman03 Combustion ChambernareshBelum ada peringkat
- Internship On KSRTC Central Works PappanamcodeDokumen64 halamanInternship On KSRTC Central Works Pappanamcodeajay.pBelum ada peringkat
- Lab ReportDokumen41 halamanLab Reportharoon100% (1)
- Aba Aeg 2 0 PDFDokumen25 halamanAba Aeg 2 0 PDFVictor100% (1)
- 3408E Industrial Engine Electrical System: Top ViewDokumen2 halaman3408E Industrial Engine Electrical System: Top ViewxuanBelum ada peringkat
- Crankshaft Main Bearing MEDIDASDokumen2 halamanCrankshaft Main Bearing MEDIDASRECTIMANSABelum ada peringkat
- C18 Industrial Engine WRH00001 - Sensor Eg GroupDokumen2 halamanC18 Industrial Engine WRH00001 - Sensor Eg GroupBlog Teknisi100% (1)
- 5303 - 5403 Ind.Dokumen308 halaman5303 - 5403 Ind.Edinaldo GuimaraesBelum ada peringkat
- Sge S Series Gasengines NG LRDokumen6 halamanSge S Series Gasengines NG LRenconBelum ada peringkat