Full Blood Picture
Diunggah oleh
GerardLumHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Full Blood Picture
Diunggah oleh
GerardLumHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
jslum.
com | Medicine
Full Blood Picture Morphology of Blood Cells
Definition Erythrocytes
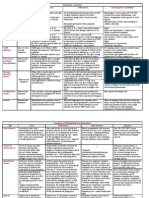
FBP = FBC + Differential count (DC) + Histogram + Peripheral Blood Film (PBF) Normal morphology
FBP = Haemogram + PBF (normocytosis normochromia)
Haemogram = FBC + DC + Histogram (non -poikilocytic, poikilocytic)
FBC = CBC = Complete Blood Count Anisocytosis
(microcytosis, macrocytosis)
Poikilocytosis
Concept Anisochromasia
Haemopoiesis occur in Bone Marrow (hypochromia, hyperchromia)
Mature cells circulate in periphery Polychromasia
Pathological process in marrow is reflected in periphery Dimorphism
Extramedullary pathology can cause abnormal peripheral blood picture Inclusion bodies
Based on Morphology, Counts Nucleated red cells
Agglutination
Indications Rouleaux formation
Clinical suspicion of bl ood disorders
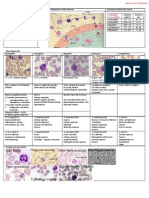
Severe anaemia prior to blood transfusion Classification of Poikilocytes
Abnormal FBC/ Histogram Round Elongated Spiculated
Assessment of known blood disorders Spherocytes Ovalocytes/ elliptocytes Schistocytes
Routine medical examination Stomatocytes Teardrop cells Keratocytes
Target cells Sickle cells Echinocytes
Reporting Hb C crystalloids Acanthocytes
RBC : Hb level + Morphology + Others HB S-C hybrids
WBC : Counts + Morphology + Others
Platelet : Counts + Morphology Inclusions in Erythrocytes
Impression : Howell-Jolly Bodies
Suggestion : Basophilic Stippling
Pappenheimer Bodies
Blood Film in Healthy Subjects Malarial Parasite
Healthy Adults Reticulocyte
Slight Anisocytosis/ Poikilocytosis Heinz Bodies
Metamyelocytes/ Myelocytes – rare
Megakaryocytes – very rare
RBC : Platelet = 10-40 : 1
Pregnancy
More variation
↑ MCV (30-35 weeks)
↓ Hb (30-34 weeks)
↑ ESR (Rouleaux)
Numerous polychromatic cells
↑ Retic. Count (6% at 25-30 weeks) Leucocytes
↑ Neutrophil/ Monocyte count
Left Shift
Platelet - Count/ Size usually do not change
Infant & Children
MCV/ MCH ↓ compared to adults
Male- Female have difference in Hb
(RBC, P CV/Hct not present before puberty)
Lymphocyte count ↑
Neonate
Hyposplenic features – Howell-Jolly Bodies, Acanthocytes, Spehrocytes
Hb, RBC, PCV ↑
MCV ↑
Neutrophil, Monocyte, Lymphocyte counts ↑
NRBC & Myelocytes – common
Retic. Count ↑ in 1st 3 days after birth
Premature Neonate
↑ NRBC, Metamyelocytes, Myelocytes, Promyelocytes, Myeloblasts
Hyposplenic features Platelets/ Thrombocytes
Develop eosinophilia often (between 2nd – 3rd weeks after birth) Normal
Large
Hyposplenism Giant
After splenectomy – Thrombocytosis, Neutrophilia Platelet clumps
After Recovery – Neutrophil counts nearly Normal, Platelet high Normal Platelet satellitism
Lymphocytosis, Monocytosis persist
Abnormal RBC features
Target cells
Acanthocytes
Howell-Jolly bodies
Pappenheimer bodies
NRBC
Spherocytes
Circulating non-haemopoietic cells Microorganisms in Blood Film
Endothelial cells Bacteria
Epithelial cells Fungi
Non-haemopoietic malignant cells Parasites
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Blood FilmDokumen2 halamanBlood FilmGerardLum100% (1)
- Haematology Case Studies with Blood Cell Morphology and PathophysiologyDari EverandHaematology Case Studies with Blood Cell Morphology and PathophysiologyPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- WBC Usmle QuestionsDokumen17 halamanWBC Usmle Questionssplinter594100% (1)
- Hematologic Pathology p65-87Dokumen23 halamanHematologic Pathology p65-87zeroun24100% (1)
- Top 10 Anemias to Know for BoardsDokumen24 halamanTop 10 Anemias to Know for BoardsSim M ChangBelum ada peringkat
- Fast Facts: Measurable Residual Disease: A clearer picture for treatment decisionsDari EverandFast Facts: Measurable Residual Disease: A clearer picture for treatment decisionsBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Blood SmearDokumen59 halaman1 Blood SmearGabi Tim100% (1)
- HAEMOPOIESISDokumen6 halamanHAEMOPOIESISDiyana ZahariBelum ada peringkat
- Liver PathologyDokumen21 halamanLiver Pathologyzeroun24100% (6)
- Adequacy Criteria: ExceptionsDokumen3 halamanAdequacy Criteria: ExceptionsPranayBelum ada peringkat
- WBC Neoplasms Review - PathologyDokumen6 halamanWBC Neoplasms Review - Pathologylas100% (6)
- Leukemias & Lymphomas - HY USMLEDokumen87 halamanLeukemias & Lymphomas - HY USMLEMatt McGlothlinBelum ada peringkat
- Practical Hematology Lab: RBC Morphology GuideDokumen61 halamanPractical Hematology Lab: RBC Morphology GuideJefferson Soriano50% (2)
- Endocrine Pathology p17-32Dokumen16 halamanEndocrine Pathology p17-32zeroun24Belum ada peringkat
- 2021 Systemic Pathology S4T1 - RBC and Bleeding Disorders PDFDokumen27 halaman2021 Systemic Pathology S4T1 - RBC and Bleeding Disorders PDFAlexis Bondad100% (1)
- Myeloproliferative DisordersDokumen2 halamanMyeloproliferative DisordersGerardLumBelum ada peringkat
- Hematologic Pathology p24-35Dokumen12 halamanHematologic Pathology p24-35zeroun24100% (6)
- Fast Facts: Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Determining risk, tailoring therapy, supporting patientsDari EverandFast Facts: Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Determining risk, tailoring therapy, supporting patientsBelum ada peringkat
- HematologyDokumen198 halamanHematologyLouann100% (1)
- All Objectives HematologyDokumen45 halamanAll Objectives HematologyNursing200980% (5)
- Hematology Tables Morphology of RBCsDokumen5 halamanHematology Tables Morphology of RBCsGlydenne Glaire Poncardas GayamBelum ada peringkat
- Safe Blood: Purifying the Nations Blood Supply in the Age of ADari EverandSafe Blood: Purifying the Nations Blood Supply in the Age of ABelum ada peringkat
- Haematology - Blood Films.Dokumen6 halamanHaematology - Blood Films.kkkssbbBelum ada peringkat
- Pathology Slides 1Dokumen28 halamanPathology Slides 1SydBelum ada peringkat
- 18 Lymphoma - Libre PathologyDokumen13 halaman18 Lymphoma - Libre PathologyfadoBelum ada peringkat
- Summary of All AnemiaDokumen2 halamanSummary of All Anemiabenlarsena93% (14)
- HematologyDokumen5 halamanHematologyIvy Jan OcateBelum ada peringkat
- Bone Marrow FailureDokumen2 halamanBone Marrow FailureGerardLum100% (1)
- Top 10 Anemias for BoardsDokumen25 halamanTop 10 Anemias for BoardsJames StaffordBelum ada peringkat
- Hematologic Pathology p36-47Dokumen12 halamanHematologic Pathology p36-47zeroun24Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 13 Neoplastic Proliferations of White CellsDokumen16 halamanChapter 13 Neoplastic Proliferations of White CellsOmar100% (1)
- Hemotology Pathology PDFDokumen15 halamanHemotology Pathology PDFMorgan PeggBelum ada peringkat
- Leukocytes Benign DisordersDokumen3 halamanLeukocytes Benign DisordersGerardLum100% (3)
- Hematologic Pathology p48-64Dokumen17 halamanHematologic Pathology p48-64zeroun24100% (1)
- WBC Pathology: Lecturer: Associate Professor T. A. GrekovaDokumen49 halamanWBC Pathology: Lecturer: Associate Professor T. A. GrekovaFaheem MusthafaBelum ada peringkat
- Frontiers in Clinical Drug Research - Hematology: Volume 4Dari EverandFrontiers in Clinical Drug Research - Hematology: Volume 4Belum ada peringkat
- Red Cell and White Cell Counting, BloodDokumen89 halamanRed Cell and White Cell Counting, BloodJovel GangcuangcoBelum ada peringkat
- Hemolytic AnemiaDokumen1 halamanHemolytic AnemiaTeus FatamorganaBelum ada peringkat
- Pocket Guide On Red Cells 2012Dokumen8 halamanPocket Guide On Red Cells 2012Dave OrlandoBelum ada peringkat
- Haematology Trainee Handbook 2016Dokumen52 halamanHaematology Trainee Handbook 2016hery_140978Belum ada peringkat
- PathologyDokumen31 halamanPathologyStudy Usmle100% (1)
- Divergent Differentiation, Creating So-Called Mixed Tumors: Seminoma Are Used For Malignant Neoplasms. TheseDokumen6 halamanDivergent Differentiation, Creating So-Called Mixed Tumors: Seminoma Are Used For Malignant Neoplasms. TheseSherwin Kenneth Madayag100% (1)
- HEMOGLOBINOPATHY GUIDEDokumen3 halamanHEMOGLOBINOPATHY GUIDEChatie PipitBelum ada peringkat
- Manage Stab Wound BleedingDokumen7 halamanManage Stab Wound BleedingJohn Christopher LucesBelum ada peringkat
- Molecular Diagnosis in HaematologyDokumen23 halamanMolecular Diagnosis in HaematologyUmar'Farouq Oni100% (1)
- Tumor MarkersDokumen68 halamanTumor MarkerspathmomBelum ada peringkat
- Myeloproliferative Disorders PDFDokumen52 halamanMyeloproliferative Disorders PDFBoneyJalgar100% (3)
- Cast in Urine SedimentDokumen3 halamanCast in Urine Sedimentfirie100% (1)
- AnemiaDokumen10 halamanAnemiaBia Payawal100% (2)
- Endocrine PathologyDokumen13 halamanEndocrine Pathologysarguss14100% (1)
- CNS Path ChartDokumen10 halamanCNS Path Chartjamesomoore100% (1)
- Clinical Lab Hematology: An Overview of Blood Cell AnalysisDokumen30 halamanClinical Lab Hematology: An Overview of Blood Cell AnalysisGerald SorianoBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract InfectionDokumen4 halamanUrinary Tract InfectionGerardLum100% (2)
- Posterior Pituitary SyndromeDokumen1 halamanPosterior Pituitary SyndromeGerardLumBelum ada peringkat
- Vesico Ureteral RefluxDokumen1 halamanVesico Ureteral RefluxGerardLumBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract Infections in ChildrenDokumen1 halamanUrinary Tract Infections in ChildrenGerardLumBelum ada peringkat
- Pituitary Gland PathologyDokumen4 halamanPituitary Gland PathologyGerardLumBelum ada peringkat
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDokumen6 halamanSexually Transmitted DiseasesGerardLum100% (3)
- ThalassaemiaDokumen4 halamanThalassaemiaGerardLum100% (4)
- Thyroid PhysiologyDokumen2 halamanThyroid PhysiologyGerardLum100% (2)
- ThrombophiliaDokumen3 halamanThrombophiliaGerardLum100% (1)
- Renal Function in Disease StateDokumen2 halamanRenal Function in Disease Statedamai140390Belum ada peringkat
- Soft Tissue InfectionsDokumen3 halamanSoft Tissue InfectionsGerardLum100% (1)
- Pituitary DysfunctionDokumen2 halamanPituitary DysfunctionGerardLum0% (1)
- Soft Tissue TumoursDokumen8 halamanSoft Tissue TumoursGerardLum100% (2)
- Skeletal Muscle RelaxantsDokumen1 halamanSkeletal Muscle RelaxantsGerardLum100% (2)
- Renal Excretion of DrugsDokumen3 halamanRenal Excretion of DrugsGerardLum100% (3)
- Prostate GlandsDokumen3 halamanProstate GlandsDragan PetrovicBelum ada peringkat
- Pathology of TestesDokumen4 halamanPathology of TestesGerardLum100% (1)
- Principles of Blood TransfusionDokumen2 halamanPrinciples of Blood TransfusionGerardLum100% (3)
- Pathology GlomerulonephritisDokumen4 halamanPathology GlomerulonephritisGerardLum100% (2)
- Pathology of DiabetesDokumen4 halamanPathology of DiabetesGerardLum100% (4)
- Pathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisDokumen5 halamanPathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisGerardLum100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Nerve InjuryDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Nerve InjuryGerardLum100% (1)
- Pathology of Thyroid DiseasesDokumen5 halamanPathology of Thyroid DiseasesGerardLum100% (2)
- Pathogenesis Chronic Complications DiabetesDokumen5 halamanPathogenesis Chronic Complications DiabetesGerardLum100% (1)
- Paediatrics OrthopaedicsDokumen5 halamanPaediatrics OrthopaedicsGerardLumBelum ada peringkat
- Pathogenesis Bleeding DisordersDokumen4 halamanPathogenesis Bleeding DisordersGerardLumBelum ada peringkat
- Overview of AnaemiaDokumen2 halamanOverview of AnaemiaGerardLumBelum ada peringkat
- Nsaids DrugsDokumen2 halamanNsaids DrugsIrene Zae MwandotoBelum ada peringkat
- Obstructive UropathyDokumen3 halamanObstructive UropathyGerardLum100% (1)
- Nocturnal EnuresisDokumen1 halamanNocturnal EnuresisGerardLumBelum ada peringkat
- The Cleavage Stage EmbryoDokumen23 halamanThe Cleavage Stage EmbryoZahra Nur AzizahBelum ada peringkat
- The Respiratory System: SubtitleDokumen89 halamanThe Respiratory System: SubtitleAaaBelum ada peringkat
- Essay ImmuneDokumen8 halamanEssay ImmuneAishah Najihah100% (1)
- Karakter Anatomi Daun Sebagai Bentuk Adaptasi Tumbuhan Penyusun Zonasi Mangrove Di Banggai Kepulauan, Provinsi Sulawesi TengahDokumen10 halamanKarakter Anatomi Daun Sebagai Bentuk Adaptasi Tumbuhan Penyusun Zonasi Mangrove Di Banggai Kepulauan, Provinsi Sulawesi TengahArpin PakpahanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-20 Locomotion and Movement: Is The Voluntary Movement of An Individual From One Place ToDokumen8 halamanChapter-20 Locomotion and Movement: Is The Voluntary Movement of An Individual From One Place ToLishaBelum ada peringkat
- Movement Organs in Humans and AnimalsDokumen15 halamanMovement Organs in Humans and AnimalsDara FatimahBelum ada peringkat
- Active Management of Third Stage of LabourDokumen27 halamanActive Management of Third Stage of LabourNagamalar RajendraBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Quiz: Cell Structure, Organ Systems, Evolution & MoreDokumen32 halamanBiology Quiz: Cell Structure, Organ Systems, Evolution & MoreChrisshalyn Sy PinedaBelum ada peringkat
- Knowing The Foundation of LifeDokumen47 halamanKnowing The Foundation of LifeAlkhair SangcopanBelum ada peringkat
- 002 Handout Basic Concepts Part 2Dokumen8 halaman002 Handout Basic Concepts Part 2Alfred BajarBelum ada peringkat
- Normal Changes With Aging in The Cardiovascular SystemDokumen4 halamanNormal Changes With Aging in The Cardiovascular SystemSheenarieBelum ada peringkat
- 5096 w07 Ms 2Dokumen6 halaman5096 w07 Ms 2mstudy123456Belum ada peringkat
- Microbiology Objective QuestionsDokumen28 halamanMicrobiology Objective QuestionscrazybobblaskeyBelum ada peringkat
- 1.1 Skeletal Student BookletDokumen8 halaman1.1 Skeletal Student BookletKotickBelum ada peringkat
- The Structure and Function of the Human HeartDokumen22 halamanThe Structure and Function of the Human HeartNunoAlmeidaBelum ada peringkat
- Zoology - Lab ReportDokumen3 halamanZoology - Lab ReportRonald Loreto MabajenBelum ada peringkat
- Assig# 3 Pathology - Docx (Ali Aasam Khan CU-1774-2020)Dokumen21 halamanAssig# 3 Pathology - Docx (Ali Aasam Khan CU-1774-2020)Ali Aasam KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine, 8th Ed-Pages-233-267 PDFDokumen35 halamanFitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine, 8th Ed-Pages-233-267 PDFHestin PrasantyBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment and Management of Women During Post-Natal PeriodDokumen82 halamanAssessment and Management of Women During Post-Natal Periodsweta0% (1)
- Human Body Review TestDokumen6 halamanHuman Body Review TestMrCiambroneBelum ada peringkat
- Muscles Covered in The Trigger Point ChartsDokumen19 halamanMuscles Covered in The Trigger Point ChartsSaninan Mat100% (5)
- Introduction To AnatomyDokumen28 halamanIntroduction To Anatomybayenn100% (3)
- Tabang Elementary School Science 4 Test on Digestion and Internal OrgansDokumen6 halamanTabang Elementary School Science 4 Test on Digestion and Internal OrgansJanice Corañes100% (5)
- Large Leaves Have A Large Surface Area, Which Would Allow Them To AbsorbDokumen5 halamanLarge Leaves Have A Large Surface Area, Which Would Allow Them To AbsorbKeziah VenturaBelum ada peringkat
- Protocol Book BWCT DominiqueS 2Dokumen126 halamanProtocol Book BWCT DominiqueS 2N AaBelum ada peringkat
- A Manual of AcarologyDokumen348 halamanA Manual of AcarologyLeonardo Daniel Ortega88% (8)
- Cell Structure and Function ActivityDokumen19 halamanCell Structure and Function ActivityrhaineBelum ada peringkat
- Teeth Number 85Dokumen16 halamanTeeth Number 85rarasBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Mcqs Test For Entry Test by Dr. Sajid Ali TalpurDokumen8 halamanBiology Mcqs Test For Entry Test by Dr. Sajid Ali TalpurDr. Sajid Ali Talpur100% (6)
- Chapter12 Physical DevelopmentDokumen38 halamanChapter12 Physical DevelopmentJhayCee100% (1)