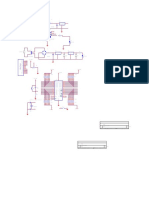
New Microsoft Office Word Document
Diunggah oleh
mpkkbtech0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
10 tayangan1 halamanAn embedded system is a special-purpose computer system. It is usually embedded as part of a complete device including hardware and mechanical parts. "Embedded system" is not exactly defined term, as many systems have some element of programmability.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
New Microsoft Office Word Document (5)
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniAn embedded system is a special-purpose computer system. It is usually embedded as part of a complete device including hardware and mechanical parts. "Embedded system" is not exactly defined term, as many systems have some element of programmability.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
10 tayangan1 halamanNew Microsoft Office Word Document
Diunggah oleh
mpkkbtechAn embedded system is a special-purpose computer system. It is usually embedded as part of a complete device including hardware and mechanical parts. "Embedded system" is not exactly defined term, as many systems have some element of programmability.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
An embedded system is a special-purpose computer system designed to
perform one or a few dedicated functions,[1] often with real-time computing
constraints. It is usually embedded as part of a complete device including hardware
and mechanical parts. In contrast, a general-purpose computer, such as a personal
computer, can do many different tasks depending on programming. Embedded
systems control many of the common devices in use today.
Since the embedded system is dedicated to specific tasks, design engineers can
optimize it, reducing the size and cost of the product, or increasing the reliability
and performance. Some embedded systems are mass-produced, benefiting from
economies of scale.
Physically, embedded systems range from portable devices such as digital watches
and MP3 players, to large stationary installations like traffic lights, factory
controllers, or the systems controlling nuclear power plants. Complexity varies
from low, with a single microcontroller chip, to very high with multiple units,
peripherals and networks mounted inside a large chassis or enclosure.
In general, "embedded system" is not an exactly defined term, as many systems
have some element of programmability. For example, Handheld computers share
some elements with embedded systems — such as the operating systems and
microprocessors which power them — but are not truly embedded systems,
because they allow different applications to be loaded and peripherals to be
connected.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- TrickDokumen2 halamanTrickmpkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- New CDokumen7 halamanNew Cmpkkbtech100% (2)
- Spi CodeDokumen3 halamanSpi Codempkkbtech100% (2)
- Flash MonitorDokumen1 halamanFlash MonitormpkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- LimitsDokumen1 halamanLimitsmpkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- Spi CodeDokumen2 halamanSpi Codempkkbtech100% (3)
- Mica DescrptionDokumen8 halamanMica DescrptionmpkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- Code For GSMDokumen1 halamanCode For GSMmpkkbtech100% (1)
- TriacDokumen2 halamanTriacmpkkbtech100% (1)
- 8051 3 Wire LCDDokumen4 halaman8051 3 Wire LCDmpkkbtech100% (2)
- Crack & SerialDokumen1 halamanCrack & SerialmpkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- VoltageDokumen3 halamanVoltagempkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- Smart Card Based Student Attendance SystemDokumen4 halamanSmart Card Based Student Attendance SystemmpkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- AddressesDokumen2 halamanAddressesmpkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- DC MotorDokumen6 halamanDC Motormpkkbtech100% (1)
- RTCDokumen7 halamanRTCmpkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- Zigbee Needs ToDokumen1 halamanZigbee Needs TompkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- Trans Prot CirDokumen1 halamanTrans Prot Cirmpkkbtech100% (1)
- Nd-Doped Ycob (Nd:Yca O (Bo)Dokumen5 halamanNd-Doped Ycob (Nd:Yca O (Bo)mpkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- SuperDokumen70 halamanSupermpkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- Stepper MotorDokumen3 halamanStepper Motormpkkbtech100% (1)
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDokumen211 halamanNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentmpkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- PiezoDokumen13 halamanPiezompkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- Some of Files inDokumen5 halamanSome of Files inmpkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
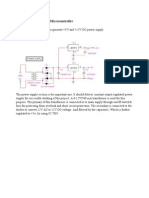
- Power Supply For 8051 Micro ControllerDokumen1 halamanPower Supply For 8051 Micro ControllermpkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- PiezoDokumen13 halamanPiezompkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- Our Own Ir SensorDokumen23 halamanOur Own Ir SensormpkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDokumen3 halamanNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentmpkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- Nd-Doped Ycob (Nd:Yca O (Bo)Dokumen5 halamanNd-Doped Ycob (Nd:Yca O (Bo)mpkkbtechBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)