X - Problem Prioritization and NCP
Diunggah oleh
Martin Lєtmaku Espina100%(2)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (2 suara)
7K tayangan5 halamanX. Problem List CUES Subjective cues: NURSING PROBLEM Ineffective airway clearance related to "Hirap ako huminga dahil ubo retained secretions" as to bacterial infection. Verbalized by the patient. Difficulty of breathing can cause anxiety to the client that is why, immediate attention must be done.
Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniX. Problem List CUES Subjective cues: NURSING PROBLEM Ineffective airway clearance related to "Hirap ako huminga dahil ubo retained secretions" as to bacterial infection. Verbalized by the patient. Difficulty of breathing can cause anxiety to the client that is why, immediate attention must be done.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
100%(2)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (2 suara)
7K tayangan5 halamanX - Problem Prioritization and NCP
Diunggah oleh
Martin Lєtmaku EspinaX. Problem List CUES Subjective cues: NURSING PROBLEM Ineffective airway clearance related to "Hirap ako huminga dahil ubo retained secretions" as to bacterial infection. Verbalized by the patient. Difficulty of breathing can cause anxiety to the client that is why, immediate attention must be done.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 5
X.
Problem Prioritization
A. Short Term Objective
After 2 days of nursing interventions the patient will not experience ineffective airway clearance. The complications
brought about by pneumonia will be prevented through proper participation to the different medical and nursing interventions.
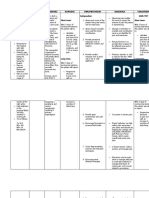
B. Problem List
CUES NURSING PROBLEM RANK JUSTIFICATION
Subjective cues: Ineffective airway 1 Airway must be given the first attention as based on
clearance related to the rule of ABC which is Airway, Breathing and
• “Hirap ako huminga dahil ubo retained secretions in the Circulation. In addition, difficulty of breathing can
ako ng ubo na my kasamang respiratory tract secondary cause anxiety to the client that is why, immediate
plema at minsan my dugo pa.” as to bacterial infection. attention must be done. Addressing the problem to
verbalized by the patient. proper health care provider will give patent airway
to the client. Oxygenation is a vital need for every
Objective cues: cell, if there are any problems related to it can easily
affect the functioning of the individual.
• Cough with phlegm Retained secretions can cause blockage of airway
• Hemoptysis which will further cause difficulty of breathing
• Restless (Fundamentals of Nursing 8th ed by Kozier and erb’s
• Diminished breath sounds p. 1299)
(crackles)
Subjective cues: Ineffective breathing 2 This demands immediate treatment/care and
pattern related to subsequent medical attention, as they can result in
• “Hirap ako huminga dahil ubo hypoventilation secondary ineffective breathing pattern. This also needs
ako ng ubo na my kasamang attention as based on the rule of ABC which is
to pneumonia
plema at minsan my dugo pa.” as Airway, Breathing and Circulation. This is an actual
verbalized by the patient. problem that needs to address.
Lack of action in this health care problem may cause
Objective cues: dyspnea which may later cause a bigger threat to the
health of the patient.
• Dyspnea Difficult and labored in breathing during which the
• Alterations of depth of breathing individual has a persistent, unsatisfied need for air
• Use accessory muscles to breath and feel distressed. (Fundamentals of Nursing 8th ed
by Kozier and erb’s p. 549)
Risk for impaired gas 3 This condition needs to be addressed immediately
exchange related to for the patient to be able to give patient awareness
alveolar-capillary about his condition in his body and to be able to
maintain a good gas exchange.
membrane changes
Lack of attention in this health care problem may
lead to impaired gas exchange which may later
cause bigger threat to the health of the patient.
NURSING CARE PLAN
Cues Nursing Inference Objective Nursing Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis
Intervention
Subjective Cues Ineffective Irritant Short Term Goal Independent
airway Assess rate/depth of Frequently present
clearance (inhalation) respirations and chest because of discomfort
movement. of moving chest wall
• “Hirap related to After 4 hours of and/or fluid in lung. After 4 hours
ako huminga retained nursing of nursing
dahil ubo ako secretions in Auscultate lung Decreased airflow intervention,
intervention, fields, noting areas of
ng ubo na my the respiratory inflammatory decreased/absent
occurs in areas the goal is met
tract airway patency consolidated with fluid. through
kasamang airflow and
secondary to Response will be adventitious breath
plema at sounds. maintenance of
bacterial maintained,
minsan my
Elevate head of bed,
dugo pa.” as infection. secretions will be change position Lowers diaphragm, airway patency
promoting chest
verbalized by frequently. expansion, aeration of and reduction
the patient. readily lung segments, in congestion.
increase mobilization and
Objective cues: production expectorated and expectoration of
secretions.
• Cough of secretions there will be
with phlegm signs
• hemoptys Assist patient with
is of reduction in frequent deep- Deep breathing
• Restless breathing exercises.
congestion. facilitates maximum
• Diminish airway expansion of the
ed breath
constriction lungs/smaller airways.
sounds
(crackles) Suction as indicated
Stimulates cough or
mechanically clears
airway in patient who
is unable to do so
Dyspnea because of ineffective
cough or decreased
Force fluids to at level of consciousness.
least 3000 mL/day
(unless Fluids (especially
contraindicated, as in warm liquids) aid in
heart failure). Offer mobilization and
warm, rather than expectoration of
cold, fluids. secretions.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Nursing Problem Prioritization - CAPDokumen16 halamanNursing Problem Prioritization - CAPWyen Cabatbat100% (1)
- Pneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokumen2 halamanPneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceNursesLabs.com86% (7)
- Updated - Prioritization of ProblemsDokumen1 halamanUpdated - Prioritization of ProblemsKaycelyn JimenezBelum ada peringkat
- Prioritization!Dokumen2 halamanPrioritization!Jane Camile Milanio Dimaunahan67% (3)
- PRIOritizationDokumen1 halamanPRIOritizationRuss ElizondoBelum ada peringkat
- List of Prioritized Nursing DiagnosesDokumen1 halamanList of Prioritized Nursing DiagnosesRonnel Alvin Antonio Adriano100% (1)
- Problem PrioritizationDokumen2 halamanProblem PrioritizationFlauros Ryu Jabien100% (3)
- Acute pain and hypertension risksDokumen2 halamanAcute pain and hypertension risksKat TaasinBelum ada peringkat
- PrioritizationDokumen1 halamanPrioritizationNarbie Jean C. DizonBelum ada peringkat
- Problem PrioritizationDokumen1 halamanProblem PrioritizationFlauros Ryu JabienBelum ada peringkat
- Prioritizing Nursing Problems for a Patient with PneumoniaDokumen1 halamanPrioritizing Nursing Problems for a Patient with PneumoniaAbigail Lonogan100% (2)
- Problem Identification 5Dokumen2 halamanProblem Identification 5John CenasBelum ada peringkat
- IX. Problem Prioritization Pay 2 FinalDokumen2 halamanIX. Problem Prioritization Pay 2 FinalMicah Jonah ElicañoBelum ada peringkat
- A List of Prioritized Nursing DiagnosisDokumen3 halamanA List of Prioritized Nursing DiagnosisRica DiazBelum ada peringkat
- Problem PrioDokumen2 halamanProblem PrioYsrael Alcantara100% (1)
- PrioritizationDokumen1 halamanPrioritizationclarheena100% (1)
- ND PrioritizationDokumen1 halamanND PrioritizationBea Dela Cena50% (2)
- Prioritization of Nursing ProblemsDokumen7 halamanPrioritization of Nursing ProblemsJoseph Raymund Fabian Huelar50% (4)
- Prioritization of ProblemDokumen2 halamanPrioritization of ProblemGenette Sy SolisBelum ada peringkat
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokumen2 halamanNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearancelarapatricia1215Belum ada peringkat
- Identified Nursing Diagnoses and PrioritizationDokumen4 halamanIdentified Nursing Diagnoses and Prioritizationrheinz-marlon-m-carlos-7771Belum ada peringkat
- Problem PrioritizationDokumen3 halamanProblem PrioritizationJohn Cenas0% (1)
- List of Prioritized Nursing ProblemsDokumen1 halamanList of Prioritized Nursing ProblemsdanaBelum ada peringkat
- List of Prioritize Nursing ProblemsDokumen1 halamanList of Prioritize Nursing ProblemsHanna SeBelum ada peringkat
- List of Prioritized Nursing DiagnosesDokumen1 halamanList of Prioritized Nursing Diagnosesdana25% (4)
- Lacerated WoundDokumen38 halamanLacerated Wounddomzlr18100% (2)
- Answer: 59.5 KG: Rationale: Although All of These Clients Might Experience Fluid Volume Deficit, TheDokumen14 halamanAnswer: 59.5 KG: Rationale: Although All of These Clients Might Experience Fluid Volume Deficit, TheMikeeBelum ada peringkat
- Body Weakness NCPDokumen1 halamanBody Weakness NCPtwicetrashBelum ada peringkat
- Impaired Liver FunctionDokumen1 halamanImpaired Liver FunctionShop Dzubiri Here100% (3)
- Pleural Effusion FdarDokumen1 halamanPleural Effusion FdarvanessabdeveraBelum ada peringkat
- Cancer Pain ManagementDokumen8 halamanCancer Pain ManagementMaryjoy Gabriellee De La Cruz100% (1)
- Nursing Priority Problem List for Fluid Volume ExcessDokumen1 halamanNursing Priority Problem List for Fluid Volume ExcessJackyleen Kate BenetuaBelum ada peringkat
- Activity IntoleranceDokumen1 halamanActivity IntoleranceJoshua D. Garcia100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Breathing GunshotDokumen3 halamanNCP Ineffective Breathing GunshotMikko Enoc100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPDokumen2 halamanNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPpa3kmedina100% (1)
- NCP - Fluid RetentionDokumen3 halamanNCP - Fluid RetentionMichelle Teodoro100% (1)
- Chinese General Hospital College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanDokumen2 halamanChinese General Hospital College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanLoveli Yuchongtian Kiok100% (2)
- NCP Impaired SkinDokumen2 halamanNCP Impaired Skinarjay2306_obcq100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective TissueDokumen2 halamanNCP Ineffective TissueFhel AragonBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDokumen2 halamanNCP Activity Intolerancerobbiematro100% (1)
- Risk For Impaired Skin IntegrityDokumen2 halamanRisk For Impaired Skin IntegrityKarl JoseBelum ada peringkat
- GENERAL SANTOS DOCTORS’ MEDICAL SCHOOL FOUNDATION NURSING CARE PLANDokumen4 halamanGENERAL SANTOS DOCTORS’ MEDICAL SCHOOL FOUNDATION NURSING CARE PLANFran LanBelum ada peringkat
- NCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionDokumen2 halamanNCP - Altered Tissue PerfusionLeigh Kristel Andrion0% (1)
- NCP - Ineffective Tissue Perfusion ECLAMPTIC SEIZUREDokumen2 halamanNCP - Ineffective Tissue Perfusion ECLAMPTIC SEIZUREkhanepot100% (2)
- Disturbed Sleep PatternDokumen3 halamanDisturbed Sleep PatternLorette Diane C. Roque100% (2)
- Problem PRIORITIZATION and NCP 1, 2, 3 of CataractDokumen7 halamanProblem PRIORITIZATION and NCP 1, 2, 3 of CataractEries Lacanlale LumbaBelum ada peringkat
- Prioritized Nursing Problem For Pneumothorax Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention RationaleDokumen3 halamanPrioritized Nursing Problem For Pneumothorax Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention RationaleJoshua VillarbaBelum ada peringkat
- Prioritization of ProblemsDokumen1 halamanPrioritization of ProblemsKaycelyn JimenezBelum ada peringkat
- NCP HyperthermiaDokumen2 halamanNCP HyperthermiaMeljonesDaanBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDokumen7 halaman6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraBelum ada peringkat
- Final NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokumen8 halamanFinal NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceHazel EndayaBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen3 halamanNCPJezza RequilmeBelum ada peringkat
- SchistosomiasisDokumen92 halamanSchistosomiasisIvan Juan75% (4)
- NCP - Risk For InjuryDokumen3 halamanNCP - Risk For InjuryMatty JolbitadoBelum ada peringkat
- Prioritized ProblemDokumen2 halamanPrioritized ProblemBernadeth LabradorBelum ada peringkat
- Aaa Gastrectomy NCP FinalDokumen13 halamanAaa Gastrectomy NCP Finallexzaf100% (1)
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDokumen4 halamanImpaired Gas Exchange NCPkimglaidyl bontuyanBelum ada peringkat
- Learning About Pediatric Urinary Tract InfectionsDokumen2 halamanLearning About Pediatric Urinary Tract InfectionsNickaela CalalangBelum ada peringkat
- PRELIM NCM 112 RleDokumen20 halamanPRELIM NCM 112 RleKylle AlimosaBelum ada peringkat
- Group 4 Case on Acute BronchitisDokumen6 halamanGroup 4 Case on Acute BronchitisseokjinworkieBelum ada peringkat
- Delhi Public School Bangalore North Science Assignment KeyDokumen3 halamanDelhi Public School Bangalore North Science Assignment KeyJanaki KrishnanBelum ada peringkat
- Optimizing Ba and Iba Concentrations For Micro Propagation of Spineless Yucca Yucca Elephantipes IJERTV8IS010004Dokumen5 halamanOptimizing Ba and Iba Concentrations For Micro Propagation of Spineless Yucca Yucca Elephantipes IJERTV8IS010004SHUBHAM JIBHAKATEBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular Physiology For University Students: S. I. Ogungbemi Department of Physiology University of LagosDokumen136 halamanCardiovascular Physiology For University Students: S. I. Ogungbemi Department of Physiology University of LagosTeeBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of BREAST CANCERDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of BREAST CANCERAlinor Abubacar100% (6)
- Physiology of The Liver: Corresponding AuthorDokumen12 halamanPhysiology of The Liver: Corresponding AuthorMansour HazaBelum ada peringkat
- Biological Level of Analysis Research GuideDokumen45 halamanBiological Level of Analysis Research GuidePhiline Everts100% (2)
- Abnormal heart sounds explainedDokumen3 halamanAbnormal heart sounds explainedmuhammad azizulhakimBelum ada peringkat
- Lung Work SheetDokumen2 halamanLung Work SheetGalo LandivarBelum ada peringkat
- Syrgery Mock 2Dokumen8 halamanSyrgery Mock 2aa.Belum ada peringkat
- Muscular System WebquestDokumen7 halamanMuscular System WebquestJxcari50% (2)
- Chapter 15 UrinaryDokumen24 halamanChapter 15 Urinary3amabelle arevaloBelum ada peringkat
- Rhopalocera (Butterfly) : FunctionsDokumen18 halamanRhopalocera (Butterfly) : FunctionsChris Anthony EdulanBelum ada peringkat
- General CharacteristicsDokumen24 halamanGeneral CharacteristicsdemanBelum ada peringkat
- Factors Affecting Renal ExcretionDokumen19 halamanFactors Affecting Renal ExcretionV. SravaniBelum ada peringkat
- Skeletal Muscle Classification and StructureDokumen43 halamanSkeletal Muscle Classification and StructureHusnain WattoBelum ada peringkat
- Kurukshetra University Date-Sheets for BA/BSc Part ExamsDokumen12 halamanKurukshetra University Date-Sheets for BA/BSc Part ExamsabhishekBelum ada peringkat
- Pancreas - Pathological Practice and Research - K. Suda (Karger, 2007) WW PDFDokumen329 halamanPancreas - Pathological Practice and Research - K. Suda (Karger, 2007) WW PDFIonut-Stefan CiobaneluBelum ada peringkat
- Division Celular Mitosis y MeiosisDokumen5 halamanDivision Celular Mitosis y MeiosisGiovanna Macías100% (1)
- June 2009 MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Biology A-LevelDokumen24 halamanJune 2009 MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Biology A-LevelAyse KerimBelum ada peringkat
- IGCSE Biology 2015 Paper 21Dokumen20 halamanIGCSE Biology 2015 Paper 21VeronicaAndrianBelum ada peringkat
- ADokumen2 halamanAイ ロBelum ada peringkat
- 4 - Subphylum UrochordataDokumen12 halaman4 - Subphylum UrochordataStudent 365Belum ada peringkat
- FixationDokumen3 halamanFixationficatBelum ada peringkat
- EMG in Weightlifting Performance During The SnatchDokumen5 halamanEMG in Weightlifting Performance During The SnatchsafaaismaeelBelum ada peringkat
- Child Development A Thematic Approach 6th Edition Bukatko Test BankDokumen36 halamanChild Development A Thematic Approach 6th Edition Bukatko Test Bankunframecizarsidquu100% (21)
- Lucknow Public School Sample Paper-Ii Biology Class - XiDokumen3 halamanLucknow Public School Sample Paper-Ii Biology Class - XiNishant singhBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Manual of Otolaryngology Clear ScanDokumen283 halamanClinical Manual of Otolaryngology Clear ScanAyman Yakout100% (4)
- Digestive Dilemmas Trivia Review AnswersDokumen46 halamanDigestive Dilemmas Trivia Review Answersapi-305436791Belum ada peringkat
- Performed Structural DesignDokumen93 halamanPerformed Structural DesignSaiful IslamBelum ada peringkat
- Trimestral Exam First GradeDokumen3 halamanTrimestral Exam First Gradeemmanuel espinozaBelum ada peringkat