Pa Tho
Diunggah oleh
tammy_deguzman5223Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Pa Tho
Diunggah oleh
tammy_deguzman5223Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
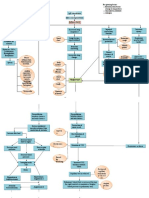
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Definition
ARF is a common life threatening process with myriad causes. It is characterized by failure of oxygenation, or
ventilation, or both.
Schematic Diagram
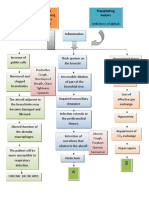
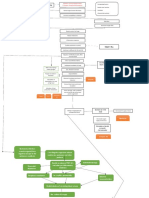
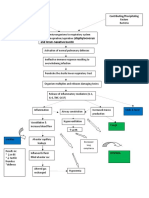
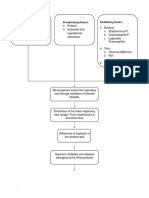
Predisposing
Age- 82 years old
COPD Precipitating
COPD
Allergens enter the upper respiratory tract
Stimulation and activation of B Lymphocytes
B Lymphocytes produces Immunoglobulin E(IgE)
IgE antibodies attached to mast cells and basophils in the
bronchial walls
Mast cells degranulation
Mast cells releases chemical mediators of inflammation
Slow- reacting substance
Histamine bradykinin prostaglandins
anaphylaxis ( SRS- A)
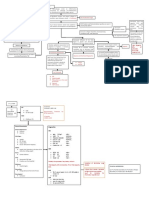
Increase blood flow Increase mucus Chemical Contraction of the
to the area of insult production mediators induced bronchial smooth
capillary dilation muscles that encircles
the airway
(bronchospasm)
Edema of the
Deposition of
Attraction of WBC airway
collagen below the
to the area basement membrane
Airway constriction
or
Fluid shifting from bronchoconstriction
the vasculature
and to the alveoli
Hyperinflation of
alveoli
Narrowing of the airway
Increase work of breathing
Decreased elastic recoil
Increase resistance to airflow
Fatigue of the muscles of
ventilation
Ventilation- Perfusion (V/Q)
mismatch and shunt
Inadequate exchange of O2 and CO2
Hypoxemia
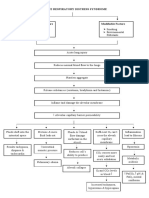
ACUTE RESPIRATORY
FAILURE
Recovery
COMPLICATIONS:
Tissue hypoxia
Subsequent organ
damage
Chronic respiratory failure
Tension pneumothorax
Lobar atelectasis
Death Pneumonia
` Pulmonary edema
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Mr. Ashish RoyDokumen45 halamanAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Mr. Ashish RoySyedzulqurnainhussainshah ZulqurnainBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderBlessyl Mae EstenzoBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology Community Aquired Pneumonia and AnemiaDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology Community Aquired Pneumonia and Anemiapa3kmedina100% (2)
- Acute Respiratory Failure Pa Tho PhysiologyDokumen4 halamanAcute Respiratory Failure Pa Tho Physiologyroseanne18100% (4)
- Patho of COPD and CorP NewDokumen5 halamanPatho of COPD and CorP NewInchan Montesines100% (1)
- Respiratory PhysiologyDokumen40 halamanRespiratory PhysiologyBookwormBelum ada peringkat
- Isabela State University: Republic of The Philippines San Fabian, Echague, Isabela Activity 2 Medical-Surgical NursingDokumen9 halamanIsabela State University: Republic of The Philippines San Fabian, Echague, Isabela Activity 2 Medical-Surgical Nursingpinoy HubBelum ada peringkat
- Patho PneumoniaDokumen2 halamanPatho Pneumoniaailyne_galicia100% (2)
- Community Acquired Pneumonia PathophysiologyDokumen2 halamanCommunity Acquired Pneumonia PathophysiologybercoaprilgraceBelum ada peringkat
- Pneumonia Parient BasedDokumen2 halamanPneumonia Parient BasedKismet SummonsBelum ada peringkat
- Broncho 2Dokumen4 halamanBroncho 2hotteenstar_23Belum ada peringkat
- Culture and Sensitivity: InhalationDokumen3 halamanCulture and Sensitivity: Inhalationjamie carpioBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Sultan Chaudhry Benny Dua Eric WongDokumen7 halamanChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Sultan Chaudhry Benny Dua Eric Wongjamil aldasriBelum ada peringkat
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDokumen1 halamanPa Tho PhysiologyRosella Delos SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of PneumoniaJeffrey RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory Physiology: Ventilation Perfusion DiffusionDokumen6 halamanRespiratory Physiology: Ventilation Perfusion DiffusionShiara Ruth EdrosoloBelum ada peringkat
- ARDS Patopi FinaleDokumen1 halamanARDS Patopi FinaleCuttie Anne GalangBelum ada peringkat
- Pa Tho Physiology PneumoniaDokumen2 halamanPa Tho Physiology PneumoniaPatrick Bryan Zabayle LacsonBelum ada peringkat
- Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: Contributing FactorsDokumen6 halamanPredisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: Contributing FactorsKen SimonBelum ada peringkat
- Asuhan Keperawatan Pasien Dengan Acut Respiratory Distress Syndroma (ARDS)Dokumen10 halamanAsuhan Keperawatan Pasien Dengan Acut Respiratory Distress Syndroma (ARDS)Sintayani YaniBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study RespiDokumen4 halamanCase Study RespiKayzhel UmaliBelum ada peringkat
- Compilation MS Sir DennisDokumen18 halamanCompilation MS Sir DennisMaria Luz S. RulonaBelum ada peringkat
- Schematic Diagram: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsDokumen3 halamanSchematic Diagram: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsDamie FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- 55-Year-Old, Male With CopdDokumen3 halaman55-Year-Old, Male With CopdRyrey Abraham PacamanaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of PneumoniaJeffrey Ramos100% (1)
- Asphyxia NeonatorumDokumen28 halamanAsphyxia NeonatorumAsha jilu100% (1)
- Pathophysiology EmphysemaDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology Emphysemanursing concept mapsBelum ada peringkat
- Pa Tho Physiology of Broncho PneumoniaDokumen1 halamanPa Tho Physiology of Broncho PneumoniaPong's Teodoro SalvadorBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory SystemDokumen8 halamanRespiratory SystemDeeza Joice CastañedaBelum ada peringkat
- Textbook Discussion On Acute Community-Acquired Pneumonia (BSN 3A-Group 6)Dokumen9 halamanTextbook Discussion On Acute Community-Acquired Pneumonia (BSN 3A-Group 6)Jica Marie Bandiola GicaroBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of PneumoniaJesselle LasernaBelum ada peringkat
- Streptococcus Pneumonae: Pathophysiology of CopdDokumen1 halamanStreptococcus Pneumonae: Pathophysiology of CopdDimpal ChoudharyBelum ada peringkat
- COPD PathoDokumen1 halamanCOPD PathoGlenn_Ancheta_2074100% (1)
- EXTRA NotesDokumen26 halamanEXTRA NotesAhmad HasanBelum ada peringkat
- COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)Dokumen8 halamanCOPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)Emily Anne86% (7)
- COPD PathoDokumen1 halamanCOPD PathoLeah May AnchetaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of PneumoniaMaria Cristina100% (1)
- Copd PathoDokumen2 halamanCopd PathoAlvin RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- Ncma 113Dokumen4 halamanNcma 113Wonie booBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of PneumoniaJuneBelum ada peringkat
- TB IldDokumen3 halamanTB IldMARYHAN M MUKHALALATIBelum ada peringkat
- Upper Airway InfectionsDokumen5 halamanUpper Airway InfectionsTreesa LouiseBelum ada peringkat
- COPDDokumen15 halamanCOPDMary Grace AgataBelum ada peringkat
- Ass Q ArdsDokumen1 halamanAss Q ArdsKristine MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology & Concept Map: Precipitating FactorsDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology & Concept Map: Precipitating FactorsVanessa Rose Vargas0% (1)
- ARDS With PathophysiologyDokumen79 halamanARDS With Pathophysiologymabec pagaduan95% (19)
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDokumen6 halamanBreathing and Exchange of Gasesadityaaggarwal821Belum ada peringkat
- PATHO AsneuDokumen2 halamanPATHO Asneupatricio_pBelum ada peringkat
- SARS PathophysioDokumen2 halamanSARS PathophysioLouise BravoBelum ada peringkat
- Woc ArdsDokumen2 halamanWoc Ardssyarifah salmaBelum ada peringkat
- Oxygenation - 1Dokumen7 halamanOxygenation - 1Cielo SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDokumen47 halamanAcute Respiratory Distress Syndromemaeliszxc kimBelum ada peringkat
- Woc Asma BronkialDokumen4 halamanWoc Asma Bronkialyedida susanaBelum ada peringkat
- Group 3 BSN3D CapDokumen6 halamanGroup 3 BSN3D CapJingky AnquillanoBelum ada peringkat
- 316 Revalida ReviewerDokumen28 halaman316 Revalida ReviewerSOPHIA PILLENABelum ada peringkat
- Copd PathoDokumen1 halamanCopd PathoRey AngeloBelum ada peringkat
- NCP 1 N 2Dokumen5 halamanNCP 1 N 2Cuttie Anne GalangBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Ge Stimulations Mast Cell Degeneration Asthma AttackDokumen4 halaman1 Ge Stimulations Mast Cell Degeneration Asthma Attacknebbie06Belum ada peringkat
- Airway Study GuideDokumen20 halamanAirway Study Guide8dkpbq7qz7Belum ada peringkat
- Raynaud Syndrome Brochure-1 1Dokumen2 halamanRaynaud Syndrome Brochure-1 1api-340995574Belum ada peringkat
- Task Exposure AnalysisDokumen24 halamanTask Exposure AnalysisDaren Bundalian RosalesBelum ada peringkat
- Social Science Class 10 Understanding Economic DevelopmentDokumen93 halamanSocial Science Class 10 Understanding Economic DevelopmentkannansesBelum ada peringkat
- A "What Not To Do" Better Sex GuideDokumen9 halamanA "What Not To Do" Better Sex GuideBenson Huang100% (1)
- Investigatory Project On Malaria: Name: M.Bhavya Class: XI C' Year: 2018 - 2019Dokumen18 halamanInvestigatory Project On Malaria: Name: M.Bhavya Class: XI C' Year: 2018 - 2019Muramsetty Bhavya0% (1)
- Module 7. Presented - The Phil Health Program On Degenerative Diseases 93Dokumen105 halamanModule 7. Presented - The Phil Health Program On Degenerative Diseases 93Roma ClaireBelum ada peringkat
- The Warehouse Group Annual Report 2020Dokumen92 halamanThe Warehouse Group Annual Report 2020Meaza Kidusan ElhamBelum ada peringkat
- Psychiatric Disability AssessmentDokumen19 halamanPsychiatric Disability AssessmentDivya ThomasBelum ada peringkat
- Mapeh 2ND QDokumen5 halamanMapeh 2ND QMaxicris SlowerBelum ada peringkat
- NPD Phase 1Dokumen2 halamanNPD Phase 1Abdullah ZahidBelum ada peringkat
- Enrolled Nurses FADokumen11 halamanEnrolled Nurses FAjoayou23Belum ada peringkat
- Aeon 4000 SDSDokumen13 halamanAeon 4000 SDSmarcos luqueBelum ada peringkat
- Et CareDokumen15 halamanEt CarePaulo GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Pork TocinoDokumen1 halamanPork TocinoMaria Ivz ElborBelum ada peringkat
- Invenia ABUS USA Brochure Feb2016Dokumen14 halamanInvenia ABUS USA Brochure Feb2016Asim AliBelum ada peringkat
- Guide State Local Emergency Operations Plans (Cpg1 8 1)Dokumen21 halamanGuide State Local Emergency Operations Plans (Cpg1 8 1)ebjlBelum ada peringkat
- Antimicrobial ResistanceDokumen46 halamanAntimicrobial ResistanceEmil CotenescuBelum ada peringkat
- 50 Maternal and Child NCLEX QuestionsDokumen14 halaman50 Maternal and Child NCLEX QuestionsShengxy Ferrer100% (2)
- Experiment 4: Roadway Lighting Evaluation And: DesignDokumen12 halamanExperiment 4: Roadway Lighting Evaluation And: DesignEdogawa ConanBelum ada peringkat
- JPNC 02 00096Dokumen9 halamanJPNC 02 00096Catalina StoicescuBelum ada peringkat
- Derma GITDokumen48 halamanDerma GITapi-3843372Belum ada peringkat
- Autism and Transactional Analysis: TranscriptDokumen26 halamanAutism and Transactional Analysis: TranscriptWanessa FernandesBelum ada peringkat
- NT90004212Dokumen58 halamanNT90004212Jelena ĆukBelum ada peringkat
- Q3-Las-Health10-Module 3-Weeks 6-8Dokumen6 halamanQ3-Las-Health10-Module 3-Weeks 6-8MA TEODORA CABEZADABelum ada peringkat
- Psychiatric Clinical SkillsDokumen376 halamanPsychiatric Clinical SkillsSamuel Agunbiade100% (5)
- July 7, 2017 Strathmore TimesDokumen28 halamanJuly 7, 2017 Strathmore TimesStrathmore TimesBelum ada peringkat
- AbstractDokumen2 halamanAbstractMunifah AzisBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Exam Questions With AnswerDokumen7 halamanNursing Exam Questions With AnswerjavedBelum ada peringkat
- Agri SBA (Broiler)Dokumen20 halamanAgri SBA (Broiler)Shanti KissoondyalBelum ada peringkat
- AM LOVE School Form 8 SF8 Learner Basic Health and Nutrition ReportDokumen4 halamanAM LOVE School Form 8 SF8 Learner Basic Health and Nutrition ReportLornaNirzaEnriquezBelum ada peringkat